The growth and development of the follicle and the subsequent ovulation period of the egg formed in it are the main processes that create the normal functioning of the reproductive systems of the female body. Thanks to them, the body prepares for subsequent conception and gestation. Failure of this mechanism is one of the most common causes of infertility. Only through IVF can the follicle be fully stimulated so that its functions work in natural conditions. To understand the proper functioning of the female body, it is important to know how the follicle grows by day of the cycle.
The condition of the female body greatly depends on the menstrual cycle.
Errors when introducing an ovulation trigger
Fortunately, this factor is easy to prevent in the future.
Sometimes the shortcomings are associated with too late administration of the drug (when the oocyte does not have time to go through the necessary stages of development), as a result of which the time between the administration of the drug and the puncture of the follicle is much less than the recommended 36-40 hours.
In other situations, there may be inaccurate administration of the ovulation trigger, when, as a result of the loss of some amount of the drug, a much smaller dose is administered.
Another possible situation is poor quality of the drug due to changes in its storage conditions or violation of production technology. As a result, the desired effect on the body does not occur. It is also impossible to exclude fluctuations in the level of hormone activity in preparations of the same batch.
What is the quantity?
Modern realities are such that women are in no hurry to have children, preferring first to get an education, achieve a certain social position, and earn money. And motherhood is postponed until later. But you can’t fool nature, and after 35 years, the number of germ cells in the ovaries begins to rapidly deplete. After all, whether a woman can become pregnant naturally depends on how many follicles remain in the gonads.
The number of follicles is established even when the girl is in the mother’s womb: in the first trimester of pregnancy, female fetuses already have ovaries with a large supply of primordial follicles, each of which contains primary oocytes. Their number is a record for a woman’s entire life and amounts to up to 2 million.
Once a girl reaches puberty, every month one follicle matures in her ovaries and one egg is released. The phenomenon of double ovulation (when more than one egg matures and is released) is quite rare.
Ovulation calculator
Cycle duration
Duration of menstruation
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- High probability of conception
Enter the first day of your last menstrual period
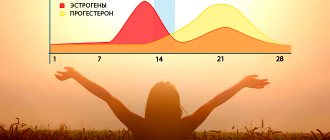
Ovulation occurs 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle (with a 28-day cycle - on the 14th day). Deviation from the average value occurs frequently, so the calculation is approximate.
Also, together with the calendar method, you can measure basal temperature, examine cervical mucus, use special tests or mini-microscopes, take tests for FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone.
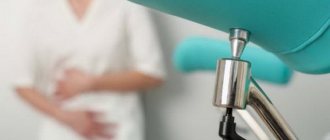
You can definitely determine the day of ovulation using folliculometry (ultrasound).
- Losos, Jonathan B.; Raven, Peter H.; Johnson, George B.; Singer, Susan R. Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1207-1209.
- Campbell NA, Reece JB, Urry LA ea Biology. 9th ed. - Benjamin Cummings, 2011. - p. 1263
- Tkachenko B. I., Brin V. B., Zakharov Yu. M., Nedospasov V. O., Pyatin V. F. Human physiology. Compendium / Ed. B. I. Tkachenko. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. - 496 p.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulation
The process of follicle maturation is called folliculogenesis. It starts after each menstruation. Under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone, several follicles begin to grow on different ovaries at once. But one remains, and it is called dominant. It is in it that the egg matures, which is destined to be released in this menstrual cycle. The remaining follicles are fading away; their time has not yet come.
If conception occurs, the maturation of new follicles is suspended until the postpartum period. If conception does not occur, the egg dies after ovulation within a day and a half, is excreted along with menstrual bleeding, and the cycle repeats again. In the life of every healthy woman, there are also anovulatory cycles, when the follicle does not mature or the oocyte is not released. It is impossible to conceive a baby during such cycles. Normally, their number is 1-2 per year, but after 36 years the number of anovulatory cycles can reach 5-6 per year, so conceiving a child becomes more difficult with age.
Certain changes in the functioning of the ovaries (polycystic ovary syndrome, ovarian failure)
In PCOS, some follicles may not contain eggs. Fortunately, the situation when oocytes cannot be obtained at all occurs very rarely. It is possible that instead of follicles, functional ovarian cysts mature, which during ultrasound are not always distinguishable from dominant follicles.
Ovarian depletion can occur as a result of:
- genetic characteristics of the body (the hereditary nature of this condition is often observed when the grandmother and mother experience menopause early);
- any surgical interventions on the ovaries (cyst removal, wedge resection), when their function is impaired due to mechanical impact;
- age factor. In particular, in women approaching 40 years of age, a decrease in ovarian function is often detected by ultrasound or hormonal profile. Such changes can be noted even from the age of 30.
In this situation, the AMH level allows you to obtain additional information. The lower its concentration (especially less than 1.0 ng/ml), the more likely it is that the follicle will mature without an egg.
