What is fibroids
Myoma (leiomyoma, fibroma, fibromyoma) is a benign neoplasm in the tissues of the uterus, which consists of fibers of smooth muscle tissue. The formation can be single, or it can develop simultaneously in several parts of the uterus.
Fibroids appear after puberty and before menopause. This is due to the main feature of the tumor - dependence on female sex hormones (progesterone and estrogen). Neoplasms cause surges and imbalances in the production of these hormones.
With the onset of menopause, fibroids, due to a decrease in the formation of female hormones, tend to shrink and even completely resolve.
Other causes of fibroids:
- endocrine disorders;
- frequent inflammation in the pelvic area;
- trauma to the abdominal cavity (frequent abortions, curettage, cleaning, bruises);
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition.
Myoma always has a round or oval shape, sometimes round tumors grow on a stalk. It begins its development from a very small size (an ultrasound examination can detect a formation 2-3 millimeters in size) and grows without treatment almost indefinitely. The size of fibroids is usually determined relative to the enlargement of the uterus due to its growth. As a unit of measurement, gynecologists take the size of the organ as during pregnancy (in weeks).
Small fibroids (up to 2.5 centimeters in diameter, i.e. up to 5-6 weeks) are most often discovered at an appointment with a gynecologist. Almost all of them grow asymptomatically and do not pose any danger to the patient.
The exception is a small pedunculated fibroid. This is not cancer, but it must be removed as soon as possible since the thin stalk can twist and cause dangerous complications: bleeding, tissue necrosis and sepsis.
Medium fibroids (up to 6 centimeters, from 6 to 10-12 weeks) are removed as necessary:
- if there is a risk of degeneration into cancer;
- if bleeding occurs;
- anemia appeared;
- bothered by pain in the pelvis or back;
- with concomitant ovarian diseases;
- rapid growth in education is recorded.
Enlargement of the myomatous node during menopause may be a sign of a precancerous condition or the development of cancer.
Large fibroids carry the most danger. Most often, fibroids larger than 6 centimeters (age 12 weeks) in diameter cause cancerous processes in the uterus.
What types of fibroids are there?
Fibroids can be detected using ultrasound, MRI, or biopsy. The tumor is divided into a number of types:
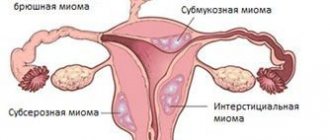
- Cervical – localized on the cervix.
- Subserous - found on the outer wall of the uterine organ.
- Submucosal - forms inside the uterine cavity, occurs rarely.
- Intramural - the formation affects the smooth muscle layer, grows deep into the fibrous fibers, and the uterine wall thickens. This pathology occurs frequently.
The nodes can grow on a stalk, actively grow and disappear on their own. You should not engage in treatment without the supervision of a doctor.
The neoplasm is divided into size groups:
- Small nodes not exceeding 2 cm. They are detected by chance, occur without discomfort, and do not require surgical intervention for treatment.
- The nodes are medium in size, up to 6 cm. They are characterized by pain and bleeding. Serious therapy is required.
- Large tumors, more than 7 cm. Removal is performed by surgery. Considered life-threatening.
For nodes growing on a stalk, removal is carried out promptly, even if they are small in size. A large formation is removed urgently. A complication occurs when the node grows rapidly - a malignant tumor may appear.
Types of uterine leiomyomas
With fibroids, it remains possible to become pregnant, and often the presence of nodes becomes known during a routine examination of a gynecologist for an already pregnant woman. This creates a danger for the development of the embryo and provokes the threat of miscarriage. During pregnancy, the tumor increases due to the growth of the uterus, but this does not threaten the life of the mother and child. The dangerous point is the fact that the node spontaneously collapses. It starts with dead tissue and leads to the formation of cysts, swelling and bleeding.
The risk group includes women who become pregnant after 30 years of age. With a small tumor, pregnancy proceeds calmly, under the supervision of a doctor. If the fibroid is large in size, then the possibility of early labor increases and the baby is born with a low weight. During childbirth, difficulties arise with the long passage of the child through the birth canal, and the fetus may be incorrectly positioned.
Can uterine fibroids develop into cancer?
Fibroids are a benign tumor and most often do not pose a threat to a woman’s life. But doctors do not so easily recommend that women undergo examination at least once a year, since the degeneration of fibroids into cancer sometimes still happens.
Every woman needs to know what causes cancer:
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drug addiction);
- unhealthy lifestyle (non-compliance with sleep and rest schedules, unhealthy diet);
- lack of regular sexual intercourse;
- absence of childbirth and lactation up to 35 years of age;
- physical overload;
- abdominal trauma.
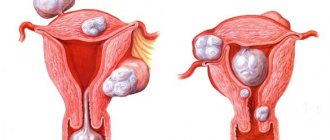
Types of fibroids
The type of fibroid depends on its local location on the body of the uterus:
- subserous (develops on the outer wall and grows towards the pelvis);
- interstitial (develops in the muscular layers of the uterus and deforms adjacent tissues);
- submucosal (develops in the submucosal layer);
- cervical (develops in the cervix).
Tumors can develop both inside the tissues of the organ and on the walls of the organ, communicating with the uterus by thin processes of connective tissue, or so-called “legs”.
Is it possible to avoid cancer with fibroids?
Cancer due to myomatous nodes is very rare, however, women should be more attentive to their health and strictly follow the recommendations of doctors:
- visit a gynecologist once every six months;
- Once a year, undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvis;
- say “no” to smoking and drinking alcohol (bad habits poison the body, which leads to failures and decreased resistance);
- adhere to the principles of proper nutrition (with fibroids, it is important that the body receives more fiber, minerals and vitamins, so you should increase the portions of fruits and vegetables);
- avoid and promptly treat any infections and inflammations;
- try to avoid medications that have a carcinogenic effect on the body;
- do not take hormone-containing medications without consulting a gynecologist;
- Avoid tanning in the sun and solarium;
- avoid excessive physical activity (physical overload greatly increases the blood supply to the pelvic organs, which can cause abnormal processes);
- do not visit the sauna and steam bath;
- keep your weight normal.
Uterine sarcoma and fibroids: differences on ultrasound
When conducting an ultrasound examination, the doctor can also presumably tell from the ultrasound data whether there are signs of malignancy: heterogeneity of the contours and structure of the formation, the presence of cavities in it, signs of necrosis or metastasis, effusion into the abdominal cavity.
When performing magnetic resonance imaging or MRI, the nuances of this neoplasm are also clearly visible.
When performing laparoscopy or laparotomy, visual signs of an oncological process can be identified. But it is worth saying that none of the above methods gives an exact answer to the question of benign or malignant uterine fibroids, and the symptoms also will not give a reliable answer.
There may be no signs of uterine cancer in the early stages of fibroids.
The only way that will give an accurate answer to the questions posed is only a histological examination of the material obtained during diagnostic or therapeutic surgery.
Do uterine fibroids turn into cancer?
Unfortunately it is so. Any neoplasm, like any at some point, but healthy tissue can subsequently become a substrate for cancer. No doctor or scientist will give a woman a guarantee that myomatous lesions of the uterus will not transform into a malignant process. Since there are quite a lot of theories about the origin of oncological pathology, no one can accurately deny the possibility of malignancy. That is, uterine fibroids, of course, can acquire the properties of a malignant process.
The only way to somehow reduce the possibility of degeneration of an existing but benign neoplasm is to create risk groups for morbidity, as well as to implement preventive measures and measures to prevent such a formidable complication.
Uterine fibroids: degeneration into cancer and how to avoid it?
- It is necessary to change your lifestyle: you need to completely give up smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, and adjust your work and rest schedule. Remove foods high in carcinogens from the diet, increase the proportion of vegetables and fruits high in antioxidants;
A recommended measure is also to reduce body weight if it is overweight. This requires the above menu correction, as well as fairly moderate physical activity. With increased physical activity and the presence of a myomatous node on the leg, its torsion and disruption of the node’s nutrition, and subsequently its necrosis, can occur. blood flow in the pelvic organs also increases, which also negatively affects the development of fibroids in the direction of its rapid increase.
A very important point, and at the same time, a big mistake of women, is self-medication of this pathology in the form of the use of physiotherapy. Any thermal effect on the uterus can improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs, thereby causing rapid progression of the pathological process. This may be a trigger for the tumor to degenerate into a malignant form.
Termination of pregnancy when it occurs in the form of abortions also provokes tumor degeneration. Abortion is a powerful hormonal stress for the body, as well as the method of its implementation, for example, curettage of the uterine cavity can be a provoking factor for such malignancy of myomatous formation.
