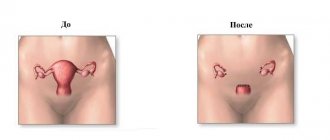
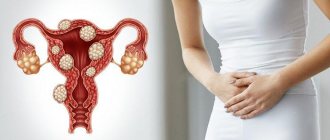
Fallopian tube removal is an operation that is performed on many women at different ages. Sometimes doctors have to cut out one, and sometimes two tubes at once. Statistics indicate that from 3 to 12% of women go through the procedure of removing appendages.
The general condition of the body, according to some experts, is not disturbed, because the fallopian tubes are only a transport system for eggs and sperm.
However, there are a number of scientific works that prove the opposite point of view. The authors point out that irregularities in the menstrual cycle, hormonal imbalances and other problems with the female reproductive system most often occur in those patients who have had their fallopian tubes removed.
Indications for surgery
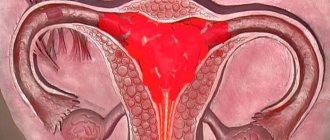
Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure whose purpose is to remove the fallopian tube. Another name for the procedure is tubectomy. During this procedure, one or both appendages are removed. The procedure can be performed for vital indications on an emergency basis. If the patient’s life is not in danger, then tubectomy is planned.
Indications for salpingectomy:
Growth and development of the embryo in the cavity of the tube. As an emergency, the procedure is performed when the embryo ruptures the appendage and the woman experiences internal bleeding.
If an ectopic pregnancy forms in the same tube for the second time.
Pelvic adhesions that grow into tubes.
Ectopic pregnancy that is not subject to conservative therapy (when the diameter of the ovum exceeds 30 mm). As for the conservative method of treating ectopic pregnancy, it is implemented with the goal that the woman will be able to become pregnant on her own in the future. In this case, the fertilized egg is pushed into the ampullary part of the tube, or a salpingostomy is placed on it.
The tube can be removed if the salpingostomy was unsuccessful and was complicated by bleeding.
With severe deformations of the fallopian tube against the background of adnexitis or salpingitis. The pipe is removed when its functionality cannot be restored.
Formation of pyosalpinx (accumulation of pus in the lumen of one or both fallopian tubes).
Planning for in vitro fertilization. Doctors in some cases insist on removing the fallopian tubes, citing the fact that IVF may be ineffective. The fact is that a reverse flow of inflammatory exudate from the tubes into the uterine cavity and “washing out” of the implanted but not implanted fertilized egg is possible. In addition, if an inflammatory process occurs in the tubes, this can lead to a toxic effect on the embryo. Sometimes it happens that the implanted embryo begins to take root in the uterus, but after some time, due to inflammation in the tubes, the woman has a miscarriage. Therefore, if a patient has had hydrosalpinx for six months and is planning IVF, then doctors insist on preliminary removal of the fallopian tubes.
The presence of hydrosalpinx in itself, without planning IVF, may be an indication for removal of the fallopian tube. This is especially true for those patients whose hydrosalpinx is of impressive size.
A combination of hysterectomy is possible (the operation is used for pathologies of the uterus, malignant neoplasms of the ovaries, etc.) and tubectomy.
Most often, the doctor decides on the possibility of removing or preserving the fallopian tubes after or during diagnostic laparoscopy.
How fallopian tubes are removed: the essence of the procedure
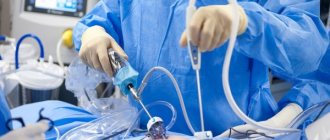
There are two types of tubal removal surgeries: laparoscopy and laparotomy. Laparoscopic intervention is a priority; it has a minimal set of contraindications, does not require extensive incisions to gain access to the fallopian tubes, and does not injure tissues and organs. In addition, patients recover quite quickly after it, and the rehabilitation period itself is much easier than after laparotomy.
If a tube ruptures due to an ectopic pregnancy, this process is almost always accompanied by severe bleeding. The development of hemorrhagic shock and other complications, even death, cannot be ruled out. Therefore, in such a situation, a woman can only undergo laparotomy. In parallel, intensive infusion and transfusion therapy will be carried out. Only through emergency surgery can the woman’s life be saved.
