Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis develops when the normal ratio of microorganisms in the vagina is disrupted, which is clinically manifested by creamy discharge with a specific amine odor (the smell of “fish”). Partial or complete loss of lactic acid bacteria in the vagina leads to excessive proliferation of other microorganisms, such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, as well as other anaerobes - Fusobacterium, Prevotella, Peptococcus, Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus , Veilonella, Vulonella, Mobiluncus. However, Gardnerella vaginalis plays a leading role in the development of bacterial vaginosis.
Changes in smear with bacterial vaginosis:
- White blood cells are usually normal or absent;
- A sharp decrease in the number of lactobacilli;
- A large number of small cocci;
- The presence of “key” cells are epithelial cells covered with a continuous layer of bacteria.
A flora smear is the method of choice for diagnosing bacterial vaginosis and there is no need for a PCR test. In some cases, bacterial vaginosis can occur in combination with other infections, which will be clinically manifested by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, itching, and dysuric disorders. If a mixed infection is suspected, it is advisable to conduct additional research methods (PCR and flora culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics).
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis is indicated to eliminate symptoms and is aimed at suppressing excessive growth of conditionally pathogenic flora and normalizing the vaginal biocenosis. It has been proven that treatment of BV reduces the risk of contracting an STI, so a number of experts advocate antibacterial therapy in women with asymptomatic disease.
Candidiasis
Candidal vaginitis is a common disease in women of reproductive age. There is an asymptomatic carriage of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and a clinically developed disease with specific manifestations. The disease occurs due to hormonal imbalance, defects in general and local immunity, disturbances of the vaginal microflora, due to long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, and psycho-emotional stress. The disease manifests itself with itching and whitish cheesy discharge, which is treated with a single dose of an antifungal drug. In cases of severe candidiasis with frequent relapses, long-term antifungal therapy regimens are used.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea appears as a yellowish-greenish discharge with swelling of the mucous membrane. The cause is diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae. When a smear from the cervical canal reveals more than 15 leukocytes in the field of view, a subsequent in-depth examination for gonococcal and chlamydial infections is a mandatory step. The study is worth conducting, since gonococcal infection causes severe purulent adnexitis, which leads to infertility in the future.
What is a polymorphic rod
Bacteria exist in various forms. Some are round or oval, they are called cocci. Others take on a rod-shaped form, these are bacilli. Still others exist in the form of a spiral, called spirochetes. Bacterial forms are not limited to just these 3 types. Some of them are polymorphic, meaning they exist in different states.
Such bacteria do not have a specific shape or differ from the three known stereotypical forms. Polymorphic bacteria change to adapt to the human genome. Polymorphic rod, which is often found in women's smears, refers to bacilli that change their shape and have different types.
Pathogenic effects of polymorphic rod
The normal microflora of the female body is a qualitative and quantitative ratio of microbial populations that have colonized a certain body system. Colonies of bacteria are involved in maintaining health. When pathogenic microorganisms begin to predominate, the microflora balance is disrupted. Among the pathogens there are both rod forms and cocci.
The article describes the reasons for the appearance of a polymorphic rod in a smear in women.
A woman's vagina is acidic because it contains a lot of lactic acid, produced under the influence of estrogen. About 97% of the bacteria inhabiting the microflora belong to lactic acid bacteria. At the same time, the microflora contains opportunistic organisms, cocci, rods, and bacilli.
Their number should not normally exceed 10.3 CFU/ml. Exceeding this parameter indicates the onset of a bacterial disease. The increase in cocci is accompanied by the growth of another conditionally pathogenic form - polymorphic bacillus.
Reasons for the appearance of a polymorphic rod
A polymorphic rod in a smear in women is a microscopic organism that creates a pathogenic environment in the vagina, cervix or cervical canal. Vaginal microflora refers to the cohabitation of different bacteria.
Some of them are present in the body normally, without causing any consequences. E. coli lives peacefully in the stomach and takes part in the process of food digestion. Likewise in the sexual sphere, many bacteria work for the benefit of health.
But this division is conditional; the microflora environment is divided into 3 categories:
- Normal microflora. Beneficial bacteria that perform a protective function predominate in the majority.
- Conditionally pathogenic. A certain number of bacteria present in the microflora do not bring any benefit to the body, but do not cause harm either. All this happens for the time being until a failure occurs in the system caused by stress, hypothermia, which weakens the immune system. Then the opportunistic forms of bacteria unite and begin to secrete waste products that inhibit the beneficial bacteria inhabiting the microflora. The functioning of the body is disrupted, and illness occurs.
- Pathogenic microflora. It is dominated by microorganisms that have a negative effect on humans. If the body is stable and the immune system is increased, then they do not cause much harm. But any failure increases the chances of getting an infectious disease, bacterial infection.
Dederlein's bacilli, which maintain an acidic environment, are responsible for the purity of the microflora.
They also take part in the creation of antibodies to various infections, maintain vaginal moisture, and inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic microbes within acceptable limits. The polymorphic bacillus is a pathogenic microbe that can attack a person at any time, affecting the cervix and cervical canal.
Dederlein's rods act as an antagonist to this microbe, preventing polymorphs from multiplying excessively. When the number of Dederlein bacilli decreases, their place is taken by a polymorphic bacilli, which indicates the formation of dysbacteriosis.
The number of leukocytes in the blood begins to increase, which are responsible for fighting bad microbes. Their increased reproduction signals that an infectious or inflammatory process has begun in the body.
