Cancer is contagious
Recently, the media have been actively refuting this myth. But for a long time it was believed that cancer is a contagious disease, i.e. A cancer patient can transmit the tumor to another person.
Any infectious process includes three main components:
- the causative agent of the disease (usually some kind of microorganism, virus, etc.);
- transmission route - the path of the pathogen from a sick person to a healthy person (the most common types of transmission are airborne, alimentary, contact);
- the presence of a susceptible human organism that can become ill.
With regard to cancer, none of these points is true: the causative agent of cancer does not exist as such, since the disease has completely different development mechanisms. But still, various infections and cancer have some relationship.
Some viruses increase the risk of developing certain cancers. For example, human papillomavirus, Einstein-Barr virus (a type of herpes virus), hepatitis B and C virus, herpes virus type eight, Helicobacter pylori.
However, there are vaccines—certain medications that increase resistance to these viruses. For example, the effectiveness of vaccines against hepatitis B and human papillomavirus has already been scientifically proven and substantiated.
Thus, cancer is not an infectious disease; it is absolutely not contagious.
Treatment of stage 1 prostate cancer
Stage 1 prostate cancer usually grows slowly, and tumor cells under a microscope look very similar to normal ones (high degree of differentiation, low degree of malignancy). The tumor is small in size, and the level of the tumor marker prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood is low. Most affected men do not experience any symptoms.
Some patients do not require treatment. It is enough to visit a doctor regularly and undergo examinations. If treatment is indicated, it usually begins with surgical removal of the prostate gland—radical prostatectomy—or radiation therapy. Radiation from external sources and brachytherapy are used - when small particles the size of grains of rice, which are sources of radiation, are injected directly into the prostate gland. Sometimes radiation therapy is supplemented with a short course of hormonal therapy.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Eating sugar leads to cancer
Sugar is vital for cells - both tumor and healthy ones. In the human body, healthy cells try to use sugar as efficiently as possible for energy. One gram of glucose produces 38 molecules.
but tumor cells use a different mechanism, which results in the formation of only two molecules. That is, tumor cells, compared to healthy ones, receive 19 times less energy from one gram of glucose. The most popular theory explains this fact by genetic changes in the structure of the tumor.
Yes, sugar is necessary for the human body. But its excess can lead to obesity. Excess body weight increases the risk of developing certain malignant tumors.
Thus, obese people have an increased risk of developing
- uterine cancer 7 times;
- esophageal cancer 2 times;
- colon cancer 1.3 times;
- pancreatic cancer 1.5 times;
- kidney cancer 2 times;
- breast cancer 1.3 times;
Thus, sugar itself does not cause malignant tumors, but it may increase the likelihood of some of them.
Nutrition for cervical cancer
During illness and after a course of therapy, nutrition is important for a woman. A proper and balanced diet will help restore the deficiency of microelements and vitamins that are required for recovery. There is a list of harmful and healthy foods.
For stage 1 cervical cancer, the following must be excluded:
- alcoholic drinks;
- limit consumption of table salt;
- salted, pickled and canned foods must be removed from the diet;
- chocolate and products based on this ingredient;
- sweet pastries made from white flour;
- Sweet carbonated drinks should not be consumed;
- It is strictly forbidden to consume fast food;
- sausage from different types of meat and other offal should be removed from the diet;
- consumption of animal fats should be limited;
- margarine and butter are prohibited.
After the operation and during the period of illness, you need to adhere to proper nutrition - cook food only by steaming, boiling or in the oven. Vegetables are best eaten raw. It is necessary to increase the amount of greens, fruits and berries. Useful products are considered:
- lean meat - chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- You should also choose low-fat fish - pollock, chum salmon, etc.;
- you need to take 1% fermented milk products;
- meat can be replaced with legumes - they are easier to digest and do not require large energy costs;
- Drinks allowed include green tea, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs.
During the recovery period, it is recommended to monitor your body weight - weigh yourself regularly. Smoking should not be done or reduced to a minimum during this time. It is useful to engage in physical therapy and perform light physical exercises on your own. Every day you need to take walks in the fresh air.
