What is “cytology” in gynecology?
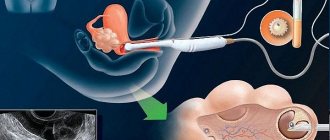
In most cases, when cervical cytology is prescribed, the girl does not know what it is. To begin with, it must be said that the cervical canal is an anatomical formation that in appearance resembles a tube. It directly connects the vagina to the uterine cavity. It contains stratified and columnar epithelium.
Taking material from this area of the reproductive system helps to identify atypical cellular formations in a timely manner. This makes it possible to diagnose a precancerous condition and prescribe appropriate treatment. Evaluation of cellular structures occurs under a microscope with high magnification. The nuclear contents of the cells are thoroughly analyzed.
What does a cytology smear show?
A common option for this type of test is the Pap test. It was first used at the beginning of the 20th century by the Greek scientist Papanikolaou. He was directly involved in the diagnosis of malignant processes in the early stages. This cytology smear also makes it possible to identify background processes of non-tumor origin that have a risk of developing into cancer.
Considering all the above possibilities of the PAP test, doctors prescribe it for the following changes in intraepithelial structures:
- abnormalities in the structure of cells of high and low severity;
- the presence of pathogenic microflora in high concentrations as a result of previous studies;
- disturbances in the menstrual cycle of unknown nature;
- diseases of the reproductive system of a viral nature (HPV, herpes);
- abnormal discharge from the vaginal cavity after menstruation.
Atrophic type of smear for cytology
The PAP test in gynecology is one of the main studies that helps identify the cellular ratio in the cervical canal. With the atrophic type of smear, in the field of view of the microscope, the laboratory assistant records a large content of squamous epithelial cells. This indicates changes in the structure of epithelial tissue, which is often recorded in dysplasia. Further diagnosis, through ultrasound, establishes the degree and severity of the disorder. A smear for pathological cytology is the initial stage of a comprehensive examination of the reproductive system.
Inflammatory type of smear for cytology
Cytology of the cervix helps to identify inflammatory processes at an early stage and prescribe the correct therapy. With an inflammatory type of smear, changes are recorded at the cellular level - the ratio of glandular cells to squamous epithelial cells may increase. At the same time, the woman notes the presence of symptoms of inflammation, which manifest themselves in changes in the cycle - acyclic discharge, an increase in the volume of menstrual blood, severe pain during menstruation.
Why else may bloody or brown discharge appear after a gynecological examination?
A gynecological examination is quite likely not the main reason for the appearance of discharge, but only a catalyst for the manifestation of symptoms of a particular ailment.
So, bleeding occurs as a symptom of the following diseases and phenomena:
- cervical erosion: Discharge that appears after examination of the cervix is quite a common occurrence if there are erosions on the epithelium. The damaged part of the membrane may periodically bleed without directly touching it; medical intervention only contributes to this;
- endometriosis: in addition to discharge, it is characterized by pain in the abdominal area;
- fibroids: such a neoplasm periodically bleeds, which can appear immediately after an appointment with a gynecologist;
- swelling: doctor’s manipulations can cause bloody mucus to appear;
- endometrial hyperplasia: with this disease, the mucous membrane thickens, and, as a result, its particles come off when touched, which causes spotting mucus;
- polyps in the cervical canal area: they are injured by any touch, which causes characteristic spotting;
- infections: provoke the development of an inflammatory process on the vaginal mucosa, making it sensitive to mechanical stress.
This is just a small list of diseases that can be detected based on the results of the examination. To correctly diagnose the patient’s condition, a complete history of all symptoms is required. Therefore, it is important that the woman at the appointment talks about all the signs that concern her.
Another possible reason when brown discharge is observed after examination is a miscarriage. This happens when a woman is not aware of her pregnancy and undergoes a medical examination at a very early stage.
Find out what characteristics the discharge has after a miscarriage.
The actions of the gynecologist can cause involuntary termination of pregnancy. Any signs uncharacteristic of a healthy woman should be diagnosed by a qualified specialist. If it is reliably known that there are no diseases of the genital organs, but discharge still often appears after examination, it may be necessary to change the doctor to a more careful one. Take care of your health and do not miss scheduled visits to the gynecologist.
A smear for urogenital diseases is one of the most common and informative methods of analysis in modern medicine. With its help, you can identify not only banal inflammations, but also prevent the development of cancer. Despite the reliability and accessibility of the method, not all women realize the need to regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo tests and often consult a doctor only in advanced cases.
When to take a smear for cytology?
Almost like any study of the reproductive system, cytology analysis is carried out on a certain day of the menstrual cycle. The procedure for collecting material is carried out 10-12 days from the moment it begins. It must be taken into account that the result may be inaccurate if there is an infectious process in the body. If necessary, the analysis is carried out even during illness, but after 2 months from the moment of recovery, a control study is prescribed. If a woman uses vaginal suppositories, performs baths, douches, analysis is possible 7 days after completion.
As for the indications for the study, doctors can prescribe the test for:
- pregnancy planning;
- frequent childbirth (3 times in 4 years, for example);
- early first childbirth (birth of the first child before the age of 18);
- placement of an intrauterine device;
- lack of examinations of the reproductive system during the last 3 years;
- the presence of visible changes when examined in a gynecological chair using mirrors;
- burdened medical history (tumor-like processes were recorded in the family on the female side).