Stages of laparotomy:
Introduction of general anesthesia.
Making an incision: according to Pfannenstiel (a transverse incision above the pubis) or an incision in the anterior wall of the peritoneum, below the umbilical zone.
Pumping out blood that has entered the abdominal cavity. The blood is collected in separate bottles so that it can be transfused in the future. However, autologous blood transfusion is only available if the patient does not have inflammation.
Removal of the uterus and appendages to detect the source of bleeding.
Applying a clamp to the isthmic part of the appendage, as well as to the mesentery. This helps stop the bleeding.
Cutting off the fallopian tube.
Sanitation of the peritoneum and suturing.
When performing laparoscopy, the surgeon performs similar actions, but the blood pumped out from the peritoneum is not transfused to the woman.
If possible, the pipes are not completely removed, but partially.
Indications for tubal resection:
The presence of adhesions only in a small area of the fallopian tube.
Will my period come if my uterus has been removed?
The reproductive system occupies a very important place in the female body. Its normal functioning affects sexual activity and general well-being. A special role in this is played by the stable arrival of menstruation.
If any problems occur in a woman’s body, doctors try in every possible way to avoid surgical intervention by prescribing drug therapy.
But it happens that removal of the uterus is the only way to preserve not only health, but also life.
Whether or not you get your period after hysterectomy depends on the extent of the intervention. And you should know this.
Indications for removal
Myomas are considered the main reason for removal of the female reproductive organ. The grounds for excision are:
- big sizes;
- great amount;
- the likelihood of transformation of benign neoplasms into oncology;
- rapid growth.
Surgical intervention is prescribed if it is not possible to treat fibroids with medication or cut them out individually.
In addition, there are other reasons for removing the main reproductive organ of a woman:
- cancer;
- serious mechanical damage;
- foci of endometriosis;
- prolapse or prolapse of the uterus.
In each individual situation, the doctor chooses the type of intervention and the required volume of excision of the reproductive organ. This depends on many factors:
- degree of development of the disease;
- accompanying ailments;
- general condition of the woman.
Hysterectomy
It happens that as a result of such an operation, the female reproductive organ is not completely removed. Depending on the characteristics of the disease, the cervix may be left.
If a woman still has ovaries, then under the influence of the hormones produced by these endocrine glands, the endometrium will form in the remaining area of the uterus. Accordingly, menstruation will also occur, but in a much smaller volume.
If the reproductive organ has been completely removed, then the mucous membrane has no room to grow, which means that menstruation stops.
When the appendages or at least one ovary are preserved, hormones are produced. If at least part of the uterus remains, then the endometrium grows on it and is rejected, and accordingly, menstruation begins.
After hysterectomy of the entire reproductive organ, there is no regulation. If bleeding appears after a few months, this is a signal of pathology.
Uterus removal
Uterine amputation is a rather complex process. And after the operation, the woman spends mental and physical energy to return to normal. Depending on the state of health and the affected area, the following is cut out during surgery:
- ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- one ovary and tube;
- cervix.
In this case, either abdominal surgery is performed, or the doctor gets to the pathology through the vagina. The consequences of manipulation and the rehabilitation period will also depend on the chosen method.
Abdominal surgery
To perform this procedure, the doctor makes an incision in the abdomen. The operation takes from 40 minutes to 2 hours. The disadvantages of this type of intervention include:
- a large scar that will remain on the woman’s body;
- high level of trauma and difficult postoperative period.
Amputation or extirpation of the uterus is performed by making an incision in the abdominal wall.
Amputation is the removal of the female reproductive organ, in which both the cervix and fallopian tubes are preserved, and the ovaries are also left. And extirpation involves the removal of the entire reproductive system. Thus, after amputation of the uterus, menstruation will continue to occur, but after extirpation, it will not.
After any type of abdominal surgery, small fragments of tissue and minor bleeding may come out. You should sound the alarm and immediately consult a doctor if:
- the blood flows without stopping for a month or two;
- large clots are separated;
- bleeding is accompanied by pain;
- The discharge is bright scarlet in color.
Through the vagina
In this operation, the mucous membrane in the upper part of the vagina is excised. This type of hysterectomy has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- lower risk of injury and complications;
- beautiful cosmetic effect;
- short rehabilitation period and faster recovery after manipulation.