Frequent use of mobile phones affects the development of tumors
Why did such a myth arise? The researchers explain:
- radio waves are absorbed by biological tissues, i.e. radiation affects the cells of our body;
- the number of mobile phones is increasing every year;
- The time spent using mobile phones is increasing as communications have become more accessible, widespread and cheaper;
- the number and duration of calls increases.
The researchers had the idea to test experimentally whether the occurrence of brain tumors is really associated with the use of mobile phones.
The INTERPHONE study involved more than 5 thousand people with brain tumors. Experts collected data on the frequency of use of mobile phones by patients. It turned out that there is no cause-and-effect relationship between the occurrence of a brain tumor and the use of a mobile phone.
Leading organizations in the world such as the American Cancer Society, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Food and Drug Administration (FDA), CDC (Department of Health and Human Services, USA) have expressed their opinion that mobile phones are completely safe.
Thus, the occurrence of brain tumors is not associated with the use of mobile phones; gadgets do not even increase the risk of cancer.
Stage I and risk of recurrence
After treatment for stage 1 cancer, there is a possibility that lung cancer will recur. It is estimated that 30 to 50% of stage I cancers may recur, and adjuvant treatments such as chemotherapy are sometimes used to reduce this risk. Repetition can occur in one of three ways:
- Local recurrence refers to cancers that appear in the lungs, close to the original tumor.
- Regional recurrence refers to cancers that recur in lymph nodes near the original tumor.
- Distant recurrence refers to cancers that recur at distant sites in the body, most often in the bones, brain, liver, or adrenal glands. When cancer recurs at a distant site, it is referred to as metastatic or stage 4 cancer.
Unfortunately, most stage I lung cancer recurrences occur at distant sites. But even with repetition, survival improves. In fact, most of the recent advances in lung cancer treatment are for stage 4 disease.
Cancer is a death sentence
The outcome of treatment and the speed of rehabilitation of a cancer patient are influenced by various factors.
These include:
- biological type of tumor (different tumors have different prognosis),
- localization, prevalence and size of the tumor,
- presence and characteristics of concomitant diseases,
- tumor treatment methods,
- patient's age.
There is also such a thing as stages of cancer. The stage determines only survival, i.e. probability of living for a certain period of time. The higher the stage, the lower this probability.
As a rule, when treating malignant tumors, oncologists use an indicator such as five-year survival rate.
According to global data, the average five-year survival rate for major cancers (lung, breast, colon, prostate, skin cancer) is 60%. This is a fairly high figure.
Survival depends on the type of tumor. One of the lowest survival rates is observed for pancreatic cancer, and one of the highest for skin cancer (basal cell).
Thus, cancer is not always a death sentence for a person. With the development of technology, most types of cancer are curable.
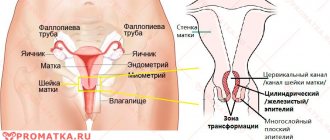
Classification of the first stage of cervical cancer
Stage 1 cervical cancer is divided into two main substages:
- microinvasive type or stage 1A (T1A);
- macroinvasive type or stage 1B (T1B).
Microinvasive cervical cancer forms predominantly in the basal layer of the epithelium in small quantities; the tumor can be detected using powerful high-resolution equipment. The preliminary diagnosis will be confirmed by histology of the obtained biological material.
Microinvasive cancer stages 1A1 and 1A2 cannot be detected visually - the size of the tumor does not exceed 3 mm. A grade 1A1 neoplasm is the preclinical stage of cervical cancer, i.e. the disease is on the border between the formation of a severe stage of dysplasia and a visually detectable neoplasm. There are no symptoms at this stage. Only foreign vaginal discharge is noted, but the first diagnosis shows the presence of pathologies of the reproductive system - inflammatory processes, erosion or dysplasia. Detection of grade 1A disease increases the patient’s chance of full recovery after the course of therapy.
Macroinvasive cancer corresponds to substage 1B of stage 1 cervical cancer. The stage refers to the clinical form of malignant pathology. The size of the tumor does not yet exceed 10 mm and is located in the cervical area, but during colposcopy with visual examination a suspicious lump is detected. After surgery to excise diseased tissue, a woman has a chance for a complete cure.
