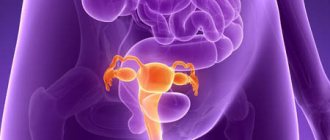
Bimanual examination in gynecology: indications, features of the procedure
Despite the existence of many laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, in practice obstetricians and gynecologists still use bimanual examination. This method is quite simple and informative. With its help, the doctor has the opportunity to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Possibilities
Bimanual examination (its other name is two-handed) allows you to assess the condition of the uterus, ovaries, and pelvic tissues. During the procedure, the doctor carefully examines the cervix, the organ itself, determines its shape and size, consistency, mobility and the nature of the surface. All this allows you to timely identify the presence of a pathological process and diagnose pregnancy.
Normally, the procedure is not associated with any pain; the patient may feel only slight discomfort.
In order to prevent various diseases, every woman should visit a gynecologist twice a year. Bimanual examination is a mandatory item during each examination of the patient.
Indications
Diagnosis of the condition of the internal genital organs is carried out not only for preventive purposes. Bimanual examination in gynecology is indicated for:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- frequent pain in the pubic area and lower abdomen;
- chronic diseases of the reproductive system;
- the presence of benign or malignant neoplasms;
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- bleeding of unknown etiology;
- the appearance of discharge that differs from normal in quantity, color and consistency;
- adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- pregnancy;
- in the postpartum period.
The list of these symptoms and conditions can be significantly expanded due to the huge variety of gynecological diseases.
Advantages of the method
The main advantage of bimanual examination is the high degree of information content. In this case, the doctor does not need any equipment.
Using palpation, the gynecologist assesses the condition of the internal genital organs (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, etc.) and promptly identifies the presence of pathologies.
In addition, during the bimanual examination, pregnancy is guaranteed to be confirmed or excluded.
Flaws
The disadvantage of this method is its dependence on the woman’s physique. As a rule, palpation is difficult in patients with pronounced subcutaneous fat. In this case, other diagnostic methods are additionally required.
In addition, each doctor can interpret the symptoms that are troubling a woman differently, which affects the reliability of the result. Nevertheless, this examination is often enough for experienced specialists to make a verdict and draw up a treatment plan.
Preparation
Before visiting a gynecologist, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- To avoid the appearance of excess discharge, you should avoid sexual intercourse the day before the examination.
- During this time, it is advisable to refrain from eating foods that cause increased gas formation. Failure to follow this recommendation will not distort the result, but may provoke an awkward situation.
- On the day of the examination, before the procedure, you need to thoroughly clean the external genitalia.
- It is recommended to empty your bladder immediately before the examination.
Thus, preparing for a bimanual examination does not require performing any special actions. The main thing is hygiene; everything else depends on the level of professionalism of the doctor.
Methodology
Before the examination begins, the specialist wipes the gynecological chair with a special solution and places a new disposable diaper on it. While the patient is positioned, the doctor puts sterile gloves on both hands. After completion of the preparatory stage, the inspection begins.
The bimanual examination technique consists of sequentially performing the following actions:
- The doctor carefully inserts the fingers of his right hand into the vagina. The left hand should palpate the internal organs from the outside - in the lower abdomen of the patient.
- A bimanual examination of the uterus is performed first. The doctor determines its position, shape, size, mobility, consistency, and surface character. Normally, the process is painless. If this is not the case, you must immediately notify the gynecologist. Patience in this case is inappropriate - any pain signals the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Next, the doctor palpates the uterine (fallopian) tubes, appendages, and ligaments. In the absence of pathologies, they are, as a rule, practically inaccessible to palpation.
- Particular attention is paid to the ovaries: they should be easily palpable, mobile and sensitive. If the ovaries are enlarged, this may indicate pregnancy or early ovulation.
- The fiber and lining of the uterus should not be palpable. Otherwise, this is a sign of the presence of adhesions, infiltration or inflammation.
After completing the examination, the doctor removes the gloves and throws them away. He then washes his hands with soap and makes notes on the patient's medical record. If there is any doubt about the existing symptoms, other diagnostic methods are additionally prescribed.
