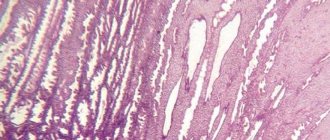
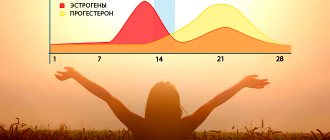
Luteal phase deficiency (LPF) is a pathological process of the menstrual cycle.
It is characterized by impaired functioning of the corpus luteum, as a result of which the production of progesterone decreases. This condition increases the risk of infertility or spontaneous abortion. In order for pregnancy to proceed without complications, the corpus luteum must constantly produce a hormone that is necessary to prepare the endometrium of the uterus, as well as ensure the gestation and development of the child. When the hormone is no longer produced in the required amount, luteal phase deficiency occurs.
Causes of the disease
Experts identify three groups of factors that provoke NLF.
Organic
These include diseases of the reproductive and other systems. The main feature is the change not only in the functions of organs, but also in their structures. Among the main causes are pathologies of the liver and reproductive system .
The first group includes:
- cirrhosis , in which replacement with connective tissue occurs, the functions and structure of the affected organ are disrupted;
- hepatitis , which is characterized by a pathological process of infectious origin;
- fatty liver , when the liver tissue is replaced by fatty tissue.
Among the diseases of the reproductive system are:
- malignant lesions of the endometrium and ovaries;
- adenomyosis;
- hyperplasia;
- endometriosis;
- formation of polyps;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometritis.
Against the background of each of the diseases, malfunctions are observed not only in the ovaries, but also in the reproductive system as a whole.
Functional
This group includes the following pathologies:
- Resistant ovarian syndrome is a disease characterized by loss of sensitivity to leading hormones that are involved in the production of sex hormones.
- Hyperinhibition.
- Polycystic disease is a disease in which the ovaries take on a honeycomb shape due to a large number of follicles.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism) and pituitary gland (hyperprolactinemia, hypogonadism).
- Exhaustion is the onset of menopause due to deficient ovarian function in women under 40 years of age.
These reasons also contribute to dysfunction of the reproductive system.
Iatrogenic
These are medical abortions and curettage of the uterine cavity for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
Other factors that can provoke LF deficiency include:
- increased loads;
- drug use;
- psychological disorders;
- rapid weight loss;
- climate change.
Such reasons negatively affect the hormonal balance, resulting in disruptions in their production and, as a consequence, incomplete maturation of the egg, regardless of whether there is ovulation or not.
Treatment of NMC
You can adjust your cycle and ovulation only after finding and eliminating the root cause. If examinations do not show any health problems, then it is possible that the reason for the failure of menstruation lies only in lifestyle, and therefore treatment is not prescribed. It is enough to change the diet, reduce emotional stress, correct physical activity, proper sleep and rest. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe vitamins. If after the measures taken the problem is not solved, you will have to contact a gynecologist again for a course of treatment.
In case of serious endocrine disorders, there is a need for hormonal treatment, but it can be avoided with minor deviations from the norm. In this case, medicine offers herbal medicine, which gently restores hormonal levels without side effects.
Menstrual pain (in the absence of illness as a cause) is well relieved by breathing techniques, acupuncture and other non-traditional methods. Since taking medications these days is aimed at relieving spasms, alternative methods are good because their effect lasts a long time. Sometimes psychotherapy sessions help. Positive results can also be achieved using traditional methods, but only after discussion with a gynecologist.
Oral contraceptives as a method of correcting NMC are prescribed by a gynecologist-endocrinologist strictly according to indications, selected individually, and the treatment process is monitored. To prevent weight gain, the doctor prescribes a diet for the period of taking OK.
To treat genital infections, antibiotics and drugs that restore the vaginal microflora are prescribed. In some cases, surgical intervention or complex therapy in a hospital will be required.
It is worth mentioning separately about working with anovulatory cycles. It is impossible to increase the number of eggs in the body, and artificial stimulation will only lead to rapid depletion, so this method is used only for the diagnosis of infertility.
Symptoms
The development of NLF is accompanied by the following clinical signs:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- infertility;
- spontaneous miscarriage.
Termination of pregnancy occurs, as a rule, in the first three months. If repeated miscarriages occur, the risk of miscarriage increases. When the concentration of progesterone decreases, the egg cannot normally implant into the uterine cavity. Against this background, infertility develops. Patients diagnosed with hypofunction of the corpus luteum most often have low weight.
Kinds
Based on numerous studies, experts have identified two forms of NLF.
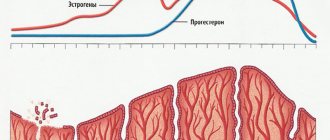
The hypoprogesterone type is characterized by
- insufficient thickness of the endometrium by the end of the second phase of the cycle;
- decrease in volume and incomplete formation of the corpus luteum;
- decrease in the concentration of the female hormone progesterone in the second phase.
The hyperestrogenic type is characterized by sufficient production of the corpus luteum, a slight decrease in progesterone concentration, and normal endometrial thickness necessary for full conception. However, there is a sharp increase in the level of estrogen in the blood fluid.
Luteal phase deficiency
The luteal phase of the cycle is the period that begins after ovulation and ends with the first day of menstruation . It is characterized by active growth of the corpus luteum. During the process of ovulation, the dominant follicle ruptures. The egg leaves its boundaries, heading towards the uterus. From this moment on, the woman's fertility increases. There is an opportunity to conceive a child.
After the egg has left the follicle, a corpus luteum begins to form on it. Based on the results of an ultrasound examination, its size can be determined. The corpus luteum provokes an increase in progesterone. It, in turn, promotes the development of pregnancy, subject to successful fertilization .
If the luteal phase is insufficient, the corpus luteum does not perform its functions properly. Its dimensions in this case do not correspond to established standards. Sometimes its complete absence is noted. This pathology causes delays in menstruation.
ON A NOTE! In medical practice, the term characterizing the disease has been shortened to the abbreviation NLF.
Diagnostics
At the first suspicion of the development of such a pathological process, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient in order to identify information regarding the medical history and complaints. At this stage, it is necessary to establish whether there is discharge with blood, when it first appeared, what color it is, what could be the cause of the menstrual cycle.
Next, the specialist analyzes the patient’s menstrual functions. In this case, the age of onset of menstruation, regularity and duration, and the date of last blood loss are determined.
It is important to analyze a woman’s life history for the presence of chronic diseases, previous operations, injuries and other pathological conditions.
After collecting the necessary information, the doctor conducts an external examination . It is important to consider all factors here:
- ratio of body weight and height;
- number of hair growth;
- pale skin and mucous membranes;
- pulse and blood pressure indicators.
In addition, the specialist must palpate the uterus and ovaries .
Among the laboratory tests prescribed:
- general and biochemistry of blood fluid;
- to determine hormones of the reproductive system and thyroid gland;
- on blood clotting.
If there is a risk of developing inflammatory or tumor processes, then additional instrumental diagnostics :
- ultrasound examination of the uterus and pelvic organs;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
To determine the condition of the endometrium, hysteroscopy is performed.
Complications
In the absence of timely therapeutic actions, the likelihood of developing certain negative consequences increases. The most common complications include:
- violation of the main reproductive function - natural reproduction;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- malignant tumor in the body of the uterus;
- disruption of the functioning of the placenta;
- fibrocystic type mastopathy;
- malfunction of the ovaries;
- fibroids.
The development of such complications negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of a woman, which further aggravates the situation, since depression is considered one of the common factors contributing to irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
Therapy
What drugs, other than hormonal ones, can cure the pathology? If the cause of the deviations is immune deficiency or genetic prerequisites, non-hormonal drugs duphaston and others are used. If there is an excess of progesterone, only hormonal therapy is indicated. Hormones are also used in the case of hyperandrogenism and hyperprolactinemia.
You can get rid of hormonal deficiency by using contraceptives in tablet form. Oral contraceptives help regulate the production of hormones and establish their balance in the body.
In the absence of ovulation, medications are prescribed to stimulate the ovaries. For endometrial pathology, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. To improve the immune status, the gynecologist prescribes vitamin complexes, acupuncture and physiotherapy.
If the pathology was caused by a nervous breakdown or an acute mental reaction to stress, patients are prescribed sedatives. If the medications do not work enough, a consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist is necessary.
Prevention
To prevent the development of luteal phase deficiency, you must adhere to some recommendations:
- promptly treat endocrine and gynecological ailments, as well as chronic diseases affecting internal organs;
- maintain a special cycle calendar;
- adhere to a balanced diet, consume more proteins;
- exercise regularly;
- do not expose the body to mental stress.
The most effective measure for preventing NLF is constant examination by a specialist.