Uterine rupture - main symptoms:
- Lower back pain
- Convulsions
- Nausea
- Lower abdominal pain
- Vomit
- Blood in urine
- Loss of consciousness
- Rapid pulse
- Uterine bleeding
- Pale skin
- Cold sweat
- Bloody vaginal discharge
- Weak pulse
- Swelling of the genital organs
- A sharp drop in blood pressure
- Hypertonicity of the uterus
- Stop pushing
- Painful contractions
- Frequent contractions
- Stopping contractions
What is uterine rupture
Uterine rupture is a severe complication of labor or pregnancy, in which the integrity of the walls of the uterus is disrupted. This condition is very dangerous for both mother and child. The main symptoms of this condition: too painful contractions, disruption of the urination process, bleeding, shock.
This pathology can be diagnosed after collecting and studying the woman’s history, as well as when characteristic signs are detected. If necessary, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination. Treatment consists of urgent cesarean section, midline laparotomy, or forced abortion. In this case, the doctor stops the bleeding, sutures the resulting rupture, or removes the organ altogether.
Today, this pathology in obstetrics is very rare, all thanks to modern equipment, which can be used to identify the disease in the early stages. This will help you choose the right method of delivery. Before labor begins, this can happen in ten percent of cases. In the first and second trimester, this deviation practically does not occur.
Obstetric tactics
Treatment of uterine ruptures is carried out only surgically, regardless of the stage of the pathology, period of birth, or gestational age (failure of the postoperative scar). The woman in labor is administered muscle relaxants, followed by tracheal intubation to stop labor. A caesarean section is then performed.
note
Obstetric tactics about 30 years ago, in the event of a threat of organ rupture and antenatal fetal death, consisted of performing a fetal destruction operation. Today, given the high traumatic nature of embryotomy and overextension of the lower segment, abdominal delivery is indicated (high risk of violent injury to the fetal sac).
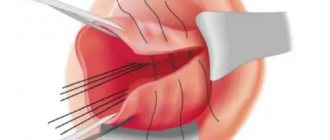
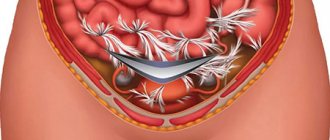
Surgery must be performed as quickly as possible. Surgical access – midline laparotomy. The extent of the operation is determined by the woman’s condition, stage and location of the damage. If possible, the uterus is preserved. During the process of transection, the fetus, placenta, and blood clots are removed from the uterus or abdomen. After removing the baby and placenta, the uterine walls are carefully examined, stitching together any damage found. When a rupture occurs, its edges are excised and the wound is sutured. If the wound on the organ is large and crushes the tissue, a hysterectomy is performed. After suturing or removing the uterus, an inspection of the abdominal organs is performed. If possible, autohemotransfusion is performed (transfusion of the patient's own blood after it is removed from the abdominal cavity and filtered).
Before, during and after the operation, measures for anti-shock therapy and replenishment of blood volume are carried out. Prevention and treatment of DIC syndrome and antibiotic therapy are also carried out.
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
8, total, today
( 41 votes, average: 4.71 out of 5)
Fetoplacental insufficiency
9th week of pregnancy: what happens to the baby and mother
Related Posts
Causes of uterine rupture
There are two factors that can influence the occurrence of uterine wall rupture during pregnancy:
- changes in the structure of the tissue of the uterine walls due to any pathologies;
- mechanical obstacles.
However, in medical practice, combined disorders are more common. We should not forget that there are also violent factors. Most of them relate to the deterioration of the woman's condition, which was not intentionally provoked by the hospital staff.
The main reasons for the gap are:
- various obstacles in the birth canal during the passage of the fetus;
- mechanical obstacles - narrow pelvis of the woman in labor, large size of the child, uterine fibroids, sexual infantilism;
- cervical erosion;
- changes in the myometrium associated with frequent abortions, curettage, scar formation after cesarean section, a large number of births;
- use of obstetric instruments (forceps, pedicle rotation, etc.);
- abdominal injuries sustained during pregnancy;
- lack of strength in a woman to give birth.
The appearance of such factors can be avoided if the internal pathological process in the uterus is detected in time. Rupture of the cervix during childbirth has extremely unfavorable consequences.
Classification
In medicine, there are many classifications of uterine rupture, but the most common is the Persianinov classification of uterine ruptures: it is used all over the world.
By time of appearance:
- during the period of bearing a baby;
- rupture of the uterine wall during childbirth.
Depending on the pathogenetic sign:
- spontaneous ruptures of the organ - mechanical, mixed or mechano-histopathic, as well as histopathic ruptures of the uterine wall;
- violent - traumatic, mixed.
