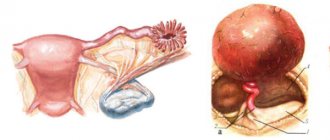
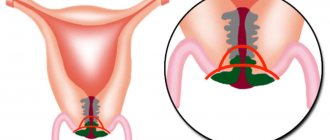
Subtotal hysterectomy is performed for uterine fibroids if the patient wants to preserve the cervix (if there are no diseases of the vaginal area and endocervix). Amputation causes less damage compared to extirpation.
Statistics show that injuries to large vessels and ureters are much less common. This operation is prescribed for pelvic endometriosis, adhesions and extragenital pathologies.
Indications
Subtotal hysterectomy with appendages is performed if the following indications are present:
- Endometriosis of the uterine body.
- Benign fibrous tumors on the wall of the uterus.
- Accelerated growth of fibroids.
- Recurrence of endometrial polyposis after conservative and surgical treatment.
- Multiple submucosal nodes that cannot be removed by hysteroscopy.
Contraindications
- Cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
- Tendency to form adhesions and fibrous tissue.
- Anemia.
- Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Intolerance to anesthesia.
- Increased size of the uterus (at least 16 weeks of pregnancy).
- Kidney and liver failure.
- Poor blood clotting.
Types of extirpation methods
Experts identify several methods of surgical treatment, taking into account the complexity of the operation and the method of its management. Depending on the volume of intervention, extirpation is classified into several types:
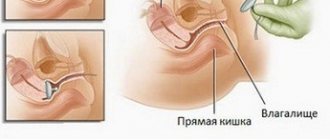
- Supravaginal hysterectomy is accompanied by the removal of the body of the reproductive organ;
- hysterectomy is the complete removal of the uterus along with its cervix;
- hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy involves cutting out a woman’s ovaries, fallopian tubes and cervical body of the reproductive organ;
- A radical hysterectomy is the removal of a patient's uterus and other reproductive organs.
Each of these operations can be carried out using several accesses:
- standard vaginal extirpation of the reproductive organ;
- abdominal laparoscopic extirpation of the uterus through the abdominal cavity along with the appendages;
- laparoscopic extirpation of the reproductive organ through the vagina;
- robotic surgery using a laparoscope;
- extirpation of the uterus and appendages using Pfannenstiel laparotomy with further suturing.
The operation is performed laparoscopically without any incisions in the abdominal cavity. Laparoscopy is performed using a laparoscope, when medical instruments and a video camera are placed into the peritoneum through incisions.
The choice of one or another technique, or both at once if the woman’s condition is too severe, is made by the attending physician, taking into account the results of the studies. In addition, attention is drawn to the nature of the disease and the degree of its complexity. Before the operation, previous pathologies of the reproductive organ and the consequences of hysterectomy are assessed, since such an intervention may be accompanied by the development of unpleasant consequences.
Life after amputation
Any type of hysterectomy (partial or total) leads to the cessation of menstruation and the impossibility of bearing a child naturally. However, preserving the ovaries allows for some time to synthesize their own sex hormones and give birth to a baby from a surrogate mother.
Organ amputation inevitably causes early menopause. The amount of estrogen produced gradually decreases, so women are prescribed hormone replacement therapy. Otherwise, extirpation does not affect the quality of life.
Read
Also:
- How to dye your hair without dye and is it possible?
- Is it harmful to sunbathe in a solarium without underwear?
- Curettage of the uterus - all about the procedure
- Anatomy of the uterus: location, structure and functions
- Fallopian tube laparoscopy
- What is hysteroscopy of the uterus
Indications and contraindications for treatment
The main indication for surgical intervention to remove the genital organ is considered to be pathological conditions in which conservative therapy does not bring the desired result. In addition, surgical treatment is carried out when malignant tumors are detected in the patient, which reach a significant size or continue to progress.
