Sudden pain in the lower abdomen may mean a woman has ruptured one of her ovaries. Most often, this is the bursting of blood vessels and stromal tissue, Graafian vesicle, and corpus luteum cysts.
Gynecology refers to the condition as ovarian apoplexy; it is accompanied by pain and all the symptoms of blood loss. As a result of the rupture, the integrity of the organ is compromised, and hemorrhage occurs in the abdominal cavity. This is due to the location of the ovaries: they are located outside the uterus, hanging in the lateral cavities of the small pelvis, each is attached to it by the mesentery.
Can an ovarian cyst burst?
Ovarian cyst rupture occurs in patients of reproductive age. This phenomenon is due to the fact that apoplexy is associated with ovulation and follicle growth. If the release of eggs from Graaf's vesicle is impaired, the risk of the formation of pathological growths of ovarian tissue increases.
In gynecological practice, functional and other types of tumors are distinguished. Such a gradation is necessary to determine the treatment tactics for a woman. When functional formations are identified, there is a high risk of self-healing - resorption, possibly supplementing therapy with medications and folk methods. However, such tumors require monthly monitoring of the dynamics of the process: there is a risk of rupture of the pathological focus.
If other types of neoplasms are detected, surgical intervention is recommended. In such cases, the risk of complications is higher.
Attention! Rupture is more often provoked by certain factors. When determining appendage growths and deciding to monitor the formation, it is necessary to discuss with your doctor what not to do.
Ruptured endometrioid cyst
Endometrioid cysts are removed surgically due to the high probability of rupture of the cystic capsule and the possibility of transformation into a malignant formation.
A tumor of this type is predominantly located in the vicinity of large vessels supplying the ovary. Endometrioid formation on the ovary is not isolated; often foci of endometriosis are detected on the surface of the peritoneum, bladder and other organs.
Spontaneous rupture of an endometrioid cyst with spillage of contents into the peritoneum is dangerous for the development of intestinal paresis and adhesions.
Tumor perforation is characterized by severe, paroxysmal pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Possible loss of consciousness. There is also a weakening of intestinal motility and bloating. The patient's body temperature may be normal.
Rupture of ovarian cyst: ICD code 10
According to the generally accepted medical classification, non-inflammatory lesions of the uterine appendages are coded N83. This category includes all types of cysts and complications of the disease. Follicular tumors are designated N83.0, ruptured cysts of the corpus luteum of the ovary are designated N83.1. Code N83.2 includes other and unspecified types of adnexal vesicles.
Important! This gradation is used exclusively for medical workers and documentation, including sick leave.
It is important to know!
Follicular ovarian cyst (cysta ovarii follicularis) is a type of functional formation in ovarian tissue. A cyst is formed from folliculus ovaricus - a follicle that did not have time to rupture or burst.
ICD 10- This is the international classification of diseases, Tenth Revision. The document is used as the leading statistical classification framework in healthcare. It is reviewed every ten years under the guidance of WHO (World Health Organization). The International Classification of Diseases is considered a normative document that ensures the unity of methodological approaches and international comparability of materials.
Cyst of the left and right ovary according to ICD 10 refers to non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus and has code N83.
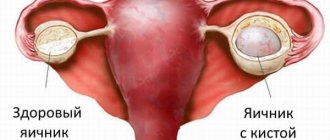
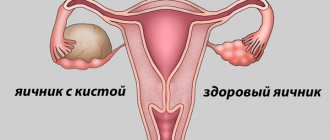
An ovarian cyst is a benign formation in the form of a capsule containing fluid inside.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors of the highest category perform diagnostics using innovative equipment, use modern treatment protocols and provide rehabilitation measures that shorten the recovery period.
Causes of ovarian cyst rupture
Rupture of a left ovarian cyst can be caused by the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance, manifested in disruption of ovulation processes;
- accession, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process of the appendages;
- physical overexertion, lifting heavy weights;
- rough sexual intercourse;
- injuries, falls, blows to the lower half of the abdominal cavity;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system.
In some cases, the tumor bursts without any special triggers: at rest, during sleep.