There are substages of stage 1 pathology with characteristic features:
- The tumor of the first degree is located within the boundaries of the cervix, without going beyond its limits.
- Stage 1A or T1A is microinvasive cancer.
- The cancerous process at substage 1A1 (T1A1) grows into the stroma of the cervix up to 3 mm; its width can reach 7 mm.
- Stage 1A2 or T1A2 is characterized by penetration into the stroma up to 5 mm, but the size of the neoplasm does not exceed 7 mm.
- A tumor of grade 1B (T1B) is defined as macroscopic, difficult to determine visually, but the depth of germination does not correspond to stage 1A.
- Cancer at stage 1B1 (T1B1) can be detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist; the size ranges from 10-40 mm.
- A grade 1B2 (T1B2) induration extends beyond 40 mm and is considered a visible tumor.
If there were no cases of cancer in the family, then I won’t have it either.
About 95% of malignant tumors are sporadic, i.e. they do not depend on whether blood relatives have had cancer or not.
But there are certain risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing cancer. First of all, it's age. Age is the only risk factor that we cannot influence. Risk factors also include alcohol consumption, smoking, long-term chronic inflammatory diseases and so-called carcinogenic factors.
But all of them only increase the likelihood of occurrence - nothing more, i.e. the presence of these factors will not necessarily lead to the development of a tumor in a person.
But in 5% of cases there are hereditary tumors, hereditary cancer syndromes: Cowden syndrome, Lynch syndrome, Gardner syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome and some others.
If a person has any of these inherited syndromes, then they need to undergo screening programs several years or even decades earlier than others.
Thus, only in 5% of cases can cancer be inherited, and in most cases the presence of cancer has nothing to do with heredity.
Disease survival
It is quite difficult to cure such an oncological disease, especially with folk remedies. It is for this reason that patients with this diagnosis are observed in specialized institutions for the rest of their lives. Many women use various folk remedies, but, in fact, without special treatment they are ineffective. If the operation was performed in a timely manner, the patients live for more than 5 years. Properly selected therapy for stage 1 cancer results in complete recovery in almost 90 out of 100 cases.
Causes of cervical cancer
On the forums you can find the following reviews about this disease:
Ler, 34 years old, Moscow: “My friend was diagnosed with stage 2 cervical cancer, and she constantly complains of uterine bleeding. Doctors say that the chances of recovery are minimal and have prescribed a course of radiation. We all hope for the best and support her."
Olga, 45 years old, Kaliningrad: “During pregnancy, I learned about grade 3 dysplasia, and doctors warned about the high risk of developing cancer. I decided to keep the baby and now, 9 months after giving birth, I was diagnosed with cancer. Tomorrow I’m going to the medical center, and I don’t know what stage of the disease it is yet. I hope that everything will be fine and my life will not stop there.”
Important: A particular danger to a woman’s health is when cancer cells spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes. When the pathology moves to the third stage, the chances of survival do not exceed 40%.
The most unfavorable prognosis is observed when distant metastases appear and various complications develop. With this pathological condition at the last stage, the prognosis for survival over 5 years is no more than 10% of women.
CC is considered a complex and insidious disease that can be fatal. Often, a malignant tumor can be detected in advanced stages, which greatly reduces the chances of recovery. Women are recommended to visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year, which will allow cancer to be diagnosed in the early stages and effective treatment to be selected.
Video: Early stage cervical cancer surgery
Surgery for early stage cervical cancer
Treatment for cancer is worse than the disease itself
There is a myth that living with cancer is physically easier for the patient compared to treating the tumor.
Today, three main methods of treating malignant tumors are used: surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. As a rule, all three methods are used in combination.
There are many undesirable consequences of cancer treatment, including baldness, weakness, nausea, cardiotoxicity and many others.
The consequences of cancer treatment affect the quality of life, but with the availability of a wide range of medications, they are much easier to tolerate.
An oncologist has two global goals: to increase the patient’s life expectancy and to improve his quality of life. In this situation, it can be difficult to strike a balance.