Reasons why the number of polymorphs in the microflora increases:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- refusal of barrier contraceptives;
- frequent and unsystematic douching;
- uncontrolled long-term use of antibiotic drugs;
- hormonal changes during menopause, during pregnancy, and with menstrual irregularities;
- diseases caused by infections;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids that weaken the immune system;
- damage to the vaginal mucosa.
Diagnosis of polymorphic rod
A polymorphic rod in a woman’s smear is determined using bacteriological analysis. To carry out diagnostics, a smear is taken for microflora. Using a smear, it is difficult to determine the specific type of bacteria that predominates in the microflora.
For this purpose, bacteriological culture is carried out, on the basis of which not only the type of bacteria that has settled is determined, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics is determined. The results obtained enable the doctor to diagnose gynecological diseases: colpitis, vaginosis. Often a large accumulation of polymorphic rods indicates the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
The influence of microbes on microflora:
| State of microflora | Violations | Forms of disorders |
| Normal | Absence of negative microflora, predominance of lactobacilli | Normal state of the vaginal environment |
| Intermediate state | The number of lactobacilli is moderate, the presence of rods, gram-positive and gram-negative cocci. There are leukocytes and macrophages. | Normal condition in healthy women, teenage girls, without objective complaints. |
| Vaginal dysbiosis | There are few or no lactobacilli. Numerous colony of polymorphic rods and cocci. The white blood cell count fluctuates. |
Bacterial vaginosis
During pregnancy, the predominance of polymorphic rods negatively affects the health of the woman and the unborn child. Tests can be taken at clinics, where the cost of a smear does not exceed 300 rubles. Bacteriological culture costs from 600 to 800 rubles.
Coccal flora
Rods in a smear can be represented by small forms - cocci. These forms are separated into a separate group - coccal flora. Studying these rods under a microscope made it possible to name them that way. They have a cocoon shape, round in shape resembling a spiral or rod.
Their detection in a smear can mean both normal and pathological - it all depends on the number of coccal representatives and their type.
There are two types of cocci: gram-positive (Gr+) and gram-negative (Gr-). They are named after the scientist Gram, who was the first to study the possibility of identifying these bacteria by staining them.
- gram-positive cocci are a group of bacteria belonging to the opportunistic flora. This includes streptococci, enterococci and some others. The same Doderlein stick is included in this group. It is important to know that all these cocci can be present in certain quantities in a smear of a healthy woman. An excess of pathogenic forms indicates the need for treatment;
- Gram-negative cocci are pathogenic flora found only in a smear of a woman with pathologies and diseases. These include gonococcus, Escherichia coli and some others.
An important point in the treatment of any disease caused by an excess of coccal flora is the determination of positivity or negativity (Gr+ or Gr-).
Gram-positive forms respond better to treatment and the process goes faster than when fighting gram-negative pathogens. It's all about the permeability of the bacterial wall, which among the “negative heroes” is more resistant to internal penetration.
Prevention of the appearance of polymorphic rods
To avoid microflora disorder:
- You should not use scented intimate hygiene products or antibacterial soap.
- Try to change pads and tampons as often as possible, and do not leave them in the vagina all day.
- Sex should be protected, reduce the number of casual sexual contacts.
- When purchasing underwear, give preference to cotton products to allow air access to the external genitalia.
- Include fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet. Limit sweets and sugar, because they do not contribute to the formation of normal vaginal microflora that is resistant to the development of vaginitis.
Prevention
To prevent aerobic vaginitis, as well as to prevent its relapses, gynecologists recommend that every woman:
- adhere to the rules of a healthy diet, constantly consume fermented milk products;
- reduce the amount of foods high in sugar you eat;
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics;
- use condoms during casual sexual intercourse, as well as when changing a permanent partner;
- boost immunity;
- treat any viral and infectious diseases, especially if they cause genital diseases.
By following these simple rules, many women will be able to avoid not only the occurrence and, as a consequence, treatment of vaginitis, but also many unpleasant diseases of the female genital area.
A flora smear is aimed at identifying infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital area (cervical canal, vagina and urethra). Microscopy of a smear from the surface of the mucosa allows you to determine the number of epithelial cells and inflammatory cells (leukocytes), the type and number of microorganisms present (bacteria, protozoa or fungi).
A smear is taken in the mirrors using a spoon, brush or a special bacteriological loop, after which the material is distributed in a thin layer on a glass slide and dried at room temperature. It is mandatory to mark the place where the smear is taken. The resulting preparation is stained and examined under a microscope.
The most informative smear is when:
- the material is collected during the active phase of the disease.
- no local or general treatment was carried out before taking the material, or 4 weeks after the end of taking antibacterial drugs orally, or 10 days after local treatment.
- The material is collected in the middle of the menstrual cycle (in the absence of obvious clinical manifestations of the disease) or in the active phase of the disease in the absence of bleeding.
- during the day before the procedure there was no sexual intercourse, no use of any vaginal means, including douching, vaginal douches, tampons.
- toilet of the external genitalia on the eve of the study was carried out without the use of soap and gels.
- It is not recommended to take a bath the day before collecting the material.
- It is not advisable to conduct a transvaginal ultrasound or colposcopy one day before the smear.
- It is also not recommended to urinate 2 hours before the smear.
