Diseases of the female genital area can cause infertility, so it is better to try to avoid them. Some of them do not appear for a long time, and symptoms arise when the disease is already advanced. But experts draw conclusions about the state of the patient’s body, taking into account the regularity of the monthly cycle and the woman’s well-being on her menstrual days. Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of yellow discharge before, during and after menstruation.
Ideally, periods should be regular and equally intense, without bleeding ahead of schedule.
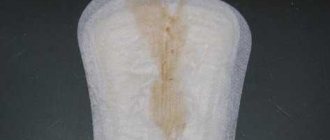
Yellow discharge - what is it?
A woman constantly discovers vaginal discharge on her underwear. By their consistency and quantity, you can determine the phase of the monthly cycle. In the first half they are transparent, in small quantities. During ovulation, the discharge becomes transparent, mucous, similar to egg white. In the second phase of the cycle, hormonal changes lead to the discharge becoming thicker and increasing in quantity. Their color is white with a yellowish tint. Therefore, yellow color on the eve of menstruation can be regarded as normal. If droplets of blood are added to such secretions, they turn brown and pink. Thick yellow discharge has a slight specific odor. There are absolutely no unpleasant symptoms.
What is the norm
Not every patient has a picture that fully complies with the standard. Before menstruation, many people experience “irregular” vaginal discharge that is yellow, whitish or light green in color. This phenomenon cannot be called pathological, since in this way the genitals are protected from harmful microbes, and they cannot actively reproduce. In a normal situation, this secretion does not cause discomfort. Before menstruation, the discharge is abundant, but due to body temperature, most of it evaporates, and very little comes out.
At the beginning and end of the monthly cycle, different secretions are normal.
- The amount of mucus may vary depending on the phase by 0.06-4 ml. per day. Before critical days, the volume is slightly larger, but if there is no mucus at all, and at the same time you feel normal, no pathology is noted here.
- The mucous secretion that appears before menstruation does not smell at all or smells acidic. If on other days the discharge is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, this should alert the patient.
- During ovulation, the secretion becomes viscous, similar to the white of a raw egg. When menstruation approaches, it becomes creamy, and after it it becomes liquid again.
- The consistency of the secretion is always uniform, but sometimes it contains small lumps formed by epithelial tissue.
- At the beginning of the cycle, the secretion is slightly cloudy and colorless, and before the onset of critical days it turns white. When the mucus gets on your underwear, it may appear yellowish as the oxygen reaction occurs.
- A yellow substance is normal; there should be no unpleasant sensations, such as burning. Otherwise, you need to get tested for diseases.
Causes of yellow discharge
Due to changes in the vaginal microflora, yellow discharge may have a pronounced color, smell, and be accompanied by unpleasant sensations. What could it be?
- Bacterial vaginitis or colpitis . Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. There are several causative agents of the disease - bacteria, fungi, pathological microorganisms. The vagina becomes colonized with pathogens that inhibit the growth of beneficial bacteria. As a result, vaginal dysbiosis appears, followed by inflammation. The discharge becomes thick and yellow. A woman feels additional symptoms of the disease - an unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, burning of the genitals, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. Acute vaginitis without proper treatment becomes chronic. Then yellow discharge appears constantly, especially noticeable on the eve of menstruation.
- Cervical erosion . There are several reasons for the occurrence of erosion: when the onset of sexual activity is too early or when this process is delayed up to 30 years; sexual infections; abortions, injuries; immune, hormonal disorders. Erosion manifests itself as a violation of the monthly cycle, brown discharge in the middle of the cycle, after sexual intercourse, pain during urination. If an infection is added to the erosion, a yellow mucous purulent discharge appears. Cervical erosion is diagnosed during examination. It is treated with medication and cauterization.
