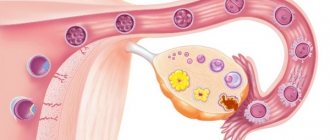
Empty follicle syndrome (EFS) is considered to be the absence of eggs in the follicular fluid if the patient’s blood concentration of estradiol is normal, the trigger was introduced efficiently, the ovaries respond well, and follicle aspiration was performed at the proper level. This syndrome was first described in detail in 1986. Caroline Colum, along with other specialists, noticed that conceiving a child is impossible due to the fact that there is no egg in the follicle. But they could not explain the mechanism of this action. Also, modern medicine has not even been able to answer this question.
Empty follicle syndrome
The presence of “empty” follicles can be reliably stated only by examining these dummies during IVF under a microscope.
Yes, the liquid obtained by puncture of the ovaries does not contain germ cells, as well as other parts that should be in a normal follicle.
That is, to put it simply, everything is a cyst! Fortunately, the likelihood of total cyst formation in a woman of reproductive age is low and occurs rarely. More often there is a mixture: full-fledged follicles and follicles “from a past life” (atretic, in which there are no cells).
In the 50-60s. of the last century, a certain scientist Rubin offers methods for indirectly determining ovulation - endometrial biopsy and functional diagnostic tests (measurement of basal body temperature, smears on the “hormonal mirror”). He was the first to identify empty follicle syndrome, as well as the possibility of immunological incompatibility between men and women.
Despite the fact that the formation and growth of a cyst itself occurs even in a completely healthy woman at a young age with an average frequency of 1-2 times a year, this discovery plunges women undergoing an IVF cycle into shock.
Remember, no one except reproductive doctors can ever see, either by basal temperature or by ultrasound, whether there is an oocyte in the follicle or not.
Accordingly, the possibility of oocyte abnormalities and empty follicles can never be ruled out in advance until the doctor obtains follicular fluid and examines it under a microscope.
It is designed in such a way that the body receives the command to “start the growth of eggs” from the higher centers of the head, but taking into account the opinions of the lower levels: the ovaries and other hormonal centers (including the adrenal glands and adipose tissue).
Therefore, associated problems: obesity, polycystic disease, endometriosis, adhesions increase the likelihood of cyst formation.
Stress is also dangerous for a young woman planning a pregnancy. Most people know that during World War II, many young women “fell into” anovulation, even to the point of missing menstruation due to stress, hard work and malnutrition.
Then there was simply no time for childbearing; it was necessary to forge victory over the enemy in the rear. In peacetime, a healthy woman may have stress and other, stronger priorities over reproductive tasks in this particular menstrual cycle.
These include quarrels with her husband, caring for parents, the transitional age of older children, and her own career ups and downs. Then, in a given menstrual cycle, it may not be growth, but a blockage of the production of germ cells. And, of course, more often this happens to a patient over 35 years of age.
(more details in the article “Getting Pregnant at Forty”)
USEFUL INFORMATION: How to take a scraping from the urethra for ureaplasma in men
It must be said that the hormonal background of the body is very dependent on the food and water that you have to consume daily, as well as on the presence or absence of vitamins.
Normalization of nutrition and metabolism is the most important task before IVF and during IVF treatment. Read about health improvement before IVF in the article “2-3 months before the protocol.” And don’t forget about your husband’s lifestyle, of course.
About this in the article “Preparing your beloved man for a successful protocol”
As you know, IVF is a rather complex and expensive procedure that takes a lot of time and money, but, alas, does not guarantee a positive result.
The reasons for failure can be different, both physiological and psychological. And if your doctor will help you sort out the first ones, then psychological problems, as a rule, remain unattended in the process of preparing for IVF. However, their influence on the result is very great!
- How to find out: is your infertility a consequence of psychological problems?
- How to eliminate the influence of negative psychological factors during the IVF process?
- How to increase your chance of IVF with psychological help?
Online diagnosis of psychosomatic causes of infertility in women will help you answer these questions. Based on the test results: identification of psychological barriers to pregnancy; recommendations from practicing psychologists.
Sign up for testing here.
Signs of ovulation
Monitoring sensations during ovulation not only increases the chances of pregnancy, but also helps a woman identify complications associated with the reproductive system.
Increase in basal temperature
Basal body temperature is the lowest body temperature at rest after prolonged sleep. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the indicator is just below 37 °C and, as it approaches ovulation, it gradually decreases to values of 36.3-36.5 °C. The process of egg release and a surge of progesterone increase the temperature to 37.1-37.3 ° C, and the fertile period begins.
Charting your basal body temperature is one of the most popular methods for tracking ovulation. Measurements should begin to be taken every morning before getting out of bed several months before the expected conception by inserting a digital thermometer into the rectum. The data is entered into a special chart, information from which helps determine the onset of ovulation in subsequent cycles.
Change in cervical mucus
Cervical mucus is a natural fluid in the female body that is produced in the cervix during the menstrual cycle. At the time of ovulation, under the influence of estrogen, the mucus acquires an elastic and transparent consistency, reminiscent of egg white. Thus, the body creates a favorable environment for sperm, which easily penetrate the barrier between the vagina and cervix.
What could go wrong
The process of egg development does not always occur normally. A situation may occur when in a particular menstrual cycle there are no follicles in the ovaries. What does it mean? In this case, the egg does not mature, which means that conception naturally becomes impossible. In addition, the menstrual cycle fails, and there is a lack of menstruation on time.
The absence of follicles can be either a temporary phenomenon or a sign of infertility. This is also one of the symptoms of the onset of menopause, when the resource of germ cells laid down in the prenatal period is depleted, or their maturation fails.
Disorders associated with the maturation of an empty follicle are also often observed. In this case, pregnancy is also impossible.
A slightly different situation - the growing follicle in the ovary does not burst or does not open completely
, that is, he becomes persistent. Such a violation also provokes cycle disorders, and the accumulated fluid in the sac can transform into a follicular cyst. Over time, when the process normalizes, the cyst resolves on its own, but with frequent failures of this kind, polycystic ovary disease develops.
Symptoms of egg ovulation
Most women do not feel the ovulation of the egg, but there are some signs that suggest the development of the process:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen: about 20% of women may experience pain in the lower abdomen, localized in the area of the burst follicle. It lasts several hours or a day, but if intense sharp pain appears, then this is a reason to consult a doctor;
- Increased libido: the most favorable days for conception are the period of egg ovulation, including a few days before and a day after. Therefore, nature provides for increased sexual desire for successful fertilization;
- Discharge: Some women notice an increase in thin vaginal discharge.
Deviations from the norm
If the quantitative composition of follicles in the ovary exceeds 10, this is considered to be a violation. Such a pathology can be diagnosed only by ultrasound results. Moreover, their number does not change at all over the course of the cycle. During an ultrasound examination, a large number of small bubbles are noted. If their number increases several times, the woman is diagnosed with polycystic disease. characterized by the formation of multiple follicular formations along the periphery.
Polycystic disease can interfere with the formation of a dominant element, the ovulation process and conception. The development of such problems can provoke nervous disorders and stress. In this case, polycystic disease does not require special treatment, and the deviations will easily return to normal.
However, in some cases, underdevelopment of follicular elements requires special therapy. These include the following:
- if oral contraceptives were chosen incorrectly;
- if endocrine problems occur;
- when gaining excess weight or, conversely, sudden weight loss.
If the follicles in the ovary are higher than normal, this does not necessarily mean that polycystic disease has developed or is a signal of any illness. It is likely that the reason for this was overwork, stress, and constant emotional overstrain. In this case, after the first ovulation their number returns to normal.
Since obesity can provoke follicular failure and lead to an imbalance in the functioning of the ovaries, women are advised to monitor their diet and pay due attention to physical activity. Every woman should regularly visit a gynecologist-endocrinologist
USEFUL INFORMATION: Recovery after removal of uterine fibroids
This will allow you to promptly identify the pathology and promptly begin to treat it.
Every woman must regularly visit a gynecologist-endocrinologist. This will allow you to promptly identify the pathology and promptly begin to treat it.
Only a gynecologist can determine why the follicles in the ovaries are formed abnormally from the norm after undergoing certain tests and a special examination.
Causes of Empty Follicle Syndrome
The mechanisms of this phenomenon remain not fully understood.
