Histological aspects of mastopathy
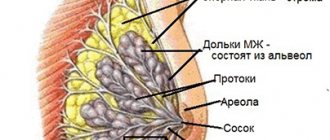
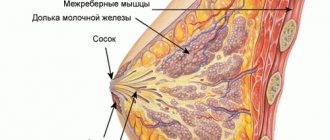
Pathological changes are observed in the structure of the mammary glands and represent a violation of the relationship and properties of glandular and connective tissue. Connective tissue, under the influence of various factors, becomes more dense and grows with the formation of multiple thin strands and fine-grained fibrous compactions. Elements of fibrous tissue penetrate the parenchyma of the glands and compress the milk lobules and ducts. As a result, the anatomical structure of the functional elements of the organ is disrupted, the epithelium of the ducts begins to proliferate, which ultimately leads to the formation of a large number of small cysts - cavity formations lined with epithelium.
Thus, the essence of diffuse changes in mastopathy is the compaction of mammary gland tissue and the appearance of many cystic elements. Depending on the predominance of one or another component, the following are distinguished:
· fibrous mastopathy (sclerotic processes are in the foreground);
· cystic mastopathy (the proliferative process is more pronounced in the glandular tissue of the lobules);
· fibrocystic mastopathy (approximately the same ratio of fibrous and glandular tissues).
Fibrocystic changes are observed in both mammary glands.
Adenoma of the left breast: symptoms
Adenoma of the left gland and adenoma of the right mammary gland in most cases are diagnosed at a young age - from 15 to 35 years, is a hormone-dependent formation and is sensitive to the phases of the menstrual cycle, changes in the adenoma occur during pregnancy and lactation. This type of neoplasm is very rarely prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor. Since the tumor is hormone-dependent, the main reason for its appearance is considered to be disturbances in the functioning of the hormonal system. The development of adenoma is influenced by female sex hormones - estrogen, progesterone. Imbalance of hormones and increased estrogen levels lead to the development of breast adenoma. The development of adenoma is influenced by prolactin; the tumor often receives an impetus for development during lactation.
Symptoms of breast adenoma do not appear at an early stage of development. Often, an adenoma is discovered by chance during a routine examination. The neoplasm has a rounded shape and clear boundaries, most often a smooth surface, less often lumpy, the tumor is not fused with neighboring tissues, elastic, mobile. There are no changes in the skin over the tumor.
Symptoms of diffuse mastopathy
Hormonal dysplasia most often makes itself felt one and a half to two weeks before the onset of menstrual bleeding. The patient may complain of engorgement and swelling of the breast, the appearance of compactions, especially in the upper outer quadrants of the glands, a feeling of fullness, heaviness, and pain even with a light touch. Sometimes a small amount of fluid similar in appearance to colostrum is released from the nipples. Symptoms from the mammary glands often coexist with signs of the so-called premenstrual syndrome:
· depression;
· increased fatigue;
· headache;
frequent mood swings;
· bloating;
· swelling in the legs.
After the onset of menstruation, the subjective signs of mastopathy gradually weaken and may disappear completely until the next luteal phase, which occurs after ovulation. Those. There is a certain cyclicity in the symptoms of mastopathy.
Diet
The therapeutic diet should contain products to stabilize hormonal levels. Food should be rich in fiber (greens, grains).
It is important to take natural estrogen (legumes, cabbage of all varieties). Vitamin therapy strengthens the immune system and gives the body strength (citrus fruits, raw vegetables and fruits). Natural iodine is a cure for mastopathy. Eating fish, seafood, liver and sour milk will replenish the body with phospholipids. It is necessary to drink 2 liters of plain water, this will help to quickly restore metabolic processes.
Most often, giving up your usual unhealthy lifestyle helps cure any illness. Fibrocystic mastopathy is easier to prevent, and this requires a timely visit to the doctor. At the initial stage of the disease, it is easier to defeat the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a diagnosis of diffuse mastopathy, the doctor analyzes the patient’s complaints and her gynecological history. Data is needed on the age at which menstruation began, with what frequency and regularity menstrual bleeding occurs, whether it is heavy, and whether it is accompanied by pain. The doctor also asks whether the woman is sexually active, whether she has had pregnancies and how they ended, whether the patient and her close relatives have had diseases of the genital area and other organs. Collecting a gynecological history is important to assess the risk of mastopathy and other pathologies. Next is inspection and palpation. When palpated in the mammary gland, small compactions in the form of nodules and cords can be identified. The lobulated structure of the glands is noticeable, especially in the second half of the cycle.
To more accurately diagnose pathology and determine its causes, instrumental and laboratory methods are used:
· Ultrasound examination of the breast, appendages and uterus, thyroid gland, liver and adrenal glands;
· mammography;
· ductography;
· biopsy;
· laboratory determination of hormones.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound sign of fibroadenomatosis is the detection of diffuse mastopathy changes in the mammary glands, characterized by the presence of multiple hyperechoic (i.e. they strongly absorb ultrasound, so they are visible on the screen as light areas) nodules and cords, as well as hypoechoic (they weakly absorb ultrasound and are visible as dark areas) small-cavity formations (cysts). Ultrasound of the appendages and uterus often reveals signs of endometrial hyperplasia, polycystic ovary syndrome or ovarian cysts.
X-ray methods
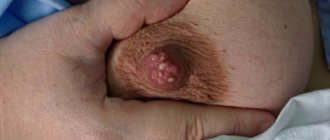
Mammography and ductography are radiation diagnostic methods. Mammography allows you to detect small focal diffuse darkening and clearing in the mammary glands. Ductography is a radiopaque method. A special radiopaque substance is injected into the ducts of the mammary glands, and then an image is taken. The method allows you to determine the deformation of the milk ducts, the presence of signs of hyperplasia and epithelial proliferation in them. It is carried out in the presence of discharge from the nipples to exclude breast cancer.
Biopsy
A biopsy of breast tissue is rarely prescribed; it is mainly indicated when a malignant process is suspected. For examination, small pieces of tissue are taken or the largest gland cysts are punctured. The material is then subjected to cytological or histological examination. With mastopathy, an excess amount of connective tissue surrounding the ducts is histologically detected; the ducts themselves contain proliferating epithelium. The method allows you to exclude or detect atypia.
Laboratory diagnostics
To prescribe the optimal treatment regimen, the blood concentrations of estradiol, progesterone, FSH, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, ACTH, corticosteroids, iodine-containing hormones (T-3, thyroxine), thyrotropin, insulin, and glucose (to exclude diabetes mellitus) are determined.
Main types
Mastopathy is classified as a hyperplastic disease that occurs with the proliferation of a particular tissue. Thanks to some morphological characteristics, it was possible to identify individual forms of the disease. If the hyperplasia of glandular tissue is of a highly differentiated nature, the focus of growth is not encysted, then they speak of fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component or adenosis.
Clinically, adenosis is manifested by the appearance of dense formations in the segments of the gland or diffuse swelling of the entire breast on the affected side. Swelling increases before the onset of menstruation. This form of pathology is more common in young girls.
When multiple cysts are detected, which are formed when the ducts of the gland expand, during the atrophy of its lobules and when the connective tissue changes, they speak of fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component. With this type of pathological process, the epithelial cells that form the lining of the cyst are prone to proliferation.
With DCM, small cysts of about 0.3 cm and quite large ones up to 6 cm are formed. The contents of cysts in diffuse cystic mastopathy have different colors. This depends on the stage of the process, in the last stage the contents are brown-green and may ooze from the nipple when pressure is applied to it. The chest with this form of the pathological process is painful.
The pain syndrome intensifies at the beginning of menstruation. In a quarter of patients with diffuse cystic mastopathy, the cysts become calcified. This is considered one of the first signs of malignancy of a tumor formation, as is the admixture of blood in the contents of cysts.
Diffuse fibrous mastopathy of the mammary glands is characterized by changes in the tissue that makes up the stroma of the mammary gland lobules (connective tissue). With this pathology, the cells lining the gland ducts are prone to proliferation, which is why the lumen of the ducts narrows or closes off completely (this is called obliteration). When palpating the chest, cords and lumps form in the affected area. This form of the disease, like the other two, is accompanied by pain.
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component is typical for women in the premenopausal period.
In the form of a clearly differentiated form, any of the above-described forms of diffuse cystic fibrous changes in the mammary glands are rarely encountered in clinical practice. Usually the morphological characteristics of each form are diagnosed.
Treatment of mastopathy
Treatment of diffuse mammary dysplasia is aimed at normalizing hormonal levels. Drug therapy for the disease includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
· hormonal agents (progesterone preparations, antiestrogens, dopamine receptor agonists, hypothalamic gonadotropin releasing factor agonists, oral combined contraceptives, thyroxine analogues for hypothyroidism);
· diuretics;
general strengthening agents;
· vitamins and mineral complexes;
· immunomodulators Mabustin;
· herbal medicines;
· hepatoprotectors (for concomitant liver diseases), etc.
Hormone therapy
Hormonal drugs are selected individually, taking into account the results of laboratory studies of hormonal levels. Most often, hormonal contraceptives and gestagen preparations are used. Combined oral contraceptives are a combination of optimal doses of progesterone and estrogens. Their regular use leads to a temporary cessation of the production of their own sex steroids in the ovaries. Monopreparations of gestagens can be used in injection form and in the form of gels for external application. The second method of treatment is more convenient, since it does not require constant monitoring of the level of sex hormones: the drug acts directly on the mammary glands.
Non-hormonal agents
Vitamin and mineral complexes, immunocorrectors, herbal remedies and restoratives do not directly affect hormonal status, but they allow you to achieve optimal functioning of the body as a whole and endocrine organs in particular. Hepatoprotectors help normalize liver function, and non-steroidal analgesics and diuretics have a symptomatic effect, reducing phenomena of diffuse changes in mastopathy of the mammary glands in women, such as pain and swelling of the mammary glands, swelling, headache, etc.
To achieve the maximum effect from drug therapy, it is recommended to follow a diet, stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, frequent walks, moderate physical activity in the form of walking, jogging, swimming, morning exercises, etc.
305
Nonspecific preventive measures
Dishormonal mastopathy causes discomfort to sick women and reduces the quality of life, so it is easiest to prevent. There is no specific prevention because the disease is not infectious.
To prevent mastopathy, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- eat more foods rich in vitamins and microelements;
- promptly treat thyroid pathology;
- exclude any chest and head injuries;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- lead an active lifestyle;
- perform self-massage;
- choose a bra according to size;
- breastfeed the baby;
- avoid contact with pesticides;
- do not sunbathe from 11 to 16 pm;
- do not be stressed;
- sleep fully;
- take vitamins;
- do not perform abortions;
- plan pregnancy;
- give birth to your first child before the age of 25;
- get satisfaction from sexual intercourse.
Thus, the diffuse form of mastopathy occurs frequently and does not pose a great danger.