The disadvantages include:
- difficulty visually examining the abdominal cavity;
- increased risk of hurting the bladder or rectum;
- difficulties encountered in stopping bleeding.
In our country, this type of manipulation is carried out in cases of prolapse, prolapse of the uterus or sex reassignment operations. Therefore, laparoscopy is increasingly used to remove organs of the female reproductive system.
Women whose ovaries were preserved during surgery experience rehabilitation more easily. This occurs due to the fact that these endocrine glands continue to produce hormones, and the balance of biologically active substances in the body is not disturbed.
Menstruation after surgery
Regular menstruation after removal of the uterus is possible only if it is not completely excised, but some part remains, for example the cervix. Then the endometrium will grow on it, which is rejected every month, provoking cyclic discharge.
But for this it is necessary to leave the ovaries, since menstruation occurs under the influence of the hormones that they synthesize.
Also, due to the presence of these endocrine glands in the body, it ages more slowly and better resists environmental factors.
After excision of the ovaries, hormonal changes and surgical menopause with all its manifestations begin.
Thus, in order for menstruation to continue, the body must have ovaries and at least part of the uterus.
If all this has been removed, and 2 months after the manipulation, prolonged bleeding is still observed, then this is a sign of pathology. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
To understand when to be wary, we recommend reading more information about the normal color of menstrual blood.
Before and after surgery, women need to take antibiotics to avoid infection. They are not prescribed only in case of individual intolerance to this type of medication.
No critical days
After a hysterectomy, it is often very difficult for women to come to terms with it emotionally. When realizing the absence of a reproductive organ, a representative of the fairer sex feels worthless in terms of realizing the main female goal. To a greater extent, this is reminded by the absence of menstruation and the scars left after the operation.
To prevent postoperative stress from turning into prolonged depression, the man nearby needs to be as caring, patient and loving as possible. Women in such a psychological state are very vulnerable and vulnerable, even if they do not admit it. After all, other representatives of the fair half of humanity experience menopause and menopause within a few years.
Even an extremely stressed woman can experience a state of panic when her period suddenly disappears.
Therefore, it is important for all relatives and friends to show keen interest and participation in the fate of a loved one. The main thing is to give positive emotions and distract from sad thoughts. It’s good if a woman has children, and perhaps even grandchildren, then it will be much easier to survive post-operative pain than for a girl who was just planning to become a mother.
Treatment and consequences
For the first 2 months, women who have undergone hysterectomy are not advised to be sexually active. This is necessary so as not to injure or infect the sutures left after surgery.
Also, for up to 6 months, you should avoid lifting weights, active physical exercise, taking hot baths, and under no circumstances should you be nervous.
If the cervix and appendages remain, the normal menstrual cycle will be restored approximately 4–6 months after the manipulations. Those who have had their ovaries removed are prescribed hormonal medications to alleviate the symptoms of early menopause.
Source: https://TopGinekolog.ru/menstruation/menstrual-cycle/mesyachnye-posle-udalenija-matki
Complications after tubal removal
Among the possible complications after removal of the fallopian tube, the most significant are the following:
Development of inflammation. It is accompanied by an increase in body temperature immediately or several days after the operation.
Bleeding, formation of hematomas in the peritoneal cavity, or in the thickness of the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Hematomas indicate that the woman has problems with blood clotting, or the surgeon performed the hemostasis procedure poorly.
Nausea and vomiting. These complications are a consequence of the anesthesia administered, or arise as a result of intestinal irritation. The intestines most often “suffer” after laparoscopy, when carbon dioxide is injected into the peritoneum.
The formation of adhesions that can disrupt the functioning of all internal organs. Moreover, there is a risk of their formation both after laparoscopy and after laparotomy.
It should be understood that the above complications occur infrequently.
Causes of missed periods, negative test and pain in the lower abdomen
Many women have periods when a missed period, a negative test, or pain in the lower abdomen put her into a state of premature panic. These symptoms usually indicate pregnancy (in young women) and menopause (in older women). The exception is diseases and pathologies.
Menstruation (menstruation) is the period of the menstrual cycle during which blood is released from the vagina. The blood itself is thick, dark, and may contain lumps and clots. During this process, a section of the inner uterine layer, the endometrium, is also released along with the blood. Bloody discharge is the result of damage to the blood vessels of the uterine layer. During the period of death of the mucous membrane in the uterus, these vessels are destroyed, but only if the fair sex is not pregnant.
What are the causes of delayed menstruation?
Often, menstruation is accompanied by symptoms such as pain, nausea, dizziness, and fever. All of them directly depend on the individual characteristics of each woman. The menstrual cycle depends on various factors. These may be short-term changes in hormonal levels, stressful situations, diseases of the genitourinary system. A delay in menstruation or pain in the lower abdomen may indicate a serious problem. A longer period of delayed menstruation (amenorrhea) may indicate the presence of a disease.
Despite the fact that modern women have the opportunity to diagnose their pregnancy, they buy a test that determines the early stages of pregnancy. The obvious reason for the absence of menstruation is still the fact of pregnancy.
a quick way to get pregnant at home Sometimes you just need to stay at home for at least one day to take a break from the hustle and bustle of life. Today we invite you to get sick, of course, not for long. In order to stay at home and skip school, it is necessary not only to
Additionally, women who abruptly stop taking birth control may not get their period for 3 months or more.
Source
Consequences of the operation
The uterus and fallopian tubes share common nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels. In addition, the condition of the mammary glands and the neuroendocrine system as a whole depends on their work. Therefore, disruption of these connections negatively affects the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
Hormonal imbalance is one of the consequences of surgery to remove the fallopian tubes.
Women complain of symptoms such as:
Nervousness, irritability, tearfulness;
Painful sensations in the heart area;
Rush of blood to the upper half of the body.
Symptoms tend to intensify before the next menstruation, and they do not bother all women (observed in approximately 42% of cases).
About 35% of patients notice menstrual irregularities 2-3 months after removal of the appendage. During an ultrasound, they are diagnosed with an enlarged ovary on the side where the fallopian tube was removed. Over time, it undergoes sclerotic changes, which is caused by disruption of the flow of lymph and blood.
There is also an alternation of normal menstrual cycles with disrupted ones. There may be a decrease in the performance of the luteal body and cessation of ovulation. However, such conditions are rarely observed.
The following changes occur in the mammary glands:
The glands become rough in 6% of patients;
The breasts become larger due to diffuse expansion of the lobules in 15% of patients;
The thyroid gland increases in size and its functioning is disrupted in 26% of patients;
The following symptoms may also develop: excess weight gain, the appearance of body hair, and the formation of stretch marks on the skin.
These symptoms are especially pronounced in those women who have undergone surgery to remove both appendages.
Reasons for missed periods after Regulon
Oral contraceptives are a new era of protection against unwanted pregnancy. There are many methods of protection - from barrier contraceptives (condoms) to calculating “safe days” according to the calendar. Any method does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection against pregnancy, but as time has already proven, hormonal contraceptives are the most reliable.
Oral contraceptives are also used as drug therapy. They are popular among women with hormonal imbalances, unknown or disrupted menstrual cycles, and among women with uterine fibroids in the initial stages.
The principle of action of the drug Regulon
Regulon is an oral contraceptive that includes a progestin, desogestrel, and an estrogen component, ethinyl estradiol.
The drug is indicated for contraception, for menstrual irregularities, for the treatment of premenstrual syndrome, for dysfunctional uterine bleeding
The principle of action of regulon is based on the inhibition of pituitary hormones, which are responsible for the normal menstrual cycle. Progestogens inhibit the production of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. They inhibit ovulation and interfere with the penetration of sperm into the uterine cavity.
Thanks to ethinyl estradiol, the density of cervical mucus increases and its composition changes. At the same time, the environment into which sperm enter becomes more aggressive after sexual intercourse, which prevents them from safely reaching their destination.
A small amount of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones contributes to inhibition of egg maturation, normal development of the corpus luteum, and follicle rupture. The insufficient endometrial layer also grows. If normally the thickness of the layer should be from 1 cm, then while taking the drug it does not exceed 4 mm. Thanks to this, the fertilized egg, if the egg and sperm are
Source
Search form
Login to the site
Sections of the site
Rehabilitation
In the early rehabilitation period, the woman is advised to administer antibiotics, which helps prevent the development of possible inflammation.