- Salpingitis. Infectious inflammation of the uterine tubes. The acute form of the disease occurs with fever, intoxication, chills, pain in the lower abdomen, and yellow vaginal discharge. The disease rarely occurs in isolation. Accompanied by inflammation of the ovaries, bladder, and uterus. The disease can be caused by pathological microorganisms that enter the body during sexual intercourse from the intestines. Nonspecific salpingitis appears as a result of birth trauma, abortion, manipulation of the genital organs, prolapse of the vagina, installation or removal of an intrauterine device. Acute salpingitis manifests itself as general weakness, pain in the abdomen, lower back, sacrum, radiating to the rectum. The discharge is serous-purulent with a yellow tint.
- Adnexitis . Inflammation that covers the fallopian tubes and ovaries. The pathology leads to constant discomfort in the peritoneum, adhesions, cysts, menstrual irregularities, and infertility. Most often, the disease is caused by pathological microorganisms that penetrate sexually or from the intestines. Against the background of inflammatory processes, the vaginal mucosa becomes irritated, causing burning and swelling. The discharge is yellowish with an unpleasant odor.
- Allergy. It may occur as a reaction to synthetic underwear or intimate hygiene products. Manifested by redness, burning, itching. The discharge is yellow without an unpleasant odor.
If conception does not occur
In the absence of pregnancy, discharge after ovulation is also a normal state of the reproductive system. They may remain slimy for several days after the release of the egg, but should not have a strong odor or blood.
Normal discharge after ovulation is characterized by:
- Continues until the onset of menstruation, does not cause discomfort in the external genital organs;
- Stable frequency of volume;
- They have no color or are yellowish;
- There is no pain during urination or during sexual intercourse;
- May intensify due to physical activity;
- Significantly change the consistency before sexual intercourse.
The sour smell of discharge after ovulation and generally throughout the entire menstrual cycle does not always mean problems with women's health. Their aroma is negatively affected by poor hygiene and the use of unsuitable hygiene products. The smell of discharge changes due to a sharp change in climate, after certain medications and in case of intestinal poisoning.
Even discharge characteristic of pregnancy may actually mean its absence. Why is this happening? The man and woman systematically prepared for conceiving a child and kept their bodies healthy. They also calculated the favorable day for conception and performed sexual intercourse according to certain rules. After all the manipulations, the woman even felt the first signs of pregnancy - pain in the lower abdomen, discharge after ovulation, indicating the consolidation of the fetus. But after a few days, the couple will be disappointed - the arrival of full menstruation.
When is yellow discharge considered normal?
Failure to maintain personal hygiene causes yellow discharge. Initially they are white, but when left on the laundry for a long time they acquire a yellow tint. Over time, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply in the discharge and turn the white color yellow. If a woman continues to ignore the rules of hygiene, she risks developing thrush, vaginitis, and inflammation.
Yellow discharge can be considered normal if it appears in the second phase of the cycle and does not contain an unpleasant odor. A woman does not experience discomfort during sexual intercourse or urination. The discharge does not affect your general well-being in any way.
Norm
In healthy women, the discharge before ovulation should be translucent, transparent or liquid, similar to egg white, slightly viscous. They usually have no specific odor, or have a slight one. Thus, the vaginal environment is favorable for sperm to move faster towards the target. Heavy discharge does not last long, about two days.
During ovulation, the female body undergoes some changes. This can be expressed by: painful sensations in the lower abdomen, chest pain, changes in taste, changes in hormonal levels. A characteristic symptom is vaginal discharge. Starting to appear some time before ovulation, they are transparent in appearance and have great viscousness.
After release, the eggs are more abundant than usual. They persist for several more days after the release of the egg, and correspond to the natural state. Later they become thicker and decrease in intensity. This can be explained by the fact that the work of progesterone (steroid hormone) is aimed at preserving the created fertilized egg. The mucus thickens under its influence, and its color may change. The color changes to reddish, yellowish, cream, beige.
The normal color of the discharge is:
- transparent appearance, with small streaks of blood;
- pink-beige, brownish;
- yellow, light yellow;
- brown smearing.
Pink-beige, brown are associated with the release of the finished egg. Brownish color - often occurs 7 days after ovulation. If there is no pathology, then it fits the norm and means a possible pregnancy.
