Classification of cervical ruptures
Cervical rupture in 98% of cases is a consequence of abnormal labor. There are:
- Independent:
- Due to weak tissue stretch. Typical for primiparous women after 29 years of age. (In the USSR they were placed in the risk group of “starparous”);
- Rapid labor (for primiparous women up to 5 hours, for multiparous women up to 2 hours);
- Large child (weighing more than 4 kg);
- Narrow pelvis of a woman in labor (determined by a gynecologist).
- Violent when the doctor carries out surgical measures to accelerate the birth of the fetus (by using forceps, a vacuum, or pulling the fetus out by the butt).
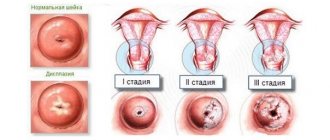
Based on the degree of damage, the rupture is classified into 3 degrees:
- 1st degree - a tear on one side (rarely on both) no more than 1.5 cm. During childbirth, the cervix opens, its edges stretch and thin. Full dilatation is achieved with a diameter of 10–12 cm. At this moment, the woman in labor feels pushing and the midwife allows her to push. It happens that the expectant mother begins to push early or does not do it during a contraction, the walls of the uterus cannot withstand it and tear.
Cracks up to 0.5 cm are accompanied by weak vaginal discharge, and can often go unnoticed.
- 2nd degree – from 2 cm or more, but the tear does not extend beyond the edges of the uterus. This happens if a woman with a narrow pelvis gives birth to a very large child naturally. The fault lies with the diagnostician who carried out control measurements of the mother's pelvis and fetal parameters on a prenatal ultrasound.
Grades 1 and 2 refer to uncomplicated ruptures.
- Grade 3 – complicated rupture, more than 2 cm, affecting the vaginal vault or peritoneum. Accompanied by severe bleeding. The woman in labor experiences: decreased blood pressure, pale skin, increased pulse, cold sweat.
It is possible to detect tissue deformation and determine its degree only after the birth of the child and placenta. Medical staff evaluate you for complications. Undiagnosed cracks in a timely manner lead to the development of infection, large blood loss, or the formation of rough scars.
Prevention and treatment of ruptures during childbirth
If ruptures are accompanied by heavy blood loss, the woman is prescribed intravenous infusions using hemostatic drugs and saline. To prevent inflammation, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial therapy. Local antiseptics are also a mandatory part of the treatment of cervical ruptures.
Prevention of cervical injury:
- Gymnastics to strengthen the vaginal muscles (during pregnancy) is an effective and productive way. Suitable for both first-time mothers and multiparous women. An old seam on the neck is not an obstacle to training.
- Correct breathing. Reduces the pain of childbirth, stimulates the healthy development of labor, and prevents the formation of complications.
- Use of special gels. Indicated on the recommendation of a doctor for women at risk of ruptures. The gel facilitates the movement of the baby through the birth canal and reduces the risk of tissue injury.
And although the picture described looks frightening, according to various estimates, from 10 to 39% of women in labor encounter such a pathology as cervical ruptures. Competent treatment, compliance with all recommendations, a healthy and calm attitude to the situation will help the young mother recover as quickly as possible.
Causes
The cause is not always a disruption in obstetrics. The condition of the uterus itself before pregnancy or during childbirth may also contribute to this:
- Poor elasticity of wall tissues. Age after 25 years or previous abortions;
- If the cervix is not fully dilated, the baby puts pressure on the walls at birth;
- Large child;
- Rotation of the fetus with straightening of the spine in the cervical region;
- Rapid or prolonged labor;
- Rough scars on the neck from old cracks or surgery;
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the uterus;
- Poorly healed erosion or dysplasia;
- Incompetence of the person performing the birth;
- Narrow maternal pelvis;
- Early rupture of amniotic fluid;
- Natural birth with breech presentation;
- Use of forceps or vacuum.
The presence of one of the listed reasons in a woman in labor does not always lead to pathology. But it requires some control.
Cervical rupture can occur at any time:
- Before giving birth
A scar from previous operations can cause suture rupture in a second pregnancy, which will lead to miscarriage or premature birth with complications.
Also, a violation of the integrity of the uterus can be a consequence of an ectopic pregnancy.
To prevent such adverse consequences, constant competent supervision by a specialist is required.
- During childbirth
Tears during childbirth are a consequence of too much stretching of the cervical tissue. During natural childbirth or surgical intervention, pressure occurs on the walls of the cervix and damage to it, which in turn leads to deformation. If the deformity is more than 2.5 cm, the doctor must decide to perform an emergency caesarean section. Quick diagnosis and surgical intervention reduces the risk of consequences.
- During sex
It is extremely rare that violent sex life causes the formation of tears. This occurs during sexual intercourse with the use of foreign objects. When injured, severe pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal bleeding, weakness and dizziness are felt.