No one can say for sure whether uterine fibroids will degenerate into cancer or not, so when such a diagnosis is made, you should immediately seek medical help in order to begin conservative or surgical treatment in time, depending on the clinical situation, the size of the tumor, and the woman’s age. After all, doctors all over the world have come to the conclusion that it is necessary to introduce preventive medicine to the masses in order to prevent diseases, rather than engage in lengthy and expensive treatment.
Signs of malignancy of formation
Fibroids develop into cancer with a probability of 1 in 1000 cases. According to statistics, this most often happens between the ages of 55 and 65 years.
The first sign of malignancy of tumors in the body is rapid growth. However, fibroids are an exception to the rule, and even an increase of a few centimeters per year does not mean that the tumor has degenerated into cancer.
The risks of developing sarcoma increase with age. The growth of education after menopause is a bad sign.
When it is necessary to consult a doctor to exclude the development of cancer and to begin treatment of growing fibroids in a timely manner.
- Bleeding of bright scarlet or red-brown color began.
- Discharge from the vagina is disturbing (blooding, increased discharge, pus or ichor has appeared).
- Any pain appeared in the abdomen or back (aching, sharp, cramping, etc.).
- Growth of education by more than 2 centimeters per year according to ultrasound results.
- Abdominal enlargement not associated with excess weight gain.
- There were problems with the menstrual cycle (delays, absence of menstruation, prolonged bleeding).
- Changes in general condition - weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue.
- There are problems with urination or defecation (frequent urge, incomplete emptying of the bladder and bowels, pain when going to the toilet, constipation).
- Depression due to fibroids.
All these signs do not indicate that cancer is developing. A huge number of other female diseases have similar symptoms: inflammation of the tissues of the vagina, uterus and cervix or the growth of benign fibroids.
How does fibroid occur?
This formation is considered benign and consists of muscle and connective tissue of the walls of the uterus. It is difficult to determine the disease when the size of the node is small; it is not considered life-threatening and does not cause discomfort.
The tumor can increase in size; there are single and multiple tumor nodes. After menopause, spontaneous destruction may occur.
The first discomfort occurs when the volume of the tumor increases, when it is already affecting the body and threatening complications. This includes the following indicators:
- acute pain during menstruation or cycle disorder;
- difficulty urinating;
- continuous pain in the lower abdomen and back;
- bleeding, difficulty conceiving a child;
- the stomach increases.
Why fibroids occur is not known exactly. The most likely causes include heredity, hormonal imbalance, inflammatory processes in the uterine body and appendages, abortion, and age. Excess weight, damage to internal tissues, bad habits, and early puberty also affect the development of the disease.
Early diagnosis allows you to avoid complications, problems with conception and pregnancy, and surgical intervention.
How is sarcoma treated?
Degeneration of fibroids into cancer, detected at an early stage or in the precancer stage, is perfectly treatable. First of all, an operation is performed during which only the tumor, part of the uterus, or the entire uterus is removed (the degree of intervention depends on the stage of the disease). The woman then undergoes drug treatment, radiation or chemotherapy to avoid recurrence and destroy all cancer cells in the body and prevent the spread of metastases. With timely treatment of sarcoma, the prognosis is very favorable.
Uterine fibroids - no, they are not cancer. The risks of its degeneration into sarcoma with timely treatment and regular monitoring by a doctor are minimal. Take care of your health, lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid stress, regularly visit a female doctor and you will most likely never have to be treated for cancer.
Treatment of malignancy
The benign nature of the tumor should not provoke a woman to neglect her own health. At the initial stage, symptoms of the disease rarely appear, but an overgrown node causes many problems. Patients with uterine fibroids should undergo regular gynecological examinations and pelvic ultrasound.
In order not to worry about whether the tumor will turn malignant or not, after diagnosis, you need to immediately begin treatment.
Modern medicine offers two ways to get rid of uterine fibroids: conservative and surgical. In the first case, medications are prescribed to eliminate the main symptoms and stop the growth of the tumor. The second method is more radical and involves instrumental treatment methods: FUS ablation, UAE, myomectomy, hysterectomy, etc.
When a malignant neoplasm is diagnosed, immediate removal of the tumor is necessary. If the disease is advanced, removal of the uterus and sometimes the ovaries will be required. After the operation, the woman is prescribed a course of chemotherapy.