Yellow, light yellow, without a pungent odor, itching or other discomfort, means that there are no violations. Usually appear under the influence of progesterone.
If such discharge does not have a bad odor, there is no painful sensation against it, its amount periodically changes slightly, and does not cause discomfort, then it is natural.
Sign of pregnancy or not
After fertilization of the egg, progesterone levels increase. The hormone is responsible for the normal development of pregnancy during the first 3 months. All this time, the discharge is thick, with a yellow tint. If during the usual delay on the eve of menstruation the discharge becomes less, during pregnancy it remains just as abundant.
The second cause of yellow discharge during pregnancy is hidden infections in the woman’s body. If there are chronic diseases that manifest themselves with a decrease in immunity, this is exactly the case. Hormonal changes disable many vital systems. The immune system suffers, and pathogens and infections have the opportunity to express themselves in full force. Often pregnancy provokes vaginitis and thrush.
To find out for sure what the specific discharge is associated with, it is necessary to conduct a pregnancy test. With its normal development, without infections in the body, the yellow discharge will stop after 3 months. When progesterone levels begin to fall.
Should there be discharge after ovulation?
The production of secretions is a normal manifestation of the healthy functioning of a woman’s reproductive system. It’s bad if there is absolutely no lubrication, because when the egg leaves the follicle, the nature of the discharge changes. This is due to the presence of estrogen in the blood - it is this that affects the quality of mucus. The largest amount occurs at the time of ovulation. Mucus is needed in order to provide a favorable environment for the rapid movement of sperm to the target. When in the next week the discharge sharply increases in volume and thickens, has no odor and is not accompanied by discomfort, this is a good sign.
By observing the consistency and volume of mucus, you can learn to determine the most favorable time for conception.
What does yellow discharge with an odor mean?
An unpleasant odor of yellow discharge indicates the development of a sexually transmitted infection. There may be several options:
- Chlamydia . An infectious disease caused by chlamydia. Unlike other sexually transmitted diseases, chlamydia simultaneously affects the internal and external genitalia. In the absence of proper treatment, it spreads to the joints, blood vessels of the heart, teeth, organs of vision, and breathing. The incubation period depends on the woman’s immunity, lasting from 1 week to 2 months. Women are more susceptible to the disease. Men often do not notice the symptoms of the disease and pass it on to their partner. Weakness, signs of intoxication, pain in the lower abdomen, pain when urinating appear. The discharge is purulent, mucous, yellow in color with an unpleasant odor. The genitals become inflamed, there is a burning sensation, itching, which intensifies in the evening. The menstrual cycle is disrupted. Menstruation is delayed, then passes with heavy bleeding.
- Trichomoniasis. Infectious disease of the genitourinary system. The causative agent is the bacterium Trichomonas. The disease is dangerous due to complications that manifest as infertility and pathologies during pregnancy. The incubation period lasts about a month. Sometimes symptoms appear within a week. The vaginal mucosa becomes inflamed and bleeds. Against this background, a burning sensation and pain appear during sex and when urinating. The external genitalia itch. The discharge is yellow with an unpleasant odor. Periodically mixed with blood. The disease causes inflammation of the vagina and swelling of the genitals. Very rarely, cystitis develops against the background of trichomoniasis. During pregnancy, Trichomonas causes premature birth, and the baby is born with low birth weight.
- Gonorrhea. STD disease caused by gonococci. The infection affects the external genitalia, rectum, and in the chronic form of the eye in the form of conjunctivitis. Gonorrhea is often asymptomatic, which is the most dangerous phenomenon. Gradually the disease spreads to the ovaries, bladder, and kidneys. The acute course of the disease makes itself felt from 3 to 7 days after sexual intercourse. There is a feeling of cutting, tickling, burning, and frequent urge to urinate. Discharge in the form of mucus, mixed with pus, yellow in color. With an unpleasant smell of rotten fish.
This is not the entire list of diseases that cause yellow vaginal discharge. To establish the type of disease, it is necessary to undergo an examination - a gynecological examination, a smear test. Further examination will depend on the results of the preliminary analysis. Sometimes ultrasound, computer diagnostics, etc. are prescribed.