What Causes Uterine Rupture&
During childbirth, contractions occur while the baby is already moving through the mother's birth canal. The pressure of contractions can cause the mother's uterus to rupture. Cesarean section scars are often torn.
However, an unscarred uterus may rupture if one or more of the following conditions are present:
- the mother's pelvis is too small for the baby to pass through the birth canal easily and painlessly;
- when the mother has already given birth five or more times before the current pregnancy;
- abnormal release of oxytocin can cause contractions to be too strong and too frequent, which puts a lot of stress on the uterus;
- when the placental lining separates from the uterus, which can cause the baby to be partially or completely weaned from the mother's circulation;
- the baby is not in a normal position before it is born;
- negligence of doctors during childbirth or in preparation for it.
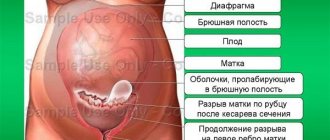
When a uterine rupture occurs, the contents of the uterus, including the baby, can enter the mother's abdominal cavity, which is naturally very dangerous.
Types of breaks
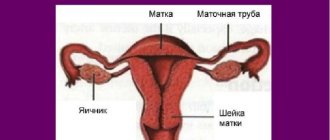
Violation of the integrity of the uterus is called its rupture. Uterine ruptures are complete “ruptura utericompleta”, when all the walls of the uterus are torn, and incomplete “ruptura uteri incompleta” - only the mucous and muscular membranes are torn, and the serous membrane remains intact.
Such a rupture most often occurs in the lower segment of the uterus, where there is a layer of loose connective tissue between the peritoneum and myometrium. The blood that spills out accumulates in the periuterine tissue and forms a hematoma of various sizes.
Sometimes another form of birth trauma occurs, such as separation of the uterus from the vaginal vaults “colpoparexis”.
Uterine ruptures can occur during pregnancy and childbirth. They can be spontaneous and violent. Unauthorized uterine ruptures occur without external intervention, and forced ones occur during obstetric operations.
When the uterus completely ruptures, its contents may spill into the abdominal cavity.
It is expected that birth by Caesarean section should occur within approximately 10-35 minutes after complete uterine rupture. The level of threat to the fetus increases sharply after this period.
With an incomplete rupture of the uterus, the tissues of the organ are torn, but the contents of the uterus remain in place.
This disruption of the uterus manifests itself in similar conditions as complete and incomplete ruptures, only after a uterine fissure the risk for the mother and baby is much less, since the bleeding is not so profuse. The fetus, umbilical cord and placenta remain in the uterus. Usually a rupture does not require treatment.
Risks during natural childbirth are much more likely with incomplete or complete uterine rupture. This usually occurs during active labor, but can begin to develop in the later stages of pregnancy. The most common reason for uterine rupture is the force of muscle contractions during childbirth.
How to diagnose an injury?
Uterine rupture occurs suddenly and is difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are often vague. If doctors suspect a rupture, they will look for signs of symptoms in the baby, such as a slow heart rate.
Doctors can make an official diagnosis only after surgery.
Symptoms
Damage up to 6 mm is not always detected immediately. Weak bleeding is attributed to hormonal changes. In this case, there is a deterioration in health, accompanied by weakness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, and increased sweating.
If the crack is more than 2 cm, severe bleeding with clots, burning and pain in the perineum appears. Nausea occurs, blood pressure decreases, heart rate changes and pain shock develops. Doctors detect such symptoms immediately and carry out immediate surgical intervention, up to and including emergency caesarean section.
Cervical rupture - the most common causes and best treatment methods
Cervical rupture is a gynecological complication that requires emergency medical attention. If it is absent, death is possible. Let's take a closer look at the disorder, highlight its causes, provoking factors, and treatment methods.
Classification of cervical ruptures
To begin with, it should be noted that a break can occur on its own, due to various reasons. But more often this happens during various surgical interventions on the reproductive system and during childbirth. Spontaneous rupture can be caused by:
- Weak stretching of the cervix during childbirth (occurs in first-time mothers after 30 years).
- Excessive stretching during childbirth - extension position of the fetus, rapid birth, large fetus.
- Prolonged compression of the uterus due to a narrow pelvis - violent rupture occurs as a result of vaginal delivery operations, which help speed up the process of the birth of the baby:
- forceps delivery;
- vacuum extraction.
In addition to classification according to the type of development (forced rupture and spontaneous), there is also a division according to the severity of the pathology. Thus, it is customary to distinguish 3 degrees of cervical rupture. Each has its own clinical picture. However, the symptoms of the disorder are similar. Because of this, only a doctor can accurately determine the degree after examining the reproductive organ.
1st degree cervical rupture
First degree cervical rupture during childbirth often develops as a consequence of the mother’s failure to comply with medical instructions. This often happens if a woman is not pushing into a contraction. At the same time, there is an increase in internal pressure due to the baby’s movement along the birth canal. This degree is set if the gap does not exceed 1 cm. It is most often located on one side.
The clinical picture for small ruptures may be mild. Doctors often talk about the asymptomatic course of this type of pathology. Especially when the gap does not exceed 10 mm. The main symptom in this case is bleeding from the vagina. Over time, its volume may increase. The woman experiences painful sensations in the lower abdomen, of a cramping nature.
Cervical rupture 2nd degree
A 2nd degree cervical rupture during childbirth develops when the size of the fetus does not correspond to the volume of the pelvis. This is possible if the infant’s anthropometric parameters are incorrectly determined during an ultrasound scan.
Because of this, doctors choose the wrong delivery tactics, which leads to rupture. With this degree, the gap does not exceed 2 cm.
In this case, it is localized only in the area of the uterus, without affecting the vaginal part.
3rd degree cervical rupture
Obstetric cervical rupture of the 3rd degree is characterized by involvement of the vagina in the pathological process. In this case, the gap completely merges with it, there is no clear boundary. This type of disorder is characterized by strong, profuse discharge from the genital tract, often with large clots. Other symptoms include:
- profuse cold sweat;
- pallor of the integument and mucous membranes;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increase in the number of heart contractions.
Causes of cervical rupture
In most cases, cervical rupture during childbirth is caused by a violation of the technique of delivery procedures. However, this can also happen due to circumstances related to the condition of the reproductive organ. Among the main causes of the pathological condition, doctors identify:
- decreased elasticity of the muscular structures of the cervix - typical during childbirth after 30 years;
- the presence of scars, inflammatory processes that affect the condition of the cervix;
- anomalies of labor - incomplete dilatation of the cervix, discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the pelvis;
- rapid labor - the expulsion phase lasts only a few minutes;
- large head size of the fetus, body weight more than 4 kg.
Cervical rupture during childbirth
During delivery, pathology of this kind is not often recorded. It is provoked by excessive stretching of the edges of the uterine pharynx and an increase in the diameter of its external opening.
As a result, the load on the cervix increases and its integrity is violated. Rapid elimination of pathology eliminates negative consequences.
Often, with a large gap, a decision is made to perform an emergency caesarean section.
Postpartum cervical rupture must be sutured in the delivery room. Sutures are applied using special, self-absorbing threads. Failure to provide assistance in a timely manner is fraught with the development of uterine bleeding, which can lead to the death of the woman in labor. To reduce the time of assistance, anesthesia is not used.
Cervical rupture during sex
Uterine rupture during sex is possible, but in practice this rarely happens. It occurs during violent, passionate sexual intercourse, with deep penetration. Trauma to the cervix leads to the development of bleeding. In this case, the woman feels a sharp deterioration in her health, weakness, dizziness, and headache. The main symptoms of this pathology include:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen, in the inguinal folds;
- the appearance of blood from the vagina (sometimes in a small amount);
- pain in the lumbar region.
Symptoms of cervical rupture
A cervical rupture of the 2nd degree and small size may not be clinically manifested. In this case, the patient notes a slight deterioration in general health.
There is practically no blood released from the genital tract; in some cases, women may notice bleeding. They often associate them with changes in hormonal levels and do not attach any importance to them.
However, as it progresses, the situation worsens.
If the gap exceeds 1 cm in size, uterine bleeding appears, which forces you to consult a doctor. In this case, the discharge contains blood clots, which indicate partial accumulation in the vaginal cavity. Under the influence of body temperature, the blood coagulates and partially comes out in the form of blood clots. In addition to discharge, such patients record:
- unknown weakness;
- deterioration in general health;
- excessive sweating.
In order to diagnose a cervical rupture, the gynecologist performs an examination in the chair. At the same time, changes in the size and structure of the uterus are recorded. The organ has swelling, which can partially spread to the vagina.
When a rupture occurs during childbirth, convulsive contractions appear - non-productive, short-term contractions of the uterus. There may be blood in the urine, and the patient herself complains of severe burning and pain in the lower abdomen.
As a result, a painful shock develops:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- decreased blood pressure;
- rapid pulse.
Cervical rupture - consequences
It is worth noting that it is not always possible to diagnose cervical rupture in a timely manner. The reason for this is the absence of bleeding or its low profusion. In some cases, the doctor is unable to detect a cervical rupture during childbirth, the consequences of which may be as follows:
- hemorrhagic shock as a result of bleeding in the late postpartum period;
- the formation of a postpartum ulcer, which gives impetus to the development of cervical pathology;
- scar formation;
- ectropion – inversion of the cervix;
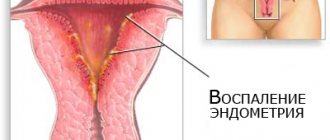
- development of ascending infection – endometritis, adnexitis;
- ICI – isthmic-cervical insufficiency, due to the failure of the muscular structures of the cervix.
