An increase in progesterone during gestation and in the second (luteal) phase of the uterine cycle is physiologically justified and is considered normal . In other outcomes, there is a possibility of pathology occurring. In this case, the amount of estrogen and progesterone is considered as a complex indicator.
Progesterone prepares a woman’s body for bearing a child, which is why it is called the main hormone of pregnancy. The substance affects the regularity of the menstrual cycle and egg maturation. The hormone is produced by the corpus luteum of the ovaries and adrenal glands; during pregnancy it is actively secreted by the placenta.
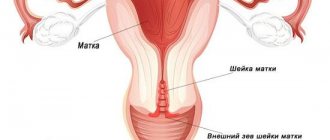
What is the menstrual cycle
The appearance of menstruation indicates puberty and a woman’s ability to perform the function of procreation. The cycle, according to physiology, can last from 25 to 33 days. It is divided into the following phases:
- menstrual - characterized by the process of rejection of the inner layer of the endometrium, it occurs from 1 to 5-7 days;
- follicular (6-14 days) - maturation of 5-7 follicles is observed;
- ovulatory, occurs on days 13-15 of the cycle, the egg is released;
- luteal - from ovulation to the date of the next menstruation.
Features of the luteal phase
The length of the menstrual cycle is usually 28 days .
The beginning of the cycle is counted from the first day of menstruation, when blood begins to leave the vagina.
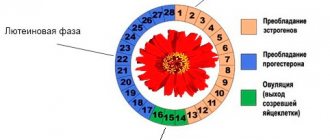
The menstrual cycle can be divided into four stages:
- menstrual phase, from 1st to 5th day;
- follicular phase, from days 1 to 13;
- ovulation phase, which occurs on the 14th day;
- luteal phase, lasting from the 15th to the 28th day.
During the follicular phase, the pituitary gland begins to secrete a hormone that stimulates the growth and maturation of eggs in the ovaries. On the 14th day of the cycle, in the ovulation phase, one of the eggs is released from the follicle and enters the fallopian (uterine) tubes.
At the site of the ruptured follicle, a corpus luteum (temporary endocrine gland) is formed, which begins to secrete sex steroid hormones - estrogens and progesterone.
On the 15th day, the luteal phase begins, continuing until the end of the menstrual cycle.
At the beginning of the luteal phase, the released egg remains in the fallopian tube for 24 hours . If the sperm does not fertilize the egg within this time, it is destroyed. If the egg is fertilized, it moves along the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it is implanted into its wall 6-12 days after the end of ovulation.
The hormone progesterone, produced by the corpus luteum, plays an important role in shaping the susceptibility of the inner mucous membrane of the uterine body (its endometrium) to the attachment of a fertilized egg, as well as in maintaining the embryo in the early stages of development.
The hormone also prevents uterine contractions and the development of new follicles, and increases basal body temperature.
Once the egg is fertilized, progesterone stimulates the growth of blood vessels supplying the endometrium and stimulates the endometrium to produce nutrients needed by the embryo.
If the egg is implanted into the endometrium, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone under the influence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin, maintaining an elevated basal body temperature for eight to twelve weeks, after which the placenta takes over this function.
If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum begins to gradually atrophy, and progesterone levels gradually drop, which means the end of the luteal phase and the beginning of the next menstrual cycle.
Luteal phase defect
As a rule, a luteal phase defect (luteal insufficiency) occurs if for some reason this phase is shortened or progesterone levels become higher than normal.
What is the role of progesterone in the female body?
Progesterone is responsible for:
- readiness for fertilization;
- the appearance of menstruation;
- preparing a woman’s nervous system for childbearing, childbirth and lactation;
- stimulation of sebum production;
- transformation of lipids into energy;
- formation of the glandular layer of the mammary gland;
- maintaining normal glucose levels;
- increased blood pressure;
- lactation process;
- libido.
Progesterone is normal in women
The hormone is not at a constant level; its amount depends on the influence of many factors. However, in medical practice there are values that are considered the norm.
Progesterone levels in non-pregnant women
| Cycle phase | nmol/l |
| Follicular | 0,3 — 0,22 |
| Ovulatory | 0, 5 — 9,5 |
| Luteal | 7 — 56,6 |
It is necessary to emphasize that the level of the hormone can be different in one woman if tested in different laboratories. This feature is explained by the fact that various reagents and equipment can be used.
Progesterone levels in pregnant women
| Week of pregnancy | Norm |
| 1 — 13 | 9-468 |
| 14 — 26 | 71,5-303 |
| 27 — 40 | 88,7-771,5 |
If the results are slightly different, don't worry. The analysis should be deciphered by a doctor; he takes into account the characteristics of the woman’s body, and it is also possible to take medications.
Indicators by day of the cycle
| Cycle days | nmol/l |
| 1-5 | 0,32-2,23 |
| 6-8 | 0,37-4,41 |
| 9-13 | 0,41-4,81 |
| 14-15 | 0,48-9,41 |
| 16-18 | 0,51-9,67 |
| 19-28 | 6,99-56,93 |
According to the age
In women of reproductive age, the rate ranges from 0.3 to 56.6 nmol/l. When menopause occurs, this value will decrease. The normal value for menopause is considered to be 0.64 nmol/l.
Foods and the hormone progesterone
I already knew that progesterone is produced in the female body through the work of the ovaries. However, I only recently found information about the possibility of influencing its level with normal nutrition. Special diets have long been used by experienced doctors to correct the level of certain hormones in the female body.
In this case, special products can be both an alternative and a supplement to the main treatment. It all depends on the specific case: minor correction of hormonal levels can be done without synthetic pills.
Important! Food products do not contain hormonal substances in their pure form - they include special substances of natural origin that can partially regulate the balance of hormones.
This effect on hormonal synthesis occurs more mildly compared to the effect of synthetic tablets. Products that are aimed at increasing progesterone inhibit estrogen (the antagonist of the first) and vice versa.
Progesterone test: how to prepare and when to take it
It is justified to prescribe analysis to women when:
- problems with conception;
- uterine bleeding, especially when the cause of its occurrence is not established;
- hormonal imbalance;
- threat of abortion;
- suspicion of the presence of a neoplasm of the ovaries or adrenal glands;
- the use of progestins and the presence of adverse reactions to them;
- when there is a need to determine the condition of the placenta.
The analysis does not require special preparation; it is better to take it on the 21st day of the cycle, on an empty stomach.
Recommended:
- 2 hours before the test do not smoke;
- the day before donating blood, avoid spicy, fatty foods, as well as tea and coffee;
- postpone taking medications, if this is not possible, you need to inform your doctor.
Functions and purpose
Progesterone is of great importance for the process of conceiving and bearing a child - the norm in pregnant women will depend on the period of gestation. The hormone is produced by the body itself – the endocrine system. With normal functioning of the latter, there is no danger of a shift in the parameters of the biologically active substance.
Progesterone is not only involved in the menstrual cycle, but also in conceiving and carrying a child. It will reduce the activity of the uterus so that it does not get rid of the implanted fertilized egg. With shifts in the hormonal system, the fertilized egg has no chance of securing itself in the uterine cavity.
Progesterone during pregnancy is an important hormone that is responsible for:
- The process of conception and subsequent attachment of a fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus. If there is not enough hormone, the muscles of the organ reject the fetus.
- Eliminating the risk of rejection of the developing fetus by preparing the immune system to accept a third-party protein (the genetic structure of the fetus also contains protein from the child’s father).
- Preparing for childbirth.
- Strengthening the body and preparing it for pregnancy and excessive stress.
- Formation of the mammary gland for feeding the baby.
- Correct formation of the endometrial layer. This is especially important when there is a need to secure the fertilized egg.
- The process of accumulation of subcutaneous fat in the expectant mother, so that the fetus is provided with the proper level of safety.
- Relaxes the muscles of the uterus and prevents its contraction, as well as for its normal growth.
- Normalization of a woman’s psycho-emotional state during pregnancy.
- Maintaining normal glucose levels and blood viscosity levels. the second indicator is important to ensure the normal intake of important substances, minerals, and vitamins into the child’s body, and the first is important to maintain pregnancy.
The norm of progesterone during pregnancy is determined by week. Hormone levels will gradually change as the fetus grows and develops. If the doctor suspects a lack of such a substance, he prescribes a series of examinations. A lack of such a substance can cause the development of various pathological processes in the body, so the woman will be prescribed injections or pills. This is especially important in early pregnancy. A decrease in progesterone levels during pregnancy serves as the basis for subsequent hospitalization.
If there is not enough progesterone in a woman’s body, fertilization may not occur at all.
Progesterone is higher than normal, what are the reasons?
An increase in progesterone levels can be caused by:
- disruption of the functioning of the organs of the woman’s endocrine system;
- ovarian tumor;
- malignant neoplasm of the uterus;
- cessation of menstruation.
During pregnancy this occurs due to:
- pathological processes associated with impaired fertilization of the egg;
- delayed maturation of the placenta;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- multiple pregnancy.
Vitamins
Vitamins occupy a special place in normalizing hormone levels:
- it is effectively reduced by A and C;
- T indirectly affects progesterone, as it inhibits the production of estrogen;
- the combination of group B with vitamin D lowers the level of the substance.
High levels of progesterone negatively affect a woman's condition . Its excessive concentration during pregnancy indicates a disruption in the development of the placenta and fetus. To determine how to reduce the active substance, the doctor must identify the root cause of the hormonal imbalance. After this, complex therapy is carried out, it is adjusted depending on the dynamics of the patient’s condition.
Lack of progesterone, what are the reasons?
The causes of hormone deficiency are:
- dysfunction of the adrenal cortex;
- reduction in the duration of the luteal phase;
- diseases of the genital organs in a chronic form;
- the use of medications that help reduce progesterone;
- non-compliance with the rules of rational nutrition;
- women staying on diets;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis.
In addition, a decrease in hormone levels accompanies the onset of menopause.
In pregnant women, progesterone concentrations may decrease with:
- accelerating the process of resorption of the corpus luteum;
- placental insufficiency;
- long-term exposure to stressful situations;
- post-term pregnancy.
Low progesterone
A decrease in the concentration of progesterone in the blood indicates the presence of pathology. Much attention is paid to this phenomenon during pregnancy. A discrepancy between the hormone level and the term indicates a risk of developing pregnancy complications (fetal fading, spontaneous abortion). In the absence of pregnancy, a decrease in progesterone concentration may be associated with the presence of the following pathologies:
- uterine bleeding;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the reproductive system.
The need for therapy and ways to increase the concentration of the hormone in the blood are determined individually. Doctors, based on the results of the research and determination of the cause, decide how to increase progesterone in a particular case. To compensate for the lack of progesterone, hormonal drugs are used:
- Norkolut;
- Utrozhestan;
- Duphaston;
- Veraplex.
What to do if the level of progesterone in the blood changes
The gynecologist should determine the cause of the deviation from the norm and prescribe treatment. If the hormone is overproduced, therapy will be aimed at eliminating the provoking factor.
In case of progesterone deficiency, the use of drugs such as Utrozhestan, Duphaston is considered justified. The dosage is selected individually for each woman. It is contraindicated to prescribe progestins for:
- neoplasms of the mammary glands;
- liver dysfunction;
- metrology.
Progestins are used with extreme caution in women suffering from diabetes, renal failure, and epileptic seizures.
In parallel with taking medications, it is recommended:
- avoid exposure to stressful situations;
- do not overload yourself physically;
- follow the rules of rational nutrition;
- spend more time outdoors.