Finally
Bimanual examination is a simple but quite informative way to assess the condition of a woman’s internal genital organs. With its help, various diseases are detected in a timely manner. The disadvantages of the method are its subjectivity and dependence on the patient’s physique. If necessary, other diagnostic methods are prescribed.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/337756/bimanualnoe-issledovanie-v-ginekologii-pokazaniya-osobennosti-provedeniya-protseduryi
How to palpate the ovaries through the abdomen, palpation of paired glands as a way to detect a cyst
Often, many gynecological diseases are asymptomatic. Therefore, a manual examination during a routine examination by a gynecologist may unexpectedly reveal certain pathologies of the pelvic organs. Palpation of the ovaries determines whether the organ is in normal condition, whether its size corresponds to the norm, including age, and whether examination does not cause pain.
In premenstrual age in girls, the ovaries should not be palpable at all. If they are detected by manual examination by touch, some kind of pathology should be assumed.
In women of childbearing age, the ovary may not always be palpable, for example, if the abdominal wall is thick or tense.
Normally, the glands measure 3x2x2 cm, they are mobile and sensitive, some increase is detected during ovulation and pregnancy.
There is a difference in size - on the right side the ovaries are always slightly larger than on the left. When the patient takes oral contraceptives, the ovaries are practically not palpable and there is no such obvious asymmetry.
During the postmenopausal period, when the functions of the ovaries gradually decrease, you should pay attention to their increase, to palpable swelling and irregularities of the glands. This is evidence of a serious pathology or even ovarian cancer.
We recommend you find out: The size of the ovaries in women and their norm and How the ovarian cycle works
Clinical symptoms detected by palpation
Most often, diseases of the pelvic organs are detected already in the chronic stage, because their onset is asymptomatic. Therefore, a routine examination by a gynecologist is never superfluous even when a woman feels healthy.
The patient will not feel a slight increase in the size of the internal genital organs, and this may be an early symptom of the disease.
Palpation, being the simplest research method, can identify the disease at the very beginning and enable prompt treatment.
During the initial manual examination, the doctor may feel an enlarged ovary. This may indicate the following diseases:
- an inflammatory process caused by various bacteria and, as a consequence, the formation of adhesions,
- ovarian cysts and neoplasms of various types and nature,
- ovarian cancer.
Simple palpation, until recently, was the only diagnostic method that made it possible to identify a serious pathology that was asymptomatic, and even save a woman’s life. During menopause in women, enlargement of the ovaries and the total mass of the appendages was a priori considered a threatening symptom.
When ultrasound examination was not possible, removal of these organs was recommended. Because such a pathology in older age is a high risk of developing cancer. Now additional diagnostic studies and tests are prescribed to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
But, nevertheless, cysts and neoplasms are first discovered in women most often during a routine gynecological examination.
Palpation of the pelvic organs can reveal, in addition to an increase in the size of the gland:
- irregularities, swelling on the ovaries and cysts, when they are already quite large in size,
- presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity,
- uncharacteristic asymmetry of the glands,
- the inability to palpate the ovary separately from the uterus due to the advanced adhesive process in the appendages and its increase in size.
All symptoms may indicate the presence of certain pathologies or neoplasms in the pelvic organs. To get a complete picture, you should collect the patient’s other complaints about her health. A woman may complain of pain in the lower abdomen, general weakness, menstrual irregularities, a feeling of bloating and an increase in the size of the abdominal cavity, nausea, etc.
Important! Here it is important to distinguish symptoms related to gynecology from manifestations of other diseases. The doctor makes the final diagnosis based on the results of tests and ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs. We recommend you learn: Ovarian hyperfunction, what is it?
Misconceptions and fears
Often, the busy, busy life rhythm of a modern woman does not give her time to take care of herself and her health. Sometimes patients diagnose and treat themselves. Which leads to the disease becoming chronic or incurable.
It is impossible to examine yourself and feel for a cyst or any pathology on the ovaries. Only a qualified gynecologist can do this. If you suspect an ovarian tumor, do not be afraid of surgery. Some types of cysts can be treated with conservative medications.
But if surgery is recommended, there is no time to delay. Because we can talk about preserving life. Modern surgery makes the operation less traumatic and gentle. Removing the ovaries in our time does not deprive a woman of reproductive function.
It is possible to conceive and carry a child through in vitro fertilization.
Please note: The main thing is not to neglect basic examinations by a gynecologist, lead a healthy lifestyle and follow doctors’ recommendations. Early diagnosis of the disease provides a chance for complete recovery and preservation of all body functions. We recommend you learn: Ovarian hypofunction, what is it?
Loading…
Source: https://beauty-love.ru/zhenskoe-zdorove/palpatsiya-kak-pervichnyiy-metod-diagnostiki-zabolevaniy-yaichnikov
Ovarian dysfunction: symptoms of reproductive system failure
Today, tumor-like formations in the pelvis are a popular gynecological problem. There can be many reasons for this circumstance. The appearance of formations is provoked by gynecological infections, genetic characteristics of the body, infertility and other external and internal factors. Why is this happening? Let's discuss.
Those tumor-like formations that are localized in the organs of the reproductive system can change depending on the age of the woman. At the moment, there are many such medical troubles, and each individually requires a serious approach and professional action.
When do formations appear near the ovaries?
At a very early age after birth, girls retain the maternal hormone estrogen in their bodies. It is this fact that can provoke the formation of various cysts near the ovaries in children.
Puberty is also an alarming period; at this time, hematocolpos can be observed.
This condition provokes stagnation of menstrual blood, infection of the hymen and various pathologies of the genital organs.
In middle-aged women, a formation near the ovary
may appear during pregnancy or with uterine fibroids. Sometimes cysts are characterized by clear sizes; according to statistics, such formations range from 5 to 8 cm. As a rule, such problems go away on their own. Formations regress within 2-4 months.
During menopause, malignant formations are not uncommon; due to hormonal imbalance, when sexual function fades, the body receives enormous stress. Hence the numerous health problems that often bring a woman to the operating table.
Structure of the ovary
Externally, the ovary is protected by the peritoneum and a dense tunica albuginea. Deeper is the cortical layer, which contains a huge number of follicles, yellow and white bodies.
- A follicle (a structural unit of the ovary) is a fluid-filled “bubble” with an egg ripening inside. The dominant follicle produces estrogens.
- The corpus luteum (follicle after ovulation) is a temporary endocrine structure that synthesizes the hormone progesterone.
- The white body is the remnant of the atrophied corpus luteum.
Up to 90% of ovarian follicles undergo reverse development (atresia). Only a few go through the full cycle of formation, ovulate and turn into corpus luteum.
In the center of the ovary is the medulla. It is represented by connective tissue, penetrated by blood vessels and a large number of nerve endings-receptors.
How the ovary works Normally, during one menstrual cycle, only one (dominant) follicle develops and ovulates.
Functions of the ovaries:
- Mature eggs are formed and “released” into the fallopian tube.
- They synthesize and secrete sex hormones into the blood: estrogens, gestagens (progesterone) and, in smaller quantities, androgens (testosterone).
Ovarian cycle - diagram The ovaries belong to the second level of the female reproductive system. They have hormonal and reproductive functions.
Diagnosis of formations near the ovary
Any formation in a woman’s pelvis is accompanied by various symptoms. Endometrosis is characterized by painful menstruation. In adolescence, when a young woman is just beginning her sexual development, ovarian tumors often appear. Such formations are of the hormone-producing type.
Masculizing tumors near the ovaries are observed in people with severe virilization. That is, those representatives of the fair sex who are characterized by masculine features: a rough physique, timbre of voice, increased hair growth on the skin, etc.
Those women who suffer from menometrorrhagia after menopause are also prone to the formation of ovarian tumors.
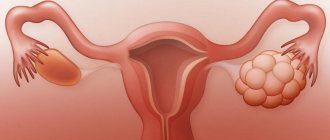
Masses near the uterus or ovaries
are diagnosed in numerous ways. Modern medicine distinguishes several main methods. During the initial examination of the patient, the doctor analyzes obvious visual symptoms: excess weight, ascites and endocrine system disorders.
An examination is performed on a gynecological chair. Sometimes it is very difficult to detect formations of the uterus and appendages due to their immobility. In turn, cancerous and soft tumors in the appendage area, as well as cysts during pregnancy, are “mobile”.
In early and teenage girls, tumors can be palpated through the abdominal wall. This fact becomes clear due to the structure of the child’s body; the tumors simply do not fit in the small pelvis and therefore protrude slightly outward. An experienced doctor can detect the problem without a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination.
Clinical symptoms detected by palpation
Most often, diseases of the pelvic organs are detected already in the chronic stage, because their onset is asymptomatic. Therefore, a routine examination by a gynecologist is never superfluous even when a woman feels healthy.
The patient will not feel a slight increase in the size of the internal genital organs, and this may be an early symptom of the disease.