Treatment of cervical ruptures
Treatment of this type of disorder is possible only through surgery. Suturing of a cervical rupture is carried out in all cases of pathology.
An exception may be superficial cracks, in which there is no blood loss. In severe cases, transsection is performed - an operation with opening of the abdominal cavity.
Used to remove a hematoma that forms when a rupture passes into the parametrium (fatty tissue).
Pregnancy after cervical rupture
Often, a history of cervical rupture becomes an obstacle to the development of a subsequent pregnancy. This is due to the adhesive process in the pelvis, which interferes with normal ovulation and fertilization.
However, even a pregnancy that has begun after a cervical rupture cannot always be carried out. Incompetence of the uterine muscles can cause premature dilatation, which causes premature birth.
Because of this, even a small tear in the cervix during pregnancy is subject to control and observation.
Often the violation can be prevented. So, prevention of cervical ruptures includes:
- timely ultrasound;
- compliance with medical recommendations;
- taking tests and undergoing research.
Second birth after cervical rupture
In order not to provoke uterine rupture along the scar during natural childbirth, doctors perform the second and subsequent deliveries by cesarean section. Surgical interventions are planned in advance. The optimal time for it is 37-38 weeks of pregnancy. The fetus is removed through an incision made in the lower abdomen. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
| Ruptures during childbirth - the best ways to avoid complications Ruptures during childbirth occur in 35% of women. The incidence of complications is 2-3 times higher in those giving birth to their first child. Read the article, which contains information about the causes of the disorder, types, methods of prevention, and special means of prevention. | Asphyxia of newborns is a complication of the birth process that accompanies 1-1.5% of all pregnancies. Pathology develops at the time of birth of the baby or in the first minutes after birth. It is important to know about this phenomenon, its causes and symptoms. |
| Stem cells - everything you wanted to know about umbilical cord blood Stem cells have recently begun to be used in medicine. Studies have proven the effectiveness of their use in the treatment of a number of diseases. However, it must be taken into account that the procedure for collecting and storing material is complex and expensive. | Birth trauma is a disruption of the delivery process, accompanied by damage to internal organs, systems of the mother and fetus. Most of these pathologies have an impact on the baby’s health, so it is important to be able to identify them by their characteristic symptoms. |
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/razryv-sheyki-matki-samye-chastye-prichiny-i-luchshie-metody-lecheniya
Diagnostics
Today, complications are diagnosed immediately in the delivery room during an examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist. When small amounts of blood appear, it is determined during what period of labor this occurred and whether there was intervention by medical personnel. An internal examination is carried out using gynecological mirrors and by palpation of the uterine cavity and abdomen for the presence of muscle tension and large 3rd degree tears. After carrying out all the procedures and making a diagnosis, the gynecologist chooses treatment. All consequences are eliminated by suturing. If the operation is performed correctly, the recovery period does not require special conditions and has no complications.
Possible consequences
If a woman has a large rupture of an organ and she has lost a lot of blood, then she experiences a state of shock.
This is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- decreased blood pressure;
- pulse slows down;
- loss of consciousness occurs.
In such a situation, the pregnant woman should receive qualified medical care. If it is not provided on time, then the risk of death increases. It should be noted that women in labor die in ninety percent of cases. The reason for this is called hemorrhagic shock. It occurs when there is a large rupture in the walls of the organ and from severe blood loss. Then the rupture of the cervix has rather sad consequences.
The absence of signs may occur at the end of the second stage of labor. But there are still some symptoms - bleeding for unknown reasons. In this case, the child may be born dead or in serious physical condition.
In this situation, it becomes necessary for the doctor to conduct a manual examination of the uterine cavity.
Complications of this pathology are also dangerous because postpartum ulcers often form after them. Infectious diseases also appear in the postpartum period. If the rupture was not sutured during surgery, then tissue scarring occurs. They lead to inversion of the cervix, and pseudo-erosion of the non-mucosal membrane of the cervix develops. Other precancerous conditions may also appear.
Consequences of a breakup
Unfortunately, the obstetrician is not always able to identify pathology directly in the delivery room. The consequences can be very serious:
- Heavy bleeding;
- Hemorrhagic shock;
- Postpartum ulcers;
- Inflammatory processes and infections;
- Cervical inversion;
Improper suturing causes the formation of rough scars. This reduces the plasticity of cervical tissues, causes miscarriages or premature births in subsequent pregnancies, causes erosions and bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of uterine rupture
The uterus can rupture on its own, that is, spontaneously, or as a result of medical intervention, that is, forcibly.