Possible causes include disturbances in folliculogenesis and the characteristics of the drugs administered. SPF is quite rare (approximately 0.045-3.4% of cases), but may be a marker of certain reproductive disorders. The absence of an oocyte in the follicular fluid aspirated from the preovulatory follicle occurs during puncture in both natural and stimulated cycles. Some researchers believed that this condition is not a syndrome, but a random event that cannot be predicted at the stimulation stage using ultrasound or hormonal testing. Other studies have suggested that SPF may be an indicator of impaired folliculogenesis, when early oocyte atresia occurs with an adequate response to stimulation. SPF was also associated with a violation of the properties of human chorionic gonadotropin administered as an ovulation trigger, but this version was later abandoned.
A number of studies have shown that using a GnRH agonist instead of hCG as an ovulation trigger has a beneficial effect on the production of mature oocytes. This may be due to the fact that administration of a GnRH agonist causes a peak in FSH release, promoting maturation of the oocyte nucleus and cumulus proliferation. In addition, this hormone stimulates the production of plasmin in the follicular fluid, which, in turn, activates collagenase, which ensures rupture of the follicle wall. The proliferation of cumulus cells promotes the detachment of the oocyte from the wall of the follicle before its rupture.
For a long time, the issue of prognosis of the fertility of such patients and the likelihood of repeated failures when attempting to obtain oocytes remained controversial. The retrospective study included 3004 follicular punctures. All patients were divided into two groups depending on the number of attempts (group 1 - one case of SPF, group 2 - more than one case of SPF).
All women underwent a complete examination of the reproductive system, including measurement of basal temperature, endometrial biopsy in the middle of the luteal phase of the cycle and/or determination of the concentration of progesterone in the blood serum, hysterosalpingography, postcoital test, and analysis of the partner's ejaculate.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Quota for IVF in the Krasnoyarsk Territory
Infertility of unknown origin was diagnosed if all indicators were within normal limits, and the absence of pathology was confirmed by the results of laparoscopy.
A total of 200 IVF cycles in 35 patients were analyzed. 89% were stimulated cycles. In the first group (1 case of SPF) 137 cycles were performed, in the second group (more than 1 case of SPF) - 63 cycles. The frequency of SPF was 19.7% in the first group, and 44.4% in the second group.
The age of the patients included in the study ranged from 25 to 48 years. It was found that in both groups, in women under 34 years of age, only one cycle ended with SPF. In those aged 35 to 39 years, repeated cases of SPF were noted in 23.5%, in patients over 40 years old - in 57% of cases.
All clinical pregnancies were observed only in the group of patients with a single SPF. Thus, the study once again demonstrated the obvious influence of such factors as a woman’s age on the quality of the obtained oocytes and the effectiveness of IVF programs.
When does ovulation occur?
In 90% of women of childbearing age, the menstrual cycle lasts from 28 to 32 days and is divided into three main phases: follicular, ovulatory and luteal.
Follicular phase
The first phase begins from the onset of menstrual bleeding and lasts for 10-14 days. Under the influence of hormones in the ovary, a certain number of primary follicles are activated and their maturation begins. At the same time, the uterus begins to prepare for pregnancy, initiating the formation of a new layer of the endometrium.
During the last five days of the follicular phase, one (in rare cases two) of the follicles separates from the cohort and continues its maturation to a dominant state. It is he who will subsequently release the egg for its passage through the fallopian tubes and subsequent fertilization.
Ovulatory phase
The levels of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, which reach maximum values at the end of the follicular phase, lead to the rupture of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg from the ovary into the fallopian tubes, from where it begins its journey to the uterus with the help of cilia pushing it. At the site of the burst follicle, a corpus luteum forms, which begins to produce progesterone and prepare the uterine mucosa for possible pregnancy.
The timing of ovulation varies from cycle to cycle and woman to woman, but usually occurs 14 days before the next period. The fertile period, taking into account the lifespan of sperm and egg, ranges from 12 to 24 hours from the moment the egg is released. The exact time of ovulation can be determined by charting your basal temperature and using an ovulation calendar.
Luteal phase
The fertilized egg moves to the uterus within 7-10 days, where implantation and development of the embryo occurs during its attachment to the wall. The corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone to maintain the pregnancy and prevent the release of new eggs. By 10-12 weeks, its main functions are taken over by the placenta, and it disappears.
If fertilization fails, the egg dies within 12-24 hours after ovulation. Hormone levels return to normal, and the corpus luteum gradually disappears.
In approximately 1-2% of cases, two eggs are released into the fallopian tubes during ovulation. This condition is usually observed in women over 35 years of age. Fertilization of two different eggs by two different sperm results in the birth of twins.
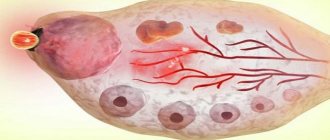
Dominant follicles and their role
The dominant follicle is the element that is the largest and most mature, providing protection to the egg ready for fertilization. Before ovulation, it is capable of reaching two centimeters in size. Usually located in the right ovary.
Having reached a state of maturity and being under the influence of hormones, the dominant follicle ruptures and the ovulation process occurs. The egg quickly moves to the fallopian tubes. If the dominant element does not mature, then there will be no ovulation.
There are situations when dominant formations mature in both ovaries at the same time. There is no need to worry about this. Most likely, such a woman has every chance of conceiving twins after ovulation. However, this is only possible if the dominant elements in both the right and left ovaries have both ovulated at once. This doesn't happen often.
Ovulation of the egg
Ovulation of an egg is a monthly process that occurs approximately in the middle of the menstrual cycle, but its physiological and pathological deviations cannot be excluded. After ovulation, the egg enters the abdominal cavity, but in order to prevent it from disappearing forever, the villi of the fallopian tube capture it inside. It is worth noting that the villi of the fallopian tubes receive information in advance where exactly the process will occur. Therefore, they immediately capture the egg after ovulation to prevent it from entering the abdominal cavity.
Ovulation of the egg is regulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary system and ovarian hormones. From the first day of the menstrual cycle, the maturation of several follicles begins, which stimulates FSH, but only the dominant follicle will complete the process. Gradually, the concentration of estrogen and LH in the blood increases, under the influence of which the egg ovulates.
After ovulation, the egg is located in the ampullary section of the fallopian tubes, and in place of the burst follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, producing progesterone. If the egg and sperm meet and fertilization occurs after ovulation, the corpus luteum is not destroyed and continues to synthesize the hormone necessary to prepare the endometrium and the woman’s body for future pregnancy. But if the egg is not fertilized after ovulation, then it is destroyed after 24-48 hours and is released along with menstrual blood, and atresia of the corpus luteum occurs.
During normal functioning of the body, the process of ovulation of an egg occurs at the same time every month. But under the influence of external and internal factors, everything can change: stress, physical activity, illness. climate change. Hormonal disorders, etc.
You can determine the onset of ovulation of an egg using a basal temperature chart, an express test, a blood test for LH, and an ultrasound of the ovaries. You can get a consultation and conduct the necessary research methods at the IVF Center clinic in Volgograd.
Persistent follicle
The question of what a follicle is is asked by those who have received a similar diagnosis. Pathology means that the formation of the dominant element occurred as it should until the very moment when it was supposed to burst. This did not happen and the egg, accordingly, is not released. Regardless of where the appearance of a persistent follicle was diagnosed on the right or left ovary, ovulation does not occur. The cause of the disease may lie in hormonal imbalances in a woman, in cases where the male hormone is present in excess. If you do not intervene in such a process in a timely manner, then the development of infertility is possible.
The essence of treatment comes down to hormonal therapy.
At the initial stage, medications are taken that will suppress male hormones in the body.
The second stage involves the introduction of hormones intramuscularly. In addition, it is necessary to carry out massage procedures, laser therapy, and ultrasound effects on the pelvic organs.
Viability of the egg after ovulation
After ovulation, the egg remains active and viable for 24 hours. If unprotected sexual intercourse occurs at this time, then the probability of successful fertilization after ovulation is quite high. It is worth noting that sperm are viable for several days (3-5 days), so if they entered the fallopian tube before ovulation and did not meet an egg, then they can wait for it for some time.
After ovulation, the egg is located in the fallopian tube, where, as a rule, fertilization occurs. If fertilization is successful, after ovulation a zygote is formed, which begins to divide and grow. After ovulation, the fertilized egg gradually moves through the villi of the fallopian tubes towards the uterine cavity and on days 5-7 reaches its destination and begins to look for a suitable place for implantation.
In most cases, only one full-fledged egg is formed after ovulation, but sometimes two dominant follicles mature, from which 2 mature eggs emerge. When two eggs are fertilized after ovulation, a multiple pregnancy is formed.