According to clinical signs:
- threatening;
- started;
- accomplished.
According to the nature of the gap:
- tear;
- incomplete rupture;
- full.
By place of appearance:
- bottom of the organ;
- body of the uterus;
- lower segment;
- separation of the organ from the vagina.
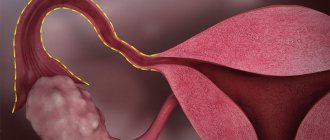
Complete rupture of the lower segment of the uterus.
Each type of rupture has its own signs, upon the appearance of which the doctor can make a diagnosis.
In addition, there are degrees of cervical rupture that have occurred:
- 1st degree cervical rupture – damage no more than twenty millimeters;
- cervical rupture of the 2nd degree - more than twenty millimeters, although they do not reach the vaginal vaults;
- 3rd degree ruptures reach the vagina and affect its vaults.
In addition, perineal ruptures are also classified in obstetrics.
Cervical rupture
In addition, the cervix is an important part in the reproductive system in terms of its functions:
- First of all, this is a protection function. It is thanks to its structure, as well as the mucus produced, which is a kind of barrier to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, as well as sperm. Only during the period of ovulation does the secretion acquire slightly different characteristics in composition allowing sperm to enter the uterine cavity, but the risk of contracting various infections also increases.
- In addition, the cervix is involved in the process of childbirth. During pregnancy, it protects the fetus and its membranes, as well as the placenta from pathogens. And subsequently participates in the process of the fetus leaving the uterine cavity. The birth process of a child largely depends on the condition of the cervix.
Cervical rupture is a fairly common pathology in obstetric practice; in gynecology it is much less common, and can only be associated with traumatic effects, as well as possible sealing of the myomatous node.
During childbirth, this pathology occurs more often. The risk group for cervical ruptures includes primiparous women; multiparous women have much fewer cases of ruptures.
Causes
The reasons can be very different, among them are:
- The presence of inflammation in the vaginal area and on the cervix itself, as well as chronic inflammatory processes in the uterus. Chronic cervicitis leads to the fact that the organ tissue becomes affected by infiltration, swelling appears and cells can disrupt their architecture. In some cases, when the process is neglected, sclerotic processes may develop, leading to impaired cell extensibility. The wall of the cervix not only stretches worse, it also opens poorly during labor.
- Age-related defects. With age, the amount of elastic tissue in the cervical tissue decreases. Moreover, this process is absolutely physiological, since it is inherent in all tissues of the body. Similar processes begin to occur from 30 to 35 years of age. This is why doctors recommend not delaying the birth of your first child.
- Scar changes. If a woman has a history of various surgical procedures in the cervical area, in particular these include diathermocoagulation, cryodestruction and laser vaporization, as well as suturing after a previous birth, the process of scar formation occurs in the tissues, i.e. connective tissue that is not subject to stretching.
- Development of cervical dystonia. This is a process in which blood circulation and lymphatic drainage in the cervix are disrupted due to disruption of the muscle fibers, which begin to stretch and contract unevenly. This condition leads to the fact that the neck begins to acquire greater density, mainly due to the circular type of fibers. Currently, it is considered as one of the forms of severe complications during childbirth - discoordination of labor. This not only causes ruptures, but also makes it difficult for the fetus to exit the uterine cavity.
- Presence of placenta previa. This is one of the forms of pathology, which is associated with the fact that the placenta begins to grow into the tissues to which it is attached and contributes to their softening. This happens with the cervix, where even with partial attachment to the cervix, there is a process of disruption in its structure.
- The occurrence of rapid labor. As a result, there is a process of increasing pressure in the uterine cavity, which does not correspond to the readiness of the cervix for this process. Due to the developing powerful pressure on the neck, tissue rupture occurs.
- Inadequate readiness of the cervix for childbirth. Most often, this is a medical error when the process of artificial delivery begins when the cervix is not fully ripe. Normally, the tissue of the cervix should soften and undergo gentle stretching as the child passes, but if the process of creating artificial attempts or introducing agents that stimulate an increase in tone begins, violent destruction of the tissue occurs.
- The process of tissue hypoxia. This is a fairly common reason, which is due to the fact that the head is located in the pelvic floor for a long period of time and disrupts blood flow, pressing the tissue against the bone ring. Most often, a similar picture is characteristic of the development of a narrow pelvis.
Such reasons are more typical when there is excessive load on the internal os, through which the process of giving birth to a child begins.