Yellow discharge appeared before the end of the menstrual cycle: could I be pregnant?
Many women experience yellow vaginal discharge as a premenstrual symptom that occurs naturally before menstruation but goes away once menstruation begins. A yellowish color usually indicates the presence of a very small amount of blood in the discharge, which means your period could start at any time. If this is your case, then you may also experience other premenstrual symptoms such as cramps. Keep in mind that your discharge may still be yellow during your menstrual period, especially during the first two days. However, if you notice yellow discharge but no period, you should wait at least ten days before taking a pregnancy test.
Sometimes yellow discharge may occur in case of late period, but usually it returns to normal once the period begins. The same applies to the missing period, although the discharge may be brownish rather than yellow. If you continue to experience yellowish discharge instead of your period, call your doctor to further investigate the underlying cause. Many times, a change in the color of your vaginal discharge may indicate a vaginal infection that should be treated immediately to prevent complications.
What to do?
If yellow discharge appears, first of all you need to evaluate your own feelings. Then calculate the phase of the menstrual cycle.
- In the absence of alarming symptoms, in the second phase of the monthly cycle, you need to calm down and calmly wait for the approach of your period.
- If there is a delay, a pregnancy test should be performed. Perhaps the reason for the specific discharge is in it.
- If you have itching, burning, or any other painful symptoms, you should go to an appointment with a gynecologist.
- You should analyze your sex life over the past three months. Because the incubation period of some sexually transmitted diseases lasts just that long.
- If the cause of the yellow discharge is an allergy, irritating factors should be excluded. Replace synthetic underwear with natural ones and wash with regular warm water. Stop using panty liners. Allergies are eliminated with local ointments and antihistamines.
- The washing procedure should be carried out twice a day. Change linen every day.
Yellow discharge is considered normal in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy. All other cases should be regarded as dangerous. The cause must be sought together with a specialist. If you have a disease, it is necessary to undergo full treatment. Untreated infections become chronic and affect other organs.
What discharge is alarming?
Many infections worsen precisely after ovulation, so the characteristic pathological discharge may intensify.
What genital leucorrhoea alarms women:
- plentiful, white, curdled;
- bloody, dark brown;
- dark yellow, dark gray, dull green.
Abundant white curdled leucorrhoea, accompanied by a specific sour odor and itching of the genitals, are signs of thrush. It is caused by the fungus Candida.
Dark brown and with a lot of blood, also sharp and bad smelling, accompanied by pain in the abdomen and lower back, can mean inflammation of the endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity). The development of chronic endometritis is often suspected.
Bloody leucorrhoea also appears as a result of hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body when using hormonal contraception. They are stronger when they use a hormonal or conventional intrauterine system.
The mucus has an unnatural greenish, putrid, gray, earthy color, and smells very bad - it may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted infections. In such a situation, it is most often gardnerella, and the disease is gardnerellosis.
If you have an incomprehensible and disturbing abnormal discharge that does not correspond to the norm, you should definitely consult a doctor and not self-medicate. It is advisable to undergo an examination, tests, and sometimes, on the recommendation of a doctor, you need to do an ultrasound.
Treatment of pathological discharge
Diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms are usually treated with antibiotics or antiviral agents. At the same time, a course of vitamins and medications is prescribed to help prevent vaginal dysbiosis.
Thrush is treated with antifungal agents for both internal (capsules) and local use (suppositories and suppositories). During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the doctor will prescribe topical medications so as not to harm the baby’s well-being. Taking complexes that restore the natural balance of microflora can help prevent periodic relapses characteristic of this disease. This is the only way to get rid of this unpleasant disease.
Brownish and yellow vaginal discharge with endometriosis will disappear after eliminating the manifestations of the disease with hormonal therapy, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, enzymes and sedatives.
If this symptom appeared during menopause, then taking plant estrogens, and in difficult cases, hormone replacement therapy will help restore the balance of hormones. Any medications should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor.