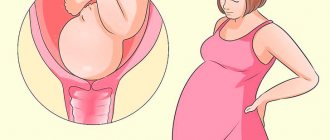
Uterine prolapse, or uterine prolapse, is one of the most common forms of pathological location of the internal genital organs in women of any age.
It most often occurs in women after menopause, but can also occur in young women.
With prolapse, the cervix is not visible from the genital slit, but if, with straining or any physical stress, it falls below the genital slit, then this indicates partial prolapse of the uterus.
Prolapse of the posterior, anterior wall of the uterus, cervix: symptoms
Prolapse of the posterior, anterior wall of the uterus, cervix.
Signs of pathology appear already in the last stages of the disease. Initially, prolapse of the posterior and anterior walls of the uterus and cervix is practically asymptomatic. The woman has no pain, no discomfort. uterine prolapse may appear and this will be accompanied by unbearable pain.
WHEN THE POSTERIOR WALL OF THE VAGINA IS DOWN , when the process enters an irreversible stage, the following symptoms appear:
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen and lower back
- Pain in the vagina itself
- Long and heavy menstruation
- Unpleasant sensations and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Worth knowing: During the development of pathology, the posterior wall of the uterus can affect the rectum, causing its deformation, as well as constipation, hemorrhoids and subsequently fecal incontinence.
In addition, a woman’s sexual desire is dulled, leading to pelvic dyssynergia. Almost always, uterine prolapse provokes the development of varicose veins, which leads to swelling not only of the genitals, but also of the lower extremities. A woman feels constant heaviness in her legs and even pain after walking for a long time.
WHEN THE ANTERIOR WALL OF THE VAGINA IS DOWN , the following symptoms are observed:
- Decreased vaginal sensitivity.
- Narrowing of the vaginal passage.
- Painful sensations in the perineum and lower back. It usually intensifies after exercise.
- Feeling as if there is a foreign object in the vagina.
- Impaired urination - retention or, conversely, involuntary release of urine.
Displacement of the anterior vaginal wall can cause infections in the genitals. In later stages, discharge is observed in the form of leucorrhoea, and later with blood clots.
WHEN THE CERVICAL WALLS DESCRIPTION, the following symptoms occur:
- Painful intercourse
- Heaviness with excessive pressure in the lower abdomen
- The external genitalia become swollen
- Urinary or fecal incontinence
- Aching pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the groin area
- Menstruation disorder
- The vaginal mucosa becomes covered with erosions and ulcers
In the first stages of any of these pathologies, a woman does not turn to a gynecologist, since nothing bothers her. But during a medical examination, the doctor will definitely notice a small prolapse and prescribe treatment.
Is the pathology visible on ultrasound?
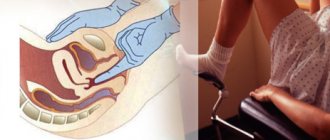
First of all, among the methods for diagnosing uterine prolapse, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination..
When an ultrasound probe is placed at the vaginal opening, the doctor can see the entire urethra, bladder, and part of the rectum, as well as abnormalities in their locations.
During the study, the doctor observes the position of the cervix, deviations of the urethra, and the presence of rectal deformation.
NOTE!
It is with an ultrasound that the doctor can confirm the diagnosis and accurately measure how much the uterus is below the normal level.
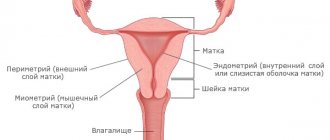
Uterine prolapse: causes
Prolapse of the uterus
The disease occurs due to the weakening of the muscle tissue on the abdominal wall, on the pelvic floor, which helps keep the organs in normal condition. Due to the fact that intrapelvic pressure rises, the organs shift to the bottom. Also, the causes of uterine prolapse can be:
- Multiple births
- Perineal injuries
- Multiple pregnancy
- Birth of a big baby
- Uterine fibroids
It is important to constantly keep your body in good shape. If you do not play sports, then, accordingly, there will be weakening of the muscles and sagging of the organ.
Principles of treatment
What treatment for prolapse after childbirth will depend on the following factors:
- degree of omission;
- the presence of other gynecological ailments;
- need for childbearing function in the future;
- patient's age;
- how much the neighboring organs are lowered;
- what is the degree of surgical risk?