Is bleeding dangerous after examination by a gynecologist?
When undergoing an annual medical examination, every woman is obliged to visit a female doctor in order to exclude the presence of diseases of the genitourinary system, and if they are present, to cure them in time. Sometimes this results in complaints of spotting after an examination by a gynecologist, accompanied by discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the lower body.
What are the dangers of inspections?
It happens that a woman, after being examined by a doctor, discovers brown discharge. This is considered the norm: when collecting material for research, small vessels are damaged, so a small volume of blood released due to instrumental intervention is allowed.
The occurrence of spotting after a gynecological examination is also provoked by the behavior of an overly nervous woman who, fidgeting in her seat, can cause mechanical damage inside the vagina with a sudden movement.
Blood vessels are fragile, so a visit to a specialist for a considerable number of representatives of the fairer sex ends with scanty discharge of light or dark brown color. If after a couple of hours they stop on their own, there is no need to worry.
Sometimes manipulations performed by a doctor can speed up the onset of menstruation, at the beginning of which spotting brown discharge also appears.
An alarming reason is a bloody mark observed on underwear within two to three days after a visit to the antenatal clinic. There is a possibility that a serious injury has occurred or a hidden illness has made itself felt. It can be confirmed by elevated temperature, pus, and unpleasant odor. During sexual intercourse, pain, discomfort, and itching are observed.
In case of heavy bleeding that resembles menstruation, you must immediately visit a medical facility to identify the cause and eliminate the consequences.
You cannot ignore the situation when discharge appears after a smear during pregnancy, even when it is very insignificant. The doctor should conduct an examination no earlier than the eighth week to prevent placental abruption.
After all, when taking an analysis, you have to “scrape off” the cells of the mucous membrane, which is likely to cause tissue injury, leading to miscarriage. There are times when, at an extremely short period of gestation, the gynecologist himself provokes abortion of the fetus with sudden movements.
In this case, bleeding may occur even the next day, when it is too late to take any action.
Symptoms such as lack of strength, exhaustion, vomiting, fever, accompanied by hemorrhage from the reproductive organs may indicate spontaneous abortion. Do not neglect the recommendation of doctors to go to the clinic for preservation and undergo additional examinations.
Bloody discharge after examination in pregnant women
If, with caution, discharge is still observed after examination by a gynecologist during pregnancy, this can be caused by:
- injury to tissues to which blood flows;
- separation of the mucus plug;
- damage to internal organs, which is dangerous and requires medical intervention;
- abruption or placenta previa.
When checked in the fortieth week of pregnancy, bloody or brown discharge often indicates imminent labor. This is usually preceded by the rejection of the mucus plug, which clogs the uterus, protecting the fetus from infection.
Normally, small discharge is not accompanied by annoying symptoms such as itching and inflammation. If they occur, this indicates possible pathologies.
In the early stages of pregnancy, hemorrhages can threaten the development of inflammatory or infectious diseases, deformation of the cervix, and miscarriage.
Spotting can occur after examining the expectant mother's cervix, cytology, since this organ is very traumatic, any external invasion can cause damage to the epithelium and, as a result, discharge from the genital tract.
Existing neoplasms inside the reproductive organs (polyps, tumors) are very often traumatized during examination, causing hemorrhage. This should worry you and be a reason to contact a specialist.
What to do if there is bleeding after a gynecological examination
If, after returning from the female doctor, bleeding begins, you should pay attention to its nature: color, thickness, frequency and volume.
Short-term (several hours or one day) small bleeding caused by manipulations with the gynecological speculum is allowed. After returning from the doctor, you should carry out the necessary hygiene procedures, change your underwear, and lie down. If scarlet or dark blood continues to flow, you should not endure it, you need to urgently go to the hospital.
Heavy discharge should alert you when it is accompanied by:
- significant pain in the lower torso or vagina;
- increased discomfort;
- burning sensation in the genitals;
- unpleasant odor;
- impurities of pus;
- heat;
- labored breathing;
- cardiopalmus.
In these cases, emergency assistance is required to identify the problem in a timely manner and correctly solve it.
Examination after examination in a chair can reveal the following pathologies:
- Endometriosis. It occurs in 10–15 percent of women of childbearing age and is characterized by painful periods, vaginal discharge, and uterine bleeding. The mucous membrane of the uterus grows into other organs and tissues of the pelvis, disrupting their function.
- Polyps are benign neoplasms into which a significant number of vessels grow, and at the slightest damage they begin to bleed. At the initial stage of development, they may not manifest themselves in any way and may not bother the woman, so they can only be detected during an examination by a specialist.
- Hyperplastic growth of the endometrium. The inner layer of the uterus grows, and there is a high probability of the process progressing to oncology.
- Cervical dysplasia. If left untreated, damage to the epithelial structure can lead to irreversible consequences, in particular cancer.
- Myoma, fibromyoma.
- A tumor of a malignant nature.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis).
All of these pathological abnormalities are characterized by bloody discharge.
Contact bleeding suggests the presence of problems in the female body. In rare cases, in the gynecological chair you can “catch” an unpleasant infection - bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis. This happens if the doctor neglects the rules of hygiene. Precursors of such infections, as a rule, are discharge mixed with blood immediately after examination.
