The frequency of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs ranks first among all gynecological diseases and accounts for about 65% of all visits to antenatal clinics. Early onset of sexual activity, frequent changes of sexual partners, as well as the latent course of most inflammatory diseases lead to the formation of their chronic forms. It should be noted that among all patients with such problems, more than 80% are nulliparous women under the age of 25, so pregnancy often occurs against the background of various inflammatory diseases.
Causes
The occurrence of adnexitis in a woman’s body is associated with infections (bacteria), which directly trigger the inflammatory process. But you need to know that not every organism is affected by infections in this way. This usually requires a certain predisposition. Since the environment of the fallopian tubes itself is sterile, a healthy immune system is quite capable of protecting them from the negative effects of any microorganisms. Therefore, symptoms of adnexitis occur in women with weakened immune systems. A number of factors may contribute to this weakening:
- exposure to diseases such as tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, chronic tonsillitis;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle;
- stress, overwork, hypothermia;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- intrauterine manipulations (curettage, use of an intrauterine device, hysteroscope for examination, etc.).
Thus, if a woman has a healthy immune system, then, despite the presence of sexually transmitted infections in her body, she will be able to resist any microorganisms.
Spicy
The acute form is characterized by general symptoms in the form of weakness, increased body temperature to approximately 38 degrees. In this case, there is pain in the lower abdomen, tension in the abdominal muscles, which is accompanied by pain on palpation. Headaches, chills, muscle pain, and difficulty urinating may also occur. At the same time, as the disease transitions to a subacute form, the listed symptoms begin to gradually subside.
The result of a complication of the acute form of adnexitis is an adhesive process in the pelvic organs. If an infection gets into the ovaries, cavities filled with pus may appear. If you start this process, the merging of these cavities will lead to an ovarian abscess: it will turn into a sac filled with pus. Another possible complication may be the spread of infection to the abdominal cavity, which will lead to its inflammation and the possibility of developing peritonitis.
Improper treatment of the acute form can lead to the disease developing into a chronic form.
A little about the structure
Inflammation of the appendages and uterus is also called inflammatory disease of the female pelvic organs. This includes not only inflammation of the uterus, but also processes occurring in the abdominal cavity or subcutaneous fat. Inflammatory diseases include:
- Myometritis – inflammation of the uterine myometrium;
- Endometrium - inflammation of the uterine mucosa;
- Endomyometritis is a combination of the first two diseases;
- Salpingitis is an inflammatory process in the fallopian tube;
- Pelvioperitonitis – inflammation of the peritoneum;
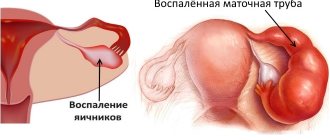
- Salpingo-ophritis, also known as adnexitis, is a simultaneous inflammation of the ovary and fallopian tube; a distinction is made between unilateral and bilateral adnexitis.
The inflammatory process can be sluggish or pronounced, but in any case it affects the menstrual cycle and reproductive health of a woman. Let's consider for what reasons a focus of inflammation appears and whether it is possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the appendages.
Chronic
As mentioned above, the symptoms of the chronic form differ from the acute one. This course is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen (aching) with flow into the groin and vagina. In some cases, referred pain is also observed. Symptoms additionally include cycle disruption, irregular menstruation, changes in their duration (both decreasing and increasing), heavy and painful discharge. Exacerbation in the chronic form occurs during menstruation, in case of hypothermia, as well as surgery.
The duration of this disease quite seriously affects the female body. Due to inflammatory processes, changes occur in hormonal terms. This is facilitated by the negative influence of microorganisms on the ovaries, the organ responsible for the production of hormones. All this can lead to neuroses, excitability, fatigue, and changes in weight.
Frequent exacerbations can also affect a woman’s libido (decreased), and also lead to painful sensations during sexual intercourse. The disease most often subsequently leads to infertility, as well as susceptibility to the development of ectopic pregnancy.
Why is inflammation of the appendages dangerous?
Any gynecological disease in the absence of therapeutic measures is fraught with the development of infertility. As for adnexitis, its main danger is that it can cause an ectopic pregnancy. This is due to the formation of adhesions on the fallopian tubes, which prevent the passage of a fertilized egg into the uterus. Elimination of adhesions is possible only surgically. However, not all such operations are successful.
