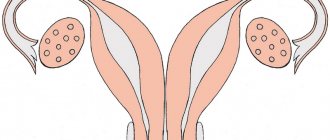
Pathologies of the female genital organs can be very diverse. This may be underdevelopment of individual organs, incorrect anatomical structure, as well as duplication of the uterus and vagina. These developmental anomalies are often accompanied by impaired reproductive function.
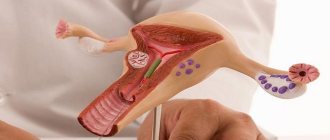
Pregnancy in the rudimentary uterine horn is a fairly rare occurrence. The accessory horn is a separate formation and is connected to the normal uterine horn by a pronounced stalk. Sometimes a woman may not realize that she has a bicornuate uterus. But pregnancy in a rudimentary horn can pose a serious threat to her life and health.
What does a one-horned uterus mean?
A one-horned uterus is a pathology in which only one half of the reproductive organ is observed. With the disease, the woman also has no appendages. Pregnancy in this case is accompanied by the risk of miscarriage and weak contraction of the uterus during the birth process. The vestigial horn is the underdeveloped half of the organ of the reproductive system. A photo of a one-horned uterus is presented below.
Symptoms
The appearance of the first clinical signs of the disease depends on the type of defect. With a functioning closed rudimentary horn, they appear soon after menarche. Characterized by algodismenorrhea.
Violation of the outflow of menstrual blood from the pathological organ leads to the formation of hematometra and hematosalpings with unilateral pain on the 3rd - 4th day of the female cycle. Retrograde reflux of secretions can be accompanied by acute abdominal syndrome, the development of endometriosis and adhesions in the pelvis. In most cases, problems with the reproductive organs in women are similar in their symptoms. Summarizing them, we get the following clinical picture:
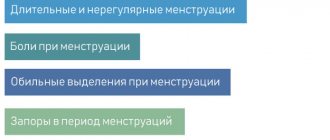
- painful and heavy menstruation or lack thereof;
- unilateral abdominal pain radiating throughout the entire circumference;
- tumor-like formations;
- involuntary miscarriages;
- miscarriage.
The consequence of all this is infertility.
Provoking factors
The anomaly in question belongs to the group of birth defects. It occurs during organogenesis, at 10-14 weeks of fetal development. The female reproductive system is formed from the Müllerian ducts. During intrauterine development, they merge into a single whole. When the ducts are not completely aligned, such types of defects as a single or bicornuate uterus occur.
The following reasons are identified for improper formation of the genital organ in the fetus:
- maternal poisoning with drugs or poisonous gases;
- heart defects in a pregnant woman;
- increased radiation exposure;
- infection of a pregnant woman with syphilis, rubella or measles;
- exposure to radiation;
- the expectant mother has bad habits - excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, drug use;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- endocrine pathologies in a pregnant woman.
In the presence of these factors, the Müllerian ducts in the fetus merge at different levels, which causes abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
A one-horned uterus is often accompanied by the absence of one of the kidneys. The disease is treated in girls during adolescence.
Causes
A unicornuate uterus belongs to the category of congenital anomalies. The disease occurs during the formation of organs during the embryonic development of the fetus. Most often this occurs in the range from 10 to 14 weeks of gestation, since the reproductive system in women is formed from the Müllerian ducts. It is during this period that the fetus in the womb experiences their fusion into one whole. In the case of their incomplete fusion, this pathology occurs, which is called a one-horned uterus.
Today, a list of factors is known, under the long-term influence of which the incorrect formation of the female genital organ in the fetus occurs. The main ones are:
- severe intoxication of the expectant mother with medicinal drugs or poisonous gases;
- congenital or acquired changes in the structures of the heart, leading to impaired blood flow in a woman;
- presence of bad habits (smoking and alcohol abuse);
- drug addiction;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- exposure to radiation and exposure;
- infection with infectious diseases, sexually transmitted diseases and more;
- lack of oxygen and nutrients for the full development of the baby.
The factors described above can cause disruption of the fusion of the Müllerian ducts and, accordingly, the occurrence of congenital pathology in the fetus.
Signs
Pathology can be detected during an ultrasound or gynecological examination. The defect manifests itself in a characteristic clinical picture, which serves as a reason to contact a specialist. Symptoms that are observed with an anomaly:
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen before and during menstruation;
- discomfort during intimacy;
- complete absence of menstruation.
Unicornuate uterus is a rare disease. The reproductive organ in this case is smaller in size compared to normal values (2 times).
Diagnostics
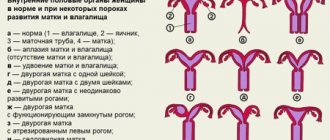
The presence of an anomaly is determined by symptoms and using additional diagnostic methods. Signs of pathology suggest a problem in the reproductive system. Instrumental examination methods allow us to identify the type of birth defect. There are 3 types of uterine deviation from the norm:
- The presence of a rudimentary horn not connected to the body of the uterus.
- The presence of a rudimentary part communicating with the main horn.
- No rudiment.
A gynecologist can determine the presence of a one-horned uterus based on the following signs in a woman:
- delayed menstruation;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- excess body hair.
In most cases, anomalies in the structure of the organ of the reproductive system do not manifest significant symptoms. The problem is discovered during the inspection.
Diagnostic measures to identify a defect consist of:
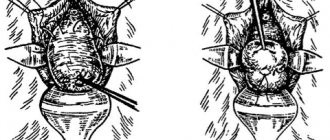
- Gynecological examination. The doctor examines the patient’s vagina on a chair using special mirrors. As a result of the examination, the specialist will be able to identify not only the presence of an anomaly, but also its type (saddle-shaped, one-horned or two-horned uterus).
- Ultrasound examination. Deviations in the structure of the organ are determined using transvaginal or transabdominal ultrasound.
- Hysteroscopy. The gynecologist examines the uterine cavity using magnifying equipment.
- Tomographic research. This diagnostic method is prescribed in extreme cases - when it is impossible to determine the type of problem using other measures.
A one-horned uterus with a rudimentary horn is diagnosed without problems. The treatment regimen depends on the severity of the pathology and its type.
Kinds
This pathology is an extremely rare occurrence, but still occurs. Pathological changes in the uterus can cause major problems in sexual life. In some cases, during sexual intercourse, a woman may experience severe pain, which can lead to loss of consciousness.
Girls suffering from the disease are very concerned about the issue of pregnancy, because the purpose of every representative of the female half of the population is to give birth to a baby.
If she has no additional anomalies, and the fallopian tube functions normally, then the onset of pregnancy and the subsequent full development of the fetus is quite possible.
The course of the resulting pregnancy largely depends on the size of the existing part of the uterus, but in the case of the presence of an underdeveloped second horn, a rudimentary horn, the development of various kinds of problems and complications is possible. When a fetus enters this abnormal compartment, its development immediately stops and, as a result, the pregnancy freezes, and in some cases bleeding and a purulent process occur.
In medical practice, there are four main types of anomalies, namely:
- one-horned uterus without a rudimentary horn;
- with the presence of a vestigial horn;
- uterus, which has a rudimentary horn but no cavity;
- true one-horned uterus.
Conception followed by pregnancy is possible in almost all of the pathologies described above. In cases where the existing rudimentary horn is an obstacle to the development of gestation, it must be removed through surgery.
Picture taken from il-de-butik.ru
Treatment
There are no ways to completely cope with the defect in question. Medicine has not yet developed treatment methods that restore the reproductive functions of women with congenital malformations. To combat the anomaly, surgery or laparoscopy is usually prescribed.
Abdominal section
Surgical intervention is performed in stages:
- The doctor makes an incision in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and bandages the rudimentary element.
- The surgeon removes the underdeveloped part of the uterus along with the tube to prevent ectopic pregnancy, which can develop in the blind tube.
- After excision of the tube, the surgeon removes the ovaries (if any).
The vestigial part can be attached to the reproductive organ using the common myometrium or fibrous ligament. In the latter case, during the operation the surgeon dissects the ligament.
If the element is attached to the uterus by the myometrium, then surgical intervention is performed according to a different scheme. First, the specialist identifies and ligates the artery of the reproductive organ located below the horn. In this case, it is important to correctly determine the bifurcation of the arteries between the rudiment and the uterus, so as not to disrupt the integrity of the myometrium. After excision of the rudiment, the incision site should be tightly closed with sutures. This procedure reduces the likelihood of rupture of an organ of the reproductive system during pregnancy.
Laparoscopy
Treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- After diagnostic measures and anesthesia, the doctor grabs the appendage with serrated forceps.
- Using ultrasonic scissors, the doctor cuts the round ligament of the uterus.
- The anterior or posterior part of the uterine ligament and the vesical fold of the peritoneum are dissected to the junction of the rudimentary part and the genital organ.
- The vessels are tightened with threads or coagulated with forceps. The latter option is preferable since the diameter of the threads used is small. After this, the vessels are cut with an ultrasonic scalpel.
- The horn is separated from the uterus. Excision is performed slightly above the point where the rudiment branches off from the main part. The endometrium of the horn is necessarily removed to prevent the attachment of the fertilized egg in this area.
- Endoscopic suturing of the wound occurs. This method reduces the likelihood of suture rupture during subsequent pregnancies and childbirths.
During laparoscopy, not only the underdeveloped element is removed, but also the ovaries, fallopian tube and adhesions from the rudiment are removed.
Complications after this method of intervention appear only in rare cases. Already 2-3 hours after laparoscopy, women are allowed to walk. Discharge is carried out on the 2nd day after the intervention
Features of the operation
As a rule, in order to save the patient’s life, an operation is performed, which consists of removing the excess horn along with the ovary and the tube located on this side. The severed round ligament is sutured to the bottom of the remaining second horn of the uterus. A timely operation can save the patient from death.
Based on all of the above, we can imagine three main scenarios for the development of events during the pregnancy of a rudimentary horn:
- The most favorable option is when the doctor and patient know about the rudimentary horn, and the operation is carried out in a timely manner;
- The most unfavorable option is when neither the patient nor the doctor knows about the pathology. As a rule, pregnancy ends with uterine rupture;
- A common option is when the presence of an ectopic pregnancy of this type is detected during examination (laparotomy). Then a decision is made about the need for surgical intervention.
Currently, medicine is at a fairly high level and has the means to quickly identify pathology and take measures to correct the situation.
We wish you good health and spiritual harmony. We are waiting for responses, reviews and comments on the topic of the article. Don't forget to share links to the material on social networks.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery depends on several criteria:
- woman's age;
- degree of severity of pathology;
- surgical techniques.
Immediately after the intervention, women experienced an improvement in their condition and increased performance. 2 months after laparoscopy, patients with a unicornuate uterus were allowed to plan a pregnancy. This is due to the absence of a scar after the intervention. Unlike traditional surgery, endoscopic surgery does not affect the possibility of giving birth naturally.
Is pregnancy possible?
Can a woman with a unicornuate uterus get pregnant? The answer is yes. Conceiving a child is possible if the pathology is not complicated by other gynecological diseases. The main problem with a one-horned uterus is the difficulty of attaching the fertilized egg to the deformed walls. This condition leads to spontaneous abortion and is a cause of infertility. Read this article for more details.