Attention! Patients with adnexal growths need to avoid the main causes leading to rupture of the formations.
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst in women
Signs of ovarian cyst rupture vary depending on the strength and severity of the complaints. Main symptoms:
- sudden sharp pain in the lower abdomen, often on the affected side, the attack of pain is stronger;
- discomfort spreads to nearby structures: perineum, rectum;
- Tension of the abdominal wall is noted;
- intestinal motility is disrupted;
- false urge to urinate or defecate appears;
- pulse increases, blood pressure decreases;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, dizziness;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- loss of consciousness.
Most symptoms are associated with blood and tumor contents entering the abdominal cavity. Without timely help, inflammation develops - peritonitis.
How to understand that an ovarian cyst has burst
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst vary depending on the severity and severity of the lesion. A rupture of a neoplasm of the appendages can be suspected when a stabbing pain appears on one side, gradually intensifying and spreading to the entire peritoneum. Typically, tissue tearing is provoked by physical activity, sexual activity, and injury. In any case, if uncharacteristic symptoms appear, it is necessary to seek consultation to diagnose the process and timely treatment.
Attention! More often, apoplexy in follicular formations occurs during ovulation. When the corpus luteum degenerates, rupture occurs in the second half of the cycle, with an increase in blood supply to the pelvic organs.
Pain when an ovarian cyst ruptures
When an ovarian cyst bursts, a woman feels a dagger-like sharp pain from the tumor. At this moment, hemorrhage occurs in the ovarian tissue. As a result of irritation of the peritoneum with blood and a reflex spasm of the vessels supplying the pelvic organs, the pain spreads to the entire abdomen. There is discomfort in the groin, epigastric area, and perineum.
Discharge from a ruptured ovarian cyst
A common symptom when a pathological vesicle bursts is a change in the type and amount of vaginal discharge. There is bloody, yellowish, whitish discharge from the genital tract. Bleeding usually does not correspond to the degree of impairment. Due to the huge number of diseases of the reproductive system that lead to such a symptom, it is not considered a characteristic sign of a cystoma. However, a change in the nature of the discharge against the background of a painful attack forces women to seek help and receive the necessary help.
Apoplexy of the ovary.
Ovarian apoplexy is a sudden hemorrhage into the ovary, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of its tissue and bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
SYNONYMS: Ovarian hematoma, bleeding from the ovary, rupture of a corpus luteum cyst, ovarian rupture.
ICD10 CODE
N83.0 Hemorrhagic follicular ovarian cyst.
N83.1 Hemorrhagic cyst of the corpus luteum.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Ovarian apoplexy is a disease of women of reproductive age. It ranks third in the structure of all acute gynecological diseases, accounting for 17%. Among the causes of intra-abdominal bleeding, apoplexy accounts for 0.5–2.5%.
CLASSIFICATION
Depending on the clinical form:
- painful, or pseudoappendicular, which is characterized by pain accompanied by nausea and fever;
- anemic, reminiscent of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy, in which the leading symptom is internal bleeding.
Both forms occur with equal frequency. A third form (“mixed”) has also been described, characterized by a combination of features of the first two forms. Since varying degrees of bleeding are observed in all cases of ovarian apoplexy, the division into these forms is not entirely legitimate.
In this regard, it is advisable to classify clinical forms of ovarian apoplexy according to the severity of the disease, determined by the nature and severity of pathological symptoms and the amount of blood loss.
Depending on the amount of blood loss and the severity of pathological symptoms:
- mild (blood loss 100–150 ml);
- moderate (blood loss 150–500 ml);
- severe (blood loss more than 500 ml).
This classification guides the doctor when choosing tactics for managing patients with ovarian apoplexy.
ETIOLOGY
Ovarian apoplexy can be caused by exogenous and endogenous causes. Endogenous causes include: incorrect position of the uterus, compression of blood vessels, leading to disruption of the blood supply to the ovary, compression of the ovary by a tumor, adhesions and inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
Predisposing factors include: previous inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, which lead to sclerotic changes in ovarian tissue and blood vessels. The role of endocrine factors, such as menstrual irregularities and drug-induced ovarian hyperstimulation, cannot be ruled out. Bleeding from the ovaries can be caused by blood diseases with impaired blood clotting and long-term use of anticoagulants.
Exogenous causes include violent sexual intercourse, horse riding, abdominal trauma, vaginal examination, surgery, and enema. However, in some patients, ovarian rupture may occur at rest or during sleep.
The risk of ovarian bleeding increases in patients taking anticoagulants for a long time.
PATHOGENESIS
Apoplexy can occur as a result of changes in the vessels and tissues of the ovary, which are facilitated by hyperemia, varicose, sclerotic vessels, inflammatory processes, and small cystic changes in the ovaries.
Bleeding from the ovary is preceded by the formation of a hematoma, which causes sharp pain due to an increase in intraovarian pressure. Then the ovarian tissue ruptures. Even a small tear (up to 1 cm in diameter) can lead to heavy bleeding. Ovarian apoplexy can occur in different phases of the menstrual cycle: least often in phase I, when the follicles are still at the stage of maturation and are poor in blood vessels, more often during the period of ovulation, in the stage of vascularization and flowering of the corpus luteum. A significant increase in the level of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland during ovulation and before menstruation leads to ovarian apoplexy. The most common source of bleeding is the corpus luteum or its cyst. The possibility of rupture of the corpus luteum during pregnancy cannot be ruled out.
CLINICAL PICTURE
The clinical picture is determined by the nature of the bleeding and the presence of concomitant pathology. Ovarian apoplexy is always accompanied by bleeding and pain.
Leading symptoms of ovarian apoplexy:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- bloody discharge from the vagina, usually quickly stopping after the disappearance of pain;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
Provoking moments:
- physical stress;
- sexual intercourse;
- injuries.
DIAGNOSTICS
The diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy is established on the basis of complaints, anamnesis and examination data. On examination - pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes, tachycardia, slight hyperthermia, blood pressure - normal or low. Slight bloating of the abdomen, pain on palpation on the affected side, and symptoms of peritoneal irritation of varying severity are noted. Ultrasound and laparoscopy are the most informative in diagnostics.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive safe method that allows you to identify physiological and pathological changes in the ovaries. Depending on the volume of blood loss, free fluid in the retrouterine space is determined in varying quantities.
Clinical and laboratory examination reveals anemia of varying severity; some patients have leukocytosis (from 9500 to 15,000/l).
Laparoscopic diagnosis is highly accurate (98%).
Considering that the manifestations of ovarian apoplexy are also characteristic of other acute diseases of the abdominal organs, it must be differentiated from:
- disturbed tubal pregnancy;
- acute appendicitis;
- torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst;
- intestinal obstruction;
- perforated gastric ulcer;
- acute pancreatitis;
- renal colic;
- pyosalpinx.
In rare cases, the diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy cannot be established even during surgery. More often this happens when an inflamed appendix is discovered during appendectomy, which is removed without first examining the uterine appendages. The clinic of ovarian apoplexy develops according to the type of acute diseases of the abdominal cavity, and therefore consultation with a surgeon and therapist is indicated.
TREATMENT
An important point in the treatment of patients with ovarian apoplexy is the most gentle tactics, which largely depends on the degree of intra-abdominal bleeding.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
In hemodynamically stable patients with the disappearance of peritoneal symptoms and a small volume of fluid in m/t, conservative treatment with observation. Conservative therapy includes: rest, cold on the lower abdomen, hemostatic drugs, antispasmodics, vitamins.
In case of massive intra-abdominal bleeding and hemorrhage into the ovary, reliable hemostasis requires removal of the ovary.
Conservative treatment must be carried out in a hospital under round-the-clock supervision. Deterioration of the general condition, the appearance of objective signs of internal bleeding or an increase in anemia are indications for surgical treatment.
Conservative management of patients with a mild form of apoplexy, the impossibility of removing blood clots and washing the abdominal cavity (i.e., everything that is possible during laparoscopy) leads to the development of adhesions of the pelvic organs, infertility and relapse of ovarian apoplexy. For mild forms of apoplexy, tactics are currently being reconsidered in favor of laparoscopy in cases where a woman is interested in preserving reproductive function.
Indications for emergency laparoscopy:
- complaints of pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of fluid in the pelvis, visible on ultrasound.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
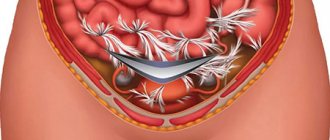
If necessary, diagnostic laparoscopy becomes therapeutic. Surgical intervention in patients with ovarian apoplexy is carried out using laparoscopic or laparotomic access. Currently, the main goal is the elimination of pathological changes while maintaining the integrity of the organs and reproductive function of the woman.
Surgery with laparoscopic access has significant advantages:
- psychological effect due to the absence of cosmetic defects and pain;
- quick recovery from anesthesia;
- early active behavior
- less use of analgesics in the postoperative period;
- shorter hospital stay after surgery;
- achieving full rehabilitation - reproductive function in women.
The question of the extent of surgical intervention for ovarian rupture is sparing intervention on the ovary. The basis is an understanding of the importance of the ovary as an endocrine and generative organ, which dictates the need to preserve any size of its functioning part.
The operation is performed as conservatively as possible. The ovary is removed only if there is massive hemorrhage that completely affects its tissue. If the corpus luteum of pregnancy ruptures, it is sutured without performing a resection, otherwise the pregnancy will be terminated.
Apoplexy can be bilateral. In this regard, during the operation it is necessary to examine both ovaries, fallopian tubes and appendix.
In women with ovarian apoplexy, during laparoscopy it is advisable to perform organ-preserving operations: hemostasis (suturing or coagulation of the ovary), evacuation and removal of blood clots, and less commonly, ovarian resection.
The following stages of endoscopic surgery for ovarian apoplexy are recommended:
- stopping bleeding from an ovarian rupture: coagulation, suturing or resection of the ovary;
- removal of blood clots from the abdominal cavity;
- examination of the ovary after washing the abdominal cavity with sanitizing solutions.
The duration of disability depends on the surgical approach: after laparotomy - 12 days, after laparoscopy - 7 days.
PREVENTION
Prevention of recurrence of cysts after surgical treatment can also serve as a prevention of ovarian apoplexy. They offer a three-stage management of patients with ovarian cysts:
- dynamic observation for three months;
- anti-inflammatory (absorbable) therapy, according to indications - the use of hormonal drugs;
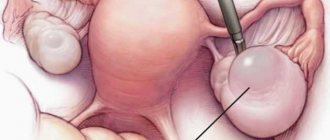
- puncture of a cystic formation under the control of transvaginal echography.
Diagnostics
Adnexal cysts can lead to serious consequences for reproductive health, so treatment must be started promptly, before complications occur. When the first signs of a neoplasm appear, you should immediately seek help from a gynecologist. Examination and questioning help the specialist make a diagnosis. The cyst and tumor rupture are clearly identified with the help of additional studies:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix;
- laparoscopy.
Important! Apoplexy of the right ovarian cyst occurs more often and is more complicated, which is associated with the blood supply to this area by a vessel extending directly from the aorta.
Laparoscopy
Using laparoscopy, diagnosis is carried out if the following conditions are noted:
— the patient’s condition is assessed as average (in severe forms of the disease, laparoscopy is not performed)
- absent: fever, high temperature, acute inflammatory processes.
So, in gynecology, specific symptoms and methods of diagnosis are indicated: apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary. It should be noted that differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude errors. This is due to absolutely similar symptoms of ectopic pregnancy and hemorrhage into the appendage. However, if the patient’s condition is serious, urgent surgery is indicated in both cases.
What to do if an ovarian cyst bursts
A ruptured capsule of an ovarian cyst cannot be treated at home. If you have symptoms reminiscent of rupture of tumors on the appendages, you should seek help. Some women report some improvement after the sharp pain when the tumor bursts. In fact, this phenomenon is temporary; doctors call this symptom a “light period”. The body initially copes with the bleeding, and health improves. Afterwards, a breakdown in compensatory capabilities occurs, the condition worsens sharply, without assistance at the moment there is a high risk of death.
Important! If you suspect a ruptured vesicle on the appendages, seek medical help immediately.
Emergency care for a ruptured ovarian cyst
Usually, when a painful attack occurs, which is the main symptom of rupture of a neoplasm of the appendages, patients take antispasmodics and painkillers at home. If a woman knows about the diagnosis and is warned about the possibility of rupture, these drugs are always in the medicine cabinet. However, it is advisable to refrain from taking medications, ensure rest and take the woman to the nearest hospital for treatment.
With an ovarian cyst, rupture with hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity is especially difficult. In this case, it is necessary to lay the patient down and give cold to the stomach. It is not advisable to take medications until the ambulance arrives. Drugs can distort the clinical picture and make it difficult to assess a woman’s condition.
What is Ovarian Apoplexy? Symptoms, causes, classification and complications
Ovarian apoplexy is a gynecological problem that any woman can face. It is a rupture of organ tissue as a result of excessive pressure in the peritoneum. If in such a situation the vessels are damaged, internal bleeding opens, which poses a high health hazard.
Ovarian apoplexy
Ovarian apoplexy is an injury to the reproductive organ. Most often it occurs with increased fertility or at the stage of transformation of the follicle into the corpus luteum.
As a result of tissue damage, bleeding occurs, which contributes to the development of anemia. If measures are not taken in time, the consequences can be disastrous. One of the most common complications is loss of reproductive function.
In the absence of competent assistance, the risk of death increases.
Ovarian apoplexy
The ovaries are paired organs, 2 cm wide and 3 cm long.
They are responsible for the process of egg formation, regulating the level of sex hormones. During ovulation and before critical days, they increase in volume and become more vulnerable.
Under certain circumstances, organ rupture may occur, followed by bleeding into the peritoneum. The woman’s condition is directly dependent on which part of the appendage is damaged.
Apoplexy can spread to the ovary itself and to cystic formations or follicles.
Healthy ovaries in women (Left section)
Ovarian apoplexy - ICD code 10
N83.0 Follicular ovarian cyst.
- Graafian follicle cyst Hemorrhagic follicular cyst (ovarian)
N83.1 Corpus luteum cyst
- Hemorrhagic cyst of the corpus luteum
N83.2 Other and unspecified ovarian cysts
- Retention cyst } Simple cyst } of the ovary Excluded: ovarian cyst: . associated with a developmental anomaly (Q50.1). neoplastic (D27) polycystic ovary syndrome (E28.2)
N83.3 Acquired atrophy of the ovary and fallopian tube
N83.4 Prolapse and hernia of the ovary and fallopian tube
N83.5 Torsion of the ovary, ovarian peduncle and fallopian tube
- Twisting: . additional pipe. Morgagni cysts
N83.6 Hematosalpinx
- Excluded: hematosalpinx with: . hematocolposome (N89.7) . hematometer (N85.7)
N83.7 Hematoma of the broad ligament of the uterus
N83.8 Other non-inflammatory diseases of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus
- [Masters-Allen] broad ligament rupture syndrome
N83.9 Non-inflammatory disease of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus, unspecified
Classification of the form of ovarian apoplexy
To choose the right treatment, you need to correctly determine the form of the pathology. Apoplexy is classified depending on the intensity of the pain syndrome and the nature of the hemorrhage. The following types of rupture are distinguished:
- Anemic (hemorrhagic);
- Painful (without blood flow into the abdominal cavity);
- Mixed.
With painful apoplexy, the vascular cavity is damaged, but blood does not penetrate into the abdominal cavity. In this case, discomfort in the peritoneum is present, but no changes in general well-being are observed. In the mixed form, a painful type of rupture first develops, and then it transforms into hemorrhagic.
The anemic type of apoplexy is considered the most dangerous, as it is accompanied by hemorrhage. When internal bleeding occurs, there is a risk of hemorrhagic shock. It is accompanied by a lack of oxygen to vital organs.