In addition, inflammation of the appendages damages the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ, reducing resistance to infections. If salpingoophoritis is not treated, then hormonal imbalances subsequently occur, and a large number of cysts and other neoplasms are formed. Other consequences of the disease:
- nervous system disorders, irritability,
- menstrual cycle irregularities,
- periodic abdominal pain,
- painful menstruation,
- fast fatiguability.
Diagnostics
Identification of adnexitis, as well as its forms of development, involves the use of both general clinical and private medical research. Thus, diagnostic measures include, first of all, a gynecological examination. It is able to show the degree of inflammation of the uterine appendages, and sometimes of the uterus itself. He also does a number of tests that can show the presence of infection in the body or indicate another cause of the disease. These include a general blood test, a smear for microflora, PCR (allows you to diagnose so-called hidden infections), colposcopy (if necessary) and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
In the case when the diagnosis is carried out for a woman planning a pregnancy, it is advisable to perform laparoscopy. This is explained by the accuracy of the results obtained and the speed of the analysis itself. This minimizes the likelihood of false readings.
To be completely confident in the diagnosis, along with the tests, one should take into account the entire clinical picture, which consists of the patient’s complaints and his full medical history.
Adnexitis and pregnancy
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy are two concepts that are not recommended to be combined. That is why pregnancy planning is an important stage, which allows us to identify all diseases that impede this process. When diagnosing adnexitis, especially its chronic form, pregnancy should be postponed for the period of treatment, since the process of chronic adnexitis is accompanied by exacerbations, which, among other things, can be caused by hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
However, it happens that diagnosis occurs after pregnancy. There are two options here: either the onset of an exacerbation (which is most often characterized by pain in the lower abdomen and characteristic discharge), or the non-occurrence of an exacerbation (this is dangerous because the woman may not know her diagnosis, and the infection will begin to spread more and more throughout the body).
Lack of treatment for adnexitis during pregnancy can lead to infection of the fetus, which can happen both intrauterine and during childbirth, when the child is no longer protected by any amniotic membranes. All this boils down to the fact that you should think carefully before conceiving a child if you are diagnosed with chronic adnexitis, and it is best not to take risks and refuse until the doctor suggests a favorable period.
BabyMother
When planning a pregnancy, it is important to get rid of any diseases of the woman’s genitourinary system. After all, they not only interfere with rapid conception, but also have a negative effect on the fetus. The most common problems are considered to be inflammatory processes in the ovarian area. Is it possible to get pregnant if the appendages are inflamed? Will adnexitis (salpingoophoritis) affect the development of the fetus? We will cover these questions, which are of interest to all women who are responsible for the upcoming birth of their baby, in our article.
Inflammatory processes occurring in the area of the uterus and appendages cause diseases united by one name - inflammation of the pelvic organs.
These include the following pathological inflammations:
- Myometritis;
- Endometrium;
- Endomyometritis;
- Salpingitis;
- Pelvioperitonitis;
- Salpingo-oophoritis.
Adnexitis (salpingoophoritis) is an inflammatory process that occurs in the area between the fallopian tubes and ovaries, affecting both organs. Depending on the location of inflammation, there are unilateral and bilateral forms of the disease.
The disease can occur with pronounced symptoms or have a sluggish form. However, regardless of the characteristics of the manifestations, adnexitis always interferes with the natural functioning of the female reproductive system, having a negative impact on the entire menstrual cycle.
There are several causes of inflammation of the appendages. Moreover, each of them can be complemented by the other, further weakening the body’s defenses with such a “combined attack.”
The most common factor that causes the disease to develop is infectious microorganisms. They can enter the vagina from the intestines (Escherichia coli) or through sexual contact when infection occurs through the fault of a partner. “Sexual” infections are extremely dangerous, since for a long time they may not declare their existence in any way, and when they appear, indicate a chronic course of the disease. For example, chlamydia is difficult to diagnose, since the disease in the acute phase of development has very nonspecific symptoms. In this regard, the woman does not receive the necessary treatment, and the disease becomes chronic.