But in some cases, the rupture begins in the area of the external pharynx; this usually occurs when:
- The birth of a child with a large body weight. In this case, the size of the head, as a rule, also increases, and therefore, the tissues cannot always stretch properly. This group also includes the independent birth of children with defects, the most common of which is hydrocephalus.
- Incorrect position of the fetus when labor begins with the head in extension, as well as if extension occurs faster than necessary. In this case, the baby begins to move along the birth canal with its head, which is not the smallest diameter, which should happen normally.
- Rupture of the cervix can also occur due to surgical intervention on the tissue. The cause of the rupture can be obstetric forceps, a vacuum extractor, as well as the process of removing the child during a pelvic or breech presentation.
Risk factors
There are quite a lot of them, but they may not always lead to ruptures:
- First of all, this is one of the most rare pathologies in which there is a violation of the structure of connective tissue.
- It is also an innate infantilism. There is insufficiently active development of the cervix due to structural defects, as well as possible hormonal deficiency.
- The presence of diseases on the cervix, this includes not only erosion, but also dysplasia, as well as cancerous lesions.
- The presence of a tumor process in the area of the internal os, as well as on the neck itself.
Currently, experts distinguish several degrees of cervical rupture:
- 1st degree of rupture. This is a small damage to the cervical tissue on one or both sides, which is no more than 2 centimeters in length and is not accompanied by any clinical symptoms. In some cases, no additional treatment measures are required. Most of these needles heal by surface tension and do not show the development of cervical scar tissue.
- 2nd degree cervical rupture. This can cause gaps larger than two centimeters, but in the case of a healed one, one of the distinguishing features from a third-degree rupture is that the edges of the wound should not reach the area of the vaginal vault less than 1 cm. In this case, very often the ruptures are multiple and, as a rule, , linear. In this case, they will have an uncomplicated option and can be sutured by an obstetrician-gynecologist in the delivery room without the use of anesthesia. Externally, they may manifest themselves as bleeding; there will be a discharge of blood without the appearance of clots. It flows out in the form of a stream with a bright red color. After suturing, bleeding is easily restored and the risk of infection in such cases is low.
- 3rd degree. These are complicated ruptures in which there is a transition to the arches or beyond them. In this case, the most dangerous rupture is one that extends beyond the internal os or to the limits of the parametric tissue. In some cases, there may be a cervical rupture occurring circularly along the edge of the internal pharynx. In this case, a pronounced bleeding clinic develops. Blood can come out in a stream and form into clots; stopping such bleeding can be quite difficult. If there was previously pressure in the cervical area or there was crushing, then there may not be heavy bleeding. Also, scanty discharge with extensive lesions may be a consequence of internal baking of blood into the abdominal cavity.
Such conditions are considered serious organ damage and require surgical intervention with the transition to laparotomy. The procedures are performed under general anesthesia. In some cases, assistance from specialists in a related field may be required. In case of rupture, the woman feels severe pain in the perineum or lower abdomen. It can be so intense that it leads to painful shock.
Symptoms of uterine rupture
The uterus can rupture on its own, that is, spontaneously, or as a result of medical intervention, that is, forcibly.
Spontaneous occur due to:
- structural changes in the tissues of the uterine walls - abortion or postoperative scarring;
- various obstacles in the birth canal that prevent the fetus from moving forward.
Violence occurs during the birth process, when it is necessary to use obstetric forceps or other medical instruments.
An organ rupture is also distinguished by the area of damage, for example:
- complete, that is, the rupture occurs along all layers of the uterine wall and penetrates into the abdominal cavity;
- incomplete - the defect occurs only on the mucous and muscle layers, and the abdominal part is not affected.
If the mother’s pelvis is too narrow and the fetus is large, then the pathology has three types.
Threatened uterine rupture
It is characterized by:
- the integrity of the uterine walls is not broken;
- pain occurs, and the lower part of the organ is too stretched;
- swelling of the external genitalia and cervix appears;
- frequent and painful contractions.
Incipient uterine rupture
The following symptoms appear:
- layers of the uterine wall begin to rupture;
- contractions accompanied by pain and cramps;
- there is blood when urinating;
- the area above the womb begins to increase;
- blood is released from the vagina;
- The fetus is diagnosed with active movements, and its heartbeat slows down.
Complete rupture of the uterine wall
It can be defined like this:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- the skin becomes pale, cold sweat appears, the woman in labor loses consciousness;
- contractions stop;
- the pulse is palpable weakly;
- pressure readings drop sharply;
- vaginal bleeding begins;
- parts of the dead fetus can be discerned through the abdominal wall.
There are also three types when the uterus ruptures along a scar during pregnancy:
Threatening gap:
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting.
Started stage:
- increased muscle tone of the uterus;
- sharp pain upon palpation of the organ;
- frequent strong contractions with various breaks;
- vaginal bleeding;
- low fetal heart rate.
Accomplished:
- severe pain in the uterus;
- blood from the vagina;
- stopping pushing;
- low blood pressure and increased heart rate.
In any case, urgent medical intervention is required.
Diagnostics
Uterine rupture is diagnosed based on the collected history and visual examination of the woman. If necessary, an ultrasound examination is prescribed. Most often, an accurate diagnosis needs to be established in a short time, because this pathology develops very quickly and its treatment must be carried out without delay.
In a situation where a doctor makes an incorrect diagnosis based on symptoms, the risk of death for mother and child increases many times.
During the history taking, the doctor asks the following questions:
- the nature of the pain that appears;
- are there any discharges of various types from the vagina;
- sexual diseases that were previously;
- previous surgical interventions;
- the course of previous births.
Basically, the development of this pathology is easily determined before the onset of the birth process, and for this it is necessary to do an ultrasound examination. The results must be reported to the obstetrician-gynecologist who will deliver the baby.
During a physical examination of a pregnant woman suspected of developing this condition, pay attention to:
- blood pressure indicators;
- heart rate;
- heart rate.
The doctor also conducts:
- palpation of the abdominal cavity;
- gynecological examination to determine the size and muscle tone of the uterus, as well as the presentation of the fetus;
- ultrasound examination, if the above methods fail to make a correct diagnosis (ultrasound will show the thickness of the organ wall, visible violations of integrity, and indicate the stage of the rupture);
- cardiotocography.
Fetal cardiotocography.
It should be noted that pregnancy, if ruptures are detected, must be urgently interrupted by delivery, because any delay threatens the life of the mother and child.
Preventing the death of a child
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of a child’s death, but to do this you must follow the following rules:
• Mother and father must give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs) even before conception. • It is important to treat somatic diseases, chronic diseases, and urogenital infections before pregnancy. • It is necessary to establish the correct sleep and wakefulness regime, to create comfortable conditions for work and rest. • Expectant parents should eat right. • It is important to avoid stress. • Once pregnant, a woman continues to lead a healthy lifestyle, and her husband should support her in every possible way. • It is important to regularly undergo diagnostic tests in order to identify defects in time and take the necessary measures. • Future parents must find a qualified and trusted specialist who will manage pregnancy, childbirth and monitor the condition of the mother and child. Only by following these rules can death be avoided.
Treatment of uterine rupture
In any of the above cases, cervical ruptures require treatment with:
- Surgical intervention. This must be done so that delivery occurs as quickly as possible, so emergency care will be needed in case of rupture.
- You should also stop the bleeding that has started.
At any stage of development of such a pathology, doctors try to restore the volume of circulating blood through transfusion. Prevention of infectious complications is also necessary, and for this purpose antibacterial drugs are used.
If a woman experiences a threatening rupture of the walls of the uterus, the following measures are taken:
- Immediately stop labor so that no contractions of the organ occur. To do this, the patient is given muscle relaxants (they relax the muscles in the body) and general anesthesia is given.
- This is followed by a caesarean section or other medical procedure. It depends on the condition of the fetus, that is, on its vital activity.
- During the beginning and completion of a rupture, a median laparotomy is performed to carry out a complete examination of the uterine cavity and abdomen.
- In addition, this access to organs makes it possible to remove edges and close small tears.
- If the tears are too large, then the doctor decides to remove the uterus.
- Incomplete ruptures are treated in this way - the hematoma is emptied and hemostasis is carried out.
Only the obstetrician-gynecologist who examined the patient can select the correct treatment.
Preventing maternal death
Late toxicosis most often occurs in women under 20 years of age and after 35 years of age, due to genetic predisposition, chronic diseases, excessive physical activity or hormonal imbalance. If edema occurs or rapid weight gain occurs, the daily volume of fluid should be limited to 1 liter and the amount of salt. Doctors recommend switching to a dairy diet.
In case of severe edema and nephropathy, the pregnant woman is hospitalized, transferred to a salt-free diet, and the amount of fluid consumed is monitored. If there is a risk of preeclampsia and eclampsia, medications are prescribed: diuretics, sedatives and antispasmodics. The woman is in hospital until her condition stabilizes.
Eclampsia is a very dangerous condition that requires intensive treatment to normalize the functioning of important organs. If the woman’s condition does not improve within 3-12 hours, then a caesarean section is performed.
