In vitro fertilization is often the only way for a couple to become parents. This is a modern and fairly common procedure used in many medical centers around the world for the treatment of male and female infertility. The IVF procedure is almost always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the abdominal area after puncture. This symptom is considered normal, but in some cases it can be a signal of the development of dangerous complications. Future parents definitely need to know why their stomach hurts after follicle puncture and what needs to be done if such a symptom appears.
Sometimes, after follicle puncture, your stomach may hurt. Such symptoms appear in every third girl.
Briefly about puncture
To understand why puncture has unpleasant consequences in the form of abdominal pain, you need to study the principle of collecting oocytes after stimulation. The IVF procedure begins with stimulating the ovaries to produce more eggs. For this, the woman is prescribed hormonal drugs, the action of which is aimed at the maturation of healthy, viable oocytes. On average, their number varies from 6 to 8. In some cases, up to 20 pieces are recorded.
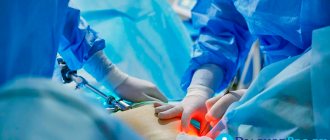
A puncture is a puncture, so it is important to understand that in order to collect eggs, mechanical damage occurs not only to the follicle, but also to the vaginal wall. The extraction process occurs under ultrasound control. During the procedure, the doctor punctures the vaginal wall and, using a special instrument - a needle, removes mature follicles.
During the puncture process, damage to blood vessels, nerve fibers and soft tissues may occur. Only an experienced specialist can carry out the procedure correctly.
Any mechanical damage causes pain in a woman. The procedure may require several punctures in the vaginal area and several in the ovaries themselves. The more eggs that are retrieved, the higher the chances of a successful conception, because not all oocytes survive and are suitable.
Puncture by laparoscopy
In reproductive medicine, another puncture method is used. If a puncture with a needle cannot be performed due to the anatomical features of the female body, the laparoscopy method is used. With this method, the puncture process is also controlled by ultrasound. If many eggs have matured, several punctures will be required.
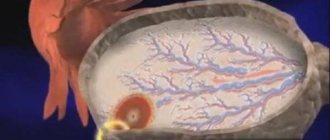
This is how the follicles are punctured using laparoscopy.
Carrying out the procedure
follicles
Local anesthesia can also be used for puncture, but for medical reasons and the wishes of patients, doctors predominantly use drug anesthesia.
During the procedure, the woman is on a gynecological chair.
In order to empty the intestines and bladder, if necessary, an enema and catheterization are performed. The specialist adheres to all standards of asepsis and antisepsis to prevent the occurrence of possible infectious diseases and other complications.
USEFUL INFORMATION: High D-dimer after transfer
The operation is performed transvaginally, that is, a special ultrasound sensor with a needle located on it is inserted into the vagina. Thanks to ultrasound imaging, the doctor can then very precisely advance the needle towards the ovaries in such a way as to minimize the risk of damage to surrounding tissue. The next stage will depend on the goal set - diagnostic or IVF.
Why does my stomach hurt after follicle puncture?
Hormonal therapy has an adverse effect on the female body; the load on it increases significantly. This is caused by the following changes:
- there are more mature eggs, and the ovaries increase significantly in size, which can lead to pain;
- blood flow increases in the pelvic organs;
- the vascular network grows in the ovarian area.
The female body reacts to such unnatural phenomena accordingly - the stomach begins to ache even before the puncture of the follicles begins, and after the puncture these unpleasant symptoms intensify even more.
The pain can persist for a certain time, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the female body. On average, the symptom is observed 1-2 days after the puncture, but if the immune system is weakened, the unpleasant phenomena may drag on. The symptoms soon go away on their own without requiring medical intervention.
It is important to know ! Minor discomfort, accompanied by mild pain in the lower abdomen, after follicular puncture is considered normal.
What you should pay special attention to
The following unpleasant symptoms and changes in the body after the procedure should alert a woman and become a reason to seek medical help:
- Sharp, paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, especially in its lower part.
- Increased body temperature - up to 38 degrees and above.
- Weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- Bleeding (discharge may be copious and have a very unpleasant odor).
If you discover such dangerous signs, you should immediately report them to your doctor from the IVF clinic. You can just call. There is no need to wait for a certain date for a personal visit; it is important not to waste time at such a dangerous moment.
Sometimes it is necessary to call an ambulance and inform medical professionals about a recent procedure. Such information will help the doctor make a diagnosis faster. In some cases, hematomas may form, which intensifies the pain and increases its duration - sometimes up to a week.