Spontaneous occur due to:
- structural changes in the tissues of the uterine walls - abortion or postoperative scarring;
- various obstacles in the birth canal that prevent the fetus from moving forward.
Violence occurs during the birth process, when it is necessary to use obstetric forceps or other medical instruments.
An organ rupture is also distinguished by the area of damage, for example:
- complete, that is, the rupture occurs along all layers of the uterine wall and penetrates into the abdominal cavity;
- incomplete - the defect occurs only on the mucous and muscle layers, and the abdominal part is not affected.
If the mother’s pelvis is too narrow and the fetus is large, then the pathology has three types.
Threatened uterine rupture
It is characterized by:
- the integrity of the uterine walls is not broken;
- pain occurs, and the lower part of the organ is too stretched;
- swelling of the external genitalia and cervix appears;
- frequent and painful contractions.
Incipient uterine rupture
The following symptoms appear:
- layers of the uterine wall begin to rupture;
- contractions accompanied by pain and cramps;
- there is blood when urinating;
- the area above the womb begins to increase;
- blood is released from the vagina;
- The fetus is diagnosed with active movements, and its heartbeat slows down.
Complete rupture of the uterine wall
It can be defined like this:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- the skin becomes pale, cold sweat appears, the woman in labor loses consciousness;
- contractions stop;
- the pulse is palpable weakly;
- pressure readings drop sharply;
- vaginal bleeding begins;
- parts of the dead fetus can be discerned through the abdominal wall.
There are also three types when the uterus ruptures along a scar during pregnancy:
Threatening gap:
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting.
Started stage:
- increased muscle tone of the uterus;
- sharp pain upon palpation of the organ;
- frequent strong contractions with various breaks;
- vaginal bleeding;
- low fetal heart rate.
Accomplished:
- severe pain in the uterus;
- blood from the vagina;
- stopping pushing;
- low blood pressure and increased heart rate.
In any case, urgent medical intervention is required.
Treatment
Surgery is the main method of treatment.
Damage up to 0.5 cm usually heals on its own. In case of mild trauma, cracks and tears are sutured with self-absorbable threads. Healing occurs quickly and lasts up to 3 weeks. No processing or medication is required. Sexual rest lasts up to 3 months.
For complex and deep wounds, abdominal surgery (transsection) is performed. When the rupture passes from the uterus to the surrounding fatty tissue, with the formation of hematomas. It is necessary to prescribe medications to eliminate inflammation, erosion and enhance the immune system.
Causes of perineal rupture after childbirth
Childbirth does not always go smoothly: sometimes the baby lies too low, he is too large, or the vaginal tissue is not elastic enough, which leads to injury to the perineum. If the perineum protrudes, changes color and begins to swell, there is a threat of its rupture.
This complication during childbirth is considered the most common - 35% of women (especially during the first birth) experience a perineal rupture.
In addition to the main reasons that can lead to perineal rupture, secondary factors can also be identified. These include: rapid labor, scarring of tissue after previous ruptures (for repeat mothers), incorrect assistance with pushing.
Most often, ruptures occur when the baby's head emerges through the perineum. The baby, or rather his head, moves along the birth canal and begins to compress the veins located in it. The movement of blood becomes difficult, the resistance of the bloodless tissues of the perineum increases, which leads to rupture.
Types of breaks:
- Spontaneous - occurs during childbirth without any intervention;
- Violent - can be provoked by a certain action of personnel or interference in the course of childbirth.
During complicated childbirth, ruptures can first affect the vagina and then move to the perineum of the woman in labor. When ruptures occur, bleeding often occurs, which is aggravated if the pregnant woman suffers from varicose veins.
Pregnancy after cervical rupture
Pregnancy after cervical rupture is possible. This requires timely prevention (ultrasound, treatment, tests).
Any crack in the neck requires careful observation. When a rough suture is formed, adhesions may form in the pelvis. They will interfere with ovulation and pregnancy itself. Premature birth or miscarriage can also be a consequence of weak tissue or the presence of a scar.
With proper treatment, specialists reduce these problems to a minimum. All subsequent births are carried out through cesarean section, so as not to provoke re-rupture of the suture. In this case, childbirth takes place at 37-38 weeks.
Tweedledum's blog
Excerpts from answers on ICN
Answered by Berezovskaya E.P.
https://klubkom.net/posts/78333
At 32 weeks, NOTHING is prescribed or carried out. Corticosteroids are administered to promote rapid maturation of the lungs. Bed rest doesn't help. They limit physical activity, ask the woman not to panic or be nervous, not to lift weights, and not to have sex. And they ask you to come back in 2 weeks to re-measure the length of the cervix. They explain that she has a 50% chance of having a premature birth, so they teach her what to do in this case.
—
- at 30 weeks they prescribed Ginipral” in tablets of 1/2 4 r. daily for a month and Indomethacin suppositories. I read in the instructions for Indomethacin that it should not be taken during pregnancy.