The following pathogenic microorganisms are no less dangerous for a woman’s reproductive organs:
- Streptococci;
- Staphylococcus;
- Mycoplasmas;
- Enterococci;
- Herpes;
- Ureaplasma.
Despite the fact that infectious lesions occupy a leading position in the occurrence of adnexitis, there are several other factors due to which the disease develops:
- Long-term states of depression and stress that weaken the body's defenses;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Regular disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- Lack of sexual activity or its irregularity;
- Constant change of sexual partners.
All these factors are closely interconnected. Thus, experiencing discomfort during sexual intercourse caused by an infection, a woman begins to abstain from intimate life. As a result, the situation worsens, since blood flow in the pelvic organs decreases, which leads to stagnation.
Adnexitis (salpingoophoritis) can occur in both acute and chronic forms. In both cases, the symptoms will be the same, but the pain with chronic adnexitis is less pronounced.
The main signs of the disease are as follows:
- Pain syndrome, which is localized in the lower abdomen, can spread to the lumbar region and legs;
- Atypical vaginal discharge;
- The appearance of painful sensations during intimacy and examination by a gynecologist;
- Body temperature may increase;
- The appearance of uterine bleeding not related to menstruation;
- Disruption in the menstrual cycle.
Diagnosis of adnexitis is carried out by a gynecologist, who, by examining smears and tests, identifies the presence of an inflammatory process. The doctor will also conduct an ultrasound scan to determine possible deviations in the size of the uterus and appendages.
All gynecological diseases, if left untreated, can lead to infertility. Salpingo-oophoritis is especially dangerous because if the pathology develops, pregnancy can occur, but due to the fact that the infection blocks the “passage” of the egg to the uterus, ectopic conception occurs.
Other possible dangers with inflammation of the appendages are the formation of adhesions on the fallopian tubes, which “prevent” the fertilized egg from reaching its “final destination.” In this case, only surgeons can remove adhesions, but operations are not always successful. Therefore, the woman is diagnosed with infertility.
The inflammatory process can, by affecting the walls of the uterus, cause damage to them, thereby reducing the ability of the organ to protect itself from pathogenic microorganisms.
Without treatment, the danger increases: hormonal imbalances occur. And since the female organs “work” exclusively under their influence, “defective” production of follicles occurs that do not have time to ripen. The result of adnexitis is numerous cysts and adhesions, which sometimes only surgeons can eliminate.
The functioning of inflamed fallopian tubes is always impaired. These disorders most often prevent sperm from reaching the egg to fertilize it. After all, infections cause numerous adhesions of the fallopian tubes, which do not allow the two important components of conception to connect. Although conception is still possible, it carries a serious risk of ectopic pregnancy. After all, the adhesions also block the exit of the egg from the tube.
So, salpingoophoritis and pregnancy are an extremely dangerous combination. After all, you can get pregnant with chronic salpingo-oophoritis, but the chances of successfully carrying a baby are low. And the presence of adhesions leads to ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
If you still manage to get pregnant with salpingoophoritis (adnexitis), you need to know that this is a high-risk pregnancy.
We list the main complications of pregnancy with adnexitis:
- Miscarriage, which is possible both in early and late stages;
- Bleeding;
- Premature placental abruption;
- Disturbances in fetal development caused by infections;
- Fading pregnancy;
- Hydatidiform drift;
- Delivery ahead of schedule.
During conception, with chronic adnexitis, serious hormonal disturbances are possible, which cause the rapid spread of infection. Therefore, fetal development slows down.
Most often, chronic salpingoophoritis and pregnancy leave very serious consequences in a woman’s body: after a miscarriage, complications arise that lead to infertility.
Therefore, the fact that you can get pregnant with inflammation of the appendages cannot be regarded as a chance for a successful birth of a baby! Conception should be planned only after a full course of treatment and recovery after it.
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages is prescribed by the attending physician depending on the reasons that caused it, as well as the form of development of the pathology.
Both acute and chronic adnexitis require antibiotics. Sometimes therapy is carried out in a hospital setting, because you need to complete the entire course of treatment, which includes eliminating the root cause of the disease with the help of intravenous medications and physiotherapy.
It is possible to cure chronic salpingoophoritis, but it should be understood that this is a very long process that requires constant medical monitoring based on repeated studies and tests.