It is not prohibited to take a smear for flora on other days, however, you need to understand that the diagnostic significance will be low due to the large number of false positive results.
In any case, the conclusion about the presence of any disease should be based on two criteria - clinical manifestations and smear results.
Flora smear is normal
The normal microflora of the vagina is very diverse and contains a large number of bacteria. In women of reproductive age, the dominant microorganism is lactobacilli , however, in addition to them, ureaplasma (in 80%), gardnerella (in 45%), candida (in 30%) and mycoplasma (in 15%) are found - these are opportunistic microorganisms that, when reduced, immunity can multiply excessively and lead to inflammation and require appropriate treatment. In the absence of clinical manifestations, such as pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor or itching in the perineal area, the detection of these microorganisms should not be interpreted as pathology.
Chlamydia and viruses can also be found in women who do not show any complaints, however, these agents are not part of the normal microflora and their presence indicates a hidden infection.
The vaginal microflora is dynamic and can change on different days of the menstrual cycle. There are periods when lactobacillary flora dominates and days when gardnerella predominates. A significant imbalance of microorganisms, accompanied by clinical symptoms, underlies conditions such as bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis. These conditions can often recur with even the slightest change in the woman's general health or the use of antibiotics. Women with a family predisposition are especially affected.
A flora smear (general smear) is the first step in assessing the infectious and inflammatory process of the urogenital area. It allows you to quickly determine one of the following conditions:
- Norm
- Vaginal microflora disorder - bacterial vaginosis
- Infection caused by fungi of the genus Candida - thrush
- Sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea and trichomoniasis
- Nonspecific (bacterial) vulvovaginitis - leukocytes in a smear in large numbers without detectable specific microbial flora. If a large number of leukocytes are detected in the smear and there is a clinical picture of inflammation, it is possible to prescribe a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys up to 90% of bacteria. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, to determine the infectious agent, it is necessary to carry out bacteriological culture, since it is microscopically impossible to determine the exact type of microorganism that caused the inflammation. Bacterial culture is usually accompanied by determination of sensitivity to antibiotics, which allows you to select the optimal drug and achieve a good treatment effect.
Treatment methods for polymorphic rod
To correct the microflora, the root cause of dysbiosis should be established. If pregnancy or gynecological surgery is not planned, then you can do without medications, waiting until the balance is restored on its own. If aggravated symptoms are present, drug treatment is required.
A polymorphic bacillus that has multiplied in the microflora, as evidenced by a smear taken from a woman, is treated in 2 stages.
Initially, it is assumed that antibacterial and antiseptic drugs are used that suppress the proliferation of pathogens. At stage 2, drugs are used that restore the microflora. Between stages 1 and 2 of treatment, medications are prescribed that destroy the biofilm that pathogens create to reduce the activity of cells that protect the body.
Therapy with antibacterial drugs has side effects in the form of death of natural flora and is not always effective, due to the fact that pathogenic organisms take various forms. Many bacteria have increased resistance to many drugs.
Medications
Antibacterial drugs:
- Metronidazole. The drug is taken after meals, twice a day, 2 tablets. Treatment is carried out for 10 days. It is recommended to use intravaginal suppositories simultaneously with the tablets. Use a suppository in the morning and evening. Candle therapy is carried out at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Price of the drug: 10–30 rubles.
- Atrican. The tablets are taken orally with meals, 1 capsule 2 times a day, morning and evening. Treatment lasts 4 days. It is not recommended to increase doses. The price of the drug is 2—–300 rubles.
- Ornidazole. Vaginal tablets are used 1 pc. daily before bed, for 5 days, for trichomoniasis. To treat vaginitis, 1 piece is inserted deep into the vagina. before bedtime, for 7 days. The drug costs from 70 rubles.
- Clindamycin. It is used in the form of suppositories, the course of treatment is 3 days, suppositories are administered 1 pc. for the night. The drug has many side effects; use must be discussed with your doctor. The price of the drug is from 300 to 500 rubles.
Medicines based on lactobacilli improve the effect of antibacterial therapy:
- Vagilak. Take 1 capsule per day with meals. Improvement occurs after 2 weeks.
- Lactozhinal. For therapeutic purposes, it is used for 7 days, 1 vaginal suppository 2 times a day. For prevention, take 1 suppository once a day.
- Gynoflor. The drug is used during menopause, 1-2 tablets intravaginally, for 12 days.
- Trioginal. Take 1 capsule intravaginally in the morning and evening for 2 weeks.
A drug that destroys bacterial biofilm:
- Vaginorm-S. Vaginal tablets, taken daily, 1 piece, for two weeks.
Other methods
Treatment involves the use of biological products that restore the biocenosis of the vaginal microflora.
These are dental preparations:
Traditional methods
A polymorphic bacillus in a smear in women, discovered during a visit to the doctor, may be a sign of vaginal dysbiosis, which can be treated with home remedies.
Treatment with tampons:
- It is good to moisten the tampon in natural milk or yogurt.
- Insert it into the vagina, pushing it as far as possible and leave it for several hours.
- For moistening, you can prepare a mixture consisting of milk and turmeric powder at the rate of 1 tsp. powder per 200 ml of warm milk.
- Soak the tampon in a solution consisting of 3% hydrogen peroxide diluted in equal quantities with water. The tampon is inserted into the vagina for 30 minutes.
- Coconut oil has preventive and antibacterial properties. You can also moisten a tampon with it for a hygienic procedure and leave it in the vagina for 2 hours.
Apple cider vinegar is a good pH restorer. You can add it to a warm bath and sit in it for 30 minutes.
Herbs with medicinal properties:
Herbal infusions are used for douching, lotions, and baths.
Possible complications
The formation of large colonies of pathogenic bacteria in the vagina threatens inflammation of the vaginal walls and cervix. Over time, bacteria will penetrate into the uterus itself, which will lead to the development of endometritis and adnexitis. Inflammation can affect the urethra and bladder.
The accumulation of bacteria, the body’s reduced readiness to resist, leads to sexually transmitted infections: herpes virus, gonococci, chlamydia.
Disruption of the normal microflora in women, one of the reasons for which is a polymorphic bacillus found in a smear, is not a harmless disease at all. You should not put off visiting a doctor, because vaginal dysbiosis leads to serious problems.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Analysis procedure
Every woman has had a smear test for bacillary flora at least once, but not everyone knows what it is.
This test is a simple and painless procedure. The gynecologist takes samples for examination during a gynecological examination with a special spatula or phytobrush and places them in a special container.
Typically, a smear is taken from the vaginal walls and cervix. Biological material is collected in a gynecological chair.
Video about the causes and methods of treatment of polymorphic bacillus in women
About microflora disorders:
How to decipher the results of a smear on the flora:
At the first symptoms, you need to go to the doctor and get tests done. I once delayed it so much, the treatment was long and expensive. Any problem must be solved in the early stages by listening to your body.
As a result of diagnostic procedures, rod flora is often detected in a smear - what it is can be understood by specifying the type of microorganisms identified.
There are several types of sticks: some are a mandatory option for the norm, while others warn of the development of pathological processes.
Rod flora in a smear
Special laboratory tests for flora are carried out to study the conditions of the microflora of the genital organs in women and men.
A flora smear is one of the most common and diagnostically effective types of research in gynecology and urology.
During the procedure of taking an analysis, biological material is taken from the patient’s genitals with special instruments for examination under a microscope.
The results of the smear become known within a couple of days. Based on the analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of infection (or traces thereof) in the genital organs of men and women, inflammatory processes, pathological imbalance of microflora and other deviations from the norm.
Decoding the results
After taking the material in the laboratory, it is examined and examined. Below there is a table that contains normal indicators and deviations.
A specialist can confirm that the data obtained are considered normal in the following situations:
- The resulting material reveals cells with an epithelial structure. They have a cylindrical single-layer variety;
- When taking a smear from the transition area, the presence of cellular structures from stratified epithelial tissue will be the norm.
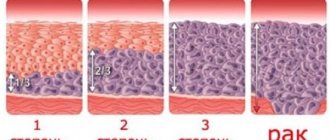
According to the results, 5 classes are distinguished:
- Indicators of cellular structures correspond to physiological norms. No violation is detected;
- The presence of small changes in cells that can be associated with cervicitis and colpitis;
- Single cellular structures with an altered nucleus or contents from the cytoplasm are identified;
- There are individual cells with an oncological structure;
- The presence of a large number of malignant cellular structures.
When is rod flora detected in a smear?
In a smear, women will normally always have rod flora, because it is the presence of Dederlein rods in large quantities that contributes to the health of the female body.
There is a special classification of smear purity for vaginal microflora:
- The first degree of purity indicates the woman’s complete health. The analysis reveals a large number of lactobacilli - normal vaginal microflora;
- the second degree implies a high content of Dederlein bacilli and allows a small number of leukocytes in the smear - no more than 10 per 1 cm 2 in the material being studied. This is also one of the norm options. In pregnant women, the white blood cell count may be slightly higher;
- with the third degree of purity of the smear, pathological changes in the vaginal microflora are detected - a very small number of gram-positive beneficial bacilli are observed, per 1 cm 2 there are from 10 to 30 leukocytes, and the flora is mixed, may contain cocci (spherical bacteria), and large and small bacilli ;
- The fourth degree of purity of the analysis is characterized by a large number of leukocytes (representing the main composition of the smear), the absence of normal flora, mucus, rods and cocci in the smear.
In women with regular sexual intercourse, tests may show mixed flora at the end or beginning of the menstrual cycle, during decreased estrogen production or under the influence of ovarian pathologies (with severe hyperfunction).
Mixed flora with rods and cocci can be a sign of gynecological diseases or sexually acquired infections, because the development of opportunistic microflora is often accompanied by other, more serious diseases.
In little girls and women during menopause, due to the characteristics of hormonal levels, analysis may also show a mixed flora.
Gram rods in a smear in women: the norm, what is it?
In diseases of the reproductive system in women, gram bacilli are usually detected in a smear.
Gynecologists strongly recommend that all women undergo a smear test for flora in order to prevent various diseases.
When a woman complains of discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen, a smear is taken first. It is very important to decipher the results obtained in a timely and correct manner.
Features of microflora
A significant number of different microorganisms constantly live in the human body. Their presence ensures the normal functioning of all systems and organs.
Microorganisms, such as bacilli and cocci, are found in the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, intestines, and in women also in the vagina.
In a normal state, when the immune system performs its functions in full, a balance is maintained between beneficial and pathogenic bacilli.
The cells of the mucous membrane contain glycogen, which serves as food for bacteria. Depending on the form, microorganisms are defined as rods and cocci, having a positive or negative gram reaction.
In modern gynecology, a smear is considered one of the methods for identifying the pathology of the female reproductive system. The microflora of the female genital organ includes mainly lactobacilli or gram bacilli.
All rods living in the vagina of women are divided into the following groups:
- obligate;
- transient;
- optional.
Obligate rods include those that are constantly, in the required quantity, present in the mucous membrane of the female genital organ. The sticks create a protective barrier that prevents the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
Transient cocci and bacilli include those that accidentally enter the vaginal mucosa. Among such representatives there may be beneficial, neutral, and pathogenic species.
Gram rods, which are examined after taking a smear, carry information about the properties of the microorganism.
Facultative microbes are not found in all women and this is a kind of norm. The qualitative composition of microflora depends on several factors.
Changes occur during menstruation, with age and with diseases of the genital area. There is a clear dependence on climate, intimate hygiene and the state of immunity.
The physiology of the female reproductive system is designed in such a way that lactobacilli and bifidobacteria mainly live and develop on the walls of the vagina.
In healthy women, these rods form an acidic environment in the vagina. In an acidified environment, the reproduction and development of other bacteria becomes impossible.
Thanks to this protective mechanism, a healthy environment is maintained in the vagina. An important feature of the rods is the ability to firmly attach to the mucous membrane, creating a reliable barrier to pathogenic bacteria.
A smear, when taken from women for preventive purposes, almost always shows a positive gram reaction.
READ Normal columnar epithelium in a smear
When the normal state of microflora is disrupted, vaginal dysbiosis appears and develops.
Pathogenic bacilli and cocci are found in significant quantities. Accordingly, gram rods in the smear will have a negative sign.
This condition is usually caused by hormonal imbalance, long-term treatment with antibiotics, infectious infections and poor hygiene.
Dysbacteriosis often develops when the immune system is weakened. Treatment is carried out individually and only after the gynecologist takes a smear and makes the correct diagnosis.
Microflora smear
According to the current recommendations of gynecologists, a woman needs to visit the examination room at least once every six months.
This mode allows for timely detection of emerging abnormalities and diseases that may occur in women in the genitourinary system.
A gynecological smear is considered one of the simple and effective ways to obtain initial biological material for research.
Taking the analysis takes a minimum of time and does not pose any health hazard. The procedure is completely painless.
A smear is taken even from women during pregnancy. The analysis data provides the doctor with the necessary amount of information for a preliminary diagnosis.
Gynecologists recommend that women planning a pregnancy, or those who have undergone long-term treatment with strong antibiotic-based drugs, do a smear on the flora.
The procedure is mandatory if women experience the following symptoms:
- periodic abdominal pain;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor and unusual color;
- regular itching in the genital area.
Gram rods in any smear carry specific information about the quality of the microflora. At the same time, the analysis allows us to detect the presence of diseases transmitted through sexual contact.
The normal content of certain microorganisms was calculated experimentally. When the bacterial balance is maintained, women do not experience any unpleasant and, especially, painful sensations.
To determine the true value of gram rods in a smear, the patient needs to properly prepare for the test.
In order for the results of the analysis to be reliable, one day before the scheduled date you must abstain from sexual intercourse, do not douche and do not use any vaginal medications. Experts recommend not urinating for 2 hours before a smear.
A smear for analysis is taken from three areas - the vagina, urethra, and cervix.
In the results decoding form this is presented as follows:
- V – vagina, vagina;
- C – cervix, cervix;
- U – urethra, urethra.
According to the current rules, analysis results are issued for each point separately. Samples of the mucous membrane, which also contain gram bacilli, are taken using a special spatula.
The smear is placed on special devices available in the laboratory and sent for examination. A woman can receive results the next day.
Processing of received data
The information obtained as a result of laboratory testing is deciphered by a gynecologist. In this context, it should be noted that the division of rods into gram positive and gram negative has been carried out since the biologist with the surname Gram made his discovery.
The meaning of the discovery is that different microorganisms turn different colors when exposed to the same reagent.
Gram negative rods are highly resistant to antibiotics. This property is explained by their thick shell. To neutralize such bacteria, stronger drugs must be used.
The accuracy of the results depends on proper preparation for the smear, and the accuracy of the diagnosis is determined by the qualifications of the attending physician.
The following cells may be present in the test material:
- gram positive rods;
- fungi;
- leukocytes;
- squamous epithelium.
Gram positive rods form the basis of healthy microflora. When a significant concentration of such rods is present in a smear, this is normal.
If the concentration of rods decreases, then this fact is assessed as the development of bacterial vaginosis. The presence of fungi or their spores is grounds to suspect the first stage of thrush.
When there are leukocytes in the smear, in addition to gram bacilli, there is nothing wrong with that. Leukocytes are an element of the immune system and are necessary in the body to destroy pathogenic bacteria.
However, if the number of cells is more than 30 in the field of view, then there is a high probability of an inflammatory process occurring in the vagina.
The same pathology is evidenced by the high content of squamous epithelium and negative gram rods in the smear.
Epithelial cells line the inner surface of the vagina. When vaginitis develops, the immune system stimulates increased production of squamous epithelium.
Vaginal cleanliness
Determining the concentration of gram rods in a smear is very important. If the current norm is not violated, then the woman has no reason for serious concern.
If there are deviations that are recorded in the analysis results, the gynecologist assesses the current situation and makes an appropriate diagnosis.
Bacterial vaginosis is most often diagnosed. The insidiousness of this disease is that it occurs without visible symptoms. Vaginosis is sometimes mistaken for thrush.
Every woman needs to know that these are two completely different diseases: both the treatment methods and the drugs used are different.
If bacterial vaginosis is not treated promptly, the disease becomes chronic. Ultimately, this leads to serious complications, including infertility.
The appearance of vaginosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- white or light gray vaginal discharge;
- constant itching in the genitals;
- pain during urination and sexual intercourse.
The presence of gram rods and other bacteria in the smear serves as a guideline when prescribing a course of treatment for bacterial pathologies. Based on the data obtained, the specialist determines the level of vaginal cleanliness.
The first level of purity is characterized by an optimal bacterial balance. The second level is characterized by the presence of not only gram rods, but also coccal organisms and yeast fungi.
READ What is a sign of coccobacillary flora in a smear?
:
At the third level, the number of leukocytes is increased, while the number of gram rods is minimal. High concentration of pathogenic bacteria.
At the fourth level there are a lot of leukocytes, and the entire microflora is represented by pathogenic bacteria. In essence, this is an acute inflammatory process.
In such a situation, immediate treatment is required, otherwise the woman’s health is in serious danger.
Additional types of research
In practice, it often happens that a smear for microflora shows a normal result, but women exhibit certain symptoms that cannot be ignored.
Despite the fact that the norm of gram rods is observed, representatives of pathogenic microflora are present in the vagina.
The reason for this condition is that some microbes, such as chlamydia, cannot be seen under a microscope due to their small size.
To detect such microorganisms, it is necessary to use more sensitive research methods. For this purpose, a biochemical blood test is performed.
When examining a smear for the presence of gram bacilli and other bacteria, bacteriological culture is performed. Using this procedure, the main causative agent of the infection and its concentration in the vagina are determined.
Bacteriological culture is mandatory:
- when registering all pregnant women;
- for inflammation and microflora disorders;
- if a gonococcal infection is suspected.
It should be noted that sowing is also carried out after completion of a certain course of treatment in the case where antibiotic-based drugs were used. As a rule, the study is scheduled a week after completion of treatment.
Simultaneously with bacteriological culture of the smear on gram rods, the sensitivity of microorganisms to the effects of antibiotics is determined.
Today, the attending physician has a large range of antibiotic drugs at his disposal.
Pathogenic bacilli that settle in the vagina in women have different susceptibility to the effects of these drugs.
:
Medical practice shows that treatment with antibiotics of a certain group does not always lead to positive results. This happens because the drug was chosen without taking into account the characteristics of the vaginal microflora.
The presence of gram bacilli in a smear in women does not always indicate the absence of pathology. A large number of pathogenic cocci and bacilli have the ability to mimic and do not indicate their presence in a certain environment for a long time.
Specialists have been well aware of these features for a long time. The more insidious the pathogenic bacillus, the more accurate the diagnosis and the more radical the treatment.
To avoid serious troubles, women at any age must strictly observe the rules of intimate hygiene, refrain from casual sexual contact, periodically take a smear test and eat right.
Are you here:
26671 6 (2 2,50 out of 5)
Source: https://moydiagnos.ru/issledovaniya/mazok/gram-palochki.html
Features of gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis (unlike diseases such as trichomoniasis and gonorrhea) is a pathology of a non-venereal nature. As a rule, the root causes of the development of the disease are not related to the sex life of patients.
Thus, gardenelosis often occurs even in people who are not sexually active at all. The key factors that trigger the pathological process can be even ordinary stress, ARVI, chronic lack of sleep and an unbalanced diet.
The diagnosis of gardnerellosis is usually made in men. In women, the disease is diagnosed as bacterial vaginosis.
The gardnerella bacillus creates an environment favorable for the development of chlamydia, the growth of gonococci and trichomonas.
With the development of gardnerellosis, normal aerobic microflora can gradually be completely replaced by anaerobic organisms, which is accompanied by vivid clinical symptoms.
Like any opportunistic microflora, Gardnerella bacilli can live in the body in small quantities without provoking pathological changes.
In fact, it stimulates the active reproduction of Gardnerella:
- reduction in the amount of normal microflora that perform protective functions;
- general decrease in the functioning of the immune system;
- change in acidity level.
In men, this disease can occur only as a result of internal problems, including due to neglect of personal hygiene rules, but often patients, ignoring the minor discomfort that develops as a result of the onset of the pathology, infect women.
In women, bacterial vaginitis occurs both due to internal factors and as a result of transmission of active pathogenic microorganisms from a sexual partner. A man cannot become infected with gardnerellosis from a woman.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis include:
- sensations of itching in the genital area and burning sensation when emptying the bladder;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- copious gray mucus discharged from the urethra and having a strong fishy odor.
The burning sensation occurs due to the fact that, under the influence of opportunistic microflora, the urethral mucosa is damaged, and under the influence of urine, pain and pain appear.
In women, gardnerellosis is usually more severe than in men, whose symptoms are often intermittent in nature with declines and peaks of exacerbations.
Infection of a pregnant woman is dangerous because the pathology can affect the intrauterine development of the fetus.
The disease can be avoided by maintaining a high level of general and local immunity, following the rules of hygiene and monitoring your health.
Men and women should periodically undergo preventive examinations, taking smears for microflora.
It is better to responsibly treat gardnerellosis once under the guidance of a specialist than to periodically return to relapses of the pathology, which is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and creates favorable conditions for the development of other diseases.
A woman who cares about her health should visit a gynecologist at least once a year, and ideally every three months. During the examination, the doctor must take material for examination from the cervical canal, cervix and vagina in order to determine the level of cleanliness of the vagina and identify the disease in time. Normally, the microbial flora is rod-shaped or mixed, where the bulk of the bacilli present are beneficial lactobacilli, which look like rods with a thick wall and are of the same size.
Causes
Aerobic vaginitis occurs in women as a result of a decrease in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina and the colonization of its mucous membrane by microorganisms. Aerobic vaginitis is most often detected in young girls and women during menopause. This is explained primarily by the low amount of the hormone estrogen in the blood during these periods of life.
Most often, the causative agents of this disease are:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- streptococci.
These microorganisms normally live in small numbers on the external part of the genital organs or in the intestines. Therefore, the disease often occurs due to poor hygiene or after unprotected anal-vaginal sexual contact. In the second case, after the bacteria enter the vagina from the intestines, all favorable conditions arise for their further reproduction and progression of the disease.
In addition to estrogen deficiency, the following factors can be identified that influence changes in the vaginal microflora and the appearance of the inflammatory process:
- endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs, oral contraceptives or antidepressants;
- the use of cytostatic drugs in the treatment of cancer;
- a decrease in the body’s defenses and the body’s inability to fight pathogenic microflora;
- promiscuity;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the genital organs;
- wearing synthetic underwear;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys or bladder;
- performing hygiene procedures too frequently.
What does a smear test for flora show?
A smear is taken for analysis using a disposable special spatula. The resulting scrapings are applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory, where they are stained with the desired dye, dried, and then examined under a microscope. This is a microbiological analytical method.
It allows you to see:
- in a woman’s smear there is rod flora , which means the presence of lactobacilli, gram-positive bacilli that maintain an acidic environment and suppress the proliferation of harmful bacteria;
- squamous epithelium, which lines the mucous membranes, and its amount varies depending on the day of the menstrual cycle;
- leukocytes involved in the destruction of pathogenic microbes;
- mucus is observed as a product of the glands, it is necessary to maintain normal humidity;
- the appearance of polymorphic rod flora ; we will consider what this means for the body below.
The smear is analyzed in the laboratory under a microscope using special dyes
Microflora research
A smear for the bacillary flora is periodically taken from women for preventive purposes.
If there are no health complaints, doctors perform a smear once every three months during a routine gynecological examination. In this case, a smear is taken from the vagina and cervix.
More often, a smear is prescribed if the patient has complaints of unpleasant nagging pain in the lower abdomen, itching sensations in the genitals, pain during intercourse, or vaginal discharge with an unusual consistency and unpleasant odor.
An unscheduled smear for bacillary flora is prescribed if pregnancy is planned.
The test is considered safe, so it is also performed on pregnant women for additional health monitoring. During pregnancy, a smear is done at least three times.
Since the bacillary microflora of the vagina and uterus changes significantly during long-term use of antibiotics and other potent drugs, it is advisable to conduct research at the end of a long course of treatment.
A study of bacillary microflora must also be carried out if a woman has a new sexual partner, with whom intimate life is supposed to be open. Tests are prescribed after any unprotected sexual intercourse.
To prepare for a smear, you need to follow a number of recommendations. 3-5 days before the study you should abstain from any sexual relations.
The analysis is carried out no earlier than three days after a transvaginal ultrasound examination and examination by a gynecologist.
The analysis is not carried out during menstruation, as well as during an acute form of an infectious disease. A couple of days before the smear, it is better to stop using topical contraceptives, lubricants, douching and treating the genitals with antiseptic drugs.
On the day of the bacillary microflora study, you should not wash with soap or intimate gels.
Sometimes it is necessary to check the concentration of certain bacteria on a specific day of the menstrual cycle.
To determine the date of menstruation and ovulation, it is recommended to use special calendars or applications on your mobile phone.
If a woman can provide the doctor with a menstrual schedule several months in advance, a smear test will be scheduled on a suitable day.
Specific recommendations for preparing for a smear for bacillary microflora should be obtained from a gynecologist or from the laboratory where the diagnosis will be made.
Commercial medical centers usually provide booklets that contain all the necessary information to prepare for a specific test.
Polymorphic rod flora
The group of polymorphic rod flora includes bacilli that have different sizes and shapes of rods that differ in thickness from useful samples. Such microbes are much smaller and are called gram-negative.
This provokes the occurrence of diseases, from dysbiosis to inflammatory and infectious processes.
Symptoms
Polymorphic rod flora found in a smear in large quantities is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the cervix and cervical canal. Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- there is a large amount of discharge of a light, gray or greenish color, sometimes even purulent;
- an unpleasant sour smell appears;
- worries about itching and discomfort;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- unpleasant sensation during bowel movements;
- pain in the lower abdomen and perineum.
Self-medication mistakes
Very often, women mistake the above signs for thrush and begin to treat themselves, driving the situation into a dead end. This absolutely cannot be done. If the slightest deviations in the functioning of the reproductive system appear, you need to visit an antenatal clinic to establish the cause and properly get rid of it.
The need for bacterioscopy
Representatives of the polymorphic rod flora can settle on the walls of the vagina in the form of a white coating, which is detected by the gynecologist during examination. It is difficult to determine exactly what kind of bacillus it is, therefore, as a rule, bacterioscopy is prescribed. After collection, the test material is placed in a special environment where microbes germinate. This helps to identify all their varieties and identify not only the type of pathogen, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics that can destroy it.
Additional diagnostics
The main way to confirm excess coccobacillary flora is to take a smear for laboratory testing .
A smear is taken from the vagina and cervix. This is necessary to identify the degree of activity of the pathology.
Additional diagnostic methods are used:
- colposcopy for the purpose of diagnostic examination of the vulva, vagina, and its walls to identify changes in the mucosa;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs to identify the condition of the inner layer of the uterus;
- PCR diagnostics of the infectious agent;
- general blood test as an indicator of general condition.
The results of all diagnostic procedures are brought together and analyzed, then a diagnosis is made indicating the cause of the disease .
What can a low number of leukocytes in a woman’s blood mean? Our article will answer the question.
Cutting pain in the left lower abdomen in women - what does it signal? Find out in this publication.
If a woman has pain in the lower abdomen on the right, what are the possible causes? Read in this material.
State of the flora
In practice, the most often used is to evaluate the analytical results of the material under study microbiologically, according to which the following stages of purity are distinguished:
- Grade 1 characterizes a completely healthy woman, when rod flora is visually detected in a smear in large quantities with an admixture of single epithelium and a small amount of mucus;
- Grade 2 is also inherent in healthy women, but here, in addition to the lactobacilli and epithelium present in sufficient quantities, single cocci are added. This situation should not cause concern, since it is considered the norm and is observed in a sufficient number of girls who are sexually active;
- 3rd degree does not have a very favorable picture. The smear is dominated by cocci, a small number of rods, the number of leukocytes increases (more than 10 in the field of view), the performance of the rod flora decreases, what this means is not difficult to guess: an inflammatory process develops;
- Grade 4 is marked by the presence of only cocci, no rods at all, a large amount of cervical epithelium, a growing number of white blood cells, and an increase in discharge. This indicates the occurrence of bacterial colpitis.
In the latter case, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may recommend colposcopy in order to form an opinion about the level of damage to the cervix and cervical canal.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of flora purity
Treatment based on tests
When conducting a smear examination, the tests are sent to the doctor, and after reading the results, he draws a conclusion about the state of the flora and decides whether there is a pathology, which microorganisms are interested in it, and how to bring the lactobacilli to a normal state. In this case, treatment with suppositories or tablets is recommended, and antibiotics are used if necessary.
Rod flora during pregnancy
It is more difficult for a pregnant woman to overcome such a problem. From the moment of conception, hormonal levels change. Its fluctuations lead to changes in the ratio of microflora in the vagina. The environment changes, which makes it possible for the development of bacteria that cause inflammation or some kind of infection.
Good rod flora during pregnancy is the key to the health of the child
Therefore, there is no need to explain what rod flora is in a smear of the expectant mother. This is an indicator of the health of her and the future baby. The first examination of a woman is done when she is registered, and then repeated twice, at 30 and 36-37 weeks. All these measures help to identify and treat pathological processes in a timely manner in order to prevent the child from becoming infected with pathogenic bacilli when passing through the birth canal during birth.
Tips and tricks for maintaining flora
To ensure the reliability of the smear before going to the doctor, there are several points that every woman should take note of:
- three days before visiting the antenatal clinic, abstain from sexual intercourse;
- do not douche;
- Do not get tested during your period.
In order for rod flora to live in large quantities in the vagina, you must adhere to the following rules:
- keep the genitals clean, wash yourself at least once a day;
- use special intimate hygiene products that do not disturb the acidic environment of the vagina;
- douching should only be done as prescribed by a doctor, since it also washes out beneficial microbes;
- do not get carried away with thongs and panty liners;
- when changing partners, use protective equipment;
- establish a regime of work and proper rest;
- strengthen the immune system in all available ways;
- develop a balanced diet;
- Avoid stressful situations whenever possible.
| Vaginitis | An increased number of macrophages, leukocytes is visible, there are gonococci, spores, and mycelium. | Nonspecific or mycotic vaginitis, gonorrhea. |
Treatment
Before prescribing treatment, the gynecologist may prescribe tests for STDs to the patient.
Aerobic vaginitis requires the following treatment, regardless of what stage it is at:
- the use of broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. They can be used either orally or topically;
- therapy for diseases and pathological conditions that cause aerobic vaginitis (hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders);
- abstaining from sexual intercourse until the end of treatment or using condoms;
- examination of the woman’s sexual partner and, if necessary, treatment (aerobic vaginitis is a microflora disorder, not an STI, so if the partner does not have signs of inflammation in the urethra or bladder, it does not need to be treated).
For a speedy recovery, patients are also recommended to undergo sanitation (irrigation of the vagina and treatment of the labia with antiseptic solutions). At the moment, in the treatment of aerobic vaginitis, the use of drugs based on chlorhexidine brings good results. For ease of use, they are usually available in the form of vaginal suppositories. Among their main advantages are:
- no negative impact on healthy mucous membranes. In addition, these drugs quickly cleanse the vagina of pathological discharge and eliminate swelling;
- The duration of treatment always depends on the form of the disease. Thus, eliminating aerobic vaginitis in a chronic form requires more time than treating the disease in an acute form. In the second case, the duration of therapy is usually no more than 7-10 days.