Palpation, being the simplest research method, can identify the disease at the very beginning and enable prompt treatment.
During the initial manual examination, the doctor may feel an enlarged ovary. This may indicate the following diseases:
- inflammatory process caused by various bacteria and, as a consequence, the formation of adhesions;
- ovarian cysts and neoplasms of various types and nature;
- ovarian cancer.
Simple palpation, until recently, was the only diagnostic method that made it possible to identify a serious pathology that was asymptomatic, and even save a woman’s life. During menopause in women, enlargement of the ovaries and the total mass of the appendages was a priori considered a threatening symptom.
When ultrasound examination was not possible, removal of these organs was recommended. Because such a pathology in older age is a high risk of developing cancer. Now additional diagnostic studies and tests are prescribed to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
But, nevertheless, cysts and neoplasms are first discovered in women most often during a routine gynecological examination.
Palpation of the pelvic organs can reveal, in addition to an increase in the size of the gland:
- irregularities, swelling on the ovaries and cysts, when they are already quite large;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- uncharacteristic asymmetry of the glands;
- the inability to palpate the ovary separately from the uterus due to the advanced adhesive process in the appendages and its increase in size.
All symptoms may indicate the presence of certain pathologies or neoplasms in the pelvic organs. To get a complete picture, you should collect the patient’s other complaints about her health. A woman may complain of pain in the lower abdomen, general weakness, menstrual irregularities, a feeling of bloating and an increase in the size of the abdominal cavity, nausea, etc.
Important! Here it is important to distinguish symptoms related to gynecology from manifestations of other diseases. The doctor makes the final diagnosis based on the results of tests and ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs.
We recommend you learn: Ovarian hyperfunction, what is it?
Special methods for detecting formations near the ovaries
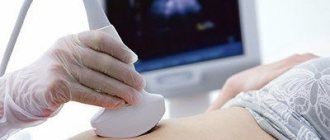
When clinical methods of identifying a disease become ineffective, medicine turns to more precise scientific methods for help. Ultrasonography of the female genital organs is used.
If ultrasound is not enough, computed tomography or MRI is used. Thanks to modern diagnostic technologies, identifying pelvic and abdominal tumors is not difficult.
Various formations near the ovaries
in this case they are well visualized.
When a formation in a woman’s pelvis has an irregular, complex shape, is characterized by spines or a dense consistency, a biopsy is prescribed.
Intravital sampling of cells or tissues from the body is taken using a special method; this type of diagnosis is prescribed only by a doctor. Tumor markers are also often recommended. The list of important laboratory and research procedures is compiled by Dr.
Doctors also conduct a pregnancy test; such analysis applies only to women of reproductive age.
Causes and types of ovarian inflammation
The cause of inflammation of the ovaries is infection. Depending on the nature of the infection that causes the disease, two types of oophoritis are distinguished: nonspecific and specific.
Non-specific. The causative agents of infection are opportunistic microbes. They are always present in the human body and are activated when the immune system is weakened, hypothermia, or stress. Such microbes are staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, and Candida fungi.
Specific. Inflammation is caused by sexually transmitted infections (syphilis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea), as well as tuberculosis pathogens.
Inflammation of the ovaries can occur as a result of the following processes:
- penetration of infection from the external genitalia through the cervix, uterine cavity and fallopian tubes;
- infection from the intestines and urinary organs due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- spread of infection to the ovaries due to intestinal inflammation or appendicitis;
- infection during abortion, installation of an intrauterine device, surgery on the pelvic organs;
- transmission of infection through blood or lymph from other organs susceptible to inflammation (for example, with sore throat).
Addition: The occurrence of oophoritis is facilitated by factors such as weakened immunity, hypothermia, uncontrolled use of certain medications, overwork, stress, and lack of nutrition.
How are gynecological formations treated?
Pelvic tumors are treated in different ways. Treatment depends on the patient’s age, her lifestyle, chronic ailments and the general condition of the body. Doctors pay attention to all factors. In addition, each individual case requires an individual approach. So, for example, an ovarian cyst can be different: follicular, corpus luteum cyst, endometrioid, etc.
If the formation is a cyst on the ovary, not exceeding 8 cm, then such problems are not treated. As a rule, the disease disappears on its own within 3-5 months. In some cases, surgical intervention, as well as medication, cannot be ruled out.