Treatment of infertility, which is caused by large adhesions blocking the tubal lumens, requires the mandatory participation of surgeons. Laparoscopic sanitation is recognized as the most popular and effective method of surgical intervention. Using this technique, you can remove accumulated purulent discharge, remove adhesions and eliminate infection in the uterine cavity by irrigating it with antibiotics.
After chronic adnexitis has been cured, the woman is shown restorative therapy, which will allow her reproductive organs to function naturally.
A successful pregnancy after salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) is quite possible. This statement is confirmed by many women who suffered inflammation of the appendages and were able to bear and give birth to healthy babies. However, you need to remember that the earlier pathological disorders are identified, the higher the chances of getting pregnant quickly and without consequences. Chronic stages of inflammation are less treatable, and it will take much longer to eliminate them.
Therefore, at the first signs of inflammation, you should consult a doctor in order to begin treatment as quickly as possible. And when planning a pregnancy, taking tests and examining a gynecologist will protect the expectant mother from possible unpleasant surprises.
Chronic adnexitis (inflammation) affects the uterine appendages, in particular the ovaries and fallopian tubes, and is sluggish. The patient may not even suspect the presence of a pathology and learns about its existence when faced with the problem of conception.
There are chances of pregnancy, but they are reduced for the following reasons:
- disruption of the production of female sex hormones (hormonal imbalance);
- deformation of ovarian tissue and thickening of their mucous membrane;
- failure to ovulate;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes, which is complicated by the presence of scars and adhesions.
The onset of pregnancy largely depends on the degree of patency of the fallopian tubes. That is why the patient needs to be examined for their patency and the presence of adhesions. If the diagnosis shows the absence of this pathology, then pregnancy is possible.
In some cases, even in the presence of adhesions, the egg and sperm enter the uterine cavity, where the process of fertilization occurs.
When diagnosing unilateral chronic adnexitis, the chances of a successful conception are significantly higher compared to the bilateral form of the pathology. But exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease negates the chances of getting pregnant.
During pregnancy planning, a gynecologist may recommend surgical treatment to increase the chances of a successful conception. For example, laparoscopy may be prescribed to restore the lumen of the fallopian tubes. After treatment of the disease, the patient is required to undergo a course of health therapy.
The danger of pregnancy when diagnosing chronic adnexitis lies in the ectopic attachment of the fetus. This means that the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus for further development, but remains in the fallopian tube. This process is complicated by the presence of scars and adhesions, which are a consequence of chronic adnexitis.
Pregnancy against the background of chronic inflammation of the appendages usually occurs with a high probability of complications.
Another danger is too great a risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus. The decision on further actions is made on a case-by-case basis.
If you managed to avoid infection of the fetus during gestation, then there is a risk of infection of the child during the natural process of delivery. This is why patients diagnosed with chronic inflammation of the appendages are often shown a cesarean section.
If pregnancy does occur against the background of inflammation, then there is a risk of exacerbation of the inflammatory process. And this is due to a decrease in the immune function of a pregnant woman. Exacerbation of chronic adnexitis threatens:
- threat of abortion;
- development of polyhydramnios;
- premature birth and rupture of amniotic fluid;
- weak labor;
- postpartum endomyometritis.
If the cause of the disease is sexually transmitted infections, the gynecologist usually recommends terminating the pregnancy. If there is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, then treatment is applied. The latter depends on the severity of the process, the duration of pregnancy and the sensitivity of the patient’s body to antibiotics.
Pregnancy planning must be carried out along with the diagnosis of the pelvic organs. The condition of the appendages with chronic adnexitis requires constant monitoring and control.
How to get pregnant with adnexitis? This question interests many women, since this disease occurs in every fifth who seeks help from a gynecologist. It is important, after the diagnosis has been made, not to leave treatment to chance, this is the only way to be sure that the pregnancy will be successful. Let's learn in more detail about how exactly adnexitis affects the course of pregnancy and how to bear a healthy child.