-the combination of two tocolytics is strictly NOT recommended.
———————
If, according to ultrasound, the length of the cervix is within the normal range (2.5 cm or more), if the internal os is closed (no more than 10 mm), I would advise then changing the doctor.
———————
Usually the stitch is placed at 14-16 weeks. At later stages, a suture is applied only according to strict indications. Any suture is accompanied by a risk of miscarriage.
The two most common complications of suturing are damage or inflammation of the membranes (chorioamnionitis). With elective suture, membrane damage occurs in the range from 1 to 18% of cases, and inflammation in 1-6% of cases. With urgent and emergency suturing, rupture of the membranes can occur in 50-65% of women, and infection of the membranes in 35-37% of cases. At the same time, the effectiveness of suture and the level of positive pregnancy outcomes in such cases are low. That is why, when applying a suture to the cervix, the correct selection of pregnant women for whom such treatment will be effective is very important.
———————-
Pessaries are practically not used abroad, because their ineffectiveness has been proven. In addition, this is a foreign body that is constantly in [email protected] #$%& and irritates the cervix, which is not desirable in case of ICI.
————————
Limit physical activity and try to lie down more for the next week. Use intravaginal suppositories or progesterone tablets (Utrozhestan). The effectiveness of such treatment is not high, but we still do not know how effective or ineffective the use of progesterone will be in your (specific) case. The attempt is not torture, but I know several women whose cervix was 19 -20 mm and managed to carry the pregnancy to term (I repeat, again, that the level of effectiveness is not very high, but it helps some women).
Considering your age. You won’t be taking progesterone all the time, and it won’t affect the baby at this stage - the laying of organs has occurred and there won’t be much harm.
—————————
The older a woman is, the greater her risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
————————-
No medications are prescribed except on the day of suturing. Tocolytics at the onset of labor and the presence of a suture are also contraindicated (the cervix may rupture). Applying a suture to the cervix allows pregnancy to be carried out in 80-95% of cases with instmic-cervical insufficiency, if the operation is performed on time. Without a suture, such women have a 25-27% chance of pregnancy.
—————————
after stitching:
1) there is no particular point in lying down, because according to research this does not affect the situation (except for multiple births)
2) After suturing, only short-term tocolytics are used, only once, i.e. immediately after surgery. This is either indomethacin or nitroglycerin, but if the period is too short, then nothing. Almost nothing else is used. Tocolytic therapy has its own strict indications for use, including strict pregnancy periods.
3) No one prescribes antibiotics abroad. Some doctors recommend the use of a short course of antibiotics only if an emergency stitch is placed on the cervix (at a later stage), because there is a high risk
Chorioamnionitis. The approach is always individual.
4) How are you going to sanitize the seams? Of course not needed. And the less you pull the cervix, the better. Absolutely none of your concern, so to speak.
5) Tone is not dangerous, because the uterus is a muscular organ and constantly reacts to everything with contractions. But manipulations on the cervix can provoke strong contractions of the uterus like contractions and lead to termination of pregnancy.
6) No additional smears are taken if there are no complaints about pathological discharge. Such a pregnancy is equated to a normal one, except that the woman continues to be at risk for premature birth.
7) and in light of the question above: what dynamics of the length of the neck and the opening of the internal pharynx should be after suturing (ultrasound)? Should everything lengthen and close? How fast? What if it shortens and opens further? Or is this an unimportant factor?
The length of the cervix may not change, i.e. it can remain short. The internal pharynx may also remain in the same state. The point is that if there is no progress for the worse, i.e. the cervix does not shorten even more, there is no pain or discharge, the fetus is developing normally, this indicates the effectiveness of the operation. So, returning the cervix to normal length is not always necessary. An ultrasound, but usually no more than once a month, is performed to see if the cervix is contracting further and if there are other complications after the suture.
———————
It is not clear what to do with the prescription of dexamethasone, which looks like an extremely dubious medicine with a very systemic effect on the body, with a poorly studied effect on both the child and the mother. (I searched through everything available in simple Russian language on the Internet). It is not very clear how it works to eliminate the threat.
For ICI, it is indicated as a prophylactic dose according to a special regimen between 24 and 32 weeks of pregnancy with a high risk of PREMERATE BIRTH.
—————————
a short cervix of 23 mm at 20 weeks and a dilation of the internal os of 3.8 mm suggests that there is a 50% chance of giving birth within 2 weeks. Tocolytic therapy is not prescribed, especially since there is no labor. Utrozhestan in the form of tablets is NOT effective in this case (and this has been proven). Some doctors recommend vaginal progesterone suppositories from 24 to 32 weeks of pregnancy, but most still do not prescribe them because the effectiveness of such therapy is very low. A pessary is not recommended, as it is a foreign body and has no effectiveness; on the contrary, it can speed up labor. Bed rest also does not preserve such pregnancies. This means that the only possible option may be the vaginal use of progesterone, and not in the form of tablets by mouth.