Cancer patients want to know as much as possible about their diagnosis, causes, possible consequences and proposed treatment methods. Most often, patients trust the method recommended by the doctor. Experts try to minimize the negative consequences of therapy.
Thus, treatment of a malignant tumor in most cases is no worse than living with this disease.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the stage, location and extent of spread of the tumor process. Standard therapy includes surgery, a course of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
In complex treatment regimens, Indian generics of anticancer drugs are used, which improve the tolerability of chemotherapy and speed up the recovery process. Medicines with appropriate quality certificates can be purchased at the India Express online pharmacy https://india-expres24.com/onkologiia/. The medications described are not intended for self-medication and can only be used with prior agreement with a doctor.
Depression contributes to cancer
There is a misconception that negative emotions and severe depression can lead to cancer.
A study was conducted in which people with severe forms of depression took part. As a result, it was proven that the risk of developing a malignant tumor in people with depressive disorders is exactly the same as in people without such disorders.
Thus, a bad mood has absolutely no effect on the occurrence and development of a tumor and is not even a risk factor for its development.
Palliative care
Palliative care is treatment aimed primarily at relieving symptoms caused by cancer rather than a cure, and to improve the quality of life of patients and their families. Palliative care can help people live more comfortably. This is an urgent humanitarian need for all people in the world suffering from cancer and other chronic killer diseases, especially in places with a high proportion of patients with advanced disease and low likelihood of cure.
Palliative care can alleviate physical, psychosocial and spiritual problems for more than 90% of patients with advanced cancer.
GMOs cause cancer
GMO (genetically modified organism) is an organism whose genotype has been artificially changed. People have been breeding GMOs for quite a long time. One of the main methods for obtaining GMOs is selection.
At the moment, there are no studies that the consumption of GMOs leads to the development of cancer.
Thus, GMOs do not lead to the development of cancer; science has not proven otherwise.
Basic methods for diagnosing stage 2 lung cancer
Since a lung cancer tumor may not manifest itself in any way for a fairly long period of time, you should not rely on independently identifying the main signs of such a dangerous disease. To effectively diagnose the disease, it is best to use special techniques and the assistance of qualified specialists - oncologists.
Another difficulty lies in the fact that lung tissue cancer in stages 1-2 is very similar in its symptoms to a classic case of pneumonia.
In addition, even the results obtained from the studies may not reflect the real picture of the degree of developing pathology. Early diagnosis of the disease as a preventive measure will help not only to detect lesions at an early stage, but to save the patient’s life in the future.
The main method for diagnosing cancer tumors today continues to be radiography. Stage 2 lung cancer leads to:
- to disturbances in the normal functioning of pulmonary ventilation,
- to narrowing of the closest bronchus.
An x-ray allows you to see an area with obvious dark areas. Significant obstructions in the patency of the area of the bronchus under study can also provoke pneumonia. In such cases, the image shows the damaged area, where the volume of tissue is significantly reduced, and uneven compactions are observed on the surface. A tumor in a peripheral location leads to inflammatory processes in the lymphatic vessels.
The second main method for diagnosing a cancerous tumor is computed tomography. The appointment of such a study occurs in the case of planning surgical intervention to eliminate the affected areas of the lungs.
The main goal of this technique is to analyze the depth of penetration of tumor lesions into adjacent tissue structures and analyze the degree of damage to the area under study, including the condition of the lymph nodes.
Depending on the size of the lymph node, the following deviations can be determined:
- The norm is no more than 1 centimeter.
- An enlarged node of more than 1 centimeter is the first sign of pathology.
- When the size of the lymph node increases to 1.5 centimeters or more, the presence of metastases in the lymph node can be diagnosed.
In addition to the above diagnostic methods, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is also used. Widely applicable for studying a specific localization of emerging tumors. This technique is absolutely safe for the patient, does not harm human health and does not in any way affect the condition of the body as a whole. The only contraindication to MRI is the presence of metal implants or prostheses in the body of the patient being examined.
Additional research methods
Additional measures to examine tumors help determine the specific type of tumor. Including the determination of the malignant or benign nature of the formation, as well as to determine the extent of the spread of the process.
Among the most famous and popular research methods are:
- Bronchoscopy. Helps detect a tumor if it has spread into the bronchial lumen. Detects infiltration of the walls of the bronchi, determines their compression.
- Mediastinoscopy. Used in case of suspected lymph node metastases. For this technique, general anesthesia is recommended.
It is performed by removing a small sample of lymph tissue through a small incision in the patient's neck.
- Biopsy. One of many effective methods. This is a morphological and immunological method of examining the body, where the main material for analysis is samples of neoplasms.
- Complete blood analysis (examination). The method is applicable not for initial diagnosis, but for its specification. In this case, cancerous lesions can confirm the level of hemoglobin, an increase in tumor markers or ESR.
X-rays can only reveal the focus of inflammation, and additional research methods provide a more comprehensive picture of damage to lung tissue.
People with dark skin do not get skin cancer
Statistically, skin cancer occurs more often in people with fair skin.
The main cause of skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet rays. Protection against them is provided by melanin, which is less in people with fair skin.
A study by scientists has confirmed that skin cancer occurs in people with dark skin. But the survival rate of such dark-skinned patients is much lower than that of lighter-skinned patients. This is due to the difficulty of detection and the frequency of detection, since it is more difficult to detect a neoplasm on dark skin than on light skin.
One notable example is reggae musician Bob Marley, who died at the age of thirty-six from late-diagnosed acral melanoma, a melanoma that develops on the skin of the nails.
Thus, skin color has no effect on the risk of skin cancer, and people with dark skin can also be diagnosed with it.
Life expectancy
Because lung cancer has a reputation for being aggressive and has a poor prognosis, questions about survival often arise. Before we go any further, it is important to note that treatment for lung cancer is improving and survival rates are also improving. Besides, every case is different.
Variables that influence survival rates
Some of the variables that can affect lung cancer survival include:
- Your specific type and location of lung cancer: About 85% of lung cancers are considered non-small cell lung cancer. These cancers tend to spread more slowly than small cell lung cancer, although small cell lung cancer tends to respond well to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, at least initially.
- Location of your cancer: Although surgery is often chosen for stage 1 lung cancer, some of these tumors are located in areas that make surgery risky. If surgery is not an option, there are two types of radiation therapy that can be used for curative purposes: stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and proton therapy. (Survival is slightly better with VATS vs SBRT lobectomy).
- Molecular profile of your tumor: We currently have treatments for people with certain genetic changes in their tumors. Molecular profiling (gene testing) should be performed for all patients with non-small cell lung cancer. The drugs are available for people with EGFR mutations, ALK rearrangements and ROS1 rearrangements, and clinical trials are evaluating treatments for lung cancers with other genetic profiles. (These treatments are not typically used to treat stage 1, but are available if the cancer is expected to recur or spread.)
- Your age: Younger people tend to live longer than older people with lung cancer.
- Your gender: Life expectancy for a woman with lung cancer is higher at every stage of the disease.
- Your overall health at the time of diagnosis: Being generally healthy at the time of diagnosis is associated with a longer life expectancy and a greater ability to resist treatment, which can prolong survival.
- How you respond to treatment: Side effects of treatment vary from person to person and may limit your ability to tolerate treatment.
- Other health conditions you may have: A health condition such as emphysema or heart failure may shorten your life expectancy with stage 1 lung cancer. Those without COPD have a better prognosis.
- Smoking: Quitting smoking before surgery for stage I lung cancer appears to significantly improve survival. Currently, most people who develop lung cancer do not smoke, but for those who do, there are many reasons why people with cancer should quit smoking, including survival.
- Where you are treated: Several studies have shown that people who have lung cancer surgery at a facility that performs most of those surgeries (such as a cancer center) have better outcomes.
In addition to all the differences noted above among people, each cancer is also different. From a molecular perspective, if there were 100 people in a room with stage I lung cancer, they would have 100 different types of cancer at the molecular level. Different molecular characteristics may lead to different tumor behavior.
Statistics
In addition to the variations between different people and different cancers, it is important to keep in mind that statistics are often several years old. Many of the treatments that are now available to treat lung cancer were not available when these numbers were obtained. For example, there are several immunotherapies and targeted drugs that have been approved since early 2015.
Currently, the overall 5-year survival rate is 49% for people with stage IA lung cancer and 45% for people with stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. These rates may be higher for people who have lung cancer detected only through screening, and may be as high as 90%.
Antiperspirant use leads to breast cancer
A study was conducted in which 813 women aged 20 to 74 years with breast cancer took part.
According to this study, the use of antiperspirants is absolutely not associated with the development of breast cancer.
Subsequently, several more studies were conducted that similarly confirmed the absence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the occurrence of breast cancer and the use of antiperspirants.
Thus, there is currently no evidence linking the use of antiperspirants and the occurrence of breast cancer.
The vicissitudes of human evolution
No matter how harmonious the arguments about the accumulation of mutations with age may look, there is at least one serious gap in them. The fact is that cell division occurs most rapidly during intrauterine development and the first years of life. It is at this time that most “errors” occur in genes. With age, tissues renew themselves more and more slowly. Why then do the risks increase in older people?
The answer must be sought in the theory of evolution and the characteristics of the life of our primitive ancestors. In the Stone Age, rarely did anyone live past the age of thirty. A person spent his entire life trying to grow, get stronger, and gain experience. We can say that the birth of children and caring for them in the early years was the apogee, the main meaning of life. Soon after, many people died from infections, natural disasters and the teeth of predators.
For the survival of the population, it was necessary for people to live until the moment when they could leave offspring. All this time, the body’s defense mechanisms operate at peak efficiency. This was facilitated by natural selection.
Nature did not try very hard to ensure that a person survived as effectively at an older age. As reproductive function fades, changes begin to occur in tissues: chronic inflammation develops, they work less efficiently, and immune defense decreases. “Incorrect” cells are given good opportunities to survive and reproduce uncontrollably. The risk of the formation of clones of such cells and their degeneration into a malignant tumor increases.
This may all sound cruel. But in contrast to this cruelty of the laws of biology, humanity has created humane, highly developed medicine. Thanks to the efforts of doctors, the life expectancy of modern people is increasing, and new opportunities are emerging to combat cancer and other serious diseases.
Another paradox is that cancer risk peaks around age 70 and then declines. Among people aged 90 years and older, the incidence of cancer is greatly reduced and it is less likely to cause death. Why this happens remains to be seen. This may be due to the fact that centenarians are initially less susceptible to oncogenic mutations.
Below are the average ages at which different types of malignant tumors are diagnosed:
- Breast cancer - 62
- Lung cancer - 70
- Prostate cancer - 66
- Colorectal cancer – 68
- Bladder cancer - 73
- Melanoma - 63
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - 63
- Thyroid cancer - 51
- Kidney cancer - 64
- Leukemia – 66
- All types of cancer - 65
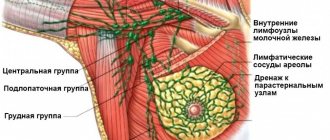
Breast implants lead to breast cancer
In fact, women who have and those who do not have implants are equally at risk for breast cancer.
But there is a very rare disease - anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the breast. This is not a disease of the breast tissue, but of the lymph nodes. And it is the presence of breast implants that influences the development of this disease.
The basic risk of developing this disease is three per 100,000,000 cases, and the risk of development in the presence of implants is already 203 per 100,000,000 cases, i.e. the risk increases by 67 times. However, the absolute incidence of this disease is extremely small.
Thus, breast implants are not associated with breast cancer, but do increase the risk of breast lymphoma.
Treatment of stage 1 cervical cancer
It is possible to determine the type of oncological neoplasm by conducting a histological examination and conization of the suspicious area. If there are abnormal cells in the tissues of the operated area, repeat histology is performed. Sometimes a hysterectomy is prescribed using the Wertheim method - radical resection of the tumor. During excision, the uterine body, ligamentous apparatus of the uterus, regional lymph nodes are removed and 20 mm of the vaginal cuff is captured. After the excision procedure, the diseased tissue is again sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
Features of treatment for stage 1A cervical cancer
Treatment of microinvasive cervical cancer demonstrates the following features:
- When LVSI pathology is detected in a girl at a young age, it is necessary to preserve fertility, and extensive conization of the organ is performed.