To minimize the risk of adhesions forming, the following measures are taken:
Doctors try, whenever possible, to use laparoscopic surgery, which is minimally traumatic.
Before completion of the operation, barrier absorbable gels are injected into the abdominal cavity. For some time they contribute to the fact that the surfaces of the organs are located at a distance from each other. This is a measure aimed at preventing adhesions.
After the operation, the patient is raised the next day.
The woman is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis with iodine and zinc.
Calm walking and other moderate loads can prevent the formation of adhesions, or reduce the risk of their formation to a minimum.
After the operation, the woman is prescribed a course of antibiotics and given subcutaneous injections of aloe extract for 14 days. It is possible to prescribe Longidaza vaginal suppositories.
For 6 months after removal of the fallopian tubes, it is mandatory to take contraceptives to prevent pregnancy.
It is important to properly care for postoperative sutures, which will prevent their inflammation. You should avoid taking a bath and wash in the shower. In this case, the seams must be closed to prevent water from getting into them.
For a month after surgery, doctors recommend that patients wear slimming underwear.
Intimacy is absolutely prohibited during the first month after surgery.
You do not need to adhere to any special diet. However, you should temporarily exclude from your menu foods that increase gas formation in the intestines. Therefore, you need to give up legumes, whole milk, yeast baked goods and pastries, cereals, meat and carbonated drinks.
Is it possible to get pregnant without fallopian tubes?
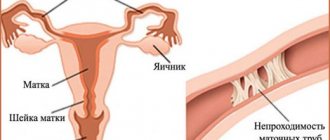
Without fallopian tubes, a woman cannot become pregnant naturally. To date, doctors have not been able to develop an analogue of the fallopian tubes, although they have been trying to make them for many years. The first attempt to implant artificial appendages was made back in the 70s of the last century. However, it was not successful, so it did not take root in medicine.
The only method that can help women without both fallopian tubes conceive and carry a child to term is in vitro fertilization.
If there is no fallopian tube, where does the egg go?
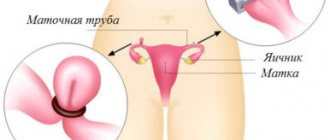
When both fallopian tubes are in place, they use fimbriae to capture the egg released from the ovary into the abdominal cavity and gradually move it into the uterus. It is also possible for a sperm to meet an egg in the tube and fertilize it. In the peritoneal cavity, the egg can exist for two days, after which it dies.
When a woman has one tube missing, the following options are possible:
Ovulation will not occur, the follicles will begin their reverse development. This situation is most often observed against the background of hormonal imbalance.
The egg will be released into the abdominal cavity, and after 2 days it will die and be destroyed in it.
The egg will float around the abdominal cavity, can reach the tube that remains intact, and pass through it to the uterus.
Of course, it is much easier for fimbriae to capture the egg that is released by the ovary from the side of the healthy tube. If a woman has both appendages removed, the ovaries either undergo reverse development, or the egg will constantly die in the peritoneal cavity.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after removal of the fallopian tubes includes the introduction of a daily dose of an antibiotic into a vein before the operation and/or in the immediate postoperative period to prevent inflammatory processes.
Reducing the degree of formation of adhesions is carried out by reducing the trauma of the operation, carefully performing hemostasis, introducing barrier biocompatible absorbable (absorbable) gels into the abdominal cavity at the end of the operation, which temporarily separate the opposite surfaces of the organs from each other, as well as early activation of the patient, physiotherapeutic treatment, etc. d.
Scanty bleeding after removal is also possible in the first 2-3 days, especially if the operation was associated with rupture of the appendage or with hematosalpinx in a disturbed ectopic pregnancy. However, this is not a complication, since the presence of bloody discharge from the genital tract is explained by the reflux of blood into the uterus before and/or during the operation.
In the majority of women in the postoperative period, the menstrual cycle is restored to its previous regime. When calculating it, the day of the operation is equal to the first day of the last menstruation.
In some cases, menstruation after removal of the fallopian tube may occur on the 2-3rd day, which may be due to rapid adaptation of the body's reproductive system or short-term hormonal imbalance. Often their duration may exceed that before surgery. If menstrual bleeding is light, it should not be a cause for concern. Otherwise, curettage of the uterine cavity is performed and conventional hemostatic therapy is prescribed.
Sometimes the menstrual cycle does not return for 2 months, which is quite acceptable. A longer period indicates a woman’s stressful state, but more often it is associated with endocrine dysfunction. Such violations require clarification of the cause and the appointment of appropriate sedative therapy and hormonal correction.
Where does the egg come out after removal of the fallopian tube?
For the fusion of the sperm with the egg and conception, it is not particularly important that ovulation takes place - in the left or right ovary. After ovulation, the egg enters the abdominal cavity, where it can remain in a viable state for 2 days, during which it is captured by the tubal fimbriae. The main point is the meeting of the germ cells and the fertilization of the egg.
If one of the appendages is missing, it is possible:
- lack of ovulation and the appearance of atretic follicles (with reverse development) due to hormonal disorders;
- death and destruction of the egg in the abdominal cavity;
- its migration along the abdominal cavity to the opposite tube, capture by fimbriae and transition to the uterine cavity.
Of course, the process of capturing the egg by the fimbriae proceeds easier and faster if ovulation occurs on the side opposite to the salpingectomy. In the case of a bilateral tubectomy, only the first two options are possible.
When can you plan to conceive after surgery?
After removal of one fallopian tube, a woman will be able to become pregnant on her own in 56-61% of cases. Moreover, this does not depend on the type of surgical intervention. Doctors indicate that you need to plan a pregnancy no earlier than six months after the operation. A number of experts recommend that a woman wait 1-2 years while taking oral contraceptives. During this time, it will be possible to normalize the functioning of the neuroendocrine system and the body will be ready to bear a child.
After removal of the fallopian tubes, 42% of patients develop infertility, and in 40% of cases, the ovaries stop working with their previous strength. Moreover, the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases 10 times. Therefore, IVF is the only method that allows a woman to conceive a child after removal of the fallopian tubes.
Can tubal plastic surgery replace them?
Gynecologic surgeons may perform surgery to repair part of the fallopian tube, calling the procedure a fallopian tubeplasty. It is carried out after removal of the deformed area of the appendage.
As for the complete restoration of the fallopian tubes, this operation is not advisable. The fact is that a woman’s own appendages have the ability to contract so that the egg can move through them and reach the uterus. After plastic surgery, the tubes lose their ability to contract, which means fertilization will be impossible. Therefore, the operation is performed only when a small section of the appendage needs to be replaced.
Author of the article: Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna | Gynecologist, reproductive specialist
Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received from the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2010). In 2013, she completed her postgraduate studies at NIMU named after. N.I. Pirogova.
10 Proven Reasons to Eat Chia Seeds Every Day!
Reading time: min.
Today, infertility is a common disease among women. To eliminate this disease, surgery is often prescribed. A frequently performed operation is laparoscopy, which is recommended if there is a cyst in the ovaries and if there are problems in the fallopian tubes. After this operation, hormonal treatment is recommended, after which menstruation should occur. But it is not uncommon for menstruation to be delayed after tubal laparoscopy. In such a situation, a woman is recommended to become pregnant within six months after surgery.
Reasons for missed periods
Delayed menstruation is one of the most common reasons for women to visit a gynecologist. To find out the origin of this pathology, it is necessary to consider in detail the physiology of the female body.
How to determine if your period is late
As a rule, the appearance of the first menstruation, or menarche, in girls occurs at 12-14 years of age. At this time, a woman’s hormonal background is just beginning to establish itself, so for the first year or two after menarche, periods come irregularly. This is a completely normal phenomenon, provided that it does not drag on for several years. Otherwise, consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
The nature of menstruation after tube removal
The reproductive system has a kind of memory. Even after eliminating the problem, the female reproductive organs may not function properly. However, it's not just about the operation. The cause of various disorders is rather the factors that led to it - a chronic inflammatory process, ectopic pregnancy, various gynecological diseases.
Here are the problems women face during their first menstruation after tubal removal:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen. Painful sensations are associated with contractions of the uterus, which radiate to the area of the fallopian tubes in which surgical manipulations were performed. Tissue restoration occurs differently for everyone. If inflammation in the operated tissues is still present, then fluctuations caused by a spasming uterus may cause excessively painful periods.
- Weakness. Women tolerate general anesthesia differently. During surgery to remove the fallopian tubes, it is necessary, but it can greatly undermine the immune system, and due to the hormonal changes that the reproductive system undergoes after the removal of one of the important organs, various symptoms of hormonal disorders may be present, including lethargy, drowsiness, or, conversely, mood swings , tearfulness, etc. And the operation itself is a great emotional shock that requires recovery.
Delayed menstruation and stomach pain
If your period is late and your stomach hurts very badly, then this condition may give you reason to think about pregnancy. Pain in the lower abdomen is completely normal if you are pregnant. It is advisable at this moment to take a pregnancy test, which can confirm or refute your state of pregnancy or lack thereof. It is worth understanding that the reason for a delay in menstruation lies not only in pregnancy, but also in severe stress, a sudden change in climate, a change in lifestyle, or significant changes in work activity. The female body reacts quite sharply to all changes that may occur in life.
Reasons for missed periods
If the true reason for the delay in menstruation is stress, then somehow your life will return to normal and your menstruation will begin. A delay in menstruation may indicate hormonal imbalance, pathologies, irregular menstrual cycle, puberty and development of the body, menopause. If your period does not start, then remember - you may have recently taken some medications, the side effect of which is gastrointestinal tract disturbance and menstrual cycle disruption. In no case should you wait several months for menstruation to resume; be sure to go to the doctor for examination. Even if the pain in the lower abdomen in the absence of menstruation is not very severe, you need to start worrying about your own health.
Infections that are sexually transmitted from your partner: chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, as well as a number of other pathologies. If the reason for the delay in menstruation is an infectious process, then in this case you may feel an unpleasant odor from the vagina and itching. Also, this condition is in most cases accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. If you have such symptoms, you should definitely go to the doctor.
Source
What to pay attention to
After tube removal, not only the intensity of pain may change, but also the volume of menstrual flow. During the first menstruation, they can be quite intense and long-lasting. At the same time, if there was no ovulation in this cycle due to severe stress, menstruation may be quite scanty, because due to estrogen deficiency, the endometrium could grow poorly. The duration of menstruation after surgery can normally reach 5 - 7 days as a result of recovery processes in the body or while taking oral contraceptives, which can be prescribed after the intervention. If menstruation lasts more than 7 days, this is already bleeding.
As mentioned above, menstruation after tubal removal can be noticeably painful. This is the norm. But if the bloody discharge has a strange smell, your temperature rises, and the pain is so severe that it cannot be relieved with antispasmodic drugs, then this may be a sign of an infectious process that was the result of surgery or non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period. If you notice anything unusual in your sensations, contact your doctor immediately.
What are the reasons for missed periods, besides pregnancy?
The way a woman's reproductive system functions can be used to judge her overall health. The appearance of cycle disorders and delayed menstruation indicate abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine, nervous and other systems. Regular periods of normal duration indicate that the level of hormones is normal and the woman is able to become pregnant. The reasons for the delay of menstruation can be the processes of natural age-related changes, the body’s reaction to external factors. Deviation from the norm is often a sign of a serious illness.
What is considered a missed period?
It is considered normal if a woman’s period comes in 21-35 days. A delay of more than 10 days is a pathology if it is not associated with a physiological restructuring of the body. Every woman experiences a slight delay in menstruation 1-2 times a year. If this repeats constantly, then you need to see a doctor for examination.
There are natural reasons for a missed period. In addition to pregnancy, this could, for example, be lactation or menopause. If the delay is not associated with normal physiological processes, then the nature of the pathology must be immediately established to avoid complications.
Physiological causes of delayed menstruation
The menstrual cycle is a strict sequence of processes associated with preparing the female body for pregnancy. Even a completely healthy woman can experience malfunctions of this mechanism under the influence of external factors. These include:
Hormonal changes in the body during puberty. For 1-2 years, periods come irregularly, even missing for several months due to the immaturity of the ovaries. Then the cycle is established. If this does not happen, then it is necessary to find out the cause of the violation.
Source