————————
Let's start with Duphaston . Regardless of whether you had surgery on one of the ovaries or not, the corpus luteum of pregnancy only functions until 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, and that’s it. Then the ovaries enter a state of menopause. They can be removed - the pregnancy will not fail. This has been proven by clinical studies. So, any prescription of progesterone after this period, supposedly for the purpose of maintaining pregnancy, does not justify itself and is an ordinary overreach, reinsurance of ignorance of modern obstetrics.
Leukocytosis is a condition of pregnancy, there is NO WAY OUT of it, so you need to take it calmly. Staphylococcus lives on the skin of the perineum and periodically gets into [email protected] #$%&. In small quantities it is not dangerous.
2 cm may be the absolute norm for some women, and with such a cervix they carry pregnancies to term without any problems. But that’s why I write and say everywhere: DYNAMICS is important in obstetrics. After all, from a small embryo a fetus of 3.5 kg grows. In other words, pregnancy is a dynamic state where there is acceleration, not just speed, and has its own laws of dynamic changes.
Hospitalization is carried out only in cases of stitching, pain, bleeding. For cervical lengths of 2 cm or less, inpatient monitoring is recommended due to the high risk of pregnancy loss. For women with a cervix larger than 2 cm, outpatient monitoring is recommended if there are no complaints, because hospitalization does NOT improve the outcome of pregnancy, and, on the contrary, introduces too much stress into a woman’s life.
Bed rest is recommended only during the period of suturing the cervix and for women with a very short cervix (less than 2 cm). Unfortunately, bed rest practically DOES NOT improve the outcome of pregnancies with isthmic-cervical insufficiency . The use of bed rest is more a tribute to the tradition of the old school of obstetrics than, indeed, a method of treatment. It is accompanied by an increased risk of thrombus formation and thromboembolism. A slight improvement in outcome after bed rest was seen only in multiple pregnancies.
Wearing a bandage does not change the situation with isthmic-cervical insufficiency for the better. On the contrary, it often leads to compression of the abdomen, which can worsen the situation.
Sexual activity during isthmic-cervical insufficiency was prohibited by the old school of obstetricians. Modern recommendations differ from old ones. After applying a suture, if the length of the cervix returns to normal or at least does not decrease below the critical size (2.5 cm), then sexual activity is not contraindicated. If vaginal probes are inserted to perform an ultrasound, why should penile insertion interfere with pregnancy? Orgasm is also not contraindicated. Most likely, a psychological factor is triggered - the fear of losing pregnancy, which is why many women refuse sexual activity.
I repeat once again, after applying a suture and stopping the shortening of the cervix, women lead the same lifestyle as all pregnant women, with the exception of limiting physical activity, lifting weights and, in some cases, sexual activity. You can swim in both the river and the sea.
—————————————-
During normal pregnancy, the cervical canal may expand (but not more than 4 cm), and the length of the cervix may slowly shorten. It is believed that progesterone affects the condition of the internal pharynx (isthmus), the main lock that protects against dilatation of the cervix and loss of the fertilized egg and fetus.
There are risk factors involved in the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. These include:
- Termination of pregnancy in the past using an instrumental method using cervical dilators;
- Diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity using cervical dilators;
- Improper management of labor (forced), leading to cervical rupture;
- Surgical treatment of “erosion” of the cervix (cauterization, freezing, laser treatment, conization, etc.);
- Anatomical defect of the cervix (congenital short cervix, etc.)
Vaginal flora and sexually transmitted infections have nothing to do with the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
Pregnancy in the cervix and its consequences
Pregnancy in the cervix (medical cervical pregnancy) is a rather dangerous pathology of pregnancy development.
Even 20 years ago, removal of the uterus for this type of childbearing was the only possible method of treatment. This was caused by probable heavy bleeding and, without immediate surgical treatment, led to the death of the pregnant woman.
Nowadays, the latest research and experiments have allowed gynecologists and surgeons to help the patient preserve the reproductive organ.
Treatment is possible only under the strict supervision of a doctor. A woman is prescribed special medications depending on her physiological state.
More than 50% of women after such medical and surgical treatment can become pregnant again and give birth naturally.
Features of suturing internal and external tears
At the beginning of the elimination of birth ruptures, the doctor conducts an inspection of the uterus and vagina, if necessary, eliminating and suturing existing damage, then proceeds to suturing external injuries. Stitching occurs layer by layer - damaged tissues are compared and fastened with special threads. For suturing the following can be used:
- catgut - threads made of natural material (cattle intestines), which themselves dissolve under the action of enzymes. The resorption process takes 30 days, but the material loses its strength within a week after application, which is why pieces of threads may begin to separate;
- vicryl is a multifilament material of synthetic origin, developed as an analogue of catgut. It dissolves in tissues independently under the influence of liquids. The process is completely completed within 60–70 days; Vicryl Rapid - is less durable, but dissolves faster (in about 40 days);
If the edges of the injury are smooth (for example, as a result of an episiotomy), a cosmetic intradermal suture is used, in which the thread passes through the thickness of the tissue in a zigzag, appearing on the surface only at the beginning and end of the incision. But most often a standard suture is applied, which tightens both sides of the tear with external punctures.
The rupture can be sutured with both classic and cosmetic sutures.
The need and type of anesthesia during suturing are determined by the nature of the injury:
- Sutures are placed on the cervix without anesthesia, since after childbirth this area is practically insensitive. A woman usually does not feel pain, but she may be bothered by discomfort in the perineum from the instruments and hands of doctors;
- when suturing vaginal tears, the pain is more pronounced, so local anesthetics (Novocaine or Lidocaine) are used. For complex injuries that require long-term work, short-term intravenous anesthesia is administered;
- sutures on the perineum are applied either without anesthesia or with local treatment, depending on the complexity of the injury and the sensitivity of the woman;
- serious uterine ruptures require large-scale intervention with dissection of the abdominal wall - this procedure is performed only under general anesthesia.
Prevention of cervical rupture
The basic rule of prevention is the correct course of pregnancy and childbirth, namely:
- All chronic diseases and inflammations are diagnosed and treated before pregnancy;
- Conception is carried out no earlier than 2 years after all medical interventions;
- Registration in the housing complex for up to 6 weeks or observation until birth;
- Quitting alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- Carrying out physical activity under the supervision of a gynecologist;
- Assessment of indications and contraindications for natural childbirth;
- Adequacy of the use of forceps and vacuum - fetal extraction;
- Rational use of stimulant drugs for rapid dilatation of the uterus or uterine contractions.
Cervical rupture is an extremely unpleasant pathology of the outcome of childbirth. But, with proper prevention, timely diagnosis and competent surgical intervention, it will not cause the woman much trouble.
Happy motherhood!
Video: Sexual life after childbirth with perineal rupture
Sexual life after childbirth with perineal rupture - Stay alive! Season 4. Issue 10 from 03.14.17
Rules for caring for seams
Internal sutures do not require self-treatment and usually do not cause severe discomfort, and the self-absorbable threads applied to them do not need to be removed. Only external tears require maintenance. It means:
- keeping the damaged area clean. Sanitary pads should be changed at least once every 2 hours. It is recommended to wash yourself every time after visiting the toilet, blotting the perineum after the procedure with a soft towel. These recommendations must be followed not only in the maternity hospital, but also within 1–1.5 months after discharge;
If there are stitches, the pad must be changed every 2 hours after childbirth.
- antiseptic treatment. In the hospital, the woman is examined once a day, assessing the condition of the sutures and treating them with antiseptic solutions. This procedure is usually not required after discharge.
In addition, in the postpartum period you should adhere to a number of rules:
- minimize physical activity to avoid mechanical rubbing of tissues;
- eliminate increased stress on the perineum - avoid a sitting position for at least 10 days, otherwise the seams may come apart. In modern maternity hospitals, special buffet tables and bedside tables are provided so that a woman can eat while standing or reclining;
After giving birth, a woman with ruptures needs to avoid a sitting position for at least 10 days, so she will have to spend most of the time lying down or reclining
- Avoid eating foods that harden and cause the formation of large amounts of feces. It is advisable to delay defecation for as long as possible in order to avoid unnecessary pressure on the perineum, so women are not recommended to eat bread, cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is better to give preference to fermented milk products and dietary meat.
If the woman does not experience any symptoms of complications after arriving home, then special medical supervision over the healing of the sutures is not required. The doctor will assess the condition of the tissues during a routine examination 1.5–2 months after birth.
If, due to birth injuries, a woman cannot sit, then this must be taken into account when planning discharge from the maternity hospital. The young mother will have to drive home in a reclining position, which means it’s better not to put anyone else in the back seat. Thus, there will be only one free seat in the car - next to the driver.
Removing stitches
In the case of using classic suture material, which does not dissolve on its own, the woman will have to undergo the procedure of suture removal. It is usually performed 4–5 days after birth and does not require pain relief. The sensations during its implementation resemble sharp pinpricks - they are often compared to plucking eyebrows. Doctor:
- prepares the rupture zone;
- cuts and removes threads;
- performs antiseptic treatment of the area.
Immediately after the procedure, a woman may feel a slight burning and tingling sensation, which quickly passes. Special medical supervision is not required in the absence of disturbing symptoms after removal of sutures.