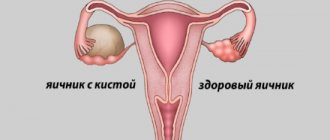
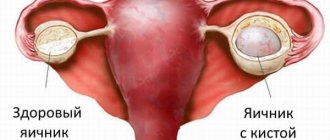
The technology of laparoscopic surgery in modern surgery of tumors on human tissues is positioned as one of the highest quality methods for eliminating tumors. This is the only type of operation that allows all abnormal formations to be cut out with the slightest damage to the body, and the patient to recover in the shortest possible time. In a short time, if certain conditions are met, menstruation returns after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst.
What is better - laparoscopy or surgery?
The main advantage of laparoscopic intervention is its minimal invasiveness. This means that there is no need to make a large incision to penetrate the affected tissue and cut off the formation. Thus, no significant harm is caused to the body - unlike other methods of surgical intervention.
Most other radical surgical methods are performed by open penetration to the source of the disease. Ovarian cysts were treated in the same way a few decades ago. After such operations, a woman, as a rule, lost not only the pathogenic body in the reproductive system, but also part of the problem organ. Because of this, the operated woman often had painful periods after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, she lost the ability to procreate and suffered chronic consequences in the form of hormonal imbalances and inflammation of the genitourinary system.
The open method of surgery is also dangerous because it takes a lot of time to restore the body. Along with this, brown discharge is often observed; after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, this is rare.
If laparoscopy is performed with maximum precision for only 30-40 minutes, then open surgery requires special preparation from the patient. A woman is required to take many different tests and undergo a number of narrow examinations. In addition, after open radical surgery on the ovaries, a woman, as a rule, recovers from several months to six months. After menstruation has failed after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, the menstrual cycle returns only 3-4 months after removal of the tumor. And this is provided that the operation to remove the cyst took place without adverse reactions.
Compared to open surgery, the laparoscopy technique looks very advantageous. In the entire history of this type of surgery, only a small percentage of patients, after cure, experienced symptomatic signs of relapse, delayed menstruation after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, or inflammation. Menstruation after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is almost never delayed. If this happens, it is due to the presence of other side ailments in the body.
Life with one ovary, what changes occur in the body after removal of the ovary
Many women faced with the need for an oophorectomy wonder how to live with one ovary. Such operations are performed quite often in modern surgical practice. This is due to the fact that the number of gynecological diseases requiring surgical treatment is increasing every year.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards rejuvenation of women who require ovary removal. Doctors are trying in every possible way to avoid surgical treatment of patients who are still planning a pregnancy. However, complex gynecological diseases and pathologies cannot be eliminated without surgical intervention.
So, without surgery it is difficult to get rid of such diseases:
- malignant tumors;
- some types of endometriosis;
- purulent lesions of the appendages and uterus.
What happens to hormones after oophorectomy?
Although the ovaries are small reproductive organs, their importance cannot be overestimated. These organs not only store eggs, but are also responsible for the production of female and male hormones. Life with one ovary changes significantly due to hormonal changes. Ovariectomy leads to changes in the condition of the entire organism.
The fact is that reproductive hormones affect all organs of a woman, including the state of the nervous system. They support healthy hair, skin and nails, and are also responsible for reproductive function. After surgery, the concentration of hormones in the patient’s blood sharply decreases.
Of course, their production does not stop, however, other organs are involved in this and are unable to maintain the number of hormones at the required level.
Postoperative consequences directly depend on the woman’s age. So, if the patient is in the menopause, we can say that the resource of eggs has already been exhausted. Therefore, if one of the organs is removed, the consequences in this case will not be particularly noticeable.
Please note: In postmenopause, the genitals practically lose their functionality, so women who have crossed the age of 50, if necessary, have their ovaries removed without hesitation. Such an operation can even be of a preventive nature.
For patients who are of childbearing age, doctors are in no hurry to prescribe surgery, so they first try to carry out drug treatment. If surgical intervention cannot be avoided, specialists perform organ-preserving surgery.
There are good reasons for this, because it is important to preserve a woman’s ability to conceive and give birth to a child, and also not to disrupt hormonal levels.
Of course, any operation is a severe stress for the female body, however, if doctors manage to preserve the organs as much as possible, life will not be so difficult for the patient.
Impact of surgery on health
After surgery, many women experience such an unpleasant consequence as post-castration syndrome. It is worth remembering that it is not observed in everyone and can have a fairly mild course. For approximately 25 percent of patients, the quality of life with one remaining organ does not change at all.
However, for some, post-castration syndrome can be quite intense. All this depends on the individual characteristics of the body. There are three groups of disorders that may accompany the postoperative period.
Typically, the first signs of this process are observed 2-3 weeks after surgery, and they become more pronounced after a few months.
The group of disorders includes the following symptoms:
- hot flashes, especially at night;
- increased sweating and feeling of chills;
- headaches and dizziness;
- hypertension and constant pressure surges even at rest;
- feeling of general weakness and fatigue;
- mood swings and irritability;
- worsening sleep and insomnia;
- decreased or complete loss of libido;
- violation of memory processes.
All these reactions begin to disappear a year after removal. Due to hormone deficiency, some patients experience sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system.
Women often suffer from vaginal dryness, discomfort in the pelvic organs, frequent urination and discomfort during sexual intercourse. Rarely, but still there are cases of disruption of other mucous membranes.
Thus, conjunctivitis, intestinal dysfunction and dry mouth occur.
If a woman has undergone bilateral surgery, the manifestations of post-castration syndrome become more obvious. Such patients face more significant hormonal imbalances.
The body stops producing sex hormones in the required quantities, which leads to atherosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, circulatory disorders, osteoporosis, deterioration of the skin and hair, and other undesirable consequences.
Treatment after surgery
After removal of one of the ovaries, treatment necessarily includes hormonal therapy. This therapy allows you to adjust the level of estrogens and progestins, the amount of which most often decreases due to the fact that one ovary has stopped producing them.
If the operation was performed for oncological indications, hormonal treatment is not prescribed. In this case, sex hormones can be stabilized using homeopathic medicines.
Drug treatment after unilateral oophorectomy must be combined with a healthy and active lifestyle.
As a rule, after just a few cycles, operated patients are able to restore menstruation. Menstruation after removal of the ovary proceeds in the same way as before, however, the process of egg development and ovulation occurs only on one side, and not alternately. It is important that the remaining organ is completely healthy and performs its functions.
Important! Often, patients with one ovary experience menstrual irregularities. This is due to the fact that the remaining ovary has to compensate for all the work. If previously the ovaries worked alternately, now all processes occur on one side. The remaining organ uses up its resource faster, which can lead to hormonal imbalances.
All this is corrected by artificial hormones. However, it is worth remembering that hormonal therapy cannot last long. Therefore, women who have undergone surgery are advised to plan pregnancy as soon as possible after their cycle resumes.
When to plan a pregnancy
The question of the possibility of conceiving a child with one ovary very often interests women. Of course, any operation on the pelvic organs can lead to infertility, especially if it is performed incorrectly or complications are observed.
Modern surgery makes it possible to make the removal of one appendage and ovary very safe for a woman’s health.
If no negative consequences from oophorectomy are observed, and hormonal therapy has allowed the second ovary to completely take over the functions of two organs, no noticeable changes will occur in the patient’s life.
In this case, menstrual cycles will be restored, and ovulation, as before, will occur every month. The only difference is that the remaining organ will exhaust its resource faster, because it will have to release eggs not every month, but every cycle.
Based on this, doctors recommend not delaying the conception of a child, especially if there are no concomitant diseases and postoperative complications. If you delay pregnancy for a long time, you can wait until the ovary gets tired and stops ovulating.
Please note: According to statistics, menopause occurs earlier in patients with an organ removed than in healthy women. Menstrual function is disrupted and it becomes impossible to conceive a child.
If a woman is healthy and an ultrasound confirms the presence of ovulation, doctors recommend not postponing pregnancy.
Of course, this does not mean that you need to conceive a child in the next year, however, you should not wait too long. If pregnancy has occurred, it is very important to make sure that it is progressing normally.
It has been statistically found that after unilateral oophorectomy, the risk of ectopic attachment of the fetus increases significantly.
To summarize, it must be said that not all women with an ovary removed experience changes in quality of life.
In most cases, such an operation has little effect on the patient’s health, provided that it is performed correctly and postoperative treatment brings positive results.
The menstrual cycle is restored quite quickly, because a healthy organ begins to be responsible for the production of the required amount of hormones. This allows a woman to conceive and bear a healthy baby.
Source: https://ProYaichniki.ru/zdorove/zhizn-s-odnim-yaichnikom.html
The importance of laparoscopy in cystic diseases
First of all, it is worth noting that this method of surgical treatment of benign tumors is used not only in the gynecological field. It is indispensable in many other cases of diagnosing abnormal formations in the human body.
Laparoscopy is useful for several reasons:
- Versatility. This type of procedure is used not only to eliminate abnormal formations and tumors. Laparoscopy is also indispensable in the treatment of various types of adhesions and connecting elements that form in the human body and often cause a delay in ovarian cysts and inflammatory processes after laparoscopy.