Bottom line
Summarizing all of the above, let's summarize:
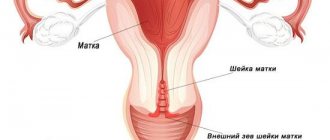
- A follicle is a vesicle in which the egg develops and protects it from external factors that may, to one degree or another, interfere with its full development.
- How long does a follicle grow? The beginning of the development of this cell coincides with the first day of the menstrual cycle. That is, the first day of menstruation starts a new cycle and then the development of a group of rudimentary cells begins, one of which subsequently becomes dominant. The growth of follicular tissue continues until ovulation, during which it ruptures and releases an egg ready for fertilization. That is, the duration of the ripening phase is 14-16 days.
- There are standard indicators for the size of a developing DF, deviations from which are most often associated with the development of pathologies of various etiologies.
Genetic factors
There is evidence of a relationship between SPF and karyotype or the presence of a mutation in the luteinizing hormone gene. Often, a blood test for karyotype is taken at the stage of preparation for an IVF program, which allows you to see deviations in advance and plan the correct approach to infertility treatment.
A study was conducted on the expression of certain genes in granulosa cells of patients with this syndrome. The authors concluded that the absence of oocytes during puncture can be explained by impaired expression of genes responsible for apoptosis, proliferation and differentiation of cells.
Features of the ovarian response to hormonal drugs
Damage to the mechanisms of normal folliculogenesis, an atypical reaction to the introduction of an ovulatory dose of human chorionic gonadotropin, and individual characteristics of hCG metabolism cannot be ruled out.
In this situation, the doctor suggests a different IVF protocol (a large number of different schemes are known, so an individual approach is possible in any situation).
The second option is to change the trigger for final oocyte maturation. It is possible to change the drug or use a double trigger.
In cases where changing medications did not help achieve the desired goal, it makes sense to try to obtain an egg without hormonal stimulation, that is, in a natural cycle.
How does the size change and what does it mean?
The size of follicular units varies depending on the time of development. Only minimal deviations from the norm are allowed.
After watching this video, you will learn about the periods of follicle maturation:
The table shows the characteristics of the days.
| Moment of cycle in days | Diameter in mm | Characteristic |
| 1-4 | 4 | 9 preovular units are formed. The eggs fill with liquid. |
| 5-6 | 5-6 | Release of weak molecules. |
| 6-7 | 9-10 | Development of a dominant. |
| 8 | 12 | Growth continues. |
| 9 | 14 | A cavity is formed. |
| 10 | 16 | Further reduction of “dead” bubbles. |
| 11 | 18 | Bubbles continue to form. |
| 12 | 20 | Enlargement of the cavity. |
| 13 | 22 | The minimum volume for the onset of ovulation. |
| 14 | 24 | The cavity is opened, and the optimal time for fertilization occurs. |
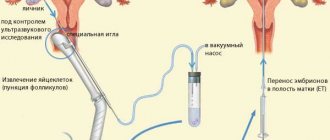
In the therapeutic treatment of female infertility using in vitro fertilization, ovarian stimulation is performed. Specialists perform an injection with human chorionic gonadotropin, then remove the mature germ cells with a needle. The mature components must reach 18–22 mm in order to be able to perform the IVF procedure.
The influence of external negative factors on the processes of follicle maturation in the ovaries
It is known that the process of forming a pool of follicles in the ovaries begins several months before the doctor sees a growing follicle in a particular menstrual cycle. If we assume that at the very early stage of development of the egg a damaging effect was exerted on it, the result may not be the same effect that we expected. Negative factors include various effects of the external environment on the body: radiation, the composition of the food used, past infectious diseases and other reasons that cannot always be objectively identified.
In such a situation, it is recommended to take a break from IVF programs for about 3 months and repeat the treatment, taking into account additional recommendations.
Treatment of empty follicle syndrome with folk remedies
After consulting with your doctor, it is possible to use some traditional recipes that promote the natural production of eggs. Herbalists advise taking internal decoctions of sage, red clover root, aloe or plantain. Such remedies will not only have a positive effect on fertility, but will also have an overall beneficial effect on the entire female body.
Remember, treatment, including traditional methods, must be prescribed and agreed upon with the attending physician. Self-medication can cause serious harm to the body!
Many experts consider aromatherapy quite effective. After all, it has been proven that essential oils stimulate the production of estrogen, which affects the maturation of new eggs. It is recommended to inhale oil vapors:
- anise;
- basilica;
- cypress;
- lavender;
- sage, etc.
Features of transvaginal puncture
Factors such as adhesions in the pelvis, uterine fibroids, endometrioid ovarian cysts and obesity can make it difficult to puncture the follicles and obtain follicular fluid. In some cases, this condition can be corrected by therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy.