Depending on the amount of blood lost, it can be:
- Light weight (50-150 ml);
- Moderate (300-500 ml);
- Severe form (more than 500 ml).
Ovarian apoplexy - causes
Normally, any natural processes involving the organs of the reproductive system should not cause discomfort to a woman. In the middle of the cycle, the egg is released, and after 2 weeks the critical days begin.
These processes contribute to an increase in the volume of the appendages and increased blood circulation. Apoplexy develops when excessive pressure is placed on enlarged organs.
Factors contributing to the development of the pathological process include:
- Problems with blood clotting;
- Adhesions in the genital area;
- Abnormal location of the uterus and appendages;
- Intense physical activity;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Active sexual intimacy;
- Deviations in vascular patency.
Women with polycystic syndrome are most susceptible to apoplexy. In this case, several follicles mature in the appendages at once, which significantly increases their volume. No less common causes of rupture also include inflammatory processes and infectious diseases.
Read more about polycystic disease here.
Ovarian apoplexy - symptoms
A rupture is always accompanied by pronounced symptoms. The main signs of pathology include severe pain in one of the appendages. Most often it is acute. When moving, the pain intensifies. The more blood fills the peritoneum, the more pronounced the discomfort will be. Other symptoms include:
- Loss of consciousness;
- Thirst and drying of the oral mucosa;
- Blood pressure surges;
- Increased urge to urinate;
- Change in skin color;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Bloating and flatulence;
- Pain shock;
- Dizziness;
- Copious vaginal discharge of a bloody nature.
Ovarian apoplexy - emergency care
When a woman develops acute abdominal pain, prompt hospitalization is required. Emergency care algorithm for ovarian apoplexy:
- Lay the woman down on a flat surface;
- Urgently call an ambulance for hospitalization;
- It is forbidden to give painkillers at home in order to make an accurate diagnosis in the clinic;
- You should not apply heat or ice, so as not to distort the picture of the attack for doctors.
Diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy
If an ovarian rupture is suspected, the patient must be hospitalized. The success of medical procedures depends on the speed of contacting doctors. Therefore, diagnostic measures must be carried out as soon as possible. Making a diagnosis rests on the shoulders of a gynecologist. It is based on the results of the following studies:
- Oral history taking;
- Preventative examination on the chair;
- Posterior fornix puncture;
- Standard laboratory examination of blood samples;
- Determining the amount of hCG to exclude pregnancy;
- Ultrasound monitoring;
- Laparoscopy.
Anamnesis
Read more about HCG here
Article about Laparoscopy.
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy
Despite the fact that apoplexy causes severe pain, taking painkillers before diagnosis is not recommended. This may complicate diagnostic measures.
The treatment method is selected based on the form of the pathology. If the hemorrhage is minor, conservative therapy is carried out. It involves taking vitamins and antispasmodics.
During the treatment period, the woman is prescribed bed rest with limited physical activity.
To relieve pain, medications are administered intramuscularly. Injections help relax muscles and supply oxygen to the tissues of the genital organs. The most common drugs with an analgesic effect include:
- No-shpa;
- Buscopan;
- Papaverine.
Papaverine tablet
In order to accelerate the recovery of platelet levels, hemostatic drugs are prescribed. Among them are Ambien, Etamzilat and Tranexam. To improve blood clotting, taking vitamins B12, B6 and B1 is indicated. To prevent the development of iron deficiency anemia, it is necessary to take supplements containing iron.
Surgical treatment is carried out laparoscopically. The operation is considered low-traumatic. During this procedure, the peritoneal cavity is cleared of formed blood clots and the destroyed tissues are sewn together. Bleeding is stopped by cauterizing damaged vessels.
In case of increased blood loss, removal of the appendage or part of it is possible. The duration of recovery is determined by the type of apoplexy. On average it varies from 2 to 4 weeks. During this period, it is recommended to take medications that stabilize the psychological state.
Ovarian apoplexy - consequences
In the absence of timely assistance, ovarian rupture can contribute to hemorrhagic shock. It develops when there is excessive blood loss. In such a situation, the risk of death and loss of fertility increases.