The following indications for extirpation are distinguished:
- prolapse of the body of the reproductive organ;
- fibroids, which are located on the neck of the organ or in the retroperitoneal space;
- malignant neoplasms affecting the ovaries;
- total myomatous nodes, which are located on the stalk;
- cancer tumors affecting the uterus or its cervix;
- multiple cystic formations:
- perforation of the uterine wall and its ruptures;
- erosions on the uterine walls, occurring in a chronic form;
- endometriosis and bleeding that appear due to various changes in the uterus.
Other indications for extirpation of the uterus without appendages are genital prolapse, recurrent erosion of the uterine pharynx or polyposis. In addition, this treatment is used in cases of abdominal obesity and the presence of contraindications to abdominal surgery.
Despite the large number of indications for such an operation, in some cases it will have to be abandoned. There are some contraindications to such an operation:
- pregnancy;
- diseases of the blood, heart, vascular and respiratory systems;
- inflammatory pathologies of the genital organs;
- identification of a source of infection in the body;
- acute and chronic diseases in the acute stage.
In some cases, a hysterectomy can be performed even if there is no threat to her life. Indications for such an operation may include severe pain, frequent vaginal or uterine bleeding and constant discomfort. Typically, such unpleasant symptoms appear when a woman has foci of endometriosis and a large number of myomatous nodes. With such a pathological condition, the patient has the right to choose: live with discomfort or agree to surgery.
Entrust the operation to the experts of the multidisciplinary clinic CELT
Our medical clinic has been operating since 1993 and provides a quality guarantee. By contacting us, you get serious benefits:
- For more than 20 years of continuous work, we have successfully completed 100,000 operations.
- All services and procedures are covered by a guarantee, the terms of which are specified in the contract. We are licensed and work officially, so we are fully responsible for the result.
- We have a full range of imported medical equipment with high precision, which is used in leading clinics in Israel, Germany and Switzerland.
- Our experts annually attend medical conferences in Europe, so they are the first in the Russian Federation to successfully use new treatment methods and have extensive experience.
- Treatment is carried out comprehensively and includes an initial examination, diagnostics, conservative or surgical treatment, and hospital rehabilitation. Having our own diagnostic center and laboratory allows us to obtain accurate test results in a minimum amount of time.
Preparation for the procedure
The outcome of the operation is determined by preliminary preparation for its implementation. Before extirpation, a routine clinical examination, colposcopy, and cytological examination are performed. Discharge from the cervical canal and vaginal part of the cervix is collected to identify atypical cells. In addition, in preparation for surgery, tests for sexually transmitted infections and other pathogenic flora are prescribed.
If there is a risk of blood clots, the patient is prescribed medications that affect the coagulation and tone of the veins. Before the operation, the patient should undergo an electrocardiographic study, thanks to which it is possible to assess the condition of the heart and blood vessels. In order to prevent infection during surgery, antibacterial drugs are prescribed shortly before surgery.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Subtotal hysterectomy
Many thanks to Inna Vasilievna Kardava for her sensitivity, professionalism, and high level of medical care.
Low bow to you. With great respect, your patient, Olga Anatolyevna Z. Read full review Olga Anatolyevna Z
26.11.2020
I would like to express my gratitude to the gynecologist KARDAVA INNA VASILIEVNA. I had an appointment with a gynecologist on November 26, 2020. Thanks to the Doctor for his professionalism, participation, and excellent attitude towards the patient. Low bow to you. Read full review
Olga Anatolyevna Z
26.11.2020
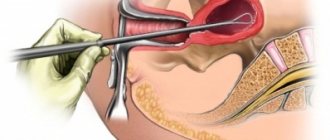
Progress of the operation
The initial stage of the operation is the introduction of the patient into anesthesia, which is selected by the anesthesiologist. The technique of supravaginal amputation of the genital organ without appendages is as follows:
- A dissection of the anterior peritoneum is made, followed by revision of the pelvic area. After identifying the uterus, the surgeon moves it towards the wound, and if foci are identified, he dissects them.
- 2 clamps are applied to the area of the tubes and uterine ligaments, followed by ligation of the appendages. After this, the surgeon dissects the uterovesical fold.
- The doctor diverts the bladder into a funnel to prevent damage to it. After this, clamps are applied to the vascular bundle or crossed.
- It is necessary to remove the uterus after making a cone-shaped lower median incision, which is sutured with catgut threads after removing the stump and the cervical canal is treated with a disinfectant solution.
Before suturing the wound, a specialist inspects it. Typically, such a surgical procedure to remove the uterus without appendages lasts from 60 to 90 minutes.
How is a subtotal hysterectomy performed?
Before surgery, general anesthesia and antibiotics are administered intravenously. The use of antibiotics avoids tissue infection and complications during rehabilitation. The operation is carried out in 7 stages:
- The round ligaments of the uterus are divided and the bladder is dissected. The surgeon uses a uterine rotator, with which the walls are stretched. An atraumatic clamp is used for increased tension. After this, the soft tissues are intersected and coagulated.
- The posterior layer of the ligament is opened and access to the parietal peritoneal cavity is created. Next, the surgeon lowers the ureter to avoid injury. The upper part of the uterine cavity ligaments is removed.
- The creation of a new window in the ligament is accompanied by the separation of the posterior layer of the serous layer in the body of the uterus. First, specialists determine the correct direction and distance to the ascending branches of the uterine arteries.
- At the level of the uterine pharynx, the uterine arteries are excised (separation of the vessels is not performed). If indicated, they are stitched and covered with a clip.
- Subtotal tubal hysterectomy is performed using an L-shaped instrument, which is a monopolar electrode. This allows the body of the uterus to be cut off with minimal damage.
- If indicated, peritonization is performed using an 8-shaped suture (infection prevention).
- The uterus is removed from the abdominal cavity using techniques similar to laparoscopic myomectomy.
Consequences of surgical treatment
Removal of the body of the reproductive organ, both with and without appendages, always leads to the onset of artificial menopause. This condition is characterized by the appearance of psychoemotional and neurovegetative symptoms of menopause, as well as the development of problems with the functioning of the body’s endocrine system.
After removal of the body of the reproductive organ, the patient is deprived of both reproductive and menstrual functions. For women who are in menopause and do not want to become pregnant again, this state of the body is only a plus. For girls planning a child in the future, deprivation of childbearing function becomes a real blow.
After hysterectomy, various complications may develop, among which internal bleeding is considered the most common. It comes in varying strengths, and the main reason for its occurrence is the application of poor-quality sutures during surgery.
After removal of the uterus, the following complications may occur:
- thrombosis in the veins of the legs;
- accumulation of purulent exudate in postoperative sutures;
- vaginal prolapse due to injury to the muscles that support the organs of the reproductive system;
- incontinence of urine and feces due to damage to the nerve trunks in the pelvic area.
A dangerous complication is inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can develop if the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are violated. The case when hysterectomy ends in the development of life-threatening complications is rare. Feedback from women suggests that many of them successfully survived such an operation and learned to live without a uterus.
In the video you can see the entire sequence of the operation to remove the uterus without appendages.
Video: Vaginal hysterectomy
Video: Hysterectomy
Video: Laparoscopy. Extirpation of the uterus with tubes. Prevention of ovarian ischemia.
Preparation and technique for removing the fallopian tube
Since tubal removal requires anesthesia, the patient will undergo careful preparation before the operation, including:
- Fluorography or chest x-ray;
- Cardiography according to indications;
- General clinical tests - blood, urine, group and Rh status;
- Examination for HIV, hepatitis, RW for syphilis;
- Coagulogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs;
- Examination by a gynecologist, colposcopy, taking smears for cytology and microflora.
After the research, the woman goes to a therapist, who gives his consent to the operation. Before the intervention, an anesthesiologist talks with her and determines the type of anesthesia and possible risks from it. The attending physician must be notified of all medications taken on a regular basis; anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and anti-inflammatory drugs are discontinued 2 weeks before tubectomy.
In the evening before the intervention, a cleansing meal, dinner and fluids are prescribed no later than 12 hours before the operation. The patient takes a shower the day before, removes hair from the perineum and pubis, and changes clothes. For severe anxiety, sedatives at night are recommended.