- Diagnosed with an LVSI+ tumor at a young age with the need to preserve fertility, wide conization of the cervix with bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy and extended trachelectomy is prescribed (the cervix with adjacent tissue and the upper third of the vagina is removed, an anastomosis is performed between the uterine body and the vagina).
- A diagnosis of LVSI cancer has been made and there is no goal of preserving fertility - a standard hysterectomy is performed with removal of the appendages and uterine body.
- The disease was detected in a woman in adulthood with other concomitant diseases - radical hysterectomy with removal of the uterine body and appendages is used.
Irradiation with radioactive substances is used in conjunction with surgery or as monotherapy. Radiotherapy courses are carried out remotely, intracavitarily, or combine both methods. In the case of diagnosing microinvasive cervical cancer of the cervical uterus of 1A degree, gamma ray irradiation is often used instead of surgery if there are certain contraindications or the patient refuses surgery. Chemotherapy courses are usually not used at this stage due to the small size of the tumor and insignificant growth into the stroma of the organ.
Therapeutic manipulations in the fight against neoplasm stage 1B
There are no specific methods for treating pathology at stage 1B. The doctor determines the course of treatment individually. This takes into account the woman’s age, medical indications, the patient’s well-being and the medical equipment of the clinic. The disease can be treated with surgery, the combined use of chemotherapy and radiation with radioactive substances, and using all three methods.
The surgical intervention consists of radical extirpation of the uterine body according to Meigs - the uterus is removed along with the appendages, the third of the vagina that is located on top, the adjacent tissue, lymph nodes and the cardinal, cross-uterine ligaments of the pelvic walls. The obtained samples of atypical tissue are sent to the laboratory for histological examination to determine postoperative manipulations.
After surgery, adjuvant treatment is used, depending on the histological results obtained regarding disease progression. Dangerous symptoms after analysis are considered:
- there are metastatic sprouts in the area of the lymph nodes;
- the degree of differentiation is defined as G3, which complicates the patient’s situation;
- the diagnosis was established with the mark LVSI+;
- the neoplasm exceeds 30 mm in size;
- endophytic growth of an atypical compaction was diagnosed - a barrel-shaped cervix was identified;
- the operation was carried out with partial resection of the diseased organ;
- The results obtained do not reflect the entire picture of the pathology.
If after histology no relapse of the pathology is detected, the woman is simply under the close supervision of a doctor. There is no treatment after surgery. If a high risk of further progression of the pathology after radical resection is detected, the patient is prescribed courses of radiotherapy with chemotherapy. Typically, Cisplatin is used once every 7 days during the entire period of exposure to radioactive substances. The postoperative method lasts up to 6 weeks.
Sometimes conservative treatment without surgery is used. Here, radiation therapy is used or the tumor is treated with drugs from the group of cytostatics. Indications for such treatment are the following symptoms:
- surgical intervention cannot be used for various objective reasons;
- the patient refused the operation;
- the neoplasm is at stage 1B2 - in this case, individual indicators are taken into account.
If a compaction of more than 40 mm is detected (corresponding to stage 1B2 of the cervical canal), courses of chemotherapy are prescribed before surgery. This allows you to stop the further growth of the atypical formation, which will help reduce the size of the tumor. Courses of therapy are selected individually. This is influenced by a lot of factors - age, health, type of pathology and medical indications.
How to protect yourself from misconceptions?
In order not to succumb to common misconceptions, it is necessary to develop critical thinking.
A critical assessment of any information that comes to you can remove many contradictions and protect against misconceptions and myths in matters of health.
Good advice for doctors would be to use recommendations and methods of evidence-based medicine, which suggests relying only on scientifically proven actions that are safe for the patient’s health.
There is a certain decision-making algorithm that doctors try to follow:
- Select the question you want answered.
- Get the best evidence, the best answers.
- Critically evaluate the best answers and evidence.
- Use the information you have critically read and comprehended in relation to your clinical practice.
Also, at any stage, it is necessary to pay attention to the use of reliable sources of information.