Skein prolapse after childbirth can be treated with the following methods:
- therapeutic exercises;
- traditional methods of treatment;
- gynecological massage;
- hormone therapy;
- surgery;
- wearing a pessary or bandage.
Surgical intervention
If grade 3 or 4 prolapse is diagnosed, and if conservative methods do not produce a positive effect, surgical treatment is prescribed.
There are the following methods for this:
- vaginoplasty. This is a corrective intervention that strengthens the muscles of the genital opening;
- suturing of ligaments. It is used to strengthen the strength of the ligamentous apparatus of the uterus, however, in this case there is a risk of subsequent infertility;
- use of alloplastics. These materials fix the position of the uterus and strengthen the ligamentous apparatus;
- hysterectomy. Uterus removal. It is indicated when it is not possible to tighten the stretched muscles, and the woman is no longer planning a pregnancy.
Conservative methods
This treatment is based on the woman performing certain sets of exercises - according to Kegel, according to Yunusov, according to Atarbekov, according to Bubnovsky, and so on. These exercises are aimed at restoring muscle tone, which allows the uterus to return to its anatomically correct place.
NOTE! It is necessary to understand that such exercises are not effective in all cases. They are prescribed in all stages of prolapse to prevent the progression of the disease, but it is possible to return the uterus to its natural position with the help of exercises only in the 1st and uncomplicated 2nd degree of pathology. Gynecological massage is carried out in the gynecologist’s office
It is also aimed at restoring the tone of the uterine muscles and is also more effective in the initial stages of the disease
Gynecological massage is performed in the gynecologist's office. It is also aimed at restoring the tone of the uterine muscles and is also more effective in the initial stages of the disease.
In some cases, a woman may be prescribed hormone therapy. It is relevant if prolapse occurs as a result of a decrease in estrogen concentration.
As for traditional methods of treatment, they are auxiliary in nature and must be combined with the main treatment.
Pessary
A pessary is a special device that is inserted into the vagina, with its help the reproductive organ is kept from falling out.
This product is made from biological and hypoallergenic materials, therefore it is completely harmless to the woman’s body.
Initially, the pessary is inserted into the vagina by a gynecologist, but subsequently the woman must learn to insert and remove it independently.
In some cases, wearing a pessary is indicated temporarily. It is used for preventive purposes while the woman receives the necessary treatment.
But sometimes a pessary is prescribed for lifelong wear. As a rule, this appointment is made if the patient is indicated for surgical intervention, but for some reason it is impossible.
With the correct size and correct installation of the uterine ring, the device does not cause any discomfort and is not felt at all.
Wearing a pessary prevents the following consequences of prolapse:
- development of infectious processes;
- displacement of the bladder walls;
- development of cystitis;
- skin diseases in the perineum and genitals;
- necrotic processes in the uterus and vagina due to impaired blood flow.
Degrees of uterine prolapse: list, photo
Doctors distinguish 4 degrees of uterine prolapse. Here is the list and photo:
Uterine prolapse 1st degree
- Initial or first degree . There are almost no symptoms. During the examination, the gynecologist points out a small prolapse of the vaginal walls. The uterus may be slightly lowered downward.
Uterine prolapse 2nd degree
- Second degree . The uterus is located inside the vagina. If the doctor asks the patient to strain and perform a functional test (bend her knees towards her or lie a little lower on the chair), then prolapse of the cervix outward is observed. At this level, pain and discomfort appear.
Uterine prolapse 3rd, 4th degree
- Third degree . At this stage, the uterus protrudes from the genital slit even at rest.
- Fourth degree . All internal genital organs fall out. A woman feels discomfort while walking and feels severe pain in the lower abdomen.
At the onset of the disease, you can easily correct the condition with exercises. In the final stages, you will have to wear a uterine ring, a bandage, or, if the doctor prescribes it, you will need surgery. Read more about treatment below.
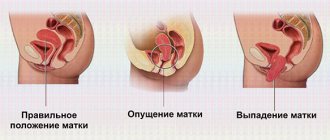
The essence of pathology
The diagnosis of uterine prolapse is made when its position is incorrect relative to the walls of the pelvis, rectum and bladder, in which the fundus and cervix are displaced below a certain anatomical level of the norm.
The causes of
uterine prolapse can be :
- frequent childbirth;
- trauma during childbirth, use of forceps and vacuum;
- perineal ruptures;
- heavy physical activity, heavy lifting;
- age over 50 years, menopause;
- congenital pelvic pathologies;
- obesity;
- frequent constipation.
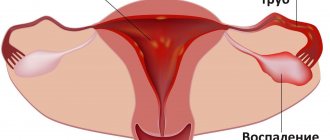
There are four stages of uterine prolapse:
- At the first stage, the uterus is already shifted to the bottom, and minor painful sensations appear. The uterus does not peek out from behind the genital slit.
- In the second stage, the uterus emerges from the genital slit during straining, heavy physical exertion, coughing, and laughter.
- At the third stage, the cervix is constantly located outside the genital slit, and part of the body of the uterus is also visible. This condition is already considered partial uterine prolapse.
- At the fourth stage - the stage of complete prolapse, the cervix and the entire body of the uterus are constantly visible from the genital slit.
How to treat uterine prolapse - what to do: surgery
Treatment of uterine prolapse
As long as the symptoms do not appear or are not accompanied by discomfort or concern, treatment is not required. However, if they cause suffering, or the uterus has changed its position too much, the help of a specialist is needed. How to treat uterine prolapse, what to do?
First, the gynecologist prescribes Kegel exercises. If classes do not help, then more global measures are taken. In later stages, surgery may be necessary. Previously, all women with this diagnosis were operated on. Worth knowing:
- Surgery is not the only option.
- Even 10-20 years ago, gynecologists quite often performed organ removal operations, although this was not always necessary.
- Today, such an intervention can only be considered when a woman suffers greatly from prolapse or, for example, uterine prolapse has already occurred.
- But even in this case, all possible risks that the operation may entail must be weighed.
Be sure not to delay your consultation if you are concerned about discomfort in the vaginal area or lower abdomen. If measures are not taken now, then irreversible consequences will arise later, which entail only complete removal of the organ.
Worth knowing: Surgery also does not solve all problems. Especially if you are overweight and do not exercise. Prolapse of the walls of the vagina, cervix, and bladder may occur. The result is urinary problems, infections and other unpleasant problems.
In many patients, even after removal of the uterus, sagging of the walls of the cervix, if it was left, and the walls of the vagina may occur. In this case, an operation is also prescribed to install a special surgical mesh, which supports the organs and prevents the muscles from sagging.
How to determine at home?
In the very early stages of uterine prolapse, the downward displacement is so slight that it is almost impossible to independently recognize the presence of displacement.
During the development of the pathology, when the cervix has already approached the entrance to the genital opening, the woman can feel it herself.
For self-examination, a woman needs to lie on her back, insert a finger into the vagina and push.
If there is uterine prolapse, she will definitely feel it.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
The diagnosis of prolapse or uterine prolapse must be confirmed by a gynecologist during a gynecological examination. Under no circumstances should you rely solely on symptoms and self-examination. If symptoms indicating prolapse are detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor, who, during the examination, asks the patient to push, after which he determines the degree of displacement of the vaginal walls. Women with genital displacement should be registered. A colposcopy must be performed.
How to treat uterine prolapse without surgery: pessary
Treatment of uterine prolapse: pessary
An alternative to surgery is a gynecological pessary or uterine ring. Helps treat uterine prolapse without surgery. This device, made of silicone or plastic, looks like a ring, depending on the application, and holds the vagina or uterus in its natural position, preventing it from further prolapse.
Remember: The pessary should be changed every six to eight weeks.
It is used inside the vagina to support the organs. This device is also installed to prevent the progression of the disease, to eliminate discomfort, and to normalize the patient’s well-being. A pessary is the most effective way to prevent serious complications and inflammatory diseases. The uterine ring can be used for the following conditions and diseases:
- When organs and uterus prolapse outside the vagina
- Diseases that occur in old age
- Before surgery
- Due to the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment
- Due to contraindications for surgery
- While maintaining a multiple pregnancy
- Treatments for urinary incontinence
The uterine ring helps to cope with pathology even if the disease is at the most advanced stage; with its help you can make life easier for patients and relieve pain. During pregnancy, the uterine ring can be used for preservation. In some cases, it is used for the following pathologies:
- Violation of ovarian parameters
- When the uterus softens
- Not opening on time
- Due to anamnestic data, which include spontaneous miscarriages, premature births and abortions
The ring can also be used due to the fact that a caesarean section was performed during a previous pregnancy, or during severe physical exertion. Read below for information on how to install a pessary and which one to choose for yourself.
What does this mean?
Prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus entails prolapse of the anterior wall , as well as the walls of the vagina. This provokes not only disruption of the functioning of all the woman’s pelvic organs, but also, accordingly, infertility.
From the genitourinary system and intestines, disturbances in urination and defecation, the appearance of hemorrhoids and prolapse of small intestinal loops are observed.
Erosion that occurs when the vaginal mucosa is damaged not only provokes severe pain, but also significantly complicates the treatment process.
NOTE!
In addition, the advanced stage of the disease leads to the need for radical surgical intervention - complete removal of not only prolapsed tissue, but also the entire reproductive system, which significantly affects the psychological state of the patient and her sexual activity - this is where family problems begin.
Uterine prolapse in old age - what to do: types of uterine rings, how to use correctly?
Uterine ring for the treatment of uterine prolapse
In old age, the disease usually already progresses. But even in this case, surgery is not always prescribed. What to do in this case? For women with uterine prolapse at 50 years of age and older, as well as for women during pregnancy or at a young age, a gynecologist may prescribe wearing a uterine ring.
Worth knowing: For the manufacture of pessaries, silicone or latex materials are used; this material has hypoallergenic properties, it is of high quality and does not cause irritation on the surface of the genital organs. There are many types of rings on the pharmacy market, each type is used for a specific case and pathology.
There are several types of pessaries:
- Ring . This device has a round shape on the outside. Using such a device, you can fix the uterus and urethra.
- Mushroom-shaped. This type of ring resembles a mushroom with a stalk; this type of device is used in cases where other types do not have a therapeutic effect. This device can be worn for no more than 1 day.
- Cubic rings are used in the most severe and advanced cases to remove physiological secretions. It is a cube with walls concave inward. They cannot be worn longer than expected.
- Cup pessaries . They have a spherical shape and a hole in the center; these devices are used in the initial stages of pathology.
There are also other types of pessaries. The doctor selects a specific type of uterine ring based on the specific clinical case and individual characteristics of the patient.
Uterine ring sizes:
- It is impossible to independently determine what size is needed, so the procedure for selecting the appropriate size is carried out only by the attending physician after diagnostic procedures have been performed.
- In the early stages of the disease or in cases of minor prolapse, it is recommended to use regular round rings for support.
- The same rings are selected for pregnant women.
- If the prolapse has reached the fourth stage, then a cup-shaped pessary is chosen.
Uterine ring for the treatment of uterine prolapse
How to install a gynecological ring:
- To do this, you need to study the instructions for use, because if the uterus prolapses, it is important to be able to insert the ring yourself.
- The first introduction is carried out under the supervision of medical professionals, after which the device is used at home.
- Some devices are installed once and cannot be removed.
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Disinfect and treat the uterine ring with the solution.
- Then treat the pessary with lubricant or cream to make installation comfortable and easy, and to prevent injury to the mucous skin.
- The next step is to insert the pessary into the vagina. Hold it in your palm, then straighten the device and apply it to the cervix
- The device should not put undue pressure on the cervix.
If you are unable to insert the pessary yourself, then ask a gynecologist for help at first. Then you will get the hang of it and do it yourself.
Types of operations
Surgical treatment of cervical prolapse and uterine prolapse is performed under general anesthesia. Before the operation, the anesthesiologist talks with the woman. If you have any allergic reactions to any medications, you must report them. The duration of surgery and the length of the recovery period after uterine prolapse depend on the technique.
Anterior colporrhaphy
The procedure involves suturing the front part of the vagina to establish the correct position of the uterus and cervix. During the intervention, it is necessary to remove the vaginal wall outside the pelvis. The stretched fabric is collected on it and cut off. This provides the specialist with access to the connective tissues of the pelvis. Here the surgeon performs suturing followed by suturing of the vaginal wall. This technique is effective in lowering the pelvic organs forward, as well as partially changing the position of the bladder.
Posterior colporrhaphy
This technique is similar to the previous one. The difference is that all manipulations are performed on the posterior vaginal fornix. The advantage of this type of surgical intervention is given to cases of prolapse or displacement of the posterior wall, as well as incorrect anatomical position of the uterus (bending).
Fixation of the uterus
Normally, the cavity of the reproductive organ is securely fixed in the pelvis. In each direction it has the same extent to the bone tissue, and in front and behind it is surrounded by excretory organs.
The intervention is performed through the perineum or abdominal route. A kind of prosthesis is attached to the inner wall of the peritoneum and sacrum, which will support the pelvic organs. The material from which the device is made does not cause allergies and has a long service life.
Median colporrhaphy – Lefort Neugebauer operation
The essence of this operation is the excision of two flaps from the vaginal area. The resulting edges are sewn together. As a result of the operation, the cavity of the reproductive organ appears above the fastened areas, which act as a support.
During median colporrhaphy, prolapse repair is performed. As a result, the vaginal muscles become shorter and stronger, and the new structure of the labia creates additional support for the pelvic organs.
Removal of the uterus - hysterectomy
An important point that the doctor pays attention to when choosing a surgical intervention technique is the woman’s desire to have children. For elderly patients, during menopause and those who do not plan to have reproductive function, it is recommended to remove the uterus during prolapse
This technique is the most effective, as it never leads to relapse.
Many patients are afraid of this operation even after menopause, because they believe that after it they will have to forget about their intimate life. In fact, this opinion is a big mistake. Once a hysterectomy is performed correctly, the vaginal cavity is preserved. A woman can continue to lead an intimate life as before. The only consequence of this treatment method is infertility.
Uterine prolapse after childbirth: how effective is the bandage?
Bandage for the treatment of uterine prolapse
A bandage is a medical support device. Made from special durable fabrics that are pleasant to the touch. This device encircles the hip area along with the perineum. The bandage is secured with Velcro and plastic elements. How effective is a bandage for uterine prolapse after childbirth? Here is the answer:
- If you wear a bandage, the uterus will no longer put as much pressure on neighboring organs as without it.
- The woman's sexual organ will be in the correct anatomical position. Thanks to this, pain is reduced, problems with involuntary urination and gas release disappear.
- It is effective to wear a bandage in the initial stages of uterine prolapse - with prolapse of degrees 1 and 2.
You can also perform Kegel exercises while wearing the brace. This device does not interfere with this.
Remember: Only a doctor should prescribe wearing a bandage. Experts often prescribe wearing this device along with a pessary, and not only after childbirth.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of prolapse with folk remedies, as a rule, is supplemented with therapeutic exercises.
Yunusov's gymnastics is a contraction of the muscles involved in the process of urination. You need to periodically simulate urinary retention. The method is very effective, but it is inferior to Kegel exercises, because more muscles of the pelvis and perineum are involved.
A few more effective exercises:
- Stand on all fours and simultaneously raise your right leg and left arm. Do five approaches;
- For the lazy, just stand on all fours for ten minutes every morning;
- Get on your knees with your hands on the floor. When bending over, you should try to touch your chest to the floor. Repeat this 20 times. Gradually, the number of inclinations can be increased to 40. The result will become noticeable after 3 months of such daily exercises;
- Standing straight, you need to raise your leg at a ninety-degree angle. This should be done with each leg 10 times;
- Exercises “bicycle”, “scissors”, “birch tree”;
- Yoga (at home).
Is it possible to get pregnant if the uterus prolapses?
When the uterus prolapses, you can get pregnant.
With 1 degree of uterine prolapse, a woman has no pain, reproductive function is preserved. Therefore, pregnancy can occur as in a healthy woman.
Pregnancy in 2nd degree also cannot be excluded. During this stage of the pathology, the woman is bothered by pain. But she may not be aware of the presence of the disease. She learns about this already at an appointment with a gynecologist, when she comes to register.
A woman with stage 3 or 4 uterine prolapse is not deprived of ovulation, and the conductive function of the cervical canal works normally. Therefore, in this case, pregnancy can also occur. Although this is unlikely, it is theoretically possible.
Disease prevention
As you know, any disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
To prevent prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus, there is also a set of measures, by performing which, you can prevent not only the appearance, but also the development of pathology:
- after childbirth, it is necessary to undergo a full examination of the genital organs for displacement or prolapse - there are special techniques for returning and maintaining the uterus in the correct position;
- if there is a pathology or risk factors for its occurrence and development, a woman is not recommended to carry and lift heavy objects, as well as moderate physical activity;
- obesity, gastrointestinal dysfunction and some systemic chronic diseases can also trigger the appearance of pathology, so timely diagnosis and treatment of such problems can reduce the risk of developing uterine prolapse.
IMPORTANT!
Women during menopause and patients with abnormalities in the development of the reproductive system are also at risk - in such cases, constant monitoring by a gynecologist is necessary with correction and treatment of the disease.
Uterine prolapse: consequences
Prolapse of the uterus
This is not bad or scary, but some women are afraid of the consequences, are ashamed of it and do not want to see a doctor. Prolapse is accompanied by rather unpleasant symptoms:
- When you cough, sneeze or laugh, a little urine is released involuntarily.
- Or vice versa, a woman goes to the toilet, but cannot completely empty her bladder.
- Sometimes there are problems with bowel movements, an unpleasant sensation of foreign bodies in the lower abdomen or when walking and sitting.
- But it also happens that prolapse is not accompanied by any symptoms.
Complaints are very varied and depend on how far the uterus has descended. These are not all the consequences. Here are a few more:
- When the uterus changes position, it can put pressure on the vagina, bladder, or rectum.
- The described symptoms appear depending on the pressure the uterus exerts.
- In addition, other organs may be slightly misaligned: the vagina sometimes bulges and can be felt between the labia.
- The bladder may slide towards the vagina, causing what is called a “cystocele” or bladder prolapse.
- If the rectum is affected, a rectocele may develop.
- If the uterus settles more, the cervix can be felt from the outside. In rare cases, the organ falls out on its own.
If uterine prolapse occurs during pregnancy, this can lead to complications. The fact is that along with prolapse of the uterus, prolapse of the cervix or vagina can also develop. The release of internal organs to the outside can provoke the development of infection, which can spread to the internal cavity of the uterus. Because of this, intrauterine infection occurs, which can lead to a delay in fetal development. Premature birth and various birth defects may also occur.
In the initial stages of pathology development, symptoms of uterine prolapse may intensify, especially in the first trimester. This is due to an increase in the size and weight of the reproductive organ due to the growing embryo.
Diagnostic methods
If uterine prolapse is confirmed, the woman must be examined by a proctologist and urologist to determine and/or exclude the presence of prolapse of the rectum (rectocele) and bladder (cystocele).
In cases of serious uterine prolapse and its concomitant diseases (fibroids, inflammation, tumors, cervical erosion), additional research methods may be prescribed:
- hysterosalpingoscopy or diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- swabs for flora and bacteria;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- excretory urography to exclude urinary tract problems;
- computed tomography of the pelvic organs.
After surgery for uterine prolapse, after treatment with gymnastics: reviews
Prolapse of the uterus
If you have been prescribed surgery, then undoubtedly you need to do it. If the gynecologist says that you need to play sports, do gymnastics and do Kegel exercises, then you need to listen to the recommendations and follow them. Read reviews from other women who describe their health after uterine prolapse surgery or after gymnastics treatment.
Natalya Sergeevna, 65 years old
I was diagnosed with uterine prolapse three years ago. It turned out to be grade 3. The doctor prescribed ointment because there was a vaginal infection. He also told me to do simple exercises and walk. At first I followed all the recommendations, but I didn’t have enough willpower and I abandoned everything. Six months ago, the uterus began to fall out and interfere with walking. I again went to consult my gynecologist. It turned out that the pathology has progressed, and now I already have stage 4 disease. Now they said that we need to have an operation. It's scary, but there's nothing left. Therefore, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, because women’s health is very important and must be protected.
Arina, 30 years old
When I came to my pregnancy appointment, the obstetrician-gynecologist, after an examination, diagnosed me with “Prolapse of the uterus.” There was no threat of premature birth, because the prolapse was 1st degree. After giving birth I had to wear a bandage. Now I’m doing Kegel exercises, it helps a lot. I realized for myself that I need to keep myself in good shape, play sports, since my general well-being and women’s health depend on this.
Svetlana, 25 years old
My grandmother, at the age of 60, was diagnosed with stage 4 uterine prolapse. It was painful for her to walk and she could not urinate normally. They had an operation. Everything was fine. After 11 years, the problems returned again: vaginal sagging appeared. After this, the bladder began to fall out along with the vaginal wall. Problems with urination appeared again. First she put in a uterine ring. But it was difficult to constantly tinker with him due to his age. Therefore, the gynecologist recommended installing a support mesh. Most likely, she will have to agree - there is no other choice.
Treatment
What to do if a pathology is detected? Treatment for uterine prolapse includes conservative or surgical treatment. To determine an effective treatment regimen, the doctor takes into account several factors:
- age of the patient;
- severity of the disease;
- presence of related problems;
- the possibility of complications after surgery;
- the possibility of preserving reproductive function.
Conservative research methods are prescribed only in the early stages of prolapse (stage 1-2). To combat pathology, non-steroidal, hormonal and painkillers are recommended.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Treatment of uterine prolapse is carried out using non-steroidal drugs, suppositories or antibiotics. Rectal or vaginal suppositories are most often used to treat inflammatory diseases in gynecology. This is explained by the rapid action of the drugs and a minimal list of contraindications to them.
To eliminate prolapse, the following is usually prescribed:
- Voltaren;
- Diclofenac;
- Terzhinan;
- Ginalgin;
- Flamax.
Non-steroidal drugs can relieve pain symptoms due to prolapse of a reproductive system organ. In addition to the analgesic effect, nonsteroidal drugs have an antiplatelet and capillary protective effect.
Among the frequently prescribed drugs in this group are:
- Nurofen;
- Piroxicam;
- Meloxicam;
- Celecoxib.
Antimicrobial agents in the treatment of prolapse are used to prevent infectious diseases - colpitis, inflammation of the appendages, endometritis:
- Pennicillin;
- Streptomycin;
- Biomycin.
Antimicrobial agents have a lot of side effects, so their use should be agreed with a gynecologist.
Hormone therapy
The main cause of the disease is a lack of estrogen in the body. Hormonal drugs are used only in the early stages of prolapse. The drugs are prescribed in tablet form, in the form of oils and creams containing estrogen.
Oral medication can be replaced with vaginal suppositories, for example, Ovestin. Chinese candles are gaining popularity. However, their use is appropriate only to prevent the development of the problem, and not for its treatment.
Surgery
Surgery is prescribed when conservative treatment is ineffective or in advanced stages of prolapse. Cervical prolapse after childbirth is eliminated using several methods:
- Vaginoplasty. The doctor performs suturing of the posterior wall of the reproductive organ, the perineum. If there is difficulty urinating or urinary incontinence, the hernia of the bladder, which was formed when it was displaced, is removed.
- Shortening of organ ligaments. The ligaments are attached to the wall of the uterus. The technique is used in rare cases, since after the intervention there is a high risk of relapse.
- Stitching the uterine ligaments together. The main disadvantage of the operation is the woman’s inability to have offspring. After the intervention, the uterus is unable to contract or stretch.
- Attachments of the reproductive organ to the pelvic floor ligaments. After the intervention, the woman will be able to maintain reproductive function.
- Strengthening the ligamentous apparatus using plastic methods. The disadvantage of the procedure is the possibility of fistulas in the pelvic organs.
- Reducing the lumen of the vagina.
- Complete removal of the uterus. It is performed only on women who are past childbearing age.
In severe cases, combined surgical techniques are used: suturing the vagina, strengthening the ligamentous apparatus and fixing the prolapsed organ.
Folk remedies
In addition to surgical treatment or conservative methods, traditional methods of treating prolapse can be prescribed. The main purpose of the funds is to strengthen a woman’s immunity and speedy recovery after illness.
- Plantain syrup: 50 g of dry leaves are poured with 1 liter of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 30 minutes. Then add 1 tbsp to the product. celery seeds and leave for 40 minutes. After cooling, add 500 g of honey to the product. Syrup is taken before meals, 50 ml.
- Dill tincture. 1 tsp collection: seeds of dill, chicory and chamomile, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 12 hours. The medicine is filtered and taken throughout the day. Duration of therapy is 3 weeks.
Women and doctors about the problems of prolapse of the internal genital organs
Having studied the Internet on the problem of prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina, I came to the conclusion that the disease is getting younger. Despite the fact that numerous sources claim that these diseases mainly affect women over 50 years of age, many young mothers who have given birth have experienced all the delights of the discomfort and pain of this pathology.
Video: Obstetrician-gynecologist A. S. Klyukovkina on methods of treating pathology
As we see, the disease is getting younger and more and more often it is young girls who have given birth who become patients in the gynecological department due to problems associated with prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina. But it is easier to treat any disease if you treat it at the first symptoms of deviation from the norm.