How to get pregnant with adnexitis
Do not delay your visit to the gynecologist
It is possible to suspect the development of adnexitis based on the following signs:
- Characteristic whitish vaginal discharge
- Lower abdominal pain
Although symptoms may vary depending on what exactly caused the disease. It is important to start therapy on time, since treatment started late can lead to the fact that chronic adnexitis can provoke the formation of adhesions in the pelvic area. It is the presence of adhesions in the tubes that makes pregnancy impossible. But even if you manage to get pregnant and the test shows two long-awaited stripes, this is not a reason to relax. The fact is that untreated adnexitis (salpingoophoritis in other words) can also affect the course of pregnancy itself. Possible complications may include the following:
- High chance of miscarriage
- Development of ectopic pregnancy
- Fetal freezing
If you found out about pregnancy already when the inflammatory process was in full swing, you need to know about the following. Since when carrying a child all a woman’s energy goes into pregnancy, immunity is at its minimum. For this reason, it is possible that adnexitis will go into the acute stage or become bilateral.
The worst case scenario is the spread of infection beyond the uterine appendages. Even a child in the womb can be affected. Most often, infection does not occur, since the baby is protected from such attacks by the fertilized egg for nine months. In each individual situation, the doctor makes a decision on how to resolve the situation.
Also, the risk of complications remains during childbirth itself. The infection can spread and infect the baby at birth. If adnexitis is in the acute stage and the due date is approaching, the doctor delivering the baby will most likely insist on a caesarean section.
Finding herself in a situation where pregnancy is accompanied by a chronic inflammatory process, the expectant mother will have to decide one of the most difficult questions in her life - whether to terminate the pregnancy. As already mentioned, chronic adnexitis can provoke miscarriage, fetal death, or ectopic pregnancy. Together with your doctor, you need to weigh the pros and cons and only then come to a decision whether to have an abortion.
If adnexitis was caused by serious STD pathogens, such as gonorrhea, syphilis, pregnancy is terminated in 90% of cases. This is justified by the fact that the treatment of these diseases occurs with the help of severe antibiotics, which will negatively affect the health and development of the baby.
There is no clear answer to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with chronic adnexitis. Any inflammatory process in the female reproductive system can cause complications, both during childbirth and during the process of conceiving a baby. When it comes to childbirth, the most common problem doctors encounter is premature water breaking.
For this reason, if the pregnancy is planned, it would not be superfluous to undergo a comprehensive examination by a gynecologist, do an ultrasound diagnosis, and also take all the necessary tests. If everything is done correctly, then you will not be able to miss chronic adnexitis. And the treatment will be timely and will not stand in the way of happy motherhood.
As already mentioned earlier, with an inflammatory process in the birth canal, difficult births can occur. Amniotic fluid may break even before contractions begin. This may be accompanied by weak labor. And the fact that a child is in a waterless space for a long time can become another reason for infection of the fetus, since the child will be defenseless against infection.
Chronic adnexitis, symptoms. Spikes
Infertility. How to get pregnant easily?
As for the duration of labor, the presence of adnexitis becomes in most cases the cause of a protracted birth. This is why the obstetrician will most likely use drugs to induce labor. And they are known to adversely affect the health of the child.
Even if the pregnancy proceeded smoothly and the birth was relatively simple, the risk of complications after the birth of the child also remains. There is a high probability of developing endometriosis - inflammation of the lining of the uterus. Its symptoms are: increased body temperature, profuse bleeding from the vagina, and a characteristic unpleasant odor. It will not be possible to cure this disease on your own; urgent hospitalization of the woman is necessary.
In conclusion, we will say that adnexitis, especially in chronic form, has a negative impact on the state of a woman’s immunity. When answering the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with adnexitis, it is impossible to answer unequivocally. It can become a real reason for not getting pregnant if the process is so advanced that adhesions have formed in the tubes. In addition, even if you managed to become pregnant with a history of the described disease, do not forget about the risks that may arise during pregnancy, as well as during childbirth and the postpartum period. In order for a woman to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child, it is necessary to take care of her health in advance by undergoing preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Inflammation of the appendages or adnexitis is a fairly common disease among the female population. It can affect women of absolutely any age - those who are in menopause or even those who have not been sexually active.
Inflammation of the appendages and uterus is also called inflammatory disease of the female pelvic organs. This includes not only inflammation of the uterus, but also processes occurring in the abdominal cavity or subcutaneous fat. Inflammatory diseases include:
- Myometritis – inflammation of the uterine myometrium;
- Endometrium - inflammation of the uterine mucosa;
- Endomyometritis is a combination of the first two diseases;
- Salpingitis is an inflammatory process in the fallopian tube;
- Pelvioperitonitis – inflammation of the peritoneum;
- Salpingo-ophritis, also known as adnexitis, is a simultaneous inflammation of the ovary and fallopian tube; a distinction is made between unilateral and bilateral adnexitis.
The inflammatory process can be sluggish or pronounced, but in any case it affects the menstrual cycle and reproductive health of a woman. Let's consider for what reasons a focus of inflammation appears and whether it is possible to get pregnant with inflammation of the appendages.
One of the main reasons is infection. This could be E. coli coming from the intestines, or other infections and fungi. Most often this occurs due to the fault of chlamydia, streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasmas, enterococci, and herpes virus. There may be combinations of several anaerobes.
Sometimes the inflammatory process develops for other reasons, including:
- Depression and stress that weaken the immune system;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Irregular sex life;
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
All these reasons are interconnected. If an infection occurs, a woman feels discomfort, possibly itching and irritation of the genitals. Accordingly, in this state the desire for sexual intimacy is significantly reduced. At the same time, prolonged abstinence from sexual intercourse reduces blood flow to the pelvic organs, causing stagnation.
In addition to this, hormonal levels are disrupted, as a result of which the follicles do not develop fully, and cysts with immature eggs are formed. This condition can result in a chronic, severe course of the disease and the need for surgical intervention.
In the early stages, symptoms may resemble heavy periods. There is a viscous, aching pain in the pelvic area, weakness, and a possible increase in body temperature to 37-37.5 ° C. In addition, a bilateral inflammatory process manifests itself:
- Spread of pain to the legs and lower back;
- Brown vaginal discharge;
- Sharp pain when examined by a gynecologist;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Minor bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- Delay of menstruation by more than a week.
If these manifestations are detected, an immediate examination and consultation with a gynecologist is required. The sooner inflammation is detected, the easier and faster it can be gotten rid of.
The diagnosis is prescribed by the attending physician, having carefully studied the clinical picture of the disease. Ultrasound is prescribed to determine the size of the uterus and appendages. The condition of the uterus is assessed by examination.
A mandatory diagnostic procedure is the collection of secretions from the cervical, urethral and cervical canals - this helps to determine the causative agent of the infection.
In addition, the doctor may require an examination of the sexual partner of the sick person, since many infectious diseases are asymptomatic in men, unlike women.
Is it possible to get pregnant with adnexitis and where to start planning a pregnancy? Experts say that there is indeed a chance to get pregnant, but the inflammatory process can seriously affect the course of pregnancy. With a high degree of probability, such a pregnancy will end in miscarriage, threatening the woman’s life.
To plan a healthy pregnancy, your doctor will prescribe medications, including oral pills and vaginal suppositories. If you seek help in a timely manner, inflammation can be cured fairly quickly, within two to three weeks. In addition, antimycotic therapy is prescribed if the cause of inflammation is fungal colonies, as well as antiviral therapy if the cause is a viral disease.
At the same time, the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant after inflammation of the appendages is considered closed - the inflammation is relieved, the appendages restore their function and within several cycles their complete restoration and conception of a child becomes possible.
Treatment tactics are chosen by the attending physician and depend on the form of the disease and the cause of its occurrence. Acute forms are usually treated in a hospital with antibiotics.
In severe cases, surgical intervention, such as laparoscopic debridement, may be necessary. It allows you to remove accumulated suppuration, dissect adhesions, irrigate the uterus with saline solution with an antibiotic, and remove adhesions of the fallopian tubes to prevent blocking their lumen.
Treatment is a complex undertaking that requires detoxification of the body through intravenous therapy and physiotherapy. The procedures include physiotherapy, mud therapy, autoplasmotherapy, autohemotherapy, and gynecological massage.
If treatment is untimely or completely absent, quite serious complications are possible, affecting not only the reproductive organs. There is a high probability of developing primary and secondary infertility.
