Curettage of a polyp in the uterus is prescribed for multiple spread of small growths, with a high risk of cancer. In essence, it resembles the complete removal of the endometrium during abortion. The urgency of the problem of polyps lies in the high risks of oncological degeneration and infertility. Modern techniques make it possible to carry out manipulation with the least harm to the mucous membranes of the uterine cavity. Today, classic curettage is combined with optical hysteroscopy.
What are polyps, their symptoms and causes
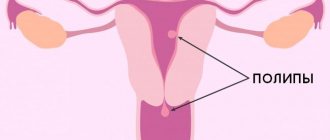
Polyps in the uterus are endometrial hyperplasia, when the mucous membrane grows in some areas of the endometrium. Polyps come in various shapes - round, mushroom-shaped, on a stalk or a thick base, as well as in various colors from pale pink to dark burgundy, and can be numerous or solitary. It is believed that the main reason for their appearance is a hormonal imbalance in a woman, usually an excess of estrogen and a lack of progesterone. Also, in combination with hormonal disorders, various inflammatory processes in the genital organs, mechanical damage, injuries during childbirth, frequent abortions (consequences), and diagnostic curettages have an impact.
There are several types of polyps: glandular, fibrous, fibroglandular and the most dangerous adenomatous. When polyps are detected, it is very important to conduct a histological examination to determine the state of the cells of the polypous tissue; if there are signs of proliferation, that is, the onset of oncological processes, such polyps should be removed along with the uterus. This is considered the early stage of uterine cancer and delaying surgery can be very dangerous.
Most often, small size polyps do not show any symptoms, however, with polyposis (multiple polyps) or with a large size of the tumor, there may be symptoms, since polyps reduce the contractility of the uterus, disrupt the natural process of mucosal rejection, causing bleeding, which manifests itself:
- uterine bleeding
- bloody, brown discharge in the middle of the cycle
- pain in the lower back and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, pain during intercourse
- also, in some cases, a polyp can make conception difficult (see boron uterus for conception) or contribute to spontaneous miscarriage
Therefore, women who want to become pregnant must have polyps removed. After radical treatment and a course of postoperative hormonal therapy, the mucous membrane gradually recovers and the woman’s health returns to normal. You can learn more about polyps in the uterus, treatment, symptoms, and causes from our article.
How to remove a polyp of the uterine cavity - methods, methods
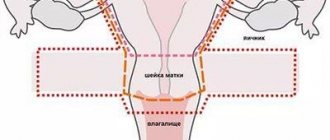
The modern method that most effectively removes endometrial polyps is hysteroscopy followed by curettage of the cervix and uterine cavity (polypectomy and curettage), as well as subsequent histological examination of the removed material. It is also possible to use separate diagnostic curettage or laser removal of polyps.
Factors such as the size of the polyp, its structure, the age of the patient, the nature of the endometrium, the reasons for the development of the polyp, as well as the presence of metabolic and endocrine diseases in the woman determine the tactics of patient management.
- If a woman has fibrous polyps, they must be removed.
- If a woman has a glandular fibrous polyp, this 100% indicates a hormonal imbalance and hormonal therapy is indicated after surgery.
- For polyps that threaten cancer - adenomatous, in women before menopause (see the first signs of menopause) or during menopause, removal of the uterus is indicated - hysterectomy or supravaginal amputation with revision of the ovaries or even removal of the appendages.
The essence
From a technical point of view, the process involves the removal of a pathological neoplasm along with the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) that surrounds it. Applicable only for small tumors; large ones cannot be eliminated using this method.
The doctor gains access to the uterine cavity through the cervical canal, so the method can be called non-surgical and low-traumatic. The recovery process after such an intervention is not too long. However, such a procedure may have some consequences and complications, as well as impose restrictions on some areas of the patient’s life for some time.
Curettage procedure
Hysteroscopy of the uterus - polyp removal
If a woman is about to undergo surgery to remove a polyp, she should go to a clinic that uses modern advances in medical technology and highly qualified doctors who use therapeutic hysteroscopy of the uterus to remove the polyp.
This is a modern method of examining the uterine cavity and removing it with minimal complications, without serious consequences for the woman’s body; it is a gentle procedure, since it is performed under the visual supervision of the operating doctor. In order for the operation to be successful, there is good visualization of the entire cavity and polyp, it is best to perform hysteroscopy after menstruation, but not later than the 10th day of the menstrual cycle. 6 hours before hysteroscopy, you should not take any drinks or food to prevent nausea after surgery.
Hysteroscopy of the uterus - removal of polyps is performed under general anesthesia, less often under local anesthesia. The operation to remove a polyp in the uterus begins with the insertion of a hysteroscope into the cervix - a thin flexible tube with a video camera at the end, which transmits an image to a monitor. Next, the uterine cavity is examined, the location of the polyp, its size, and the number of tumors are determined, after which a special tool available on the hysteroscope removes the polyp, then the removed tissue is sent to the laboratory for examination.
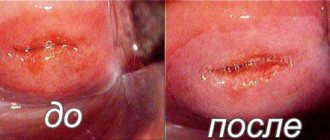
Polyps on the stalk must be removed by “unscrewing”, and the place where the neoplasm was attached or the polyp bed is treated cryogenically or cauterized with electrocoagulation, and a laser can also be used - this is done to destroy pathological tissues, in order to avoid re-growth, relapse of the disease. The duration of hysteroscopy is from 10 minutes to 30 minutes, depending on the condition of the endometrium. Read about the condition after hysteroscopy.
Preparation for the procedure
Curettage of the uterine cavity with a polyp is carried out only after sanitization of the vagina. For these purposes, the gynecologist may recommend using suppositories that have an antiseptic and antifungal effect. Additionally, it is necessary to take blood and urine tests, as well as a smear for microflora. Before the operation, colposcopy and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs are performed.
If local anesthesia is intended, then no special preparation is required. It is only advisable to abstain from sexual intercourse on the eve of curettage. When performing an operation under general anesthesia, it is recommended to do a cleansing enema and not eat anything 12 hours before the intervention.
Diagnostic curettage
Almost 30% of cases of polyps recur again after removal, so a very important condition for the operation is minimal trauma and thorough coagulation (cauterization) of the polyp bed. When a woman is offered a simple diagnostic curettage without hysteroscopy, in this case the doctor works blindly and it is impossible to remove the stalk of the polyp, so it is best to perform hysteroscopy followed by curettage. Until now, many medical institutions do not yet have modern hysteroscopes and trained personnel, so separate diagnostic curettage is still used, although less and less often.
Today, diagnostic curettage is considered an absolutely useless procedure for the treatment of polyps in the uterus. That is, first you need to do a hysteroscopy, “tear off” the polyp, cauterize the leg, and then perform a diagnostic curettage, but with the goal of obtaining the rest of the endometrium to make sure it is “normal” or abnormal.
Curettage is very often performed for urgent reasons, when heavy bleeding occurs against the background of polyps or endometrial hyperplasia; in this case, such a forced procedure prevents severe blood loss. In this case, they are scraped not for the purpose of removing the polyp (and bleeding often occurs suddenly and requires emergency measures), but for the purpose of hemostasis. With this method of curettage, first, using special instruments, the cervix is dilated, and then, using a metal loop - a curette, under general anesthesia, polyps and tissue samples are scraped from the walls of the uterus for subsequent examination.
Removal of polyps in the uterus with laser
Today, this method is used only in Moscow, but in the near future it will have to be used in every city - this is targeted removal of polyps in the uterus with a laser, which is melodramatic, does not leave scars, while maintaining reproductive function, which is especially important for women planning to have children. Since pregnancy is more likely after laser removal. In centers where modern technologies are used, a complete examination and laser removal of a polyp can be carried out in 3 hours, without a hospital stay, without disability, and without injuring the uterine cavity.
Also, for a more thorough diagnosis, it is possible to use mini-hysteroscopy or so-called office hysteroscopy, which occurs without trauma to the cervix and without anesthesia. In this case, the woman makes the choice of treatment method and assesses the condition of the uterine cavity together with the attending physician. With the help of such equipment, it is possible to determine any pathology of the uterus - uterine fibroids (symptoms of uterine fibroids), endometrial hyperplasia, intrauterine synechiae.
This is the most effective and gentle method of treatment, since the doctor controls the depth of laser penetration layer by layer, preventing injury, shortening the recovery period, blood loss is reduced, since the laser seals the vessels, the procedure does not leave scars, which is beneficial for future pregnancy, the recovery period after surgery is 6-8 months.
Discharge after polyp removal
What is considered normal after removal of uterine polyps?
- After hysteroscopy, a woman may experience minor spasmodic pain when the uterus contracts, as during menstruation
- There should be slight discharge for 14-20 days after the procedure
After the operation to remove polyps, a week later the patient should definitely undergo a routine gynecological examination, which will prescribe restorative therapy according to the nature of the polyp, the woman’s age and based on the main reason for the development of the tumor in the woman.
Contraindications for carrying out
A polyp in the uterus rarely re-forms after curettage, but to reduce the likelihood of side effects, it is recommended not to resort to surgery in the presence of sexually transmitted and infectious diseases that can cause purulent complications.
Additional contraindications:
- discharge from the genital tract of unknown etiology;
- narrowing of the cervical canal;
- immunodeficiency states;
- blood clotting disorder;
- acute mental disorders.
Treatment after removal of polyps in the uterus
If the operation is performed through hysteroscopy, then the risk of complications is minimal and it is a fairly safe procedure. But, in any case, the true cause of the appearance of such tumors should be determined in order to carry out preventive treatment after removal of the polyps.
In the first 3 days after surgery, you should take No-shpa 3 times a day to relax the muscles of the uterus in order to eliminate such a phenomenon as a hematometer - an accumulation of blood in the uterus due to cervical spasm.
Considering that polyps are often inflammatory in nature, doctors prescribe short courses of anti-inflammatory preventive therapy after surgery
The histology results, which are ready in approximately 10 days, should definitely be discussed with your doctor and should be collected and stored.
If the cause of the growth of polyps is a hormonal imbalance, and the polyps are glandular and glandular-fibrous, doctors can prescribe hormonal agents - gestagens, such as Duphaston, Norkolut, Utrozhestan. Hormonal oral contraceptives - Yarina, Janine, Jess, Regulon, Dimia.
A woman can also contact a homeopath or herbalist for possible preventive treatment using such non-traditional methods. Since treatment with folk remedies makes sense most often for prophylactic purposes, after removal of polyps to maintain immunity or hormonal levels. You can use celandine, boron uterus (see boron uterus - indications for use), as well as homeopathic preparations as prescribed by a doctor.
Can a polyp come out with menstruation?
There are many myths that a growth can resolve on its own, or that a polyp will come out during menstruation.
Important! The neoplasm attaches to the tissues of the organ and, under the influence of drug therapy, rejection occurs in exceptional cases.
Spontaneous release of a small tumor is allowed if there has been trauma to the tissue at the site of its attachment. However, there is a high probability of tumor detachment without attachment. In this case, after some time, a relapse occurs in the form of multiple growths.
This pathology requires examination and treatment.
According to doctors, polyps do not resolve on their own and do not leave the body either under the influence of drug therapy or under the influence of folk remedies.
Consequences, complications of the operation
If after surgery, both curettage and hysteroscopy, the following symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- Heavy bleeding
- Dark, unpleasant-smelling discharge
- Increased body temperature
- Pain lasting more than 2 days or acute, severe abdominal pain
What complications and consequences may arise after curettage removal surgery?
- Inflammation of the uterus
a very rare phenomenon, which is possible if the operation occurred against the background of an untreated infection, inflammatory process, and also if the rules of antiseptics and septics were violated during the operation. In this case, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- Perforation of the uterus
the formation of a puncture in the wall of the uterus, which can occur with loose walls or poor dilation. Large perforations have to be sutured, while small ones heal on their own.
- Hematometer
If there is a sudden cessation of bleeding after surgery, severe pain occurs - this may be a spasm of the cervix and the formation of a hematometer. In this case, infection and pain are possible, which are relieved by anti-inflammatory therapy and taking antispasmodics.
What should a woman not do after surgery?
Since minor bleeding is observed for 2-3 weeks after removal of the tumor, a woman should not do the following:
- Take a hot bath, steam bath, sauna, it is better to take only a shower, as overheating promotes bleeding
- Do not take acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin, which increase bleeding.
- For a month you should not lift heavy things or play sports.
- Maintain intimate hygiene carefully
- You cannot douche or have sex for a month after surgery.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist