10.17.2020 Alena Masheva Health
In this article we will look at why the cervix hurts. What causes this unpleasant symptom worries many women. In order to prevent pain in the cervix, a woman should know its structure and structure. This will save you from many problems and allow you to understand the causes of such an unpleasant pathology.
Unpleasant sensations after ovulation
A tingling sensation in the abdomen before the onset of the ovulatory period is considered completely normal. It occurs due to the fact that during the cycle a follicle is formed in the ovary, it grows under the influence of hormones and when it matures, it bursts.
The rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Tingling or pain appears on one side as the ovaries alternately oculate.
Why it stings in the uterus, signs of pathology:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increased body temperature.
- Bleeding.
Blood loss should be copious, since minor bleeding may occur during ovulation. It is considered a normal phenomenon, since the ovarian membrane is enveloped in capillaries; when they rupture, they are damaged, and a small amount of bloody discharge appears.
If there is a lot of blood, severe pain, or discomfort occurs, then you should urgently consult a doctor. The doctor will help determine the cause of discomfort and diagnose the presence of pathology at an early stage of development.
Methods for getting rid of unpleasant sensations:
- it is worth taking painkillers;
- resort to the help of antispasmodics.
Pain is an alarming sign that should be taken as a “signal”; the appearance of unpleasant sensations can be eliminated with the help of various medications. This will help alleviate the woman’s condition for a while. But if the discomfort does not go away, unpleasant symptoms bother you with a vengeance or appear with alarming frequency, then you should consult a gynecologist.
The main signs of pathology during ovulation
- Severe pain in one side.
- The appearance of blood in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
- An increase in the intensity of discharge and a change in its quality (it can be copious and emit an unpleasant odor).
The reasons for the appearance of unpleasant sensations can be different; do not forget that tingling is not always a sign of pathology.
Causes of pain before menstruation
When there is colitis in the uterus before the onset of menstruation, you should pay attention to the level of hormones in the blood. Changes in hormonal levels are considered a sign of unpleasant sensations; they bother you for a certain period of time and occur a few days before the onset of monthly bleeding.
How to recognize pathology?
- the pain is long-lasting, occurs several days before the start of menstruation and continues after its completion;
- menstrual bleeding is prolonged and heavy;
- colic in the uterus is pronounced, they are cramping in nature and intensify when lifting heavy objects.
When there is colitis in the lower abdomen before the onset of menstrual bleeding, this may be a sign of:
- Endometriosis.
- Inflammation of the appendages.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Mixing of organs.
It is difficult to understand why an unpleasant sensation occurs. In order to determine the cause of pain, a comprehensive, differentiated diagnosis will be required. Tingling in the lower abdomen, occurring at varying frequencies, can nominally occur before the onset of menstrual bleeding. But if the pain is sharp, severe, and then heavy menstruation occurs, then you should consult a doctor.
How to eliminate tingling in the uterine area using medications that you can take:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen);
- antispasmodics, to eliminate spasm of the smooth muscles of the uterus (No-shpa).
But if tingling occurs in the uterus after ovulation and before the onset of menstruation, then this is a sign of hormonal imbalance. Due to the imbalance of hormones in the body, certain changes occur, which lead to the appearance of colic or discomfort.
Symptoms appear during and after menstruation
The uterus hurts after menstruation due to a hormonal imbalance in the body. The level of hormones in the blood rose sharply and then decreased. As a result, unpleasant discomfort arose in the intimate area.
Tingling in the uterus before menstruation also appears against the background of an increase in the level of hormones in the blood. But these unpleasant sensations quickly pass. As soon as the level of hubbub stabilizes.
If this does not happen, then it’s time to see a doctor and take a hormone profile. Instability of hormonal levels can occur due to:
- Taking oral contraceptives.
- A recent abortion (no more than 1 year has passed since the procedure).
- The fact that not long ago a woman gave birth to a child (no more than 6 months have passed since the birth).
- A recent miscarriage (at least 6 months after the miscarriage occurred).
All of the above conditions lead to changes in the level of hormones in the blood. The body will need some time to recover. When the hormonal levels stabilize, the tingling will disappear.
If the discomfort does not disappear, the symptoms continue to increase, then it is necessary to urgently visit a gynecologist, since only he will be able to determine exactly why the pain occurred.
But tingling in the cervix before and after menstruation occurs due to the fact that the cervical canal expands before menstruation. When the bleeding ends, the cervix narrows, if there are erosive changes on it, then pain may occur.
Consequences
Lack of proper attention to your body and ignoring pain in the cervical region leads to such serious diseases as dysplasia and cervical cancer in the presence of human papillomavirus infection. And since this virus circulates in almost 80% of women aged 20 to 35 years, alertness should be very high. Sooner or later, an advanced disease leads to the appearance of malignant tumors.
Quite often, a woman does not suspect that she has erosion, which occurs due to frequent abortions or complicated childbirth, when leading a promiscuous sex life. And even after learning about the diagnosis, many do not rush into treatment, hoping that everything will go away on its own.
The danger comes from papillomas and polyps that form on the cervix and genitals. Papillomas are of viral origin. Polyps are growths of the glands of the cervical canal and, despite their benign nature, can degenerate in the future.
Cervical cancer is quite easily diagnosed by histological examination. But at the same time, this is one of the diseases that may not manifest itself for a long time. And the later the disease is detected, the worse the prognosis.
The occurrence of pain in the cervical region during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth in later stages.
Colic during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the cervix tingles as it closes, and certain changes in the condition may be associated with this phenomenon. Tingling also occurs during implantation of the fertilized egg; the unpleasant sensations do not bother you for long. They are not much of a concern and pass quickly.
Some women perceive pain as the first sign of pregnancy, and they are partly right. Sensations arise even before the delay occurs, since immediately after implantation certain hormonal changes occur in the body.
Stitching pain in the uterus should be considered a sign of pathology if it is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- spotting or bleeding;
- change in general condition (weakness appeared, health worsened).
During pregnancy, the stomach also hurts due to the fact that the ligaments diverge; this happens in the 2nd trimester. At 1 such pain should not occur.
So, what is this tingling? Sign of pathology or normal phenomenon? Nominally, the appearance of such sensations is not considered a pathology; pain can be bothersome in the early stages for various reasons: increased hormone levels, implantation, etc.
But if the sensations are strong, then you should not endure the pain, as it may be a harbinger of a miscarriage.
Physiological pain
There is a physiological nature of pain:
The cause of the disease will become clear only after a thorough examination at a antenatal clinic or medical center. A hidden asymptomatic course of the disease at the initial stage is possible. Neck pain can be its extreme manifestation.
So, why does the cervix most often hurt?
Other reasons and how to get rid of tingling?
When there is tingling in the uterus, this can be regarded as a sign of:
- An inflammatory process, against the background of which an unpleasant sensation appears.
- Erosive changes in the cervix.
- Bend of the uterus, change in its position.
- Dysmenorrhea.
- Ovarian cysts.
- Hypoplasia.
- Adhesive process.
- Myoma.
- When your lower abdomen hurts, your body temperature has risen, the quality and quantity of discharge has changed, you should suspect that you have an inflammatory process. Inflammation can affect the ovaries (appendages), the body of the uterus and even the fallopian tubes. If inflammation is not treated, it will quickly become chronic and cause infertility. The inflammatory process develops rapidly, it captures more and more new tissues, as a result of which the structure of the organ is disrupted, irreversible changes occur, leading to problems with reproductive function.
- Erosive changes in the cervix are another reason for the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the abdomen, in its lower part. The pain may be irregular and occur periodically. Unpleasant symptoms intensify with exacerbation of the disease, and may appear when an infection occurs.
- Secondary infection leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, the quality and quantity of discharge changes, it becomes purulent, with an unpleasant odor.
Note: In general, erosion is not dangerous, with adequate therapy. This disease will not lead to consequences, but if erosion is not treated, it can cause cancer.
- Dysmenorrhea is abdominal pain that occurs during menstruation. Pain syndrome can be primary or secondary. With primary dysmenorrhea, it is not possible to determine the cause of tingling. Pain occurs due to muscle spasm. Secondary dysmenorrhea is considered a sign of a disease of a gynecological nature.
- If the uterus hurts, or there is a tingling sensation in the side or peritoneum, then the cause may be a cyst. There are various cysts; they arise as a result of surgery. Appear on the ovaries as a result of hormonal imbalance (mainly). An ovarian cyst is not a burst follicle; it is formed due to hormonal imbalances in the body. When the level of hormones is not stable, the ovary matures in the follicle, forms, but does not burst at the right time. The follicle does not rupture and it turns into an ovarian cyst.
- Hypoplasia is excessive tissue growth. As a result, unpleasant symptoms arise. The growth of tissue leads to the development of endometriosis. If hypoplasia is not treated, it will certainly lead to the development of various complications. You can get rid of hypoplasia with the help of various drugs; drugs of the OK class are often prescribed, as well as curettage (scraping), as a result of which excess tissue is removed from the uterine cavity.
- The adhesive process occurs against the background of a chronic course of inflammatory diseases. Adhesions disrupt the elasticity of organs. When muscle tissue contracts, pain occurs. Adhesions are removed with the help of special medications that are absorbable in nature. Adhesions can also occur after abdominal surgery. They affect the elasticity of tissues and lead to the development of infertility.
Since adhesions are considered to be the cause of infertility, they are removed through surgery or excised with a laser.
- Myoma is a benign formation that is prone to growth. Myoma quickly increases in size, compresses ligaments and large vessels, and disrupts blood flow to the organ. As a result of compression, unpleasant symptoms occur. Fibroids appear against the background of hormonal problems; hormone failure leads to active growth of muscle tissue. The tumor is treated with surgery; if the fibroid does not reach a large size, then it can be treated with hormonal drugs.
Pain in the cervix: pulling, aching, discomfort during pregnancy and examination
Soreness of the cervix is a sign of quite serious diseases, but it can also be physiological.
Physiological pain includes pain that occurs during menstruation or pregnancy. The pain may appear during menstruation and during sexual intercourse or be present all the time. It may occur in inflammatory, oncological or precancerous pathologies. When this syndrome appears, a woman should immediately visit a gynecologist to identify the cause. In this article we will try to explain what can cause these same pains.
Types of pain
According to the nature of pain they are divided into:
- constant, aching – characteristic of inflammatory diseases;
- those that appear during sexual intercourse;
- periodic, weak, aching - associated with the development of benign neoplasms.
Cervical pain can be a symptom of inflammation and various precancerous diseases.
The following diseases are detected as causes of pain:
- Pseudo-erosion (ectopia) – this pathology is characterized by an abnormal position of the epithelium outside the canal cavity. The leading symptom is moderate pain in the cervical area. There is some slight bleeding.
- Erosion - the basis of this disease is the appearance of a defect in the multilayered epithelium (a scratch or a small wound). If the reparative processes proceed normally, and there are no foci of inflammation, then the wound heals. If pathogenic flora or disruption of the regeneration process is present, then healing does not occur.
- Leukoplakia - the formation is located on the cervix and consists of pale areas of keratinization. The process is a consequence of previous infections. The formation easily transforms into malignant.
- Ectropion is an eversion of the mucous membrane of the canal. The cause of formation is injury to the mucous membrane during abortion or curettage.
- Erythroplakia - the formation looks like a red spot located on the mucosa. The reasons for this process have not yet been established.
Pain in the cervix occurs not only when it is directly affected. They are present when the body of the uterus is damaged.
Cervical pain occurs with the following pathologies of the uterine body:
- endometrial cancer – with it, pain begins in the later stages;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus;
- hypertension during pregnancy caused by progesterone deficiency;
- leiomyoma is a benign tumor originating from the endometrium;
- adenomatosis - considered a precancerous condition, uncontrolled growth of cells in the mucous layer occurs due to the high content of female sex hormones;
- stenosis - a sharp narrowing of the cervical canal, there is congenital and acquired (infections, tumors, consequences of operations and diagnostic procedures);
- endometriosis (adenomyosis) – pathology is characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells of the mucous layer beyond its boundaries;
- prolapse and prolapse - disruption of the position of the uterus due to weakening of its ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor;
- lack of female sex hormones, which is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation;
- polyps are benign tumors localized in the cervix and its mucous layer;
- endometrial hyperplasia - proliferation of the glandular or basal layer.
All these diseases of the body and cervix cause pain. Differentiate using ultrasound, gynecological examination and laboratory tests.
Pain due to benign tumors of the cervix or uterine body
Pain in the cervix can be a manifestation of benign tumors - polyps and fibroids.
Polyps
The intensity of pain with polyps ranges from mild to intense. Women also note discomfort and feel that there is something in the cervix.
Unpleasant sensations in the cervix intensify with physical impact on it (gynecological examination, sexual intercourse). Polyps are usually combined with other pathologies of the female genital area. Upon examination, the expansion of the canal is visible and a formation is detected in it. Palpation creates discomfort. An additional examination method is ultrasound.
Myoma
With fibroids, the pain is localized in the lower third of the abdomen and radiates to the cervical area. It enlarges and puts pressure on neighboring organs. Depending on the type of tumor, pain varies in intensity and location. Dull pain is typical and intensifies with changes in body position.
Their intensity increases when urinating, and they haunt you at night. It hurts for a woman to sit. She feels that the pain is radiating or as if it is hitting her neck. A woman notes that her cervix hurts when she sits. Reports heaviness in the lower abdomen.
If the fibroid is localized along the posterior wall, the pain radiates to the back or anal area. Sometimes it goes to my feet. During menstruation, the pain intensifies and has a cramping character.
The phenomenon is explained by the fact that with this pathology the mucous layer is rejected worse and the uterus is forced to contract more strongly. Displacement of internal organs and disruption of their function is possible.
Pain associated with pathologies of the uterus and appendages
Nagging pain in the projection of the ovaries, radiating to the cervix, is typical for inflammation of the appendages.
Examples of pathologies:
- adnexitis;
- salpingitis;
- salpingo-oophoritis.
The intensity of the pain syndrome can vary from mild pain in chronic processes to highly intense pain in acute conditions. A woman notes pain and discomfort during intercourse. Sitting down also hurts. There is a rise in body temperature to subfebrile levels. As the infection progresses, the pain has a jerking character.
There are various discharges from the genital tract and other signs of infection. With an exacerbation of the process, general infectious symptoms may occur (nausea, dizziness, loose stools, vomiting). On examination, the entrance to the cervix is painful. Palpation of the ovarian area is painful on the left and right.
Touching the neck causes pain.
Pain in precancerous conditions and cervical cancer
These diseases pose an increased danger to the life and health of women and require special attention during diagnosis, treatment and observation.
Erosion
The cervix may hurt due to erosion, but most often there is no discomfort with this pathology. First, pain appears in the lower third of the abdomen during menstruation and radiates to the lower back. Outside of menstruation, the uterus occasionally ache or there is a slight tingling sensation. The woman feels that she is pulling her neck.
Discomfort often appears after sexual intercourse (the cervix hurts from sex). The cervix may hurt due to any mechanical impact, for example, after an examination by a gynecologist. The examination is accompanied by bloody discharge. The appearance of pain during erosion indicates the addition of a bacterial infection.
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is considered a precancerous disease. The disease has an asymptomatic onset and stings a little during sexual intercourse. Constant pain appears only in the later stages or after infection has occurred. It begins to ache in the vagina. It hurts a woman if you touch her neck.
Cervical cancer
IMPORTANT! Cervical cancer occupies one of the first places in the structure of mortality among young women among all oncological pathologies.
In the initial stages, this disease does not manifest itself in any way. Then bleeding appears after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination. There is a cutting pain in the neck area, radiating to the sacrum area.
In later stages, pain appears in the neck, which can shoot down the leg. General weakness, fatigue, and weight loss are added. The formation can compress internal organs.
Touching the cervix is extremely painful.
Inflammatory pathologies of the uterus and cervix
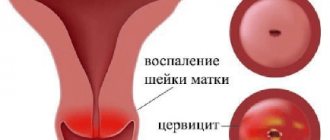
Inflammatory diseases of the neck and body are represented by cervicitis and endometritis.
Cervicitis
In pathology, the cervical canal and its vaginal part are affected. The woman notes that the cervix is enlarged and hurts.
The following symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
- the cervical canal hurts;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- stabbing in the cervix;
- discharge from the genital tract.
During a gynecological examination, you can notice redness and swelling of the cervix in the area of the cervical canal. Its mucosa is covered with areas of pinpoint hemorrhages. The neck is compacted, pseudo-erosions are formed. Touching the neck is painful. When touched with a finger, blood vessels are easily damaged and the mucous membrane bleeds.
Endometritis
This pathology most often takes on a secondary nature; it is a continuation of the ascending inflammatory process in cervicitis. It develops as a complication of adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages) and salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes).
Endometritis manifests itself:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin area;
- mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract;
- signs of general intoxication.
If the cervix shoots with endometritis, this indicates generalization of inflammation. The process can spread to fatty tissue. Inflammation of the uterus can become chronic.
It can only manifest itself as painful periods. The cervix is compacted, swelling and redness are noted. If you press on it, it is sharply painful.
A slight touch causes injury to the vessels on its surface and bleeding.
Prolapse and prolapse of the uterus
In the initial stages of the disease, the cervix bulges, pain radiates to the lower back. The pain is nagging and constantly bothers me. It intensifies with prolonged sitting. If the woman lies down, the pain subsides. She has a sensation of a foreign body in the vagina. You may feel heaviness in the lower abdomen. The woman begins to worry about constipation and frequent urination and pain.
Periodic pain in the cervix during menstruation
Moderate pain in the cervix during menstruation is considered normal if it is not of high intensity and does not last long. They may appear if menstruation was preceded by heavy physical activity or sexual contact. This may be a pressing pain in the cervix. There may be pain in the cervix of a cramping nature, which intensifies with defecation.
The causes of painful periods are:
- increased pain sensitivity;
- lack of production of natural anti-pain substances (endorphins, enkephalins);
- endometriosis;
- violation of the position of the uterus;
- increased production of prostaglandins;
- uterine fibroids;
- corpus luteum phase disorder.
If you have painful periods, it is better to consult a gynecologist.
Cervical pain and pregnancy
Pain in the cervix during short-term pregnancy indicates a possible pathology. In late pregnancy, if pain occurs for a short period, this is not a pathology. If this period is prolonged, you should contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. In any case, consulting a doctor will not do any harm and will help eliminate the possible latent course of severe pathologies.
The causes of pain during pregnancy are the following:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency - weakening of the muscle ring in the area of the internal os of the uterus;
- cervical hypertonicity - increased uterine tone due to insufficient progesterone production;
- congenital underdevelopment of the uterus - the cells of the muscle layer cannot increase normally during pregnancy and respond with an increase in tone.