Ovarian puncture technique
The technique of ovarian puncture involves transvaginal access, in which instruments are inserted through the vagina. This route does not leave scars on the skin and is less traumatic compared to laparoscopy. The second indispensable condition for puncture is ultrasound control, which allows the doctor to operate the instruments extremely accurately in the patient’s pelvis and get into the desired follicle or cystic cavity. Such manipulations are not carried out blindly.
To puncture the ovary through the posterior fornix of the vagina, special gynecological speculums, syringes with long puncture needles, forceps, and forceps for grasping and fixing the mobile cervix are used.
After treating the genitals with a disinfectant, a speculum is placed in the vagina, opening the way to the cervix, which is fixed with forceps and retracted downwards. A large-diameter puncture needle is inserted into the posterior fornix thus opened, strictly in the middle, 1-2 centimeters deep. If there is fluid in the pelvis, it can be removed by puncture. Access to the ovary passes through the free abdominal cavity under the control of an ultrasound probe inserted transvaginally.
The posterior vault of the vagina is most convenient for puncture because the peritoneum there is closest to the vaginal walls, and by puncturing the wall of the organ in this place, the surgeon immediately enters the pelvic cavity.
The described surgical technique is used to obtain eggs during IVF, as well as puncture of an ovarian cyst if the size of the cavity is relatively small, there is no obvious inflammatory process in the acute phase and the doctor does not doubt the benignity of the formation.
After transvaginal access to the cyst, the cavity is punctured, its contents are removed for cytological examination, and up to 15 ml of ethanol is injected into the cyst, which provokes collapse and gluing of the walls of the cyst with subsequent scarring. The manipulation takes no more than an hour.
The widespread use of puncture as a method of treating ovarian cysts is limited due to the risk of dissemination of tumor cells if the formation turns out to be malignant, because non-invasive diagnostics do not always allow one to reliably exclude cancer.
Another problem with this treatment is relapses, which, according to various sources, occur in a third of patients after cyst puncture, and the older the woman, the greater the likelihood of re-growth of the cystic formation. For this reason, laparoscopic treatment is recommended in premenopause and later.
Puncture of the ovaries during IVF is carried out 35-36 hours after the woman is injected with the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin, which stimulates ovulation. Eggs are selected before the follicle ovulates, at a strictly prescribed time, which ensures good quality of the resulting cells.
The event is carried out according to the scheme described above, under general anesthesia. Using a puncture needle and under ultrasound control, the surgeon selects up to a dozen or more of the most suitable germ cells, removes them and carefully transfers them into a sterile tube. The operation takes about 15 minutes.
An important condition for IVF puncture is the presence of the spouse in the clinic, since fertilization is carried out as soon as possible after the cells are removed. On the same day, the fertility specialist usually reports the result of puncture of the ovarian follicles.
After the germ cells are collected, the patient comes out of anesthesia and may experience slight dizziness and nausea, and nagging pain in the pelvic area. Scanty bleeding is also normal after puncture of ovarian follicles. In case of severe pain, it is possible to use antispasmodics, and if the woman feels well, she goes home on the day of the operation.
Video: ovarian puncture during IVF
Enlarged abdomen: normal or pathological?
The increase in size of the abdomen is another change caused by the growth of the ovaries. This is mostly normal and not a cause for concern. Enlargement of follicles and ovaries occurs due to hormonal stimulation of ovulation. Sometimes, depending on the woman’s body, too much stimulation occurs and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome occurs. With this complication, the ovaries enlarge to 12 cm or more (the norm is 3 cm). One of the main symptoms of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is an enlarged abdomen, bloating. A change in belly size may be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms:
- discomfort during urination;
- nausea;
- dyspnea;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- increased gas formation;
- stomach pain.
Such phenomena are considered normal for the first 2-3 days after puncture, if they are not accompanied by high body temperature.
After the puncture, it is very important to drink a sufficient amount of still water, at least 2 liters per day. In addition, you need to include protein-rich foods in your menu.
When to see a doctor
Contact your gynecologist-reproductologist immediately if pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by at least one of the following symptoms:
- profuse bleeding from the genital tract (as during menstruation or more);
- pulling and aching sensations in the lower back or back;
- increasing dizziness, general weakness, pale skin and fainting;
- increased body temperature;
- sharp tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall (stomach like a stone).
These signs may indicate the development of serious bleeding or a purulent-inflammatory process.
Vaginal discharge
The puncture almost never takes place without vaginal discharge accompanied by abdominal pain, because damage to the blood vessels and soft tissues in the uterus occurs. For some time after the puncture, the woman may observe mucous discharge with minor bloody inclusions. The density, quantity and duration of such discharge may vary. Heavy bleeding consisting of clots requires urgent hospitalization.
Menstruation after puncture usually begins 3-5 days after the procedure. A disruption of the menstrual cycle cannot be ruled out, so it may need to be corrected by a specialist.