- Highest efficiency. Laparoscopy is especially useful in the treatment of female infertility, which most often develops due to chronic polycystic diseases or the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. In such cases, the follicles cannot penetrate the uterus and carry out fertilization. Laparoscopy allows you to solve the problem quickly and as safely as possible.
- Accuracy. Laparoscopy is useful not only for surgical intervention, but also for diagnosing complex diseases that cannot be detected by ultrasound scanning or tomography. During laparoscopy, along with eliminating the anomaly, the doctor has the opportunity to analyze the possible consequences of laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst in order to prevent them in advance.
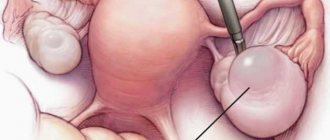
Principles of cyst excision during laparoscopy
It is worth saying that laparoscopy is performed after a complete examination of the patient’s body. The effectiveness and quality of the operation performed is directly influenced by the skill and professionalism of the doctor.
The main essence of laparoscopy is that this type of operation eliminates major tissue damage.
The operation is aimed at eliminating abnormal tissues and appendages as painlessly as possible without compromising the integrity of healthy organ tissues. The less damage and shock to the body during surgery, the faster the patient can return to a normal and healthy life. Due to the low invasiveness, the patient experiences only minor pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
It is worth remembering that in some cases laparoscopy saves from a fatal outcome of the disease. This happens when the cyst is on the verge of rupture and can burst at any moment. Rupture of a cyst is dangerous due to infection of healthy organs and tissues and intoxication of the abdominal cavity. Surgical intervention in the event of a threat of rupture is carried out under the constant vigilant supervision of an ultrasound scanner and camera.
The slightest incorrect cuts and manipulations can damage the capsule tissue. In this case, discharge after laparoscopy may be caused by ovarian cysts, spreading of fluid into the area of the problematic ovary or genitourinary system. To prevent such consequences and pain after laparoscopy, ovarian cysts a month later, most problematic benign tumors are recommended to be cut out immediately after diagnosis.
Why does my stomach hurt after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst? The pain is explained by a small, but still impact on organ tissue. As a rule, there is no need to worry about this. Soon the pain goes away.
Rehabilitation after laparoscopy
After laparoscopy, a woman does not observe bleeding after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst; she can go home within a couple of days after the treatment procedure. Scars after cuts heal quickly. The likelihood of internal inflammation, complications after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts and infections is minimized.
All patients who have undergone a laparoscopy procedure should be closely monitored and supervised by specialists during the first few days after surgery. During this period, the patient should:
- follow the regimen prescribed by the doctor;
- do not carry out long movements and strong physical exertion;
- correctly analyze the consequences after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst and eat right.
On the third day after laparoscopy, the doctor does a control test and checks the functioning and nature of ovarian recovery after surgery, the presence or absence of cystitis after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst. If all indicators are satisfactory, the patient is discharged home to undergo treatment and recovery for a month.
On what day of the cycle is laparoscopy performed?
When planning laparoscopy, it is necessary to decide when is the best time to perform the operation. The exact date is selected depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. For ovarian cysts, it is best to plan surgical intervention for the period after ovulation.
If it is necessary to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, then the operation is prescribed for the period before ovulation. This will eliminate the possibility of pregnancy.
If there are indications for emergency intervention, the surgeon will not focus on the day of the menstrual cycle. Laparoscopy is performed immediately after the patient is admitted to the hospital.
Is laparoscopy done during menstruation?
During menstruation, elective surgeries are not performed. During menstruation, blood clotting in women is impaired, so the risk of bleeding increases. If such a complication occurs, there is a possibility that the surgeon will be forced to make an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and completely remove the uterus in order to save the patient’s life.
Performing laparoscopy during menstruation is associated with the risk of developing an infectious and inflammatory process. If there are no indications for emergency surgery, then surgery is not performed during menstruation, it is postponed.
Laparoscopy during menstruation can be performed provided that the woman was admitted to the hospital with suspected one of the following diagnoses:
- cyst rupture;
- twisting of the pedicle of the cystic formation;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- development of a purulent-inflammatory process in the appendages.
If emergency intervention is necessary, the doctor focuses only on the patient’s hemodynamic parameters and test results.
On what day of the cycle is it best to do laparoscopy?
Planned laparoscopy is best performed after ovulation has completed. In phase 2, it is recommended to do diagnostic and treatment laparoscopy for infertility of unknown origin, cysts and polycystic ovary syndrome.
With a standard cycle lasting 28 days, the optimal period for its implementation is considered to be 15-24 days. It is better not to plan laparoscopy for the last days of the cycle.
For scheduled therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, day 5-7 of the cycle is selected. During this period, the functioning of the blood coagulation system is normalized, and the body will have enough time to recover before the start of the next menstruation.