All these diseases lead to the fact that a woman cannot bear pregnancy. Pain is one of the signs of an impending miscarriage. If urgent measures are not taken, this will end in spontaneous abortion.
What to do if pain occurs
The causes of pain are extremely diverse and among them there are very serious diseases. This means that women should contact a gynecologist if any kind of discomfort occurs. In addition to examination, additional research methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the uterus;
- histological examination;
- taking smears for examination;
- tank sowing the contents of the cervical canal;
- colposcopy.
After carrying out diagnostic procedures, the doctor will make a diagnosis. Treatment is carried out according to the detected pathology.
IMPORTANT! Among the diseases that cause discomfort and pain in the cervix are many precancerous diseases.
After treatment, a woman should be regularly monitored by a doctor and follow all his recommendations. These measures will allow you to notice oncological degeneration in time and begin appropriate treatment. Thereby avoiding serious operations, maintaining a high quality of life and reproductive function.
Source: https://sheika-matka.ru/diagnostika/ot-chego-mozhet-bolet-shejka-matki-vozmozhnye-ginekologicheskie-zabolevanija/
Menstruation
The occurrence of pain before the onset of menstruation is one of the main complaints with which women come to see a gynecologist. If the pain recurs regularly and begins to appear a couple of days before the start of menstruation, this means that pathological processes have begun to develop in the uterus, affecting not only the cavity, but also the appendages and cervix. If pain occurs before the onset of menstruation, you should consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis is impossible due to the fact that for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to take tests and undergo an examination.
Regular pain may indicate the development of diseases such as endometriosis, cancer, pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.
One of the symptoms of endometriosis is acute tingling, which can be observed against the background of dysmenorrhea. In this case, the pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, general weakness, migraine, dizziness, lack of appetite, etc. Pain may occur during bowel movements or during sexual intercourse.
Pain in the uterus can signal an inflammatory process, in which purulent discharge is often observed. With uterine cancer, stabbing pain may not appear immediately and is often accompanied by bleeding.
To reduce pain, sedatives or antispasmodics are recommended. In any case, it is necessary to remember that these remedies only help temporarily relieve pain, but are not able to cure the disease. Only a visit to a specialist, tests and examination will be able to identify the causes that cause pain in the uterus itself, in its cervix and appendages. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. It is worth noting that advanced diseases are more difficult to cure. They can lead to a lot of complications, one of which is infertility.
Pain during menstruation may indicate:
- hormonal imbalances;
- inflammatory processes;
- erosion process;
- cysts;
- fibroids.
To relieve pain, you can use antispasmodics (drugs that relieve spasms of smooth muscles) and painkillers. But you should not self-medicate, as this may worsen the situation. Only a specialist can prescribe the necessary treatment. For example, if tingling in the uterus is caused by hormonal disorders, the doctor may prescribe a course of hormonal medications, which are prescribed individually according to indications after the necessary studies.
Ovulation
Ovulation is the process of the release of a mature egg from the ovarian follicle, which is fully prepared for fertilization. One of the main stages of the menstrual cycle. The ovulation rhythm can undergo changes in several cases:
- Abortion (disorders observed for 3 months).
- Childbirth (rhythm disturbances observed within 1 year).
- Age period. Violations occur in women who have crossed the forty-year mark. This is how the body prepares for the premenopausal period.
During the release of the egg, there is an increase in vaginal discharge, a decrease in basal temperature (the next day it increases), an increase in progesterone levels and other indicators. Tingling in the uterus after ovulation can signal a woman about a possible pregnancy even before the delay occurs. A similar condition can also occur after childbirth or abortion.
Possible deviations
It is important to identify the reasons for this. This happens most often:
- with hypertonicity of the uterus, it is all due to low levels of progesterone or high levels of prolactin, stress, infections or physical activity;
- cervical insufficiency - in this case, the cervical part cannot withstand the pressure of the fetus or opens due to hormonal imbalance, causing pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen;
- endocervicitis - an inflammatory process in the cervical canal as a result of sexually transmitted infections or the circulation of opportunistic microflora, pathological discharge from the vagina is also observed;
- erosions - occur for a short period of time, over 10-14 days, so the patient most often does not notice the pain.
Pregnancy
At the very beginning of pregnancy, even before the delay occurs, changes begin to occur in the female body. Signs that help determine whether a woman is pregnant or not before a delay may appear differently for everyone. However, there are several basic signs that can give almost one hundred percent results.
Before the delay, a woman may experience slight vaginal discharge. They signal the implantation of the embryo on the wall of the uterus. This symptom can only give a guarantee if the woman has a regular menstrual cycle, there are no problems with ovulation, there is no erosion of the cervix and other diseases of the reproductive organs.
Before the delay, you may experience weakness, lethargy and general malaise. However, a woman may confuse this signal of pregnancy before a missed period with a common cold. Also, before the delay occurs, sleep disturbance may occur.
From the period of embryo implantation, that is, even before the delay, a woman may feel a feeling of heaviness in the uterus. After the first week of pregnancy, most women feel a slight tingling sensation in the uterus from time to time.
Acute colic in the uterus, which is combined with bleeding, can signal an ectopic pregnancy. This condition is usually accompanied by loss of consciousness and fever. If tingling is observed in the early stages and is accompanied by bleeding, then it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, as this is a harbinger of a possible miscarriage.
Tingling during pregnancy in the uterus can be observed when the position of the appendages changes. This condition may be accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. Sharp, severe pain, accompanied by bleeding from the vagina, signals necrosis of the node. Often observed in the early stages of pregnancy (first trimester), as well as after childbirth and abortion.
If the pain is not severe, and there are no undesirable symptoms such as bleeding and dizziness, then such a condition may signal possible pathologies of pregnancy.
Basically, the causes of colic are hidden in the fact that when pregnancy occurs, some changes begin to occur in the expectant mother’s body, which also affect the uterus. Against the background of such changes, some sensations may be felt that do not pose a threat to the health of the woman and the fetus.
However, if during pregnancy a woman feels tingling in the uterus, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. Even in cases where pain does not warn of the development of pathologies, it is better not to risk your health.