The appearance of adhesions between the fallopian tubes and the ovaries block the lumen of the tubes and prevent sperm from entering the cavity for fertilization. There is also too great a risk of ectopic pregnancy due to the fact that the egg cannot leave the fallopian tube due to the adhesion.
Even with successful fertilization and the birth of the fetus in the uterus, the pregnant body with salpingoophritis will reject the fetus, and blood circulation between the uterus and placenta will be disrupted. Possible infection of the fetus, premature birth and spontaneous miscarriage.
You can plan a healthy pregnancy only when inflammation therapy is completed. At the same time, treatment is continued even when the inflammatory process has disappeared, to prevent relapse. In most cases, therapy continues until the moment the child is conceived.
To avoid recurrence of inflammation of the appendages, you should have an active sex life with one partner and beware of unprotected sexual intercourse. Hypothermia must be avoided, and any infections or viruses that appear, even those not affecting the reproductive organs, must be eliminated effectively and as quickly as possible.
Women planning a second pregnancy after a cesarean section or natural birth must undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs to exclude the presence of adhesions and inflammatory foci.
A woman is also recommended to take vitamin complexes, proper rest and a diet that includes natural, healthy foods with as few substitutes as possible.
Related Posts
Sluggish inflammation in the uterine appendages without treatment is a significant risk factor for infertility. An irreversible type of loss of reproductive function occurs against the background of a pronounced adhesive process in the area of the reproductive organs: chronic salpingoophoritis and pregnancy are incompatible in cases where the fallopian tubes are obstructed.
The problem can be solved with the help of in vitro fertilization (IVF), but this is an unnatural conception that requires time, moral and material costs.
With bilateral chronic adnexitis, the best method of preventing infertility is repeated courses of therapy, creating conditions for successful conception naturally and preventing exacerbations of adnexitis.
A positive answer to the question of whether it is possible to become pregnant with adnexitis does not at all guarantee that a woman will gain the happiness of motherhood: successful conception of a fetus does not at all mean a favorable course of pregnancy and a positive outcome of childbirth.
With chronic adnexitis, the following reproductive problems may occur:
- temporary or irreversible infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy (tubal, ovarian, abdominal);
- early death of the embryo (frozen);
- miscarriage in the first months of pregnancy;
- spontaneous termination in the 2nd trimester;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine infection of a child;
- complicated course of pregnancy with the formation of congenital pathology of the fetus (fetopathy);
- inflammatory complications during childbirth and the postpartum period.
With chronic bilateral salpingo-oophoritis, it is not enough to become pregnant: throughout the entire period of gestation, it is necessary to carry out courses of conservation therapy, be examined for infections and follow the recommendations of a treatment specialist.
The following causative factors will prevent pregnancy in chronic adnexitis with bilateral damage:
- blockage of the fallopian tubes with adhesions or inflammatory exudate;
- periovular adhesive process, in which an egg ready for fertilization cannot meet a sperm;
- ovulation disorders due to oophoritis;
- hormonal changes in the female body caused by endocrine ovarian dysfunction;
- the formation of immune disorders against the background of prolonged inflammation in the appendages (autoimmune oophoritis);
- additional negative impact of concomitant infections (colpitis, cervicitis, endometritis).
The most common cause of female infertility due to inflammation in the appendages is the tubo-peritoneal factor: if bilateral obstruction of the fallopian tubes is confirmed by laparoscopy, IVF must be done to help the woman conceive a baby.
The path from identifying chronic adnexitis to pregnancy is long and complex: it is possible to quickly and easily conceive a child only if the diagnosis is made in time and there are no pronounced pathological changes in the uterine appendages.
Very important for a woman’s future reproductive function is complete and timely treatment of the first episode of acute adnexitis.
Each exacerbation of chronic salpingoophoritis requires antibiotics. In the asymptomatic form of chronic adnexitis, preventive measures must be taken and favorable conditions for pregnancy must be created. The main methods of treating infertility with adnexitis include:
- antimicrobial therapy (antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal);
- anti-inflammatory courses;
- improvement of blood flow and metabolism in the reproductive organs;
- correction of hormonal and menstrual disorders;
- treatment of all foci of infection in the reproductive organs;
- restoration of ovulation;
- therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy to assess tubal patency and dissection of adhesions.
