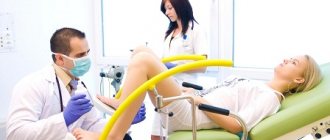
What is oncociology and its types?
Oncocytology is a microscopic examination of a biopath taken using a smear from the cervix and cervical canal.
It is conventionally divided into 2 forms:
- Simple - in this case, the biopath is taken onto a special brush, and during laboratory analysis it is smeared on laboratory glass.
- In liquid oncociology, a smear with gored biomaterial is placed in a bottle with a special reagent liquid. It is this that allows you to obtain more accurate and reliable data.
Preparing for the procedure and taking a smear
In order for the smear results to be reliable, it is necessary to properly prepare for the analysis.
Preparation for taking a smear includes abstaining from sexual intercourse for at least two days. It is not recommended to douche, insert any suppositories, or use vaginal contraceptives. Immediately before going to the gynecologist, it is not recommended to shower with gels, foams or other perfumes and cosmetics. Genital hygiene is carried out using soap. Also, you should not carry out deep cleaning of the reproductive system.
A smear cannot be taken during the menstrual cycle, or two days before and after it. White blood cell counts in this case may be false. If you do not follow the rules for preparing for a smear collection, the results may be incorrect and you will have to take a second test.
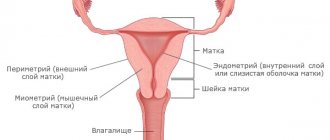
A smear is taken from several places in the reproductive system - the cervix (C), urethra (U) and vagina (V).
The sampling is carried out with a disposable sterile spatula. Smears are applied to three different glasses, each of which is signed, indicating the place from which the smear was taken. The study is carried out under a microscope in the laboratory.
This is interesting: The first signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages. Symptoms
In addition to the quantitative indicators of white cells, the presence of flat epithelium, gonococci, trichomonas, candida, key cells and other flora is detected. Pap smear results provide an overall picture of your health and may indicate the need for additional testing.
Leukocyte norms
When examining a smear under a microscope, there should be no more than 15 white bodies in the field of view of the laboratory technician. A smear from the cervix should show a value of 15, from the urethra - 5 and from the vagina - 10.
In case of a significant increase in indicators, the doctor determines the cause of the inflammatory process. It is worth understanding that an increase in white cells is not a disease, but only an indicator of the inflammatory process. To identify the causative agent of the infection, the doctor may prescribe other examinations and tests.
An increase in white blood cells can be triggered by a vigorous sex life and frequent changes of partners. In this case, this indicator is considered normal and is not a sign of an inflammatory process. The increase in performance in this case is small. More often, a deviation from the norm indicates infection of the reproductive system; the woman complains of poor health.
To identify pathogens and make a diagnosis, additional examinations may be prescribed:
- Enzyme immunoassay and direct immunofluorescence are performed
- Polymerase chain reaction test
- Tests for antibodies in the blood
- Tissue collection - biopsy
- Examination by other specialists, including consultation with a physician, may be required
Additional examinations are necessary to identify the cause of inflammatory processes. One standard smear is usually not enough. It gives only a general picture of the health of the reproductive system.
Indications for analysis
It is taken for one purpose - to accurately assess the condition of the cervical cells, the size and quality of the latter, excluding pathological neoplasms and changes. Analysis for oncocytology of the cervix reveals:
- Random division and growth of atypical cells . With this result, a second smear is performed after 3-4 months or referred for additional diagnostics, biopsy or colposcopy.
- Allows you to determine the course of the inflammatory process - this analysis will allow you to determine the causative agent of the pathological process.
How to make a smear for oncocytology: preparation and conduct
At the very beginning, it is worth deciding on the day of the analysis - many gynecologists advise carrying it out between 13-21 days of the entire menstrual cycle.
So, 2-3 days before the test, refrain from any sexual contact and douching, and an hour before the test, do not go to the toilet.
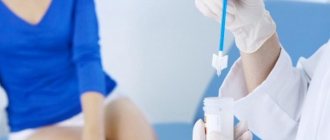
How to get tested for oncocytology? The procedure itself is simple - it does not take 5 minutes. The main thing is not to carry out the procedure during menstruation and with a diagnosed inflammatory process. The biopath is taken during a routine medical examination - a special brush is inserted into the vagina and biological material is collected from the cervical canal and external uterine pharynx, almost imperceptibly for the patient. Afterwards they are transferred to laboratory glass and examined under a microscope.
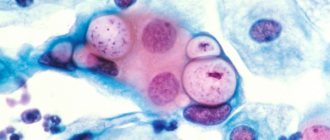
Atypical cells in the smear, what could it be?
What does the presence of atypical cells in an oncocytology smear indicate?