Many women experience such a phenomenon as tingling in the uterine cavity - this is how the body can signal the onset of pregnancy, or indicate the course of the disease. Although tingling is also typical for healthy women – we’ll talk about this later.
Why does the cervix hurt?
In this article we will look at why the cervix hurts. What causes this unpleasant symptom worries many women. In order to prevent pain in the cervix, a woman should know its structure and structure. This will save you from many problems and allow you to understand the causes of such an unpleasant pathology.
Structure
The cervix is the lower part of the organ, that is, the transition zone from the vagina to the uterus. Its shape resembles a cone or cylinder in girls and nulliparous women after childbirth. The size is influenced by several factors. The norm is a length of approximately 3-4 cm, a width of 2.5 cm. In a pregnant woman, the cervix shortens before childbirth and softens, that is, it becomes the birth canal for the baby.
Neck parts
There are 2 parts of the cervical region:
- lower, located in the vagina (vaginal part);
- upper, located above the vagina (supravaginal part).
The cervical canal runs inside the cervix. Along its edges there are pharynxes - the internal one, which leads into the uterine cavity, and the external one, which opens into the vagina. The cervical canal fills with mucus.
It is produced by glands after menstruation; it is a kind of natural protective barrier for the uterus from the effects of pathogenic microflora. The external os is a transition zone, which is considered the most vulnerable part in the cervix.
This pharynx is exposed to various risks that can provoke the formation of malignant tumors.
The main function of the cervix is childbearing, so pain in this area should alert a woman planning a pregnancy. This is a serious reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Cycle phases
The structure, size and location of the organ is influenced by the phase of the menstrual cycle:
- The beginning of the cycle - the cervix is lowered and firm, with a dense structure.
- The middle of the cycle is ovulation. The neck acquires a loose structure and softens. The mucus becomes more liquid; its consistency resembles the white of a chicken egg. Then it leaves the cervix for the unhindered passage of sperm. The lower pharynx opens, causing the cervix to rise higher. This is the most favorable period for conception, and the organs are thus prepared for this.
- The cervix descends before the onset of menstruation. A similar condition can be observed during early pregnancy.
- During menstruation, the cervical canal widens to allow blood clots to pass through.
Many patients wonder whether the cervix can hurt. This is a signal for a woman about a possible pathology. The reasons why it occurs can be very diverse.
Painful sensations can be pathological or physiological, but only a gynecologist can carry out a differential diagnosis and identify their origin.
The pain also varies in its manifestation.
Pathological pain
So, the unpleasant sensations that are caused by the disease:
- Chronic pain was caused by endocervicitis and cervicitis - inflammation of the cervical canal and the cervix in general.
- Erosion, dysplasia or cervical cancer often lead to sharp pain during sexual intercourse.
- Endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis provoke prolonged pain.
- Myomas, polyps and cysts - benign neoplasms of the cervix lead to aching pain with low intensity.
How else does your cervix hurt?
Physiological pain
There is a physiological nature of pain:
- During menstruation.
- After surgical interventions during healing.
The cause of the disease will become clear only after a thorough examination at a antenatal clinic or medical center. A hidden asymptomatic course of the disease at the initial stage is possible. Neck pain can be its extreme manifestation.
So, why does the cervix most often hurt?
Possible pathologies that occur most often
Let us list the diseases in which women often experience cervical pain. This may include:
- Erythroplakia. It is a degree of extreme atrophy of the multilayered epithelium, down to the basal layer. For this reason, the blood vessels in the defect are visible, so it looks like a red spot. Malignant degeneration of the pathology is not excluded.
- Ectropion. It is considered an eversion of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. The cause is a previous abortion, planned curettage or complications after natural childbirth.
- Leukoplakia. Small whitish areas appear on the epithelium of the cervix. This happens most often due to injuries, infections, reduced immunity or hormonal imbalances in simple leukoplakia. The most dangerous form of the disease is verrucous, which is initiated by HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis. The pathological focus is a layer of excess epithelial keratinization, which should normally be absent. Also, the possibility of degeneration of verrucous leukoplakia into cancer cannot be excluded. If you experience pain in the cervix with leukoplakia, it means that the disease is already in an advanced form.
- Erosion of the cervix. The mucous membrane of the cervical epithelium is slightly damaged and erosion occurs. Typically, a wound or ulcer can heal on its own without any therapy, provided there are no inflammatory processes. In an advanced form and with severe inflammation, the cervix will hurt and bleed during sexual intercourse. Sometimes the cervix hurts after cauterization of erosion.
- Ectopia (pseudo-erosion), congenital or acquired. The epithelium of the cervical canal is located not inside, but outside it. It can be found in the vaginal part of the cervix. The cause is improper healing of erosion. Painful sensations against the background of pseudo-erosion are extremely rare. As a rule, there are no symptoms for this pathology, and pain is observed during an incorrect examination by a gynecologist. If intense inflammation occurs, the woman will experience pain in the lower abdomen. When the cervix hurts, a doctor must determine the cause.
- Benign neoplasms – nabothian cyst, fibroid and polyp. Cysts provoke pain when they are larger than 2 cm; in such cases, a puncture is necessary. In addition to pain, fibroids and polyps often cause spotting, brown discharge and bleeding.
A cytological smear during preventive examinations by a gynecologist should be taken regularly to detect cervical diseases in the early stages. A more accurate result is observed with colposcopy and biopsy.
During pregnancy
Let's find out why the cervix hurts during pregnancy.
At this time, the doctor should especially monitor this organ. It is his condition that influences whether a woman carries a child or not.
After fertilization of the egg has occurred, significant changes await the cervix. It grows with new vessels, blood flow increases, and under the influence of progesterone, the vaginal and cervical tissues swell.
Against the background of such processes, mild pain or, rather, discomfort such as bloating may occur. When examined, the cervix has a bluish tint.
If the doctor finds that the cervix is soft and the canal is slightly open, he will suspect a threat of miscarriage.
In the last stages of pregnancy, the cervix shortens and becomes very soft - this is the first sign that labor is imminent. A mucus plug comes out of the cervical canal. A woman may experience training contractions, during which she feels pain in the cervix.
Why does the cervix hurt during pregnancy?
Possible deviations
It is important to identify the reasons for this. This happens most often:
- with hypertonicity of the uterus - it’s all due to low levels of progesterone or high levels of prolactin, stress, infections or physical activity;
- cervical insufficiency - in this case, the cervical part cannot withstand the pressure of the fetus or opens due to hormonal imbalance, causing pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen;
- endocervicitis - an inflammatory process in the cervical canal as a result of sexually transmitted infections or the circulation of opportunistic microflora, pathological discharge from the vagina is also observed;
- erosions - occur for a short period of time, over 10-14 days, so the patient most often does not notice the pain.
Papillomas and polyps
Papillomas and polyps that form on the cervix and genitals are especially dangerous. The first ones are of viral origin. Polyps are growths of the glands of the cervical canal. Although benign, they can develop into cancer in the future.
Oncology is easy to detect by histological examination. This is one of the pathologies that may not manifest itself for quite a long time.
Cervical pain during pregnancy can cause miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth in later stages.
You should follow all doctor’s recommendations and take all tests.
Therapy
If the cervix hurts, treatment should be immediate.
First of all, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis. Only after this should you begin treatment.
In the presence of erythroplakia, dysplasia, leukoplakia, or ectopia, one type of surgical intervention is required. The most popular are considered:
- cryodestruction – treatment of the affected area with liquefied nitrogen;
- radio wave treatment;
- diathermocoagulation - high frequency currents affect the problem;
- conization of the cervix - part of the cervix is removed in the shape of a cone;
- laser therapy.
Age, degree of neglect of the pathology and plans for pregnancy influence the choice of surgery. At the same time, antibacterial, antiviral, and immunomodulatory therapy is carried out.
With a diagnosis such as ectropion, the doctor first determines the presence or absence of foci of the inflammatory process. Then the cervical canal is restored. Treatment is selected on an individual basis. Complications are extremely rare.
Currently, chemical coagulation is very popular in the treatment of small ectopia. The lesion is treated with a drug (“Solkovagin”, “Vagotil”).
Most often, the manipulations are painless, but slight discomfort may be felt.
Benign tumors are usually removed surgically. But sometimes conservative treatment is enough. Hormonal medications are prescribed if the cervix hurts.
When planning a pregnancy, you should undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude cervical pathologies. If they are detected, then therapy is first carried out, after which conception can be carried out.
We looked at what it means if the cervix hurts. What to do with this pathology is also described in detail.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/454918/pochemu-bolit-sheyka-matki
The uterus and its structure
The uterus is a smooth muscle, hollow organ located in the pelvic area, its shape resembles a pear and is intended for bearing a fetus during pregnancy.
Uterus dimensions:
In a previously nulliparous woman, the uterus weighs 50 grams, and after childbirth, this figure increases to 100 grams. during the dormant period - its length does not exceed 7-8 cm, width - 5 cm.
- During gestation, the size of the uterus increases - its walls stretch up to 32 cm, and the hollow organ itself is capable of supporting the weight of the fetus up to 5 kg.
On each side, her body is supported by ligaments, providing anatomically sufficient movement during the period of gestation.
Its structure consists of the body and the neck, the isthmus - in many women it is tilted forward. The part of the organ located above the level of origin of the tubes is the fundus, on the right/left side at the very bottom there are its lateral edges, the upper ones are the corners of the uterus.
Structure of the walls of the uterus:
- The endometrium is the inner layer of the uterus. Its thickness varies from 1 to 3 mm. and it is penetrated by glands, produces secretions and is renewed during menstruation.
- The muscular, inner layer is the myometrium. It undergoes changes during gestation and its thickness does not exceed 3-10 mm.
- The outer layer is the serous membrane in the uterus and the peritoneum, which is attached to the posterior/anterior wall.
The role of the uterus in a woman’s life
The uterus performs the following functions:
Protection of the above genital organs and peritoneum from infections penetrating from the vagina
– in this case, the cervical canal takes on this role.- Regular, spontaneous cleansing of the uterine cavity and cervical canal, vaginal cavity - we are talking about regular menstruation.
- Participation in sexual intercourse and creation of favorable conditions for the movement of sperm through the cervical canal into the uterus and its cavity, fallopian tubes.
- Implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity and the creation of favorable conditions for the development of the fetus throughout the entire period of pregnancy, participation in the process of natural childbirth.
- Due to the ligamentous apparatus itself, it forms and strengthens the pelvic floor , supporting the internal organs located above it.
But as noted earlier, its most important function is reproductive , creating favorable conditions for bearing and giving birth to a child.
Neck parts
There are 2 parts of the cervical region:
- lower, located in the vagina (vaginal part);
- upper, located above the vagina (supravaginal part).
The cervical canal runs inside the cervix. Along its edges there are pharynxes - the internal one, which leads into the uterine cavity, and the external one, which opens into the vagina. The cervical canal fills with mucus. It is produced by glands after menstruation; it is a kind of natural protective barrier for the uterus from the effects of pathogenic microflora. The external os is a transition zone, which is considered the most vulnerable part in the cervix. This pharynx is exposed to various risks that can provoke the formation of malignant tumors.
The main function of the cervix is childbearing, so pain in this area should alert a woman planning a pregnancy. This is a serious reason to urgently consult a doctor.
Tingling in the uterus
As a phenomenon, tingling in the uterus can occur at any time during a woman’s life. This signal from the body may indicate the course of a number of pathological processes and should not be ignored, contacting a doctor in a timely manner and undergoing an examination.
As doctors note, such a symptom can occur in the body against the background of delayed menstrual flow - in this case, doctors say that it can be provoked by:
- Cyst or disorders caused by hormonal changes;
- Myoma or erosion affecting the cervix;
- Inflammation localized in the pelvic organs and systems.
Most women in this case do not pay attention to the tingling sensation, take antispasmodics and that’s where it all ends.
But such self-medication is a fight against the consequence, but not the root cause of tingling in the uterus, and is allowed as a one-time salvation. If such a symptom shows itself with enviable regularity, you should immediately visit a doctor.
The main causes of tingling in the uterus
The reasons that provoke pathological tingling in the uterus can be very different - from inflammation and delayed menstruation to malignant neoplasms.
Before your period
In this case, we are talking about the individual characteristics of the functioning of internal organs and the reproductive system.