When a small number of follicles have matured or there are no oocytes after puncture of several follicles (as a rule, this information is immediately received from embryologists to the fertility specialist performing the puncture), the dominant follicles are often washed with a special solution, which often still allows one to obtain an oocyte.
Key points of folliculogenesis
Folliculogenesis consists of several stages (phases).
Phase of transformation of the premordial follicle into the preantral follicle
This process begins at puberty, is gonadotropin-dependent and takes more than 4 months. In this case, active growth of the oocyte occurs. A zona pellucida (zona pellucida) appears on its surface, which consists of 4 types of special complex glycoproteins synthesized by the maturing egg. And the follicle itself increases in size and acquires an outer connective tissue membrane. Now it is called preantral or primary. Up to 10-15 follicles can be present in this phase at the same time.
Antral follicle formation phase
The oocyte continues to increase in size, and the epithelial cells located around the oocyte actively multiply and begin to secrete fluid. In this case, the follicle undergoes structural changes - a cavity and hormonally active granulosa cells appear inside it, and outer and inner epithelial membranes are formed.
This stage is also characterized by the beginning of the endocrine functioning of the follicle. The cells of its inner membrane secrete androgens, which are transformed into estrogens in the granulosa layer. During one cycle, a woman can form several antral follicles. But usually only one dominant bubble passes to the next stage, the rest are reduced. When several follicles mature at the same time, there is a possibility of multiple pregnancy.
Graafian bubble formation phase
The amount of follicular fluid progressively increases, it pushes the entire epithelium and egg to the periphery. The follicle grows rapidly and begins to protrude through the outer lining of the ovary. The egg in it is located on the periphery on the so-called ovarian mound. Approximately 2 days before ovulation, the amount of secreted estrogens increases significantly. This feedback principle initiates the release of luteinizing hormone by the pituitary gland, which triggers the process of ovulation. A local protrusion (stigma) appears on the surface of the Graafian vesicle. It is at this point that the follicle ovulates (ruptures).
As a result of ovulation, the egg, ready for fertilization, leaves the ovary and enters the abdominal cavity. Here it is captured by the villi of the fallopian tubes and continues its natural migration towards the sperm.
How is the “correctness” of folliculogenesis assessed?
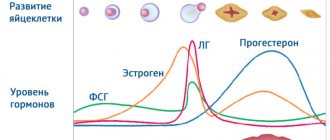
The stages of folliculogenesis have a clear relationship with the days of the ovarian-menstrual cycle. Moreover, they depend not on the age and race of the woman, but on her endocrine status.
The growth and development of the follicle is regulated primarily by follicle-stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland. It begins to be produced only with the onset of puberty. At a certain stage, folliculogenesis is additionally controlled by sex hormones, which are produced by the cells of the wall of the developing follicle itself.
Any hormonal imbalance can disrupt the process of egg maturation and ovulation. At the same time, determining the level of hormones does not always provide the doctor with all the necessary information, although it allows one to identify key endocrine disorders. Therefore, diagnosing disorders of the folliculogenesis process is the most important stage in examining a woman at the stage of pregnancy planning and in identifying the cause of infertility.
In this case, the doctor is interested in how large the follicle grows and whether it reaches the stage of Graaf’s vesicle. Be sure to monitor whether ovulation occurs and whether a sufficiently sized corpus luteum is formed. During anovulatory cycles, the maximum size of developing follicles is determined.
An accessible, informative and at the same time technically uncomplicated method is folliculometry. This is the name for monitoring follicle maturation using ultrasound. It is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require any special preparation for the woman. Folliculometry is a dynamic study. Several repeated ultrasound sessions are required to reliably monitor changes occurring in the ovaries.
In the process of folliculometry, a specialist determines the number, location and diameter of ripening follicles, monitors the formation of a dominant vesicle, and determines the size of the follicle before ovulation. Based on these data, you can predict the most favorable day of the cycle to get pregnant naturally.
In IVF protocols, such monitoring allows one to assess the response to hormonal therapy, set a date for the administration of drugs to stimulate ovulation and subsequent puncture collection of eggs. The key parameter of folliculometry is the size of the follicle by day of the cycle.
HCG level on the day of puncture
A number of researchers note the influence of hCG level on the day of puncture on the risk of SPF. If the level of this hormone is below certain levels (figures vary from 10 to 100 mIU/ml), the likelihood of empty follicle syndrome is high. In such situations, it is possible to re-administer hCG from another batch, followed by delayed aspiration of the follicles.
Despite numerous studies, scientists have not yet been able to fully understand the nature of SPF. The reasons for the recurrence of this syndrome in young women with good ovarian reserve and no abnormalities in hormonal status remain unclear. In situations where the therapy did not bring the desired result, the opportunity to become a mother can be realized using a donor egg.
Still have questions?