How to behave after IVF
A married couple who has decided on IVF undoubtedly really wants to have a child. After a successful embryo transfer, a woman needs increased love and care. It is better for her to spend the first days after the procedure at home in bed.
Successful implantation of the embryo is already the beginning of pregnancy. However, such a pregnancy has its own “whims”. Very often, at first, a woman’s body, in particular the uterus, behaves aggressively towards the implanted embryo and rejects the new life. Therefore, after IVF, miscarriages occur much more often.
It is worth saying goodbye to all bad habits that often cause miscarriages.
A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and vitamins are all that is necessary to maintain pregnancy.
It is important to remember a positive attitude and good emotions. After all, thoughts materialize!
A pregnancy test, as well as blood for hCG, must be taken at least two weeks after IVF. At five to six weeks of pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination, which will confirm the final growth and successful attachment of the embryo to the uterus.
Dangerous complications after puncture
Sometimes ovarian puncture leads to dangerous complications. These include the following serious complications, which are also accompanied by abdominal pain:
- Hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity due to damage to blood vessels. According to statistics, it happens very rarely, about 2 times in 600 procedures.
- Injuries of the pelvic organs.
- Ovarian torsion.
- Rupture of a follicular cyst.
- Injury to the ureter.
- Ovarian abscess.
As you can see, quite dangerous complications can develop after a puncture. Therefore, if after the procedure your stomach hurts very much, you should not endure this pain.
You should immediately report any pain to your fertility specialist at the IVF clinic . There is no time to waste. The sooner the doctor begins treatment, the easier and faster it will end. Moreover, you need to approach the subsequent embryo transfer as healthy and prepared as possible.
How to reduce pain
To minimize pain and alleviate unpleasant symptoms after follicular puncture, a woman should avoid physical activity and get more rest. There is no need to think about work, including household chores. It is strictly forbidden to take aspirin and its analogues. Taking this medication may increase bleeding, as it has a blood-thinning effect. To relieve pain, the doctor may prescribe No-shpa, Papaverine in suppositories, and Analgin to the patient. These drugs will help relieve spasm of smooth muscles and reduce the intensity of pain. You cannot self-medicate!
All medications should be prescribed only by a doctor.
A therapeutic diet based on protein foods will help the female body recover. Alcoholic drinks should be avoided.
Also, by following simple recommendations, you can alleviate the condition after the follicle extraction procedure. In addition to antispasmodics, cold helps relieve pain after puncture. In such cases, a cold heating pad is used, which must be placed on the stomach. Cold causes constriction of blood vessels damaged during the procedure. As a result of the action of cold, bleeding decreases. Heat, on the contrary, worsens the condition after the procedure, intensifies the inflammatory process and increases bleeding. Similar advice is often given to young mothers immediately after childbirth in order to relieve abdominal pain.
Contraindications to IVF
IVF is a medical procedure that gives infertile families a chance to become parents. However, this procedure has its contraindications. This:
- heart, blood vessels, respiratory system, liver, kidneys, digestive system, hereditary genetic diseases and others).
- Mental illnesses.
- Congenital defects, abnormal structures of the uterus.
- Benign and malignant formations in the uterus, when puncture of follicles during IVF becomes impossible (the consequences are the death of the patient).
- Acute inflammatory processes.
USEFUL INFORMATION: statistics in CRYO protocols
After treatment of the listed diseases, you can begin the IVF program. If treatment of diseases does not bring results, the only way out is to use.
After the puncture
To prevent stomach pain after puncture, do not forget about a number of recommendations even after retrieving mature oocytes from a woman:
- Stick to a diet that is high in protein and fiber.
- Food should be steamed or consumed only boiled food.
- It is recommended to increase the amount of fresh greens in the diet.
- Drink more water - up to 2 liters per day.
- To speed up the process of removing excess fluid accumulated in the body, it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt consumed, and, if possible, abandon it.
- Adequate healthy sleep will allow the female body to recover faster.
Brief summary
In order for the procedure to be successful and the specialist to receive viable oocytes, he determines the most suitable day for the puncture. To do this, an ultrasound is performed a few days before expected ovulation. A reproductive specialist monitors the maximum release of luteinizing hormone, which indicates the approach of ovulation. If ovulation should already occur and the follicles have not yet matured, the patient stops taking hormonal medications. In such cases, the procedure is repeated in the next cycle.
Write in the comments how and where exactly your stomach hurts. Did the pain start before or after the puncture? Did you tell the doctor about this, and if so, what did he advise you to do? Feel free to ask questions and share your experiences. Rate it with stars below. Thanks for visiting. Good health to you. Let complications pass you by.