How often do you visit a gynecologist? Do you perform the required range of tests? These questions should be addressed to every woman on earth, because they make you think about how attentive ladies are to their health. A significant laboratory examination is microflora analysis. To understand its feasibility, let's figure out what a smear shows on the flora in women and why it is needed.
This type of gynecological examination belongs to the bacterioscopic variety, which allows the assessment of biological material. Among its obvious advantages are the speed of execution and the accessibility of the method itself. It is performed simply and painlessly: the doctor collects the discharged substance from the mucous membrane.
Next, the biomaterial is stained, treated with a certain solution (KOH or saline), studied in detail under a microscope, and the data is deciphered by a specialist.
Discovery of the method and its importance for microbiological science
The first scientist to suggest that some methods previously used only in botany could be used in microbiology was Robert Koch.
In 1884, Christian Gram, a Danish biologist specializing in tissue staining, first tried the method of differentiating staining.
The discovery made it possible to divide all existing types of microorganisms into gram-positive and gram-negative, which served as the impetus for a new stage in the development of science in the field of microbiological research. This also made it possible to identify the resistance of pathogenic species to drugs, predict their behavior, and most importantly, develop a new generation of antibiotics that can defeat the disease.
Flora smear in women: interpretation of results
Regular visits to the gynecologist allow you to promptly identify pathologies of the female reproductive system and take the correct therapeutic and preventive measures. It is recommended to visit a doctor once every six months.
During the appointment, the specialist must take a smear from the vagina to examine the microflora.
This is a fairly informative and at the same time simple diagnostic method that allows you to suspect abnormalities in the functioning of the female reproductive system.
Indications for flora smear analysis
It is important to know what can affect the results of the study
Taking a gynecological smear for flora is advisable if women have the following clinical manifestations:
- A change in the normal color and odor of vaginal discharge.
- Pain in the lower abdomen both at rest and during sexual intercourse.
- Burning, itching in the genital area.
In addition, smears on the flora are taken when:
- preventive examinations;
- during pregnancy once every trimester;
- antibiotic therapy to exclude candidiasis.
The attending physician must decipher the smear analysis for flora after receiving the test results from the laboratory.
It should be noted that microflora analysis indicators can change not only due to any pathologies. Fluctuations in values are observed when hormonal levels change during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
In addition, changes in the smear of adult patients can be caused by contraceptive medications, neglect of personal hygiene rules, and sexual activity. Minor fluctuations are also possible depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Important! But the appearance of any pathogenic microorganisms is a signal of the presence of a disease or (more rarely) of carriage. Detection of pathogens requires specific therapeutic measures.
Rules for preparing for research
To obtain reliable results of a smear test for flora, you must adhere to the following restrictions:
- exclude sexual intercourse two days before collecting biomaterial;
- do not use vaginal suppositories, ointments, creams two days before taking a smear;
- do not resort to douching;
- carry out personal hygiene activities while taking a shower, not a bath;
- do not urinate several hours before visiting the doctor.
It is important to strictly adhere to these rules so that the result of a smear on the flora is informative.
Smear procedure
Carrying out the procedure for collecting biomaterial
A smear of women’s flora is taken by a gynecologist at an appointment. In addition, biomaterial can be submitted to private laboratories. The smear taking procedure itself consists of the following steps:
- The woman sits on a gynecological chair.
- For better access to the walls of the vagina and cervix, sterile speculum is inserted.
- Collection of biomaterial from the vaginal wall. The manipulation is painless, but inflammation may cause discomfort.
- The material is applied to the glass slide using line movements and as thinly as possible.
- Fixation of the smear. Required in cases where the smear will be delivered to the laboratory more than 3 hours after collection.
- Delivery of the smear to the laboratory.
- Glass painting. The most commonly used dye is methylene blue.
- Microscopic examination of a smear performed by a clinical laboratory diagnostics physician. The specialist determines elevated leukocytes in the cervical canal by assessing the composition of the flora. Reveals the degree of vaginal cleanliness.
- Sending the results to a gynecologist.
More often, biomaterial is taken from three points:
- flora smear from the cervical canal;
- smear from the vaginal walls;
- smear from the urethra and paraurethral canals.
Due to the anatomical proximity of the listed areas, infectious and inflammatory processes in these areas are often interrelated. To take material from each area, the doctor takes a separate sterile instrument and makes three swabs on separate slides.
After collecting the biomaterial, there is no need for any restrictions for the woman. You can take a bath, swim in ponds, and sexual intercourse is allowed.
Decoding the results obtained
Microscopy of glasses with biomaterial allows you to obtain important data about a woman’s health
To indicate the localization of material collection, the letters of the Latin alphabet are used: V, C and U.
The letter V stands for vagina, C for cervical canal, and U for urethra.
To understand the interpretation of the data obtained during the study, you should understand what microorganisms can be identified when analyzing a smear for flora.
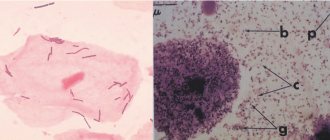
Coccal flora
Coccus microorganisms have a round shape and can be found in smears both normally and pathologically.
Gram staining of the material reveals gram-positive and gram-negative cocci. The appearance of gram + cocci in a smear is acceptable - they can be streptococci and staphylococci.
Gram-negative cocci are often pathogenic - these include gonococci, which cause gonorrhea.
Doderlein sticks
Rod flora in the vagina is the most important indicator of the health of the female reproductive system. Doderdein's bacilli are large, immobile bacilli, which are classified as gram-positive microorganisms. They are necessary to ensure healthy vaginal microflora.
Among the functions of Doderdein rods (or lactobacilli), the following should be highlighted:
- Maintaining an acidic reaction of the environment in the vagina, which is also necessary for correct fertilization: weakened male reproductive cells die, and strong ones can overcome the barrier and fertilize the egg.
- Suppression of pathogen proliferation as a result of activation of macrophages.
- Keeping the vagina clean by releasing hydrogen peroxide.
Normal flora indicators include a large number of Doderdein sticks. A decrease in their number may signal serious problems in women's reproductive health.
Leptothrix
Leptothrix in a smear
Leptothrix is an opportunistic pathogen. It is an anaerobic gram-positive rod. Under microscopy, this microorganism is easy to distinguish - it has the appearance of a thin and long rod in the shape of a hair.
An important feature of Leptothrix is that this microorganism is often detected simultaneously with serious pathogens - chlamydia and trichomonas. If leptothrix is detected when planning pregnancy, treatment is mandatory.
Normal smear test for vaginal microflora
Moderate number of epithelial cells and leukocytes, rod flora – normal indicators
To make it easier to understand the results obtained, you need to know what indicators are considered normal. So, normally, deciphering a smear analysis involves:
- Flat epithelium - up to 15 cells are allowed in one field of view.
An increase in the number of squamous epithelial cells indicates the presence of an inflammatory process, and a decrease indicates a hormonal imbalance. - Leukocytes in the cervical canal - the norm for leukocytes in a smear for flora is considered to be up to 10 in the field of view, in the urethra - up to 5, and in the cervix - up to 30.
- Doderlein bacilli are normally found in large quantities in the smear.
- Mucus in the biomaterial should be present in small quantities.
Detection of Candida fungi, gram-negative cocci, gonococci, small bacilli, and Trichomonas in the material is an indication for additional research (bacteriological analysis and other diagnostic methods) and subsequent complex treatment.
The table below shows the main indicators of a smear on the flora.
Table: What does the result of a smear on flora show?
| Index | Value is normal | Deviations | ||
| Vagina | Cervix | Urethra | ||
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-5 | An increase in the number of leukocytes indicates activation of inflammation. |
| Epithelial cells | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 | When the number increases, inflammation occurs; when the number decreases, hormonal imbalance occurs. |
| Slime | Moderate amount | Moderate amount | An increase in the amount of mucus may be an indirect confirmation of an infectious process. | |
| Microflora | A large number of Doderdein sticks | An imbalance of the flora with the identification of specific pathogens indicates the presence of a corresponding pathology. | ||
| Candida fungi | If detected - candidiasis. | |||
| Trichomonas | If detected - trichomoniasis. | |||
| Gonococci | If detected - gonorrhea. | |||
| Key cells | If detected - bacterial vaginosis. |
Leukocytes in a smear for flora
An important step in gynecological diagnosis is assessing the degree of vaginal cleanliness. There are four possible degrees, the first two of which indicate normality, and the third and fourth confirm the presence of a pathological process.
The characteristics of each degree are presented below:
- Leukocytes and epithelial cells in normal numbers. A large number of Doderlein sticks, small amounts of mucus.
- Leukocytes are within normal limits, a large number of lactobacilli, some coccal flora, possible presence of Candida fungi..
- A lot of mucus and epithelial cells - a lot of leukocytes in a smear for flora. There are few Doderdein rods; a predominance of coccal flora, the presence of fungi, and pathogenic microorganisms are possible.
- The number of leukocytes is greatly increased.
Lack of Doderdein sticks. A large number of epithelial cells and mucus. Detection of pathogenic microorganisms.
The third and fourth degrees of vaginal cleanliness require the appointment of therapeutic measures.
Features of a smear for microflora during pregnancy
During pregnancy, microflora analysis is very important
A smear test for flora is carried out once in each trimester of pregnancy: upon registration, at the thirtieth week and immediately before the expected date of delivery.
The analysis is necessary as a preventive measure to identify pathologies that can complicate the course of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as provoke illness in the child.
Important! The change in flora research indicators in a pregnant woman is explained by hormonal changes - the level of progesterone increases and the level of estrogen decreases.
Indicators of microflora analysis in a pregnant woman differ little from those in a non-pregnant woman. However, there are still differences and you need to know about them:
- Increasing the number of Doderlein sticks. Physiologically, this is necessary to protect against various pathogens and prevent the penetration and development of infection.
- An increase in the number of epithelial cells in the smear.
When pathogens are identified, the doctor prescribes gentle treatment methods, specific ones are selected depending on the trimester and the characteristics of the clinical case. External agents are more often used - ointments, suppositories or tampons.
Cell wall structure
The shell of any bacterium consists of a special substance – murein. Its molecule consists of chains of polysaccharides arranged in parallel. Polysaccharides, in turn, are interconnected by chains of amino acids arranged crosswise.
This connection determines the strength, elasticity of the shell, and its ability to keep its shape. A kind of woven mesh protects the inner layer of the microorganism from the action of destructive factors and prevents water from getting inside. At the same time, the gaps between the chains allow the cell to absorb nutrients, like pores.
In Gram-positive microorganisms, the shell is thicker and stronger, which is due to the inclusion of protein in its composition.
In negative species, the structure of the cell membrane is much more complex, which allows it to be protected from the action of such environments as saliva, gastric juice, and other liquids containing lysozyme, an enzyme with antibacterial properties. On the outside, the thinner shell is surrounded by a film of lipids and polysaccharides - a smooth surface layer.
The essence of the Gram method
The basis of the Gram method is the principle of dividing bacteria into microorganisms with “plus” and “minus” signs according to Gram, based on the different chemical composition of the cell walls of microorganisms.
To determine gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, the drug, applied to the glass in a thin, uniform layer, is first fixed by heating over a burner. Then they are dyed with aniline dye - methyl violet. After which it is fixed with iodine, allowed to dry and washed off with alcohol.
- Gram-positive (Gram+) species acquire a bright blue color.
- Gram-negative (Gram –) bacteria become discolored.
The final step is to stain the preparation with a red contrast dye, which allows you to obtain gram-negative microorganisms of red or pink color. This is due to the fact that the dye cannot penetrate the cell due to its thick outer layer, staining only the surface.
Gram staining. Cocci (spherical) - gram-positive and bacilli (rods) - gram-negative
Dead microbes acquire a brighter color compared to living ones.
conclusions
Every woman realizes that the accuracy and purity of the analysis depends on whether the preparation measures for it were followed. Of course, this type of examination is quite accurate, but laboratory technicians and equipment can also make mistakes.
Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, it may be necessary to retake the analysis (the execution time is determined by the specific method used by the equipment - the calculation of indicators can be done manually, by a laboratory assistant, or using modern computer equipment).
It is important not to neglect such an analysis and carry it out regularly, including as an annual preventive measure, at a local clinic (by registration) or a private medical center.
Now you know what a smear shows on the flora in women, measures to prepare for it and the types of pathologies that can be identified after a thorough study. Try to visit your personal female doctor more often, do not be lazy to conduct regular microflora examinations and, if necessary, follow the doctor’s prescriptions. Dear ladies, fragile women’s health is in your hands, remember this!
Characteristics of Gram-positive bacteria
Most gram-positive bacteria are pathogenic to humans. These are pathogens of dangerous diseases:
- Streptococcus (Streptococcus), which causes tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rheumatism.
- Staphylococcus (Staphylococcus) is the causative agent of blood poisoning and purulent skin diseases.
- Listeria, which causes listeriosis, an inflammation of the brain.
- Bacilli (Bacillus) are the causative agents of toxic infections, anthrax.
- Clostridia (Clostridium), causing botulism, tetanus, gas gangrene.
The last two species are spore-forming anaerobes, the rest cannot form a spore. Some are able to stain only in the active growth phase.
Gram negative bacteria
These are bacteria that become completely discolored after washing with alcohol; As a result of repeated staining with safranin, they acquire a pink or bright red color. They are more resistant to antibodies than Gram+ species.
Gram-negative bacteria mainly include opportunistic bacteria that can cause inflammatory processes and an immune response in the human body under certain conditions. Their cell membrane, consisting of a lipopolysaccharide layer, causes the synthesis of cytokines, which contributes to an increase in toxins at the site of inflammation. Subsequently, toxins carried through the bloodstream with a poisonous effect cause severe symptoms of intoxication.
Read more about deciphering the analysis (smear for microflora)
When you receive the result of the examination, you will most likely see a table with text and numerical data entered into it. These are the types of cells found in the smear, as well as a mark on their quantitative content.
Often, the results form also displays the standards of a specific laboratory. Based on them, you can independently assess the norms and deviations from them in relation to various indicators.
It is strictly forbidden to independently diagnose yourself using laboratory standards alone. This is the task of the doctor, your treating specialist.
So, what can be detected in your smear for microflora?
These are flat epithelium, mucus, leukocytes, coccal-type flora,
What does squamous epithelium mean?
This indicator is necessarily present in the smear of every woman, especially of reproductive age. This is a special type of cells lining the vagina and the very beginning of the cervix.
If, for a number of reasons, a woman’s hormonal levels change, estrogens decrease, then a sharp decrease in epithelial cells is observed in the smear. This is a pathological condition that requires medical supervision.
During menopause, epithelial cells are detected from the surface of the lower layers of the vaginal mucosa. This is a normal condition strictly for menopausal women.
The detection of such cells in a smear in women of reproductive age indicates the onset of hormonal problems (usually an increase in male hormones) and certain inflammatory processes.
What does mucus detection indicate?
There is nothing to worry about if a small amount of mucus is found in your flora smear. According to experts, this is an absolute variant of the norm, especially when it comes to analyzing material from the vagina.
And, on the contrary, the detection of mucus in material taken from the urethra may indicate pathologies of the genitourinary system.
Consulting a competent specialist can dispel all your doubts.
Leukocytes and their significance
Leukocytes are always detected in a smear, so the main thing is not their presence, but the quantity. It is known that these are special bodies designed to protect the body from bacteria and infections.
The normal value of leukocytes in a smear is no more than 15 single cells. If your indicator exceeds the designated limit, you should consult a specialist and take action.
Frequently diagnosed diagnoses include vaginitis, colpitis, and cervicitis. An abundant growth of leukocytes indicates an intensifying inflammatory process.
For example, trichomoniasis or gonorrhea will show a shocking volume of leukocytes in a smear, which cannot but attract the attention of a competent specialist.
Detection of coccal flora
What if cocci are found in the smear?
Likewise, it is not the actual presence that matters, but the quantity. This type of bacteria looks like a perfect sphere under a microscope. A small number of cocci is safe.
Does their volume exceed the volume of lactic acid sticks?
This fact allows the doctor to verify the presence of an inflammatory process or a sharp decrease in immunity.
It is known that all types of bacteria living in the human body are divided into 2 groups.
This:
- Gram-positive (staphylococci, streptococci, lactobacilli, enterococci).
- Gram-negative substances (Escherichia coli, gonococci, Proteus).
If the doctor indicates in the results of a smear for flora the presence of gram-negative cocci located inside the cells, it can be assumed that the patient has a dangerous pathology - gonorrhea.
Staphylococcus aureus detected
This type of bacteria is extremely common and not uncommon. Again, attention should be paid to its quantity. If we are talking about 5% of microorganisms of this type, then there is no reason to worry. Normally, every person has them, but they do not cause any discomfort.
If growth of staphylococcus and a parallel reduction in the number of Doderlein bacilli are observed, inflammation located in:
- cervical canal;
- or in the vagina itself.
The video will tell you more about deciphering each of the smear indicators:
Find out how easy it is to learn to decipher smear results without having a medical education. The video is advisory and informational in nature and does not exclude the need to consult with a competent doctor.