In women who have not given birth, pain and discomfort after a medical examination are observed more often than in women who have children. Their vaginal muscles are less stretched, the cervix is quite narrow, and access to it has to be expanded with instruments. As a result of the increased sensitivity of the epithelial membrane to mechanical irritants, short-term bleeding may begin.
Preparing for a smear for cytology
Liquid cytology involves assessing the material after immersing it in a special medium. Previously, a smear for cytology was carried out with the application and fixation of material on glass. To obtain an accurate result that reflects the condition of the uterine structures, a woman must adhere to the following rules before the procedure:
- exclusion of douching 5-7 days before sampling;
- exclusion of sexual intercourse for 3 days;
- do not use tampons, gels, or vaginal creams;
- do not urinate 2 hours before the procedure.
Indications for prescribing a smear test in women
Every woman at least once in her life, visiting a gynecologist, has had a smear for microflora or hidden infections. A smear is taken from the walls of the vagina, cervical canal and cervix. In laboratory conditions, microscopic examination of cells contained in biological material is carried out. This analysis allows you to assess the condition of the epithelial cells of the uterus and vagina, identify pathogenic microorganisms and sexually transmitted diseases. It is advisable to take a smear regularly, once a year, even if the woman has no visible cause for concern, since many infections may not cause any symptoms for a long time.
A smear is mandatory in cases where a woman complains of itching and burning in the genital area, unusual discharge from them, or sudden pain in the lower abdomen. As a rule, these signs indicate the presence of some disease, which can only be diagnosed using a smear test. In addition, it is advisable to conduct a study of biomaterial if a woman has had unprotected contact with a partner little known to her and there is a risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
Also, the gynecologist prescribes a mandatory smear test for women planning a pregnancy, preparing for IVF or other artificial insemination procedures (ART). For women expecting a child, a smear test is carried out three times throughout the pregnancy, since infections can be transmitted from mother to child, complicate childbirth or cause miscarriage.
In gynecology, there are several types of smear analysis, depending on the type of study.
- The most common is a flora smear or general smear, with which the doctor determines the so-called cleanliness of a woman’s vagina. What does it show? This method can determine the condition of epithelial cells and identify the presence of diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as vaginitis, candidiasis (thrush), vaginosis, cervicitis. As a result of bacterioscopic examination, some sexually transmitted diseases are also diagnosed - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. The analysis is based on the ability of different microorganisms to turn different colors depending on the degree of resistance to antibiotics. This ability was discovered by the Danish scientist G.K. Gram. As a result of staining the biomaterial, gram-positive (gram+) microorganisms are identified, which are highly sensitive to antibiotics, and gram-negative (gram-), characterized by a thinner and more complex shell and low sensitivity to drugs. Gram-negative microorganisms can cause various diseases of the female genital area. During the analysis under a microscope, a laboratory doctor counts the number of differently colored microorganisms, leukocytes, determines the shape of bacteria, their size and location. In some cases, unstained (native) smears are examined, which makes it possible to detect flagellated forms of Trichomonas. In addition, as part of the flora smear, a so-called microflora culture can be carried out. It is used in cases where the causative agent of the disease cannot be detected under a microscope due to its low concentration and to determine the genus and type of bacteria. In this case, the biomaterial taken from the woman’s genital organs is placed in a special gelatin-based nutrient medium, and after a certain time the result is studied.
The appearance of colonies of microorganisms on the nutrient substrate indicates the presence of a disease. The culture method is also used to determine treatment strategy, since during the maturation of the colony it is possible to find out which groups of antibiotics it is particularly unstable to.
- Smear for hidden infections. Hidden infections include a group of diseases that can be asymptomatic for several months or even years, causing complications, and in some cases even infertility. Today, the most reliable way to detect hidden infections is to examine a smear using PCR (polymerase chain reaction). This method is used to diagnose infections that are not detected in general smears. To carry out the analysis, a secretion is taken from the cervix, vagina or urethra and a multi-stage increase in the concentration of nucleic acid is performed and individual DNA fragments of microorganisms present in the smear are copied. As a result, the doctor can determine the species and genus of all pathogenic bacteria and their ability to cause the development of diseases. In most cases, PCR analysis is used when the presence of sexually transmitted diseases is suspected and has a practically asymptomatic course in the early stages. The advantages of the method are:
- high accuracy of identifying the infectious agent;
- the ability to determine precisely the presence of the virus, and not the products of its vital activity or decay;
- the ability to make an accurate diagnosis based on just one cell of a microorganism.
- A smear for oncocytology, or a Papanicolaou test (Pap test), allows you to detect the presence of cancer in the cervix in the early stages and begin therapy on time. The Pap test detects most inflammatory diseases, epithelial dysplasia and malignant tumors. This smear test is recommended annually for all women aged 21 to 65 years. If a woman experiences menstrual irregularities, inflammatory processes in the cervical canal, or infertility, the doctor will prescribe a smear for oncocytology without fail. It is also recommended to undergo a Pap test when diagnosing diabetes, obesity of 2-3 degrees, during pregnancy planning, when taking hormone-containing drugs and the presence of genital herpes and papilloma viruses in the body. When analyzing a smear, you can get five types of results depending on the presence and degree of pathology. The first type is a negative indicator, indicating that there are no deviations from the norm in the woman’s body and she is completely healthy. In the second type, there is an inflammatory disease that requires treatment. The third type indicates the presence in the epithelium of single cells with an abnormal nuclear structure. The fourth type is suspicion of malignant formation or erosion of the cervix, genital herpes, papillomavirus infection, parakeratosis. The fifth type is the presence of cancer that requires immediate treatment. It should be remembered that a smear shows only the degree of cell changes, but not the reason that caused them. Diagnosis requires the results of other tests, including biopsy, colposcopy and histological examination. If atypical cells are found in the smear, this will be written about in the conclusion, and the type of changes will also be indicated. If there are no special notes in the cytology smear transcript, this indicates that no pathologies were found during the study.
When choosing a day to take a smear, you need to take into account your menstrual cycle. It is advisable to take the test before the start of menstruation or a few days after its end (the optimal period is the fifth day) to avoid blood getting into the smear. Although the swab test procedure is not overly complicated, it is still necessary to take some additional steps in advance to ensure a clear result. Preparation for a smear for infection in women is as follows:
- Do not use vaginal suppositories, tampons, or ointments before the test.
- Avoid douching.
- If you have an inflammatory disease accompanied by copious secretion, you must first carry out treatment and only after complete recovery take a smear.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for one to two days before taking the test.
- Do not use intimate hygiene products the day before and on the day of the procedure.
- Refrain from emptying your bladder immediately before your smear test.
Otherwise, a woman can lead a normal life: no restrictions on diet or physical activity are required.
Taking a smear from a woman for flora, for hidden infections and for oncocytology is somewhat different. In all cases, before the procedure, the woman undergoes a general gynecological examination on a chair using a mirror.
When performing a smear on the flora, after a visual assessment of the vaginal walls, the doctor uses a special sterile spatula to collect material from three areas - the vagina, the cervix and the external opening of the urethra. In some cases, sampling is carried out only from the first two areas. The material taken with a spatula is evenly distributed over a sterile glass slide in a wide smear. Applying the material in a drop, a thick layer or a small smear is considered incorrect, as it complicates the work of the laboratory technician. In this case, materials from different areas must be applied to the glass separately from each other. On the back of the glass, the doctor makes notes about the place where the smear was taken: U - urethra, V - vagina, C - cervix. After this, the glass is dried and sent to the laboratory for testing.
When taking a smear test in women for latent infections and oncocytology, the material is collected with a special brush or using special sterile cotton swabs. Before taking the material, mucus must be removed, since its presence can give a false result. Since most microorganisms are intracellular parasites, their accurate detection is only possible by examining scrapings from the walls of the genital organs. When analyzing for hidden infections, the material from the brush is placed in a saline solution stored in the refrigerator. A smear for oncocytology is applied to a glass slide and dried.
As a rule, the procedure for taking a smear is practically painless for a woman. Contact with a speculum can cause discomfort due to the temperature difference between the body and the metal instrument. When taking material with a tampon or brush from the cervix, a slight sensation of pain may be noted, which goes away immediately after the end of the manipulation. A smear for oncocytology can sometimes cause minor bleeding for two to three days. If severe bleeding, fever, or abdominal pain occur, you should urgently consult a gynecologist, since such symptoms are not normal when taking a smear.
After a smear test, the patient receives results that depend entirely on the type of test assigned to her.
When deciphering a smear analysis for flora, you need to know the normal indicators:
- Flat epithelium (pl.ep) - in a healthy woman this figure should not exceed 15 cells in the field of view. A larger number indicates an inflammatory process, and a smaller number indicates the presence of hormonal disorders.
- Leukocytes (L). The normal amount in the vagina is no more than 10, and in the cervix no more than 30 units.
- Dederlein bacilli, which provide normal microflora of the female genital organs. In a smear of a healthy woman, they should be present in large quantities, since their deficiency indicates a disturbed vaginal microflora.
- Mucus should be present in the smear in moderate quantities. Excessive mucus discharge is a sign of inflammation or infection.
- Fungi of the genus Candida, gonococci, and Trichomonas should not be detected in the smear. Their presence indicates a disease.
In addition to these indicators, the analysis may indicate one of four degrees of vaginal cleanliness. Only the first and second degrees are normal, the third and fourth are a sign of genital tract disease.
The results of a smear test for hidden infections can be obtained 1–2 days after the test. In some cases, they may be ready on the day of the procedure. The following infections are detected using a smear:
- human herpes virus types 1 and 2;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- human herpes virus;
- human papillomavirus;
- treponema pallidum;
- mobiluncus;
- bacteroides;
- gonococcus;
- gardnerella;
- mycoplasma;
- ureaplasma;
- chlamydia.
In most cases, a smear for infection is a fairly reliable diagnostic procedure. With its help, you can identify most serious diseases of the genital area, and the cost of the analysis is quite affordable even in private clinics.
When undergoing an annual medical examination, every woman is obliged to visit a female doctor in order to exclude the presence of diseases of the genitourinary system, and if they are present, to cure them in time. Sometimes this results in complaints of spotting after an examination by a gynecologist, accompanied by discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the lower body.
How is a smear taken for cytology?
The Pap smear is performed in a clinic setting. The woman sits in a gynecological chair. During the procedure itself, the gynecologist takes cells from the cervical canal area, from the vaginal mucosa. In the first case, a special probe is used - endobrush. It is administered after a slight expansion of the uterine canal by using a dilator. An Eyre spatula is used to collect material from the vaginal walls.
When liquid cytology of the cervix is performed, during the manipulation itself the woman may feel minor discomfort and mild pain. Its appearance is due to the expansion of the cervical canal, which is supplied with a large number of nerve endings. The duration of the procedure depends on the experience of the gynecologist, and averages 5-10 minutes. The resulting material is placed in a test tube with a reagent and sent to the laboratory.
After examination by the gynecologist, blood began to appear
It is recommended that girls and women undergo gynecological examinations every year, and if possible, once every six months. But, unfortunately, it is not always possible to do just that.
Therefore, sometimes coming to the gynecologist so rarely, some problems begin. One of these problems is spotting or pain in the lower abdomen.
This can happen for various reasons and most often it is preceded by certain diseases or careless treatment by the gynecologist.
It is better to worry if blood appears during pregnancy. Because this may be a sign of serious violations.
Why is there spotting after a gynecological examination?
If there are no serious violations, and blood still starts to flow after the examination, this can only happen because the doctor used a speculum. Everyone knows that a gynecological speculum is intended for examining the vagina and cervix. If it is not used carefully, it can damage the vaginal mucosa and, accordingly, provoke light bleeding.
When taking a smear, mucosal cells are scraped off and injury can occur. If after examination the bleeding does not stop as soon as possible, you should consult a doctor again. Perhaps some kind of violation has occurred, and the injury is making itself felt. Or it could be that this is a manifestation of some disease.
In any case, it is necessary to re-examine and make sure that everything is in order or undergo treatment. There are cases when, after visiting a gynecologist, there is a feeling of itching, burning in the vagina and other unpleasant sensations. This also does not need to be tolerated, but it is advisable to immediately go to the hospital.
It is possible that an infection was introduced during the examination. Don't be shy and ask for help.
After the examination, blood began to flow - this is normal.
Quite often there are situations when, after an examination, a woman develops spotting. This may also be within the normal range, because the cervix is supplied with blood, especially during pregnancy. If light spotting appears after the gynecologist, then do not immediately despair.
Perhaps this happened due to slight mechanical damage to the gynecological speculum. Weakening of the walls of blood vessels is not a pathology, it is rather a purely individual characteristic. Therefore, there is no reason to worry.
Perhaps it is enough to simply change the doctor to a more accurate one. It is also normal for pregnant women, after examination, to experience mild pain during urination.
This is also due to the fact that a slight violation could occur during the analysis.
We can say that all bloody discharge or light spotting after an examination by a gynecologist that appears as a result of mechanical damage to the gynecological speculum is normal. There is no reason to worry. Also, do not forget about time, that all allocations must end as soon as possible.
Dangers of Gynecological Exams
As stated above, all gynecological examinations are necessary, and in some cases especially useful. Firstly, all such examinations are designed to take a smear from the walls of the vagina and cervix. Mucosal cells are precisely the substance for laboratory research.
There are cases when, after extremely careless examinations, women experience serious problems, accompanied by bleeding and pain in the lower abdomen.
In such cases, urgent assistance and further treatment are necessary. It’s different for every woman, so it’s normal to experience some discomfort or mild ointment after the examination.
If blood appears scarlet or dark for several hours or even days, you should consult a doctor.
As for various diseases, in this case everything is much more complicated. As a rule, the doctor himself must determine the presence of the disease or know about it in advance - from the woman’s medical history.
There is also a so-called two-handed examination, during which the doctor examines the position of the organs, their sizes, the presence of the necessary adhesions, as well as the possibility of developing the disease.
Unfortunately, even after such an examination, slight bleeding or discomfort in the lower abdomen is possible.
Any intervention can be dangerous, especially for a pregnant woman. Therefore, take the examination of a gynecologist seriously, in particular, the choice of a specialist.
What to do if there is bleeding after a gynecological examination?
First, it is necessary to determine the nature of the bleeding. If the blood is scarlet and smears only a little, then this may not be a cause for concern. In this case, you just need to rest and lie down for a while, which will calm your body a little.
Secondly, you need to determine the bleeding time, or rather its duration. Discharge is allowed after examination on the first day. Anything that has passed on the second or third day is dangerous. In this case, it is better to go back to the doctor. Perhaps a characteristic disorder has arisen or this is how your disease manifests itself.
There are cases when the bleeding is so strong that it is quite similar to menstruation. Then it is better to call an ambulance, otherwise you may lose a lot of blood. As a result of the examination, injury to the mucous membrane of the cervix or the vagina itself could occur.
Diseases that appear after examination by a gynecologist
The first case is difficult to call a disease, but it really exists. It's a miscarriage.
There are quite a lot of situations when in the early stages of pregnancy, about 10 days, the gynecologist himself may not notice this and with sudden movements provoke a miscarriage.
Thus, after examination, blood appears, perhaps not immediately, but only on the second day. In such cases, it is too late to engage in treatment.
If you know that you are pregnant and after a gynecological examination, spotting or nagging pain in the lower abdomen appears, then this is a clear signal of the presence of significant deviations in the course of pregnancy.
As for specific diseases, this could be cervical erosion, the presence of papillomavirus, endometriosis and others. Such diseases may well be the cause of spotting after examination.
Therefore, it is important to start treatment as quickly as possible.
As for cervical erosion, this disease can occur for a variety of reasons, but you need to seriously think about other diseases.
Symptoms of diseases
In addition to the fact that after examination, if there is a disease, bloody discharge occurs, some symptoms may be characteristic of a specific disease. For example, with endometriosis, there is aching pain in the lower abdomen. Most often this happens after a gynecological examination, and during menstruation the pain is sometimes simply unbearable.
As for blood impurities, they occur with endometrial hyperplasia. It is worth noting that such manifestations can be provoked not only by an examination by a gynecologist, but also by hormonal imbalance, excess estrogen, obesity or the presence of diabetes. Therefore, before making hasty conclusions, you need to consult a doctor.
The cause of the appearance of blood can be uterine polyps, which consist of endometriotic cells. Such benign neoplasms in the initial stages do not cause any discomfort and most often do not manifest themselves at all.
With a professional examination, the doctor can determine their presence. Symptoms of the presence of polyps may include extramenstrual bleeding, pain in the uterus or after sex, regular delays in menstruation, and others.
If you do not get rid of this problem in time, infertility may develop in the future.
All sexually transmitted infections can manifest as itching in the vagina, discomfort in the groin, burning, pain during or after sex, pain or a rotten smell. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. There are also more serious diseases that affect the reproductive system and can cause complications. These are chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and trichomoniasis.
Diagnosis of diseases due to bleeding
During heavy bleeding, it is very difficult to conduct a gynecological examination, so they resort to ultrasound examination. It does not cause any harm even to a pregnant woman. Using an ultrasound, you can determine the gestational age, the presence of certain pathologies in the uterus or other diseases.
This examination is most often prescribed after a routine examination by a gynecologist for the most accurate results. This is a kind of comprehensive examination with which you can determine the entire picture of the course of the disease or a successful pregnancy.
Most often, such an examination is prescribed for regular brown discharge without any complaints from the woman. This allows you to determine the cause.
If there is not severe bleeding, then an examination by a gynecologist with a mirror is possible. As a rule, light discharge will not interfere with determining the presence or absence of a disease and finding out the cause of such symptoms.
Bloody discharge in pregnant women after examination
The most dangerous consequence of bleeding in pregnant women is miscarriage. You should be wary of this and, first of all, be extremely careful when examined by a gynecologist.
Dizziness, nausea and weakness can also signal a threat of miscarriage, even with brown ointments. If the doctor himself cannot determine the gestational age, then it is better to undergo an ultrasound for a complete picture.
Other light spotting may indicate other less serious problems, but should not be ignored.
There are many other pathologies, but each one is highly individual, so the sign of miscarriage is not the final verdict. You may be sent to a hospital for treatment to prevent further problems.
Source: https://krasnayakrov.ru/organizm-cheloveka/zhenshina/krov-posle-ginekologa.html
Cytology smear - interpretation, normal
After a cytology smear has been performed, the results are deciphered exclusively by a doctor. Only a specialist can perform a comprehensive analysis of the situation by assessing the results of cytology. The state of cellular structures is a reflection of the state of the reproductive system. Based on the results obtained, doctors can suggest an oncological process and prescribe additional tests (colposcopy, curettage).
Atypical cells in a smear for cytology
When a woman finds out that the results of the study revealed she has poor cytology, this news becomes a cause for concern. It is worth noting that such a conclusion does not mean cancer. According to the established terminology of medical reports, this definition indicates the presence of pathological changes in the epithelial layer of the vagina and cervical canal.
According to the generally accepted methodology for assessing results, changes are designated as follows:
- 0 – the collected material is of low quality, unsatisfactory (selected in small quantities, the patient was not properly prepared);
- 1st class – indicators are normal;
- Class 2 – atypical structures are present;
- Class 3 - there is dysplasia of varying severity;
- Class 4 – precancerous condition, first stage;
- 5th grade – cancer.
Squamous epithelial cells in a smear for cytology
When liquid cytology of the cervix diagnoses squamous epithelial cells in the canal, doctors talk about a disease such as hyperkeratosis. A large number of squamous epithelial scales are recorded in the field of view of the microscope. This type of cellular structure is present in analyzes for leukoplakia. This disease belongs to benign tumors. When conducting an additional study, colposcopy, a white area is recorded on the cervix.
It is worth noting that when the smear results contain only single scales, colposcopy is mandatory. If during its implementation no changes are revealed on the surface of the reproductive organ, then the analysis is considered normal. A cytology smear performed in this case has no diagnostic value. The patient is monitored - once every 3 months the woman visits the consultation department and is examined.
Glandular epithelium in a smear for cytology
Analysis of the smear for cytology, its interpretation, further helps to establish inflammatory processes in the uterus. One of these is cervical dysplasia. With a mild degree of the disorder, the disease can be easily corrected by prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs. Moderate and severe dysplasia can be regarded as a precancerous condition. In this case, a biopsy becomes a mandatory additional study - taking a section of the affected cervical tissue for histological examination.
Polymorphic rod flora in a smear for cytology
Cytology transcripts often contain the entry “polymorphic rod flora.” In order to understand what this means, it is necessary to say that the rods present in the vagina may have:
- morphotype of lactobacilli (similar in structure and appearance to Doderlein sticks);
- small sticks.
The first type of rods makes up the normal microflora of the vagina. At the same time, the presence of single leukocytes is allowed. The presence of small rods in a large number indicates a change in the composition of the microflora, which can be recorded with vaginal dysbiosis, gardnerellosis. Such conditions require urgent medical intervention and therapy.
After taking a smear, brown discharge during pregnancy
July 25, 01:11
The trouble is over and we are already home)
We celebrated the beginning of the 16th week with our baby with a planned trip to the gynecologist. We were pleased with excellent tests, normal hemoglobin, slightly low blood pressure and 300 grams of weight gain. And at the end of the examination we were asked to take a smear.
Of course, I am against unnecessary penetration, but I couldn’t even think that a thousand times later I would regret my silent consent. (Although, to tell the truth, I’m not used to arguing with a doctor. It’s necessary, then it’s necessary!) .... An hour later, when I came home, I saw brown discharge...
no pain... Continue reading →
Discharge after smear((((
Good evening, dear girls! I haven’t been here for a crazy long time, I haven’t written anything, but I’m aware of all the events - I regularly look through your news and keep my fingers crossed for everyone!!!! Continue reading →
Does anyone know what it was???
Girls, did your sister have a dark brown discharge after taking a smear (undergoing a medical examination)? What could it be? There was one time when I came from the doctor. The procedure itself was painless. She didn't feel anything strange. I just noticed it on the panties. Did the doctor damage something? Or what could it be? One week until period. They plan to become pregnant after fasting. Continue reading →
How I lie “For safekeeping”
Pregnancy 5-6 weeks, brown discharge started on Saturday, went to the gynecology emergency department on Sunday, was prescribed tranex 2 t 3 times for 5 days and duphaston three times a day, on Monday an ultrasound did not see the reason for the discharge, no detachment , the baby is developing, at the reception at the residential complex the doctor writes a referral to a day hospital. And here is the most interesting thing, head. After an examination, the department’s attending physician prescribes me Folka and Drotaverine, they give me these tablets in bulk for eight days... Read more →
my sad story (pregnant and impressionable people should not read)…
Hello to all the girls! Well, and the promised post. Now I read you, my dears, every day, but there’s nothing to write... and 1-2 months ago I rarely even came in, I physically couldn’t.
I’ll try briefly, for anyone interested, please contact me)) So, a positive test result from 6 dpp in July, a sky-high hCG, the long-awaited pregnancy came on the 2nd attempt of IVF after 14 years of infertility (you, like no one else, should understand how much it was passed during this time and done...).
They did IVF in Nizhny Novgorod at the POMC under the federal quota (we had one unsuccessful attempt in Kazan at the Central PS under the reg. quota). Clinic, doctors, quality, I liked everything about... Read more →
Cervix bleeds in the first trimester
Good evening everyone. A month ago I was in storage with a small detachment. The ultrasound took place, everything became normal and I was prepared for discharge. During the examination, the gynecologist said that the cervix was bleeding and a slight erosion had appeared.
Nothing bothered me after that, I was only confused by the heavy discharge (sometimes white, sometimes white-transparent). Today I had a routine examination, they started taking a smear, and they said that when taking a smear, my cervix was bleeding. Based on the tests taken earlier, they found thrush and prescribed suppositories.
Actually, this is the first time I’ve had thrush... Read more →
Maternity hospital
The day before yesterday I went to see a doctor at the maternity hospital, everything was fine, nothing bothered me, and in the evening, after visiting the consultation and taking the 2nd smear during pregnancy, small brown discharge appeared... I was very scared... In the morning I went to the consultation again - there was a threat of premature birth and they sent me to the maternity hospital for safekeeping... The doctor with whom I agreed came, took all the tests, sent me for an ultrasound, CTG, a chair... The ultrasound was normal, there was no threat, but they said polyhydramnios, the amniotic fluid index was 18...
Where does it come from? The doctor says that there may be some kind of infection, inflammation... But the tests are all normal (blood, urine)... Read more →
Dysbacteriosis, lactase deficiency, Staphylococcus aureus
Immediately after being discharged from the hospital, you couldn’t be happier with your baby: so calm, cheerful, sleek. He slept for a long time and ate with appetite, and his stool had the smell and consistency of thick sour cream.
But suddenly the stool deteriorated, became watery, green and foamy, and pieces of mucus or blood streaks appeared in it.
Even with the skin, something strange was happening: at first redness appeared around the anus, but after a couple of days the entire butt was covered with some kind of scab and began to resemble a scalded tomato. Yes, and suck... Read more →
The road to happiness. That's how it all began.
To everyone who came to see us - welcome! So we are ready for our own house!!! And we decided to create it for a reason...
I know from myself how important a positive experience is!!!! Therefore, if our story instills hope in at least one of the girls - we want to add Vera - we will be very happy!!!!! So, perhaps, let September 17, 2005 be the starting point in my story.
We, now my husband, consider this date to be the beginning of our relationship (although we started communicating… Read more →
Maternity hospital
The day before yesterday I went to see a doctor at the maternity hospital, everything was fine, nothing bothered me, and in the evening, after visiting the consultation and taking the 2nd smear during pregnancy, small brown discharge appeared... I was very scared... In the morning I went to the consultation again - there was a threat of premature birth and they sent me to the maternity hospital for safekeeping... The doctor with whom I agreed came, took all the tests, sent me for an ultrasound, CTG, a chair... The ultrasound was normal, there was no threat, but they said polyhydramnios, the amniotic fluid index was 18...
Where does it come from? The doctor says that there may be some kind of infection, inflammation... But the tests are all normal (blood, urine)... Read more →
About anembryony
I copy from the site https://www.medsecret.net/akusherstvo/nevynashivanie-beremennosti/240-nerazvivajuwajasja-zamershaja-beremennost Everything is written out very successfully and completely. What I was missing when I had this case... Read more →
dysbacteriosis
good article about dysbiosis Immediately after being discharged from the maternity hospital, you couldn’t be happier with your baby: so calm, cheerful, sleek. He slept for a long time and ate with appetite, and his stool had the smell and consistency of thick sour cream.
But suddenly the stool deteriorated, became watery, green and foamy, and pieces of mucus or blood streaks appeared in it.
Something strange is happening even with the skin: at first redness appeared around the anus, but after a couple of days the whole butt was covered with some kind of scab and began to resemble a scalded one... Continue reading →
Ours are 28+6. I get a little nervous and worry a lot.
So, what do we have?1. Firstly, I suffered from ARVI. I was sick for a long time, a week and a half, and I was so tormented. All approved medications treat very slowly. As a result, I finally went to work today, but I still have a little runny nose and cough occasionally.
I regretted 20 times that I decided to take official sick leave and went to the city clinic (my parents are doctors, so I was always treated under their supervision and did not go to clinics).
There is a lot of text further)) Read more →
Article about dysbiosis
Immediately after being discharged from the hospital, you couldn’t be happier with your baby: so calm, cheerful, sleek. He slept for a long time and ate with appetite, and his stool had the smell and consistency of thick sour cream.
But suddenly the stool deteriorated, became watery, green and foamy, and pieces of mucus or blood streaks appeared in it.
Even with the skin, something strange was happening: at first redness appeared around the anus, but after a couple of days the entire butt was covered with some kind of scab and began to resemble a scalded tomato. Yes, and suck... Read more →
When pregnancy does not occur...
When pregnancy does not occur... Girls, at one time I devoted a lot of time to studying the problem of my lack of pregnancy. While searching for information, I came across some useful information (this is a forum, there’s not much time to edit, so ignore unnecessary information).
Maybe it will be useful to someone, as it was useful to me :) Although the information is more than 9 years old, and medicine has moved forward in many aspects, the basics have remained the same. Rainbow 11/10/2006, 16:28 First, I would like to insert a picture showing how conception occurs... what comes from where and where it goes.....
Continue reading →
Attention: Dysbacteriosis!!!!!
Attention: dysbacteriosis Immediately after being discharged from the maternity hospital, you could not get enough of your baby: so calm, cheerful, sleek. He slept for a long time and ate with appetite, and his stool had the smell and consistency of thick sour cream.
But suddenly the stool deteriorated, became watery, green and foamy, and pieces of mucus or blood streaks appeared in it.
Even with the skin, something strange was happening: at first redness appeared around the anus, but after a couple of days the entire butt was covered with some kind of scab and began to resemble a scalded tomato. Yes… Read more →
Good article about dysbacteriosis
Immediately after being discharged from the hospital, you couldn’t be happier with your baby: so calm, cheerful, sleek. He slept for a long time and ate with appetite, and his stool had the smell and consistency of thick sour cream.
But suddenly the stool deteriorated, became watery, green and foamy, and pieces of mucus or blood streaks appeared in it.
Even with the skin, something strange was happening: at first redness appeared around the anus, but after a couple of days the entire butt was covered with some kind of scab and began to resemble a scalded tomato. Yes, and suck... Read more →
That's why I dream of doing without a cesarean!..
Caesarean section is performed in cases where vaginal delivery is impossible or life-threatening for the mother or fetus. This is the most common operation in obstetrics.
What should a woman who has undergone this intervention pay attention to so that the postoperative period goes well? When is surgery required? Continue reading →
When pregnancy does not occur...
When pregnancy does not occur... Girls, at one time I devoted a lot of time to studying the problem of my lack of pregnancy. While searching for information, I came across some useful information (this is a forum, there’s not much time to edit, so ignore unnecessary information).
Maybe it will be useful to someone, as it was useful to me :) Although the information is more than 9 years old, and medicine has moved forward in many aspects, the basics have remained the same. Rainbow 11/10/2006, 16:28 First, I would like to insert a picture showing how conception occurs... what comes from where and where it goes.....
Continue reading →
that's why I want to give birth myself
Caesarean section is performed in cases where vaginal delivery is impossible or life-threatening for the mother or fetus. This is the most common operation in obstetrics.
What should a woman who has undergone this intervention pay attention to so that the postoperative period goes well? When is surgery required? During a caesarean section, the uterine wall is dissected.
Indications for surgery can be on the part of the mother, when, due to one or another disease, childbirth poses a threat to her health, and on the part of the fetus, when for him the birth act is... Read more →
Source: https://www.BabyBlog.ru/theme/posle-vzyatiya-mazka-korichnevye-vydeleniya-pri-beremennosti
Discharge after a smear for cytology
Often women notice that after a smear for cytology they bleed - slight bloody discharge appears. Gynecologists assure that this phenomenon is the norm. The discharge lasts 2-3 days, stops on its own, and is painless. In order not to injure the epithelial layer of the reproductive system after uterine cytology has been performed, a woman is prohibited for 7-10 days:
- have sexual intercourse;
- use sanitary tampons;
- carry out baths and douching of the vagina.