Follicle rupture occurs during ovulation, but sometimes it is completely unrelated to the process of maturation of the female gamete. In this situation, they speak of a pathology that has arisen. A newborn girl already has a set of follicles in her ovaries that are dormant. The maturation process begins only with the arrival of the first menstruation and will continue every menstrual cycle.
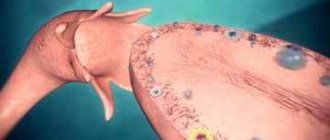
Each cycle, one dominant follicle matures. At a certain moment, its shell bursts (tears) and a mature egg emerges from it into the fallopian tube. This process is called ovulation.
But at the beginning of the cycle, under the influence of the FSH hormone, not one, but several dozen bubbles begin to mature. Then, many follicles die. Only one grows to a large size - the dominant one, which releases an egg ready for fertilization.
In this case, under the influence of hormones, the ovarian follicle ruptures. This is a natural physiological process that corresponds to ovulation.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
Each menstrual cycle (MC) consists of a follicular and luteal phase, they are separated by the period of ovulation. The first rules before the release of the egg, and the second after.
During the follicular phase of MC, the female body prepares for possible conception. During this period, under the influence of estrogen hormones, an egg matures in each follicular capsule.
Their number ranges from 10-15 pieces. But closer to the middle of the cycle, the dominant follicle is determined.
Usually it is significantly larger in size than others. It is from this that the mature egg will subsequently be released.
The remaining follicles stop their development. They shrink and disappear.
Also in this phase, thickening of the endometrium occurs. This is necessary to attach the embryo to the wall of the uterus in the event of conception. The duration of the follicular stage is individual for each woman and varies between 7-22 days.
After the egg has fully matured, the period of ovulation begins. This stage is also called the ovulatory phase. It lasts from 1 to 3 days. The body is preparing to rupture the follicle.
At this point, estrogen levels reach their maximum. The pituitary gland begins to intensively produce luteinizing hormone and its level rises sharply. About 17 hours after the LH surge, the follicle will rupture.
After the egg has been released, the reproductive system moves to the next level. The luteal phase begins. At the site of rupture of the follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which produces progesterone, the pregnancy hormone. The luteal phase, unlike the follicular phase, is stable and has the same duration - 14 days (/- 2 days).
Possible pathologies
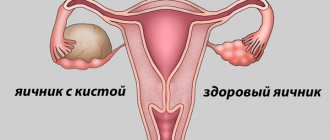
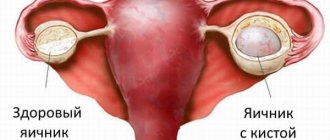
The process of follicle rupture or its absence can also be a symptom of pathology. If the membrane of the sac is very dense and does not burst, it means that the woman’s body produces too little LH hormone. Ovulation does not occur and the mature egg cannot be released. As a result, she dies, but the follicle continues to exist. This can lead to its degeneration into a cyst.
When the follicle luteinizes, the corpus luteum begins to mature in the sac that has not yet burst. The process occurs due to a violation of the sequence of its maturation.
Sometimes a ruptured follicle is confused with a ruptured follicular cyst. Such cystic formations, as a rule, resolve on their own within several cycles. Rarely, but still the cyst ruptures and then the woman needs urgent surgical intervention.
When a follicular cyst ruptures, a woman feels:
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen (it surrounds the lower back and radiates to the rectum).
- There may be loss of consciousness.
- Sharp decrease in blood pressure.
- There may be heavy bleeding.
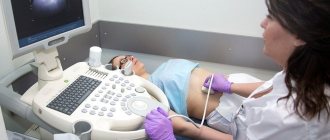
In some cases (to speed up the process) it is necessary to stimulate ovulation with hormonal agents. When an ultrasound shows the presence of a dominant follicle, in order to successfully resolve its rupture, a hCG injection is given (once). After this, ovulation occurs 24 hours later.
Main signs of ovulation
Currently, only a few women can boast of an ideal menstrual cycle. Due to the impact of negative factors on the body, the duration of menstruation often changes. This makes it more difficult to “catch” the day of ovulation. It is for this reason that it is important for every expectant mother to be able to recognize the signals that the body gives, notifying about the ability to bear children.
The ability to decipher the nature of cervical fluid (CF) can tell a woman a lot. Due to the fact that the fair sex is capable of childbearing for only a few days per cycle, the body produces a special secretion that creates favorable conditions for the viability and movement of sperm during this period.
In women, after the end of menstruation, a dry period begins or a slight dampness is felt, which can be compared to touching the inside of the cheek. About a week before the release of the egg, the cerebral fluid becomes sticky, and with each day approaching the day of ovulation they become more abundant.
After a few days, the sticky cervical fluid is replaced by a creamy or liquid substance. During this period, strong moisture is felt in the vagina, which can be confused with the beginning of menstruation.
1-3 days before ovulation, mucus appears, the main sign of the imminent release of the egg. When estrogen levels are at their maximum, the cervical fluid becomes very viscous, usually clear and reminiscent of the white of a raw egg. In addition to strong humidity, a lubricating effect appears. It is this moment that indicates the body’s readiness to conceive.
After the follicle ruptures, the nature of the secretion changes dramatically. This is due to a change in the dominant hormone: estrogen gives way to progesterone. A sudden change from moisture to dryness also indicates that the egg has been released.
The method of measuring basal temperature is considered indicative only if the basic rules of measurement are followed: the study must be carried out daily at the same time, without getting out of bed, without sudden movements, while the state of rest must last for at least 6 hours.
In the follicular phase, the temperature, as a rule, fluctuates between 36.2-36.5 °C (other normal indicators are also allowed, the main thing is that the total temperature difference between the first and second phases is more than 0.4 °C).
1-3 days before the release of the egg, the temperature drops by 0.1-0.4 °C from the average values of the first phase. When planning a child, these days it is worth starting to actively practice sexual intimacy.
After a few more days, the temperature will rise sharply by 0.4-0.6 °C. This means that ovulation has already occurred and the luteal phase has begun. Over the next 14 days (/- 2 days), the temperature will continue to increase or remain elevated due to the formation of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
If suddenly pregnancy occurs in the cycle, then the temperature will not drop, but will continue to remain at a high level throughout the entire pregnancy. If conception does not occur, then 1-3 days before the start of menstruation the indicators will decrease.
Sometimes sexual intimacy with the same partner in a certain position brings a feeling of discomfort one day, but on the other, it brings pleasure. These changes are directly related to the position of the cervix, which changes throughout the cycle: it lowers, then rises.
In its normal state, the cervix is closed, lowered and firm, like the tip of the nose. On the eve of ovulation, under the influence of estrogen, it rises, opens, becomes soft and moist, like lips. In such conditions, sperm can easily reach the fallopian tubes, where the egg is located.
When planning conception, it is recommended to have sexual intercourse exactly when the woman feels the main symptoms of approaching ovulation. You can also confirm your guesses using an ultrasound. Before ovulation, the dominant follicle is already fully formed. Its dimensions should exceed 18 mm, and the endometrium at this stage should be more than 10 mm.
Some women find out about approaching ovulation by individual symptoms. Such signs are secondary, since they do not appear in all girls or not in every cycle.
Secondary signs that may indicate readiness for fertilization:
- Enlargement of vaginal lips.
- Water is retained in the body.
- Increased level of vision or smell.
- Chest discomfort.
- Increased sexual desire.
- Performance improves.
- Bloating.
- Traces of blood. Before the egg is released, estrogen levels drop sharply, and progesterone does not yet have time to reach the required level. As a result, a small amount of blood may be released, that is, a small part of the endometrium.
- Painful sensations.
A small part of the fair sex feels when a period favorable for conception has arrived, let's describe the possible signs, symptoms and sensations on the day of ovulation. First of all this:
- Tingling in the lower abdomen on the left or right may be a symptom of a dominant follicle that has enlarged to its maximum, the membrane of which will burst in the near future.
- A sudden increase in appetite may indicate not only an increase in progesterone, but also hormonal changes that occur during ovulation.
- Bloody discharge - a few drops of light brown color indicate that the egg was released from the follicle 3-4 hours ago. However, such a symptom occurs only in a small number of women. And if intermenstrual bleeding is present, then it is necessary to make sure that it is ovulation that provokes it.
- Increased sexual desire is associated with changes in hormones and changes in the phases of the menstrual cycle.
- The appearance of stretchy transparent discharge. They have a consistency similar to raw egg white. During the period of ovulation, the “thread” of such secretions can be stretched to 5-7 cm in length.
If you plan sexual intercourse as ovulation symptoms appear, these attempts may not lead to pregnancy. The fact is that most signs appear when ovulation is either about to begin or has already occurred.
During this period of time, sperm may not have time to reach the fallopian tube (it takes them several hours to do this, but the egg lives only from 12 to 24 hours).
Signs of ovulation
Knowing some signs of a ruptured vesicle, a woman can understand that she will soon ovulate:
- The appearance of tolerable pain in the lower abdomen.
- Basal temperature drops and then rises again on the day of ovulation.
- Clear mucous discharge appears.
- A test for the LH hormone reveals an elevated level.
- Frequent mood changes.
- The breasts become more sensitive.
All symptoms disappear within a day or two after ovulation.
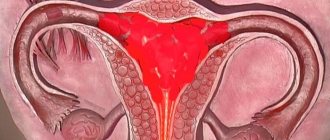
Sometimes, after a rupture of the follicle membrane, a woman experiences minor hemorrhage. This occurs due to the rupture of the blood vessels that fed the lining of the vesicle.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy
Symptoms largely depend on the form of apoplexy. The most common is mixed.
The most basic symptom is a pronounced pain syndrome, which usually appears in the middle of the cycle and coincides in time with the ovulation of the egg.
The pain is localized in the lower abdomen, but can also radiate to the external genitalia, the leg on the side of the rupture, the navel area and the rectum.
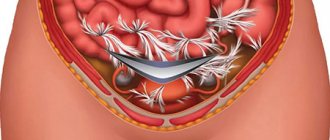
Since in the mixed form there is blood in the abdominal cavity that should not be there, it becomes irritated, usually manifested by nausea or vomiting.
The symptoms of mixed apoplexy are also largely similar to acute appendicitis or ectopic pregnancy, so the doctor must be extremely careful when making a diagnosis.
Along with the pain, signs of internal bleeding begin to appear over time: the patient’s skin turns pale, the pulse quickens, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, and body temperature can rise to 38°C.
In this case, the woman’s condition worsens quite quickly, so if you find similar symptoms in yourself or your loved ones, you should immediately call for medical help. After all, untimely treatment can lead to tragic consequences, including death.
Diagnosis of the disease
You can determine whether the egg has left its place of maturation by donating blood for hormones or using an ultrasound. Characteristic signs of the onset of the luteal phase include:
- Formation of the corpus luteum at the site of the burst follicle.
- Increased progesterone.
- The presence of free fluid behind the uterus.
- Absence of a dominant follicle.
- Transition of the endometrium to the required state.
Failure to ovulate once is not a cause for concern. Any healthy woman may not have the ability to conceive for up to two menstrual cycles. If the number of anovulation cycles is more than 2, then this indicates disorders of the reproductive system.
Signs of increased fertility help a woman navigate the functioning of her own body. Correct interpretation helps to facilitate the pregnancy planning process. This is often used when choosing the sex of a child.
Before treating the disease, it is necessary to carry out appropriate diagnosis. Patients are given a laboratory test to determine the presence of internal bleeding. In order to confirm the diagnosis, a representative of the fairer sex is prescribed a puncture of the posterior vaginal wall.