The most popular surgical method is called laparoscopy. This procedure is the most gentle, as it preserves the reproductive organs of the fairer sex. Healthy tissue of the genital organs is not injured.
Thanks to ultra-precise and effective instruments, the operation is carried out quickly and without complications.
Treatment largely depends on the type of tumor, its size and location. Only a qualified doctor can determine the type of formation. Do not self-medicate; any rash decisions can provoke irreparable consequences. Take care of your health thoughtfully.
formations near the ovaries
Does it matter which ovary ovulates in?
If a woman is healthy, then ovulation almost always occurs alternately in each ovary. The reason for this is that every release of an egg is a trauma. The follicle ruptures and slight bleeding begins.
It seems that this is not so serious, but for the ovary it is a huge “work”, after which rest is required. Accordingly, in the next cycle the opposite gland will work, and the one that has worked will go to rest. There are two methods to determine in which ovary ovulation occurs.
Source: https://gpk1.ru/bolezni/kak-nashchupat-yaichniki.html
Ovaries in women: location, where they are, size, functions
The ovaries are located along the side of the pelvis, behind the uterus. With their own ligaments, they are attached at one end to the angle of the uterus, and at the other to the side wall of the pelvis. The largest of the fimbriae surrounding the ventral end of the fallopian tube is attached to the upper tubal end of the ovary.
Most of the body of the ovary projects from the broad ligament into the abdominal cavity, but is not covered by peritoneum. Part of the broad ligament is called the mesentery or hilum of the ovary.
Normally, the glands are located symmetrically on both sides of the uterus, but anomalies occur:
- accessory - split off sections of the gonad rudiment;
- descended - located at the internal opening of the inguinal canal, in the canal itself, in the thickness of the labia majora.
Location of the female reproductive system and ovaries in women
Anomalies are a consequence of deviations in the development of the reproductive system even at the embryonic stage.
Normal ovarian size for age
The standard size of the ovary in a healthy woman is between 3.5-4 cm in length, 2-2.5 cm in width, 1-1.5 cm in thickness. It weighs 5-6 g. The right ovary is usually larger than the left. With the onset of menopause, their size decreases. The activity of the follicular apparatus fades and the ovaries gradually dry out.
| Duration of postmenopause, years | Ovarian volume, cm3 | Follicular apparatus |
| 1 | 8-10 | saved |
| 2-3 | 5-7 | single follicles |
| 4-15 | 3-6 | individual liquid inclusions |
| Over 15 | 3-4 | not expressed |
Talitsa. The normal pattern of changes in ovarian size in postmenopausal women.
Necessary research
Diagnosis of the syndrome is within the competence of a gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist. The doctor collects anamnesis, paying special attention to heredity and harmful factors.
He studies the complaints, the time of their appearance and examines the patient. Externally, the woman looks older than her age; age-related changes in her skin and hair are visible.
When examined in a chair, the doctor reveals a decrease in the size of the uterus and its appendages, and dryness of the vaginal mucosa.
p, blockquote 17,0,0,0,0 —>
To clarify the diagnosis, hormonal blood tests are performed, which reveal:
p, blockquote 18,0,0,0,0 —>
- increased levels of FSH and LH;
- insufficient concentration of estrogen and progesterone;
- low levels of prostaglandin E2.
Since only ovarian function suffers, the hypothalamic-pituitary system adequately responds to a decrease in sex hormones by increasing its activity. A trial administration of estrogen-gestagen drugs reduces the level of FSH and LH down to normal, causing the appearance of a menstrual-like reaction.
p, blockquote 19,0,0,0,0 —>
Among the imaging methods, ultrasound of the uterus and its appendages is used, during which the following is revealed:
p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 —>
- reduction in the size of the uterus;
- thinning of the endometrium to 0.5 cm or less;
- a decrease in the size of the ovaries, the absence of large maturing follicles in them.
One of the reliable ways to diagnose early ovarian failure syndrome is laparoscopic intervention. The surgeon observes small, wrinkled ovaries in the pelvic cavity, without signs of ovulation.
During the examination, the doctor takes a small piece of gonadal tissue for cytological examination - biopsy.
The resulting material is studied in the laboratory, the replacement of ovarian connective tissue and the absence of maturing follicles are revealed.
p, blockquote 21,0,0,1,0 —>
p, blockquote 22,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 —>
Causes of development of ovarian diseases
The ovaries in women, due to their close location to other pelvic organs, are affected by diseases characteristic of the latter. The transmission of infections and the inflammatory process occurs both through the lymph and through the bloodstream.
Tuberculosis of the ovaries
By the nature of its formation, genital tuberculosis is a secondary disease. Infection occurs from the main focus in the lungs through the lymphatic system, but infection of the reproductive system with tuberculosis in childhood is possible. Initially, the disease proceeds secretly, the painful symptoms are poorly expressed.
They are observed during menstruation, defecation, and sexual intercourse. As the process intensifies, body temperature rises to 38 degrees. The disease is characterized by a chronic course with wave-like exacerbations.
In case of ovarian tuberculosis, during the examination, clots of tight junctions are found on the side of the uterus. Rectal examination palpates many hard nodes of varying sizes in the area of the uterine appendages.
Mechanical damage to the uterine mucosa and fallopian tubes
Damage to the uterine mucosa usually occurs due to diagnostic manipulations after curettage, as a result of examination of the uterine cavity with a special camera (hysteroscopy). May occur in women who have used intrauterine contraception. Coils inserted into the cavity may cause minor injuries.
Any damage to the mucosa leads to the development of an inflammatory process. If the mucous membrane is intact, the microflora that is always present there does not harm the body. Mechanical damage to the fallopian tubes is possible during an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg begins to develop outside the uterine cavity.
Chorionic villi slowly penetrate the layers of the organ, destroying blood vessels and stretching the tube. A woman observes all the signs of pregnancy: absence of menstruation, change in taste, breast enlargement. At 6 weeks, an ectopic tubal pregnancy causes the tube to rupture.
The location of a woman's ovaries near the fallopian tubes during an ectopic tubal pregnancy causes the growing fertilized egg to begin to compress the veins and arteries that supply the gland. A ruptured pipe damages the blood vessels in the lining of the organ.
Inflammation of neighboring organs
Inflammation of the ovaries can begin due to an infection coming from the uterus, descending from the abdominal cavity, through the lymph from the sigmoid colon and appendix, through the blood from any source of infection in the human body.
Endometritis (inflammation of the uterine mucosa) appears after an abortion, in the postpartum period, as a result of various medical procedures. The causative agents are bacteria and microorganisms that penetrate the damaged endometrial layer. By actively multiplying, they contribute to damage to the connective tissues and muscles of the uterus. The infection spreads further along the fallopian tubes.
Pelvioperitonitis (inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum) most often occurs as a complication after surgery. Inflammation in the peritoneum itself can spread to the ovaries if it is localized in the place where the latter come into contact with it.
Acute appendicitis can cause an abscess in the right ovary. Mucus accumulating in the appendix provokes stretching of the appendix and causes its inflammation. Pressure on the blood vessels increases, blood flow decreases, purulent accumulations and tissue necrosis form.
If the vermiform appendix is turned towards the ovary, the probability of damage to the latter is very high. As a result of surgery, the ovary is removed along with the appendix.
project "New Life"
Ovarian cancer is a type of malignant neoplasm that primarily develops from ovarian tissue. Most often they are represented by epithelial tumors (adenocarcinoma, mucinous ovarian cancer, serous ovarian cancer, etc.), germ cell and sex cord stromal tumors.
Ovarian cancer causes
The reliable causes of tumor formation are unknown, therefore, when discussing the causes of the development of ovarian malignancies, doctors talk about risk factors. These include the following conditions:
- hyperestrogenism - excessive production of female sex hormones (estrogens) in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Since ovarian tissue is sensitive to their action, hormonal stimulation can lead to active cell proliferation and their malignant transformation. Hyperestrogenism is also observed when superovulation is stimulated during IVF or egg donation, during hormone replacement therapy during the treatment of menopause pathology, as well as in obesity, since adipose tissue has its own hormonal activity;
- long reproductive period with constant ovulation - early onset of puberty, late menopause, lack of pregnancy, refusal to breastfeed;
- Heredity and genetic predisposition. About 10% of cases of these neoplasms are due to genetic reasons. First of all, we are talking about mutations in the BRCA genes. The risks also increase if tumors are present in first-degree relatives.
Stages
- Stage 1 ovarian cancer - the tumor affects only the ovaries and does not spread beyond them;
- Stage 2 - the pelvic organs are affected;
- Stage 3 - the abdominal organs are affected;
- Stage 4 - the tumor extends beyond the abdominal cavity, for example, into the lungs or pleura.
Ovarian cancer in women: symptoms and signs
Symptoms of ovarian cancer at an early stage are either absent or nonspecific, so based on complaints it is difficult to suspect the presence of such a pathology. More specific signs appear in later stages.
Early symptoms of ovarian cancer:
- stretching in the lower abdomen;
- abdominal pain of unclear localization. In the initial stages, they appear suddenly and disappear just as suddenly, and for a long time;
- bloating.
Signs of ovarian cancer in advanced stages
- disturbances in stool and urination - develop due to the fact that the tumor displaces the uterus, which, in turn, puts pressure on the intestines and bladder;
- increase in abdominal volume.
As a rule, it develops due to ascites, an accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. the presence of hard palpable formations in the abdomen; - intense pain in ovarian cancer can be a sign of torsion of the tumor stalk and its ischemia. It is rare to occur as a first sign of ovarian cancer.
Common signs of ovarian cancer in women:
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- loss of appetite and feeling full from small amounts of food;
- fast fatiguability.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in 2 stages - detection of a neoplasm, its verification and determination of the stage. As a rule, a tumor is detected using radiation diagnostic methods - ultrasound, CT, MRI.
For example, ovarian cancer on ultrasound looks like an irregularly shaped formation with unclear, blurred boundaries.
Also, using these methods, a preliminary assessment of the spread of the process is made, for example, the growth of cancer into the pelvic organs or abdominal organs.
If, according to radiological examination methods, a neoplasm is detected, the patient is offered to donate blood for ovarian cancer (to determine the tumor markers CA 125 and HE 4 with the calculation of the ROMA index); this study will allow, with a certain degree of probability, to differentiate ovarian carcinoma. If germ cell tumors are suspected, the doctor may suggest tests for AFP and hCG.
The final diagnosis and determination of the stage of the disease is mainly carried out after surgery, during which material is taken for histological examination and the abdominal cavity is inspected for the presence of carcinomatosis and metastases.
Can ovarian cancer be cured?
Ovarian cancer is treated with a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. The goal of the operation is to remove the tumor mass as completely as possible, and chemotherapy destroys the remaining malignant cells and reduces the likelihood of relapse or progression of the pathology.
Surgery
The amount of intervention depends on the stage of the process. Stage one ovarian cancer allows removal of the affected organ and fallopian tube. This allows the second ovary to be preserved for a while and, if desired, the woman to give birth to a child. After this, an ovariohysterectomy is performed. Indications for such treatment are very limited.
Basically, the standard operation involves the removal of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, lymph nodes and resection of the greater omentum (this helps prevent peritoneal carcinomatosis from cancer and its spread throughout the abdominal cavity).
In addition, resection of the organs involved, such as the bladder or intestines, may be necessary.
In many patients, the disease is diagnosed at advanced stages, when the process involves the abdominal organs, distant lymph nodes, or there are metastases of ovarian cancer outside the abdominal cavity. Then treatment begins with several courses of chemotherapy, and surgery is performed after reducing the volume of the tumor mass.
Chemotherapy
As a rule, chemotherapy for ovarian cancer is carried out after surgery, which will not only reduce the volume of the tumor mass, but also synchronize the life cycle of malignant cells, which will make treatment more effective.
The selection of drugs is carried out based on the histological type of the tumor. For example, the first-line treatment choice for adenocarcinoma is a combination of platinum and taxane drugs.
After the patient has received the required number of courses of chemotherapy, treatment is stopped and active surveillance is started to detect relapse in a timely manner.
Some women may be prescribed targeted therapy with bevacizumab if indicated.
Evidence of disease progression is the emergence of new tumor foci according to ultrasound, CT or MRI, and/or an increase in CA125. The type of relapse matters here:
- platinum-sensitive - tumor progression began no earlier than 6 months after cessation of chemotherapy. In this case, you can continue treatment with platinum drugs, but in combination with other, previously unused drugs. If more than a year has passed since stopping treatment, first-line chemotherapy can be used;
- platinum-resistant - the tumor began to progress earlier than six months after stopping treatment;
- platinum-refractory relapse—the tumor progresses already during first-line chemotherapy.
In the last two cases, regimens that do not contain platinum drugs are used for further treatment. If this does not help, then they limit themselves to maintenance therapy.