If hospitalization measures are taken on time, it is possible to preserve the reproductive functions of the appendage. Early detection of the problem provides a favorable prognosis.
Long-term consequences of the pathological process include:
- Formation of adhesive process;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- High probability of relapse;
- Decreased fertility.
Ectopic pregnancy
Prevention of ovarian apoplexy
After injury to an organ, the risk of relapse of the pathological process increases. You should think about prevention during the rehabilitation period. To avoid the appearance of adhesions in the pelvis, the woman is prescribed a course of physiotherapy and medication based on hormones. In the future, it is extremely important to take the following measures:
- Visiting a gynecologist every six months;
- Limiting physical activity and heavy lifting;
- Prevention of STDs and inflammatory processes;
- Avoiding hypothermia of the genitals;
- Use of contraception for six months;
- Annual ultrasound examination;
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Ovarian apoplexy leaves a negative mark on the reproductive system. After a treatment course, a woman should take more care of her health. This will avoid re-rupture and other complications. With a reasonable approach, most women manage to successfully become pregnant after apoplexy and bear a healthy child.
Source: https://Ovulyaciya.com/zhenskoe-zdorove/chto-takoe-apopleksiya-yaichnika
Treatment of ruptured ovarian cyst
To prescribe therapy, it is necessary to establish the presence of a rupture, determine the predominant symptom, and the severity of hemodynamic disturbances. The main criterion that determines the patient’s management tactics is the amount of blood loss. The more massive the bleeding a woman has, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease. To confirm the severity of the condition, special studies are carried out.
Conservative methods
If an ovarian cyst ruptures, treatment without surgery is carried out exclusively with a confirmed painful form of apoplexy. In most cases, the main symptom of the disorder is pain; bleeding in this case is minor. The wound is small and quickly closes with a blood clot.
Conservative therapy is reduced to taking antispasmodics, painkillers and hemostatic agents. During the treatment period, the patient adheres to strict bed rest. If there are positive dynamics, treatment is continued until the symptoms disappear. If signs of deterioration appear, the patient is prepared for surgery.
Surgical methods
In most cases, if there is a rupture of the ovarian tissue tumor, surgery is performed. The scope of surgical care is mainly determined immediately at the time of the procedure. If the damage is minor, tissue can be sutured and the tumor capsule can be peeled off. If it is not possible to stop the bleeding and the organ becomes saturated with blood, it is necessary to remove the affected ovary. A ruptured right ovarian cyst is usually repaired laparoscopically.
Important! If signs of rupture appear, you should not self-medicate. Even conservative therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the close supervision of a doctor.
What is the danger of a ruptured ovarian cyst?
When a tumor bursts, the contents of the capsule and blood enter the abdominal cavity, irritating the nerve endings and causing inflammation of neighboring structures. Bleeding and peritonitis are the most severe conditions that occur when a woman does not seek treatment at the hospital.
Consequences of a ruptured ovarian cyst
With timely assistance provided when the formation bursts, serious violations can be avoided. When a cyst on the ovary ruptures, the consequences may be as follows:
- peritonitis;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- sepsis;
- increased formation of adhesions;
- higher risk of ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility;
- death.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the clinic and examination data. The doctor notes obvious signs of the disease, and it is important to distinguish an actual ovarian rupture from an ectopic pregnancy, which manifests itself with the same symptoms. An ectopic pregnancy always threatens a woman’s life.
If a woman lives an intimate life, she should immediately tell the doctor about it. A threatening condition is caused by all pathologies with characteristic symptoms: rupture of the appendage, ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis. This is why accurate diagnosis is extremely important.
Recommendations and tips
Rupture of an ovarian cyst, the symptoms of which vary depending on the degree of damage to the tissue of the appendages, can occur in any woman. To avoid complications, it is necessary to be constantly monitored by a gynecologist, promptly treat cycle disorders, and diagnose growths on the appendages. If a cyst is detected, it is advisable to follow all the doctor’s instructions and avoid things that provoke rupture. If symptoms appear that the tumor has burst, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. In most cases, treatment is surgical.