To avoid such complications, you should follow a diet. Allowed products: fermented milk products, cereals (buckwheat and oatmeal), herbs, vegetables, fruits. You should avoid smoked products, fried, salty foods, and chocolate. Doctors recommend swimming, avoiding stress and excessive physical activity.
There is a high risk of mortality during childbirth in women over 35 years of age with high blood pressure, fibroids, diabetes or excess weight. Such pregnant women should be under the supervision of a doctor, follow a diet, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
To prevent a woman's death due to infectious diseases, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs. To prevent severe bleeding, it is important to diagnose in time, identify the causes and eliminate them.
To stop bleeding after childbirth, a woman is given an injection of Oxytocin or the placenta is removed manually. If necessary, the woman in labor is hospitalized for a blood transfusion or surgery.
Death of women during childbirth is common when there is an obstacle to the passage of the fetus (incorrect position, narrow pelvis in a woman). A qualified doctor will quickly assess the situation and perform emergency surgery.
Thus, it is important to find an experienced and conscientious doctor who will manage pregnancy, childbirth and monitor the woman’s condition after childbirth. After all, the risk of death after childbirth is also quite high. A woman must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, lead a healthy lifestyle, be attentive to her health, and avoid stress.
Possible consequences
If a woman has a large rupture of an organ and she has lost a lot of blood, then she experiences a state of shock.
This is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- decreased blood pressure;
- pulse slows down;
- loss of consciousness occurs.
In such a situation, the pregnant woman should receive qualified medical care. If it is not provided on time, then the risk of death increases. It should be noted that women in labor die in ninety percent of cases. The reason for this is called hemorrhagic shock. It occurs when there is a large rupture in the walls of the organ and from severe blood loss. Then the rupture of the cervix has rather sad consequences.
The absence of signs may occur at the end of the second stage of labor. But there are still some symptoms - bleeding for unknown reasons. In this case, the child may be born dead or in serious physical condition.
In this situation, it becomes necessary for the doctor to conduct a manual examination of the uterine cavity.
Complications of this pathology are also dangerous because postpartum ulcers often form after them. Infectious diseases also appear in the postpartum period. If the rupture was not sutured during surgery, then tissue scarring occurs. They lead to inversion of the cervix, and pseudo-erosion of the non-mucosal membrane of the cervix develops. Other precancerous conditions may also appear.
Prevention
The prognosis for a pathology such as uterine rupture during pregnancy or during labor will depend on the following factors:
- severity of the rupture;
- amount of bleeding;
- timely treatment of the emerging condition.
If a pregnant woman has a complete rupture of the walls of the uterus, then the prognosis for the fetus is not very good, since placental abruption occurs.
Preventive measures should include reducing the risk of this pathology. That is, it is necessary to exclude factors that exert strong pressure on the walls of the uterus.
This condition can be prevented if a woman regularly visits her gynecologist at the antenatal clinic. If necessary, she will be given a full examination. If there is a threat of rupture of the uterine wall, then the attending physician will select the method of delivery on an individual basis.
What to do?
If you think you have a uterine rupture
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: a gynecologist, an obstetrician.
We wish everyone good health!
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Infant mortality - causes, statistics
Recently, the mortality rate during childbirth has been decreasing; in 2016 it was 5.8 cases per 1000 births. Infant mortality has decreased thanks to the federal program “Children of Russia” and the work of modern perinatal centers in 30 regions of the Russian Federation. Statistics of mortality during childbirth in Russia:
• 2008 – 11 deaths per 1000 births; • 2009 – 10 cases for the same number of births; • 2010 – 9.3 cases per 1000 births; • 2011 – 8.4 deaths; • 2012 – 8 cases; • 2013 – 7.4 deaths.
As can be seen from the figures, infant mortality is gradually decreasing.
Perinatal death (death during the period from 22 weeks of pregnancy to 7 days after birth) occurs in 35% of cases due to disorders of intrauterine development (various defects of the fetal organs). High mortality rate in premature babies weighing about 1.5 kg. But the death of a full-term, fully formed child is considered the most unfavorable.
There are many causes of death as a result of childbirth, which are divided into 2 groups:
• Conditions and illnesses of the mother that cause the death of the fetus. Reasons: premature placental abruption or discharge of amniotic fluid, gestosis, rapid labor or weak labor, etc.
• Conditions and diseases of the fetus that cause its death. Causes: malformations of organs (heart disease), diseases of the respiratory system (pneumonia in an infant), hypoxia or asphyxia, various infections (purulent infections). It often happens that a child dies during childbirth due to poor quality medical care. In addition, home births under the supervision of unskilled midwives have recently become popular.