Modern rhythm, ecology and other various factors have shown a dynamic increase in gynecological diseases among women. 90% of female representatives have at least once encountered one or another illness in their entire lives. Uterine fibroids have become one of the most common diseases in recent years. Statistics show that over the past 5 years the number of patients with this pathology has increased by as much as 7%. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by bleeding and other discharge. They are an integral part of the disease and appear even after the fibroids are removed. What they can be, what is typical for the norm, and what indicates pathology - read in this article.
Features of uterine fibroids
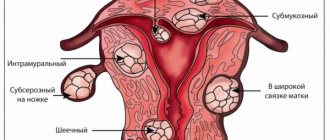
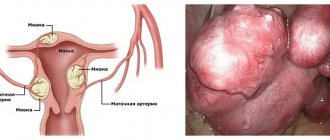
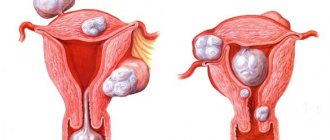
Like any other organ, the uterus consists of various structures, tissues and cells. Sometimes it happens that a benign neoplasm develops in one of these structures, which is uterine fibroids. Its nodes have a heterogeneous structure and can form in the walls of the uterus, muscle or connective tissue.
This disease can be detected by menstrual irregularities, when excessive bleeding appears. Bloody discharge can also occur between menstruation; it is accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back pain, surges in blood pressure, a feeling of weakness, dizziness, and frequent trips to the toilet. Due to prolonged bleeding, anemia and problems with conception may occur.
This disease appears for a number of reasons:
- Hormonal imbalance of female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Damage and surgical interventions in the uterine tissue, which can occur as a result of abortion, surgery and even childbirth.
- Often the cause is disruption of the thyroid gland, metabolism and the endocrine system as a whole, as well as diabetes.
- Inflammation that has developed into a chronic form.
Uterine fibroids are treated conservatively and surgically.
The need for surgery
The treatment method for fibroids depends on the degree of the disease, the size of the nodes and the dynamics of their growth.
In this case, the following indications for surgical intervention are distinguished:
- constant pain in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the discomfort does not go away, but has increasing dynamics;
- the presence of bleeding or chronic discharge with red ichor;
- disruption of the cyclicity of menstruation, which can lead to disruption in the female reproductive system;
- severe signs of anemia (nausea, weakness, pallor of the face and limbs);
- severe compression of neighboring organs by the tumor and disruption of the digestive and genitourinary systems;
- the size of fibroid nodes in diameter is more than 6 cm;
- causeless increase in tumor size (3 cm per year);
- the presence of a genetic predisposition and other signs for the transition of fibroids to a malignant formation;
- the appearance of other fibroids;
- the formation of fibroids “on a stalk”, which can lead to its twisting and a sharp deterioration in the general condition of the woman;
- chronic gynecological diseases (polycystic ovary syndrome, changes in the functioning of the endocrine system).
Types of discharge from uterine fibroids
As already noted, discharge is the main symptom by which this disease can be identified. These manifestations can be of a different nature, it all depends on in which tissue of the uterus the neoplasms are established.
The abundance of secretion may be determined by the stage at which the disease occurs. The characteristics of the body, the state of the hormonal background and immunity of a woman can also cause uterine bleeding.
Bloody
Bloody discharge characterizes the first stage of the pathology and indicates a neoplasm in the epithelial tissue of the organ (Submucous fibroid). Disruptions in the hormonal balance directly affect the state of the epithelium: its cells begin to actively grow, but not evenly, but chaotically, which makes the tissue denser in some areas and thicker in others. For this reason, the tissue may be torn away gradually, or once.
In the first case, there will be frequent, scanty discharge in the form of mucus, in which there are streaks of blood, in the second - heavy one-time bleeding of a dark color.
Mucus with blood
Scarlet discharge
These symptoms will be accompanied by increasing pain, first it bothers the lower abdomen, and then spreads to the lower back. This symptom is sometimes accompanied by general malaise, drowsiness, loss of energy, chills and rapid heartbeat.
Menstruation is also characterized by particular pain and bleeding occurs more often than in the usual menstrual cycle.
Brown
Brown discharge indicates that pathological nodules have taken root in the deeper, submucosal layer of the uterus (Intramural fibroids). Their growth leads to deformation of the tissue due to its stretching, due to which the vessels burst and, together with blood and epithelial particles, are discharged out in the form of dark clots.
Dark brown
Such phenomena usually occur regularly, alternating with short pauses. The disease may go away on its own, or it may progress. Brownish mucus is accompanied in this case by an aching, dull pain in the lower abdomen.
Purulent
Yellow and white discharge is a consequence of the location of fibroids in the fallopian tubes. This place in the reproductive system and organs of a woman is especially vulnerable to the development of bacteria and infections. Accordingly, with the appearance of a new growth here, microbes multiply with particular force, provoking purulent discharge of a yellowish and whitish hue with an unpleasant odor.
Thick purulent discharge
This can cause both vaginitis and fungal infections. Against this background, itching, burning, discomfort during sexual intercourse, vaginal dryness, difficulty urinating, and lateral pain in the lower abdomen may be felt.
Purulent clots with a pungent odor should cause particular concern, as this may indicate hemorrhage in the tissue due to necrosis of the myomatous node. In this case, infection of the genital organs and severe inflammatory processes in them are possible.
No matter in which part of the organ the fibroids settle, the consistency of the discharge can be completely different: watery, with impurities, dense, clots - all this depends on the stage and quality of the neoplasm.
Discharge after removal and treatment of fibroids
Neoplasms are amazing phenomena that can degenerate, or can exist in the body throughout life, occasionally making themselves felt. One of these is the described pathology.
Myoma can develop and live in the uterus throughout reproductive age, periodically reminding itself of bleeding, heavy and not so much, during menstruation and between them, and disappear completely with the onset of menopause.
In another case, it can grow, affecting more and more tissues, and affecting other organs with inflammation. In this situation, mandatory treatment is necessary. It can be conservative - with the help of medications, homeopathic, hormonal, medicinal, it can be suppositories for fibroids, or it can be surgical.
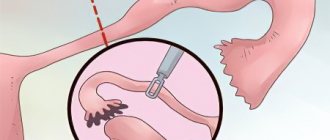
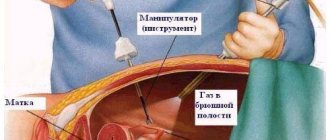
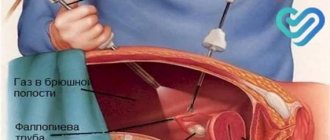
Surgical removal of the disease is called myomectomy. It can be done without penetrating the organ through the skin, using the cervix, which is called hysteroscopy. Or maybe in the form of a laparotomy - by cutting the abdominal tissues.
The choice of treatment type by specialists depends on the size of the nodes and their stage of development. After myomectomy, various types of discharge may be observed, and this is a sign of normality.
Transparent
White or clear, odorless discharge is a sign that the genital organs are returning to normal and indicate their proper functioning. They are slightly sticky, colorless, odorless and are not accompanied by pain, itching or other discomfort.
Leucorrhoea Light yellow
With blood
Bloody discharge after hysteroscopy may occur due to damage to the walls and small vessels. This is the result of a mechanical effect on the delicate tissues of the organ, which is treated with local preparations in the form of suppositories and ointments.
Bloody discharge
Curdled
White cheesy discharge indicates the development of a fungal disease - Candidiasis, popularly called thrush. It occurs as a result of weakening of both local and general immunity, which often affects female representatives by the development of candidiasis, accompanied by similar symptoms.
The secret for thrush
Menstrual flow
Uterine discharge after removal of uterine fibroids may turn out to be normal menstruation that does not occur on time. Often after myomectomy the menstrual cycle shifts. But if the consistency and abundance differ from your usual critical days, then we can talk about the fact that the suture is bleeding or the perisuture vessels are damaged.
If pain is present, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The absence of discharge after myomectomy also occurs. Most often this happens against the background of menopause. Itching, dryness, burning, discomfort when urinating, and discomfort during sexual intercourse appear here. This phenomenon can be eliminated with the help of topical remedies, such as suppositories, tablets and creams for intimate hygiene during menopause.
Treatment
If the patient is bothered by white, yellow, brown or red discharge caused by the formation of fibroids, then treatment is prescribed. The regimen is selected individually, taking into account the type of tumor, its size, concomitant diseases of internal organs, the patient’s age and the need for reproductive function in the future.
The use of hormonal drugs can achieve positive results for small fibroids. With the help of medications it is possible to regulate the menstrual cycle. Correcting the functioning of the ovaries can make bleeding less profuse and short-lasting.
If the fibroids are large, the patient is prescribed removal of the tumor-like formation. Depending on the location of the fibroids, a suitable technique is selected. If the tumor grows inside the myometrium, then the arteries feeding the tumor are “switched off”. The manipulation is minimally invasive and minimally traumatic. When the node grows into the pelvic cavity, surgical intervention is performed, which involves removing the tumor.
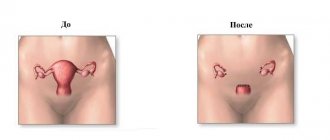
The radical method of treating fibroids is hysterectomy. Surgery is prescribed for large tumors when treatment with alternative methods is not possible.
After surgical treatment of fibroids, a woman experiences slight bleeding. Bloody discharge is a natural reaction of the body. The cavity of the reproductive organ contracts, and damaged vessels cannot be restored instantly. Therefore, in the first days after surgical treatment, a woman’s discharge is bright red, and by the end of the week it becomes brown. Gradually the ichor brightens, the mucus becomes barely pink. By 10-14 days after the operation, the discharge ends and becomes normal.
Reviews from women and specialists
Olga, 48 years old: “At the age of 32 I was diagnosed with uterine fibroids.
At first I was very worried, I read all sorts of horror stories about degeneration into cancer. But an experienced gynecologist friend advised me to observe for a while and not make sudden conclusions. For six months after my period, I experienced brownish discharge for several days, but it was not accompanied by pain. Only sometimes did I feel a pull in my lower abdomen. So I decided to leave everything as it is, periodically using preventive pharmaceutical suppositories to avoid infection and aggravation of the problem. With the onset of menopause, these symptoms disappeared along with menstruation, and after diagnosis, the doctor told me that the fibroids disappeared by themselves, and that such phenomena often occur with hormonal changes and the decline of reproductive function.” Oleg Viktorovich: “I have many patients who have undergone fibroid removal through myomectomy. This procedure is not scary at all. After it there is quite a lot of discharge, and this indicates that the menstrual cycle is being restructured. But we can talk about this if the bleeding is similar to the usual menstrual bleeding. I strongly recommend: whatever the blood discharge, be sure to contact a specialist to avoid the development of tumors and the spread of inflammatory processes.” As you can see, discharge from uterine fibroids is the most important symptom that indicates this pathology. They can be of different consistency and color, depending on the type of organ tissue in which these neoplasms are embedded. Often this symptom is accompanied by pain and general weakness.
The disease can remain in a woman’s body throughout her reproductive period, occasionally indicating scanty bleeding, or it can progress, causing pain and other symptoms.
Pathology is treated in two ways: with the help of medications and surgically by removing and curettage of nodules. In the case of surgery, discharge is also a normal, natural process.
Monitor your body regularly and stay healthy!