Pathological diseases cannot be excluded:
- If the pathological process is accompanied by frequent trips to the toilet or a delay in a woman’s menstruation, inflammation of the urinary system most likely develops. If tingling is accompanied by heavy bleeding between menstruation or discharge of pus, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
- The cause of tingling can be endometriosis and cancer, cystitis and pyelonephritis. Most often, endometriosis provokes unpleasant sensations - tingling will be accompanied by attacks of nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite and general weakness, increased pain during sexual intercourse or defecation. In any case, you should not ignore this symptom - in the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, advanced pathology can cause female infertility.
Diseases
The most common diseases in which the cervix hurts:
- Erythroplakia is a degree of extreme atrophy of the layers of multilayer epithelium up to the basal layer, due to which the defect is visible through blood vessels and looks like a red spot. The pathology is dangerous due to malignant degeneration.
- Ectropion is an inversion of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal as a result of abortion, planned curettage, or complications after childbirth naturally.
- Leukoplakia is the appearance of small whitish areas on the epithelium of the cervix. The reasons for this may be injury, infection, reduced immunity, or disrupted hormonal levels in simple leukoplakia. The most dangerous form is considered to be the verrucous form, initiated by HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis. The pathological focus is a layer of excessive keratinization of the epithelium, which should not normally exist. Verrucous leukoplakia is dangerous due to degeneration into cancer. If the cervix hurts due to leukoplakia, then the disease is already in an advanced form.
- Cervical erosion is a slight damage to the mucous membrane of the cervical epithelium. Typically, a wound or ulcer heals on its own without any treatment, provided there are no aggravating factors in the form of inflammatory processes. If there is inflammation, then without appropriate treatment healing will not occur. The cervix will hurt and bleed during intercourse.
- Ectopia (pseudo-erosion) - can be congenital or acquired. The epithelium of the cervical canal is not inside, but outside it and is visually observed in the vaginal part of the cervix. The cause of the appearance is considered to be improper healing of erosion. The cervix hurts with pseudo-erosion extremely rarely. As a rule, this pathology occurs without symptoms, and pain is observed during an incorrect examination by a gynecologist. Only when intense inflammation occurs does a woman notice pain in the lower abdomen.
- Benign neoplasms – Nabothian cysts, fibroids and polyps. Cysts, as a rule, cause pain when they are larger than 2 cm; in such cases, they need to be punctured. Myomas and polyps, in addition to pain, are clinically manifested by spotting, brown discharge and bleeding.
It is necessary to do a cytological smear during preventive examinations with a gynecologist to identify cervical pathologies in the early stages once a year. To obtain a more accurate result, colposcopy and biopsy are performed.
Nice tingle
Doctors call tingling in the uterine cavity of a pregnant woman within normal limits if the latter:
in their flow they resemble the touch of the tip of a thin needle;
- the sensations themselves manifest themselves exclusively during physical or emotional stress;
- have an exclusively short-term, sharp nature of their course and do not disturb constantly;
- other negative signs and sensations are absent in their manifestation.
Doctors consider such phenomena to be the norm - the fetus grows and stretches the walls of the uterus, muscles and fibers of nearby organs, provoking a tingling sensation.
Such pain is short-lived and goes away with a change in body position - in its manifestation and course it is short-lived and not intrusive, it manifests itself in the evening or night hours.
Otherwise, you should visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Therapy
If the cervix hurts, treatment should be immediate.
First of all, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis. Only after this should you begin treatment.
In the presence of erythroplakia, dysplasia, leukoplakia, or ectopia, one type of surgical intervention is required. The most popular are considered:
- cryodestruction – treatment of the affected area with liquefied nitrogen;
- radio wave treatment;
- diathermocoagulation - high frequency currents affect the problem;
- conization of the cervix - part of the cervix is removed in the shape of a cone;
- laser therapy.
Age, degree of neglect of the pathology and plans for pregnancy influence the choice of surgery. At the same time, antibacterial, antiviral, and immunomodulatory therapy is carried out.
With a diagnosis such as ectropion, the doctor first determines the presence or absence of foci of the inflammatory process. Then the cervical canal is restored. Treatment is selected on an individual basis. Complications are extremely rare.
Currently, chemical coagulation is very popular in the treatment of small ectopia. The lesion is treated with a drug (“Solkovagin”, “Vagotil”).
Most often, the manipulations are painless, but slight discomfort may be felt.
Benign tumors are usually removed surgically. But sometimes conservative treatment is enough. Hormonal medications are prescribed if the cervix hurts.
When planning a pregnancy, you should undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude cervical pathologies. If they are detected, then therapy is first carried out, after which conception can be carried out.
We looked at what it means if the cervix hurts. What to do with this pathology is also described in detail.
To prevent pain in the cervix, a woman should have an understanding of its structure and structure. This will help avoid many problems and allow you to understand the reasons if your neck hurts.
The cervix is the lower part of the organ and is the transition zone from the vagina to the uterus. The shape is a cone (in girls and nulliparous women) or a cylinder (after childbirth). Its size depends on several factors: normally, the length is 3–4 centimeters and the width is 2.5 centimeters. In pregnant women, before giving birth, the cervix shortens and becomes soft, which turns it into the birth canal for the baby.
The cervical region consists of two parts:
- lower, located in the vagina (vaginal);
- upper, located above the vagina (supravaginal).
The cervical canal runs inside the cervix. Along its edges are the internal pharynx, which opens into the uterine cavity, and the external pharynx, which opens into the vagina. It is filled with mucus, which is produced by the glands after the end of menstruation and serves as a natural protective barrier of the uterus from pathogenic microflora. The external os is a transition zone and is considered the most vulnerable part in the cervix, which is exposed to various risks, which can cause the formation of malignant tumors.
One of the main functions of the cervix is childbearing, so cervical pain always alarms a woman planning a pregnancy and is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
The structure, size and location of the cervix depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle:
- At the beginning of the cycle, it is lowered and hard - it has a dense structure.
- In the middle of the cycle, during ovulation, the cervix softens and acquires a loose structure. Cervical mucus becomes more liquid, resembling the consistency of a chicken egg white, and leaves the cervix for the unimpeded passage of sperm. The lower pharynx opens slightly, the neck rises higher. Such changes occur due to the fact that this is the most favorable period for conception and the organs are ready for this.
- Before the onset of critical days, the cervical region descends. A similar condition of the cervix can also be observed in the early stages of pregnancy.
- During critical days, the cervical canal is dilated, and blood clots come out through it.
Pain in the neck becomes a signal for a woman about a possible pathology. The reasons why neck pain occurs are varied.
Pain in the uterine cervix varies in its manifestation.
Pain caused by the disease:
- chronic pain initiated by endocervicitis and cervicitis - inflammation of the cervical canal and the cervix as a whole;
- sharp pain during sexual intercourse caused by erosion, dysplasia or cervical cancer;
- prolonged pain associated with diseases of the uterus and appendages - endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis;
- aching pain with low intensity due to fibroids, polyps and cysts - benign neoplasms of the cervix.
Physiological pain:
- menstrual;
- during the healing period after surgery.
The reason why the cervix hurts can only be understood based on the results of a detailed examination in a antenatal clinic or gynecological center. It is possible to detect a disease with a hidden asymptomatic course at the initial stage. Cervical pain can be its extreme manifestation.
Bad tingling
Bad tingling and nagging pain in the lower abdomen lasting more than 3 hours should alert a pregnant woman.
In particular, you should be wary of unpleasant, pronounced symptoms accompanied by:
- Attacks of nausea and gastrointestinal upset, accompanied by an increase in body temperature - this may indicate a complication of appendicitis in a woman or poisoning. But as doctors note, in the first trimester this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
- If a woman is bothered by a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdominal cavity and bloody vaginal discharge, this may indicate the course of placental insufficiency and early leakage of amniotic fluid. In this case, timely assistance, consultation with a gynecologist, and medical assistance are important due to the high risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
- With a pronounced intense burning sensation and pain when visiting the toilet and urinating , the symptoms indicate the course of infectious or inflammatory processes affecting the woman’s genitourinary system, or pathologies affecting the kidneys.
- You should also consult a doctor if you constantly feel a slight tingling sensation and feel tension in the uterine cavity - this may indicate uterine hypertonicity, which ultimately can cause spontaneous miscarriage.
Recommendations
Since any disease or problem with the reproductive system is a dangerous phenomenon, therefore, if any unpleasant sensations occur, tingling in the uterine area should not be ignored.
Timely diagnosis and treatment will help maintain a woman’s health and prevent the development and diagnosis of infertility.
In this case, doctors give their recommendations:
Regardless of the woman's general health
– she is required to undergo regular examinations and consultations with a gynecologist. At least 1-2 times a year.- You should not take painkillers before visiting a doctor, as well as any other medications , just as you should not diagnose yourself and prescribe a course of treatment. This is fraught with many negative consequences, smoothing and distortion of the symptoms of the pathology, delaying the course of treatment, and the development of many complications.
- If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, visit a doctor and undergo an examination. The danger of an ectopic pregnancy should not be underestimated - the embryo will grow, causing rupture of the fallopian tubes, which can be fatal for the woman herself.
- You should not abuse medications during pregnancy, as well as before/before menstruation - each painkiller or antibiotic should be taken in consultation with your doctor.
In all other respects, doctors are unanimous - a healthy lifestyle and do not abuse alcohol, smoke, adhere to an active lifestyle. In all other respects, only a gynecologist can give recommendations, based on the results of examination and diagnosis.
Treatment
Pain in the cervix should be treated only after an accurate diagnosis has been established as a result of examination by a specialist and all necessary tests have been completed.
Erythroplakia, dysplasia, leukoplakia, ectopia require one of the following types of surgical intervention:
- cryodisruption – treatment of the affected area with liquefied nitrogen;
- diathermocoagulation – exposure to high frequency current;
- Conization of the cervix - removal of a part of the cervix in the shape of a cone;
- radio wave treatment;
- laser exposure.
The choice of operation is made only by the doctor and it depends on age, the degree of neglect of the pathology and plans for pregnancy. At the same time, antibacterial, antiviral, and immunomodulatory treatment is carried out.
When diagnosing ectropion, the doctor first determines the presence or absence of foci of inflammation. Then the cervical canal is restored. Treatment is selected individually for each patient. There are no complications observed.
Currently, chemical coagulation has become very popular in the treatment of small ectopia. The lesion is treated with a drug (Solkovagin, Vagotil).
Treatment methods for cervical pathologies may be accompanied by pain. But most often, the process of destruction of the lesion is accompanied only by discomfort, since the cervical epithelium is not supplied with pain receptors. The larger the pathological area, the more severe the pain. The cervix hurts if removal is performed using electrocoagulation. This method is rarely used.
Benign neoplasms are treated surgically and conservatively. The most commonly prescribed treatments are hormonal medications and observation. If the methods are ineffective, surgical intervention is performed. Any of these methods brings positive results.
Why can the uterus hurt? Pain in the lower abdomen, which often occurs in women, is most often associated with some of her diseases and lesions. In most cases, fortunately, these unpleasant symptoms are caused only by functional disorders. Most often they are associated with menstruation, being one of the components of premenstrual syndrome.
In a smaller percentage of cases, pain in the uterine area is actually caused by a specific pathological process. Moreover, its development and progression often poses a direct threat to the health and life of a woman. This type of pain syndrome occupies a special place in obstetrics – its appearance often accompanies a number of pregnancy complications.
Also, the vast majority of gynecological diseases are manifested by pain in the uterus - the causes are both inflammatory processes and some functional and organic disorders. Therefore, such a nonspecific symptom in each case still has some characteristic features. It is the knowledge of these differences that allows the doctor to suspect a specific disease and carry out its timely diagnosis.
When should you see a doctor?
Regarding the question of when to visit a doctor, doctors unanimously say that if there is a deviation from the norm:
- When tingling in the uterus bothers you for more than a day,
- Bloody or purulent vaginal discharge appears,
- Body temperature rises and chills bother you.
This is especially true for pregnant women, when any change in the body and negative impact can provoke spontaneous miscarriage, intrauterine fetal death and premature birth.
Timely assistance from doctors and the attention of specialists, taking prompt measures will help preserve the life and health of mother and child.
In all other respects, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s instructions and lead a healthy lifestyle, which will have a beneficial effect on the entire body, the health of the woman and her future children.
Papillomas and polyps
Papillomas and polyps that form on the cervix and genitals are especially dangerous. The first ones are of viral origin. Polyps are growths of the glands of the cervical canal. Although benign, they can develop into cancer in the future.
Oncology is easy to detect by histological examination. This is one of the pathologies that may not manifest itself for quite a long time.
Cervical pain during pregnancy can cause miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth in later stages.
You should follow all doctor’s recommendations and take all tests.