It is possible to check the patency of the fallopian tubes only against the background of chronic adnexitis in the phase of stable remission and after a course of therapy. Often, restoring endocrine balance and eliminating inflammation in the area of the uterine appendages become the main therapeutic factors that ensure natural conception, so there is no need to rush into surgery.
It is advisable to do laparoscopy six months after drug treatment if there is no effect.
It is better to prevent infertility than to go through a long and painful path to the desired pregnancy. The following measures are used to prevent chronic adnexitis:
- categorical refusal of abortion;
- compliance with the rules of sexual hygiene;
- correct and effective treatment of vaginal and cervical infections;
- quick and correct treatment of primary inflammation in the uterine appendages;
- carrying out any gynecological procedures according to strict indications and in compliance with antiseptic rules;
- timely treatment of diseases of neighboring organs (cystitis, colitis, proctitis, paraproctitis, hemorrhoids, pyelonephritis).
It is extremely difficult to accurately and confidently answer questions about whether it is possible to become pregnant with chronic salpingoophoritis and how the resulting pregnancy will end. For each woman, the reproductive prognosis is individual, and largely depends on the following factors:
- variant of inflammatory lesion of the uterine appendages (unilateral or bilateral adnexitis);
- duration of the chronic process;
- frequency of exacerbations;
- number of medical and spontaneous abortions;
- presence in the past of diagnostic, contraceptive and surgical interventions on the pelvic organs;
- the presence of concomitant diseases.
Against the background of chronic adnexitis, pregnancy will occur if the inflammatory process is identified and treated in time, preventing tubal and periovular adhesions. Peritoneal infertility is an indication for IVF, with the help of which any infertile couple has a real chance of finding family happiness.
Treatment
One of the most important rules when treating the disease in question is no self-medication! This may lead to temporary improvement, but in the future it may cause a deterioration in the general condition. Therefore, it is important to follow all the instructions of your doctor. Treatment of adnexitis depends, first of all, on the cause of its occurrence, so all therapy should be based on a thorough diagnosis of the disease.
Treatment is carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital. The acute form of adnexitis is treated with specially developed antibacterial, desensitizing and anti-inflammatory therapy. In addition, an anesthetic may also be prescribed. Chronic adnexitis is more difficult to cure. In addition to the above types of therapies, the doctor also prescribes immunomodulators and immunostimulants, as well as resorption therapy. As a rule, the patient is prescribed physiological procedures (laser, ultrasound therapy, as well as manual therapy methods) together with gynecological massage, which help to avoid the formation of adhesions.
Treatment during pregnancy
Treatment of adnexitis in a pregnant woman is complicated by the fact that many drugs have a negative effect on the fetus. The situation in which infection only occurs during pregnancy deserves special attention, since this threatens intrauterine infection of the child. The inflammatory process itself, which already exists during pregnancy, threatens to infect the birth canal, which can lead to infection of the child during childbirth. In such cases, a caesarean section is usually recommended.
In cases where adnexitis was the result of infection with a sexually transmitted disease, the woman is strongly recommended to terminate the pregnancy. But if the inflammatory process began due to the presence of microorganisms natural to the woman’s body (candida, gardnerella), then the doctor prescribes the usual drug treatment based on the type of bacteria, their sensitivity to certain antibiotics, as well as the duration of pregnancy.
Complications
If treatment is untimely or completely absent, quite serious complications are possible, affecting not only the reproductive organs. There is a high probability of developing primary and secondary infertility.
The appearance of adhesions between the fallopian tubes and the ovaries block the lumen of the tubes and prevent sperm from entering the cavity for fertilization. There is also too great a risk of ectopic pregnancy due to the fact that the egg cannot leave the fallopian tube due to the adhesion.
Even with successful fertilization and the birth of the fetus in the uterus, the pregnant body with salpingoophritis will reject the fetus, and blood circulation between the uterus and placenta will be disrupted. Possible infection of the fetus, premature birth and spontaneous miscarriage.
You can plan a healthy pregnancy only when inflammation therapy is completed. At the same time, treatment is continued even when the inflammatory process has disappeared, to prevent relapse. In most cases, therapy continues until the moment the child is conceived.