Atypical cells are cellular elements that have an abnormal, irregular structure, size and shape. These kinds of changes in cells can occur as a result of the inflammatory process.
Moreover, the inflammatory process in the tissues of the cervix is not as rare as many women might think. After all, inflammation in the cervix can be provoked by human papilloma viruses, herpes simplex, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia and other microorganisms.
Moreover, such an inflammatory process, proceeding for quite a long time, provokes the appearance of signs of atypia in cells. This situation is described in the conclusion of a smear cytology analysis as the presence of atypical cells.
Therefore, if atypical cells are detected in a smear, it is necessary to undergo an additional colposcopy with a biopsy, as well as be tested for various sexually transmitted infections.
In addition to inflammation, the cause of the appearance of atypical cells is tumor transformation of the cellular elements of the cervical epithelium. However, the presence of atypical cells does not mean that a woman is developing a malignant tumor.
Normally, up to a million tumor cells are formed in the human body every day, which are effectively destroyed by one’s own immune system. Such tumor cells naturally form in the tissues of the cervix.
But with normal functioning of the immune system, atypical cells are simply destroyed and do not cause any tumor growths. Therefore, often the detection of atypical cells in a smear indicates only physiological processes occurring in a woman’s body.
If the cytology smear results indicate only the presence of atypical cells and the degree of atypia is not additionally described, then most likely we are talking about inflammatory changes in the cervix.
If the degree of atypia is also indicated, this means that the cells of the cervix have undergone some transformation, which at this stage is not dangerous, but theoretically, under certain conditions, they can become a source of tumor growth.
Therefore, if there are atypical cells according to the results of a cytology smear, it is recommended to undergo a colposcopy with a biopsy of suspicious areas of the cervix.
Today, a smear for atypical cells is performed almost every time a woman visits a gynecologist. Ideally, it should be carried out annually, then this allows them to be detected and treated in a timely manner, which eliminates the development of cervical cancer.
This analysis is simple and cheap. In antenatal clinics it is performed free of charge. It is also called a smear cytology or Pap test. The material for the study is collected by a gynecologist while the patient is in the examination chair. He then applies it to glass and sends it to the laboratory.
There, the doctor stains the material and examines it under a microscope. The specialist’s task is to assess whether the size, shape and structure of the cells correspond to the norm. If everything is in order, then the test is negative.
However, this does not mean that the patient has cancer. Changes in cells can occur in the presence of inflammation, which can be caused, for example, by an STD. So, a cytogram can be of 5 types:
- I – without features;
- II – inflammation caused by Trichomonas, fungi, common flora, gonococci, chlamydia, gardnerella, HPV and/or HSV;
- III – dysplasia of flat or columnar epithelium (weak, moderate, severe);
- IV – suspicion of cancer;
- V – cancer.
The result of the analysis for atypical cells depends on the quality of the material taken, as well as on the professionalism of the person who analyzes the slide.
Therefore, errors occur quite often. Having received a positive result, the patient should not be upset, but retake it and undergo a more in-depth examination.
Also, in order to get a reliable result, it is necessary to carry out the analysis correctly. A smear should not be done during menstruation; ideally it should be carried out from the 7th to 11th day of the cycle.
Two days before the study, you need to exclude sex, the use of vaginal suppositories, pills, and douching. It is advisable not to take a bath, but to limit yourself to a shower only.
The widespread use of analysis for atypical cells has reduced mortality from cervical cancer by 70%. Mostly, patients who have never undergone this test or have undergone it extremely rarely die from malignant processes of the cervix.
The role of HPV in the development of cervical cancer pathologies has been scientifically proven. Its highly ionized types are especially dangerous, the most common and dangerous of which are 18 and 16.
Women in whom they were detected in smears using PCR should undergo a cytological examination twice a year. They are 400 times more likely to develop cancer than others.
Genital herpes is also believed to contribute to the development of cervical cancer. HSV type 2 is considered more dangerous. Its combination with HPV HCR is especially undesirable.
It should be borne in mind that condoms, although they reduce the likelihood of infection with HPV and HSV, do not exclude it. The fact is that viruses are so small that they penetrate through their pores.
Therefore, it is advisable to have one permanent partner and be regularly examined by a gynecologist. It must be taken into account that HPV can begin to manifest itself after many years.
So, atypical cells in a cervical smear are an alarming symptom and require additional examination. If the patient does not undergo therapy on time, then the development of cancer in the future is possible.
Significance of the analysis
Oncocytology smear - what does it show? Conducting a laboratory smear to determine oncocytology is a very necessary measure and allows for timely detection of cervical cancer.
If oncology is detected in the early stages of the pathology, timely measures taken will allow cancer to be cured and death to be prevented.
What is vaginal microflora
A smear on the flora is an effective diagnosis of gynecological diseases in women
A woman's vagina, like other parts of the body, actively interacts with the environment. It is not sterile because a large number of different bacteria are constantly present in it. Thanks to such microorganisms, normal microflora is created in the vagina.
The vagina is home to various microscopic organisms, and one of them is Dederlein's bacillus. Such lactobacilli maintain normal acidity in the organ, and this occurs due to the release of hydrogen peroxide. Creating a special acidic environment in the vagina helps prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause the development of many gynecological diseases.
If any pathology develops in the genital organs, a change in the microflora is noted.
It is thanks to such indicators that specialists can timely diagnose the disease and determine the cause of its occurrence. Using a bacteriological smear on vaginal flora, it is possible to determine the composition of the microflora, which begins to change depending on the bacteria that have begun their active reproduction.
Who should be tested?
As a disease, cancer develops slowly and does not show itself in the early stages. Therefore, the reasons for carrying out oncocytology of the cervix may be not just preventive studies:
- disruption during the menstrual cycle.
- taking hormonal contraceptives and inserting an intrauterine device.
- Diagnosed infertility and planning a future pregnancy.
- diagnosing genital herpes and warts.
- history of HIV or HPV.
- chronic inflammation of the genitourinary system and long-term use of contraceptives.
- early sexual life and frequent change of sexual partners , several, more than 2 births.
In any case, in each individual case, the doctor prescribes his own basis for referral for laboratory testing.
How to treat an inflamed cervix
If this is vaginal candidiasis (thrush), then local treatment with antifungal drugs, for example, Clotrimazole, will be required. Medicines with active ingredients are also used against thrush: isoconazole, miconazole, natamycin, nystatin.
If this is bacterial vaginosis, key cells and coccal flora are found in smears from the cervical canal, then antiseptics like Hexicon (chlorhexidine), metronidazole or a complex drug - Terzhinan will be prescribed.
If urogenital trichomoniasis is detected, drugs from the nitroimidazoles group are prescribed: Metronidazole, Ternidazole, Neomycin, Nystatin.
For chlamydial cervicitis, take tetracycline, doxycycline and or erythromycin orally.
For actinomycosis caused by wearing an intrauterine device (IUD), you must first remove the intrauterine device. And then, there are options. These may be penicillin antibiotics:
- tetracyclines;
- cephalosporins (cefaclor, cephalexin);
- aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, tobramycin).
Broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs:
- metronidazole (metrogyl, trichopolum, efloran);
- clindamycin (dalacin, climycin, clindamycin).
The following medications help greatly:
- co-trimoxazole;
- sulfadimethoxine;
- sulphacarbamide.
In case of exacerbation of genital herpes, doctors recommend local therapy with drugs:
- "Acyclovir";
- Famciclovir;
- Valaciclovir.
If relapses of the disease are frequent, the same medications are prescribed in the form of tablets for oral administration.
If HPV (human papillomavirus) was detected in the scraping, especially if these are oncogenic types (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70), the woman is recommended to take a cytogram every 3-6 months .
Unfortunately, there is no cure for HPV. But within 1-2 years after the manifestation of the disease, the immune system overcomes the virus, and it ceases to negatively affect the cervix. The main thing is to hold out for these few months.
For atrophic colpitis (atrophic type of smear, ATM), treatment is carried out with antibacterial agents, usually of complex action, and then the woman is prescribed hormone replacement therapy (HRT) if necessary and if there are no contraindications for it.
Smear for oncocytology: explanation
In the final results of the laboratory test, doctors give a positive or negative rating. Accordingly, talk about whether there are atypical cells in the body or not.
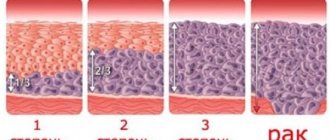
The result also determines 5 classes of cervical condition:
- The first class is considered normal, when no cancer cells are found in the uterine cavity, everything develops normally.
- Second class - doctors identify the inflammatory process.
- When diagnosing the third class, doctors detect it in small quantities. In this case, repeated analysis is required.
- In the case of a class 4 , cancer cells are present in the analysis.
- In the fifth grade, all cells in the collected biological material are atypical.
- But the final verdict after conducting a number of studies.
What should you be wary of?
What you should be wary of after a laboratory test is a diagnosis of cancer. But it is important to note that if the diagnosis of cancer shows the initial stage of oncology, you should not worry, since in this case it can be effectively treated with a properly selected course of treatment. In the later stages of cancer, a long course of therapy and recovery awaits.
We recommend reading: dyspareunia in women - symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment.
Antibacterial drug Nolicin 400 mg: instructions for use, use in gynecology. All the details are here.
Technique for using medications – intravaginally: https://venerolog-ginekolog.ru/gynecology/medicament/intravaginalno.html