Cyclic changes occur in the female body: hormone levels fluctuate, mood swings occur, and discharge of different consistency and color appears. The condition of the cervix before menstruation and on other days is an important indicator that indicates the proper functioning of the reproductive system. When palpating the organ, the obstetrician-gynecologist determines the phase of the menstrual cycle and suggests pathological syndromes.
What does the cervix look like before menstruation?
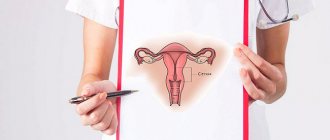
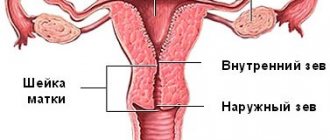
The organ is the connecting link between the uterus itself and the vagina. In the middle is the cervical canal, through which mucus and menstrual flow exit and sperm penetrate.
Position of the cervix in different phases of the cycle
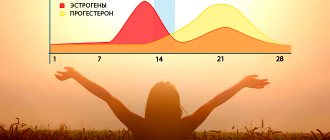
Before moving on to describing the tactile qualities of the organ, you need to understand the stages of the menstrual cycle. Characteristic changes in the tone and size of the uterus occur in each of them. There are 3 stages in total:
- The secretory (luteal) phase is a period when the body experiences high levels of progesterone. The endometrial glands produce mucus and prepare for implantation of a fertilized egg.
- Menstrual stage - if conception does not occur, the level of sex hormones in the body drops sharply. This is manifested by the rejection of the outer layer of the endometrium and its release outward in the form of menstruation.
- The proliferative phase (ovulatory) is the growth of the follicle in the ovary under the influence of estrogens, as well as the restoration of the epithelium of the inner wall of the uterus. The period ends with the release of the egg into the fallopian tube - ovulation.
Secretory stage
Immediately after ovulation, the cervix is high and difficult to palpate. At first it is soft and moist to the touch, but gradually hardens and dries out. The amount of mucous secretions decreases sharply. On the Internet you can find photos of what the cervix looks like on different days, but this is not very informative for a woman. It is better to focus on palpation sensations.
1–2 days before menstruation, the uterus enlarges, which is associated with increased production of progesterone. In this case, the lower part of the organ lowers slightly. The cervix is easily palpable due to its low location in the vagina. It has a hard, dense consistency and becomes moist. On the eve of menstruation, the cervical canal expands and can be felt in the form of a round depression in the center of the cervix.
Proliferative stage
The uterus gradually rises after menstruation, reaching its maximum height before ovulation. This is necessary to shorten the cervical canal, reducing the path that sperm must travel to fertilize the egg.
The cervix softens, by the time of ovulation it swells, becomes loose and moist, and becomes covered with copious sticky mucus. During this period, it is difficult for a woman to palpate the organ on her own.
Menstrual stage
The cervix should be firm to the touch before menstruation, and it remains the same during bleeding. During this period, the cervical os opens slightly and reaches its maximum width. Due to the enlargement of the uterus before menstruation, a woman feels discomfort and heaviness in the lower abdomen.
During menstruation, self-examination of the organ is strictly prohibited; gynecologists also try to postpone the examination until the end of the critical days.
The value of cervical palpation as a diagnostic method
Examination of the organ is included in the standard vaginal and bimanual examination of the patient by an obstetrician-gynecologist. The method provides valuable diagnostic information only when combined with speculum examination, palpation of appendages, and instrumental diagnostics.
If the doctor, upon palpation, detects an incomprehensible lump or tubercle, suspects erosion or oncology, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the uterus and pelvis 5–7 days after the start of menstruation. Ultrasound examination helps to clarify the nature and extent of the pathological process. If necessary, diagnosis is supplemented with x-ray and endoscopic methods, and cervical biopsy.
Cervix during menstruation
We found out what the condition of the cervix is before menstruation, now we will find out what it looks like directly on menstruation days. At this time, the pharynx expands slightly, as during ovulation, but the purpose of this opening is different - not readiness for fertilization, but the desire to erupt blood clots. This position of the cervix during menstruation creates fertile ground for the proliferation of bacteria and the addition of infection. That is why on critical days it is not recommended to swim in open water, visit the pool, have unprotected sex and insert foreign objects into the vagina - fingers, a speculum. Although the moderate mucous discharge that is observed during this period is designed to protect the woman from infection, it is still not worth the risk.
The condition of the cervix during menstruation requires external hygiene . Ideally, you should wash yourself twice a day, not counting the procedures after bowel movements. You cannot wipe the anus in a forward direction - such actions are fraught with infection. It is also strongly recommended not to carry out water procedures inside the vagina during this period - no douching or insertion of intimate hygiene products. Often during menstruation, women experience pain in the uterus. Most often they are associated with the rejection of blood clots. In this case, conventional antispasmodics help. But sometimes painful contractions of the cervix signal an infection or pathology in the development of the organ. Therefore, do not neglect routine examinations with a gynecologist, so as not to lead to infertility from a common illness.
By the way, it is not so much pain, which is often a sign of dysmenorrhea, as heavy discharge that warns of abnormalities - fibroids, endometriosis, bleeding disorders and acute infections. In any case, after your period, especially if the pain in the uterus has not stopped, you should consult a doctor and do an ultrasound. If the cause of discomfort is dysmenorrhea, then it makes sense, along with painkillers or contraceptives, to take a course of vitamins and Omega-3 complex. If the cause of the pain is a serious illness, you should immediately begin treatment prescribed by the gynecologist.
What does the cervix feel like during pregnancy?
Pregnancy can be suspected if prolapse and enlargement of the uterus occurs before menstruation, but bleeding does not occur. Once conception is complete, the cervix has characteristic tactile properties: it thickens and hardens, the cervical canal narrows to a barely visible slit. The organ rises high in relation to the entrance to the vagina, so problems may arise during manual examination. If a woman becomes pregnant, there is slight pain when palpating.
Pain in the lower abdomen on day 22 of the cycle
From the first days after fertilization, the body sends a woman signals about the beginning of pregnancy, long-awaited or unplanned. Menstruation stops, mammary glands increase in size, mood changes, and unusual taste preferences appear.
These and other signs most likely indicate pregnancy
It is important to be attentive to your feelings so as not to miss important changes in your life. The doctor will be able to confirm or deny the fact of conception of a child after examining the patient.
Pregnancy symptoms
Any woman, regardless of whether she dreams of a child or whether pregnancy is undesirable, would like to know as early as possible that conception has occurred. Even before the delay, the body gives many signals about the change that has occurred in it. Some symptoms can be recognized as early as 2-3 weeks after conception, while others do not appear until the middle of the second month of pregnancy.
The first signs of pregnancy are often mistaken for general ailments and acute respiratory viral infections, especially if they are single and not intense. It is worth knowing that the symptoms of the onset of pregnancy are conventionally divided into:
- reliable: when they occur, the fact of conception is irrefutable;
- speculative: pregnancy is quite possible;
- dubious: they should not be particularly trusted, since they are based on a woman’s subjective feelings.
Gestational weeks are usually counted from the start of the new cycle in which fertilization occurred: the onset of pregnancy occurs on the 1st day of menstruation.
Ovulation (the release of an egg) occurs in the middle of the cycle on the 14th day (with a normal 28-day cycle). The egg lives for 24 hours, and only during this time can it be fertilized.
In the first days of pregnancy, it is quite difficult to recognize its symptoms. But sometimes, even on the 20-21st day of the cycle, some symptoms can tell an attentive woman about her situation. At this time, the fetus is already descending into the uterus and is carefully fixed in it. Signs of pregnancy during this period are not too bright. Most women notice changes in their bodies only after a delay in menstruation.
Reliable signs
Reliable signs of pregnancy clearly indicate that a child has been conceived. These include:
- HCG rise. Human chorionic gonadotropin appears only during pregnancy and clearly indicates the successful conception of a child. The concentration of hCG can be determined using a blood test from a vein 10-14 days after conception. Qualitative determination of hCG is carried out using a pharmacy pregnancy test.
- Detection of an embryo by ultrasound. Transvaginal ultrasound examination at 3-4 obstetric weeks allows you to see the embryo in the uterus or outside it. At 5-6 weeks, the fetal heartbeat is heard during ultrasound.
- Palpation of large parts of the fetus. It is carried out in the second half of pregnancy. By palpating the belly of the expectant mother, the doctor can determine the head and pelvis of the fetus. At 18-22 weeks, the baby’s heartbeat can be heard through the anterior abdominal wall.
Possible signs
Possible signs of pregnancy are detected in the early stages. Such symptoms do not always indicate the conception of a child. Similar signs are found in various gynecological diseases. Possible signs of pregnancy include:
- Amenorrhea. The absence of menstruation in a healthy woman of reproductive age most likely indicates pregnancy. Amenorrhea can also occur with some diseases of the genital area, as well as during the period of feeding a child with breast milk and during menopause.
- Increase in basal temperature. She will confirm pregnancy if the temperature, after increasing during ovulation, by the 21st day of the cycle does not drop to its previous levels and remains above 37 degrees. For this sign to be truly reliable, basal temperature should be measured daily, several cycles in a row, strictly in the morning after waking up.
- Toxicosis. Every second pregnant woman experiences it in the first trimester of gestation. It usually appears on days 27-30 of the cycle, at the time when menstruation should arrive, but there are cases of earlier onset of toxicosis. Most often, it is he who makes a woman think about the consequences of sexual contact without contraception. Many people know the symptoms of early pregnancy related to toxicosis: vomiting, excessive salivation, morning sickness.
- Cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix and enlargement of the uterus. Determined by a doctor during a gynecological examination.
Is self-diagnosis allowed?
Gynecologists do not interfere with independent research, provided that hygiene requirements are observed. A woman should not try to determine the cervix by touch during menstruation, since at this time the genitals are most vulnerable, and the risk of infection increases. Self-diagnosis is allowed during the remaining phases of the menstrual cycle.
Before starting a self-examination, a woman is recommended to look at a photo and become familiar with the anatomy of the genitourinary system. A one-time study will not provide any valuable information, but by palpating the cervix for 3-4 cycles, the girl will learn to notice signs of pathology.
You should not carry out diagnostics too often. It is optimal to palpate the cervix once every 3 days, the maximum permissible frequency of self-examination is daily, with the exception of menstruation.
Tingling in the uterine area
Sometimes, before the onset of menstruation, some tingling sensations may be felt in the uterine area. They often indicate a disease such as endometriosis. Unpleasant sensations are also accompanied by nausea, vomiting, severe headaches, fatigue, and a feeling of constant drowsiness. Some women have no appetite.
Such sensations may also indicate that an inflammatory process has begun in the genital organs or signal the presence of cancer. In the second case, pain may be accompanied by severe bleeding.
In order for pain to begin to decrease, it is necessary to take painkillers, but do not forget that they only relieve pain temporarily.
A doctor will help you establish and understand the true cause of strange sensations in the uterus. He will conduct an initial examination and interview, and, if necessary, refer the patient for tests, and the appropriate treatment will be based on the results obtained.
For example, if the uterus is pulsating, it is greatly enlarged, sharp tingling sensations are bothering you, or the organ is too prolapsed, you need to make a correct diagnosis as quickly as possible. In many cases, this “behavior” of the uterus is caused by a hormonal imbalance, so the doctor may prescribe a course of hormonal therapy, which is selected individually for each woman.
You should undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist, because this will help detect the disease in the early stages. Advanced diseases are much more difficult to treat.
Self-examination technique
Instructions on how to palpate the cervix:
- Trim long nails.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap for 60 seconds.
- Wear rubber gloves (necessarily sterile!).
- Take a comfortable position - squatting, sitting on the toilet, lying down, standing with your leg raised.
- Gently insert your index and middle fingers into the vagina, moving along the back wall (closer to the rectum).
- Slowly moving her fingers deeper into the vagina, the woman will feel a dense, rounded tubercle (cervix) with a depression in the center.
- Then carefully feel its consistency, find the entrance to the cervical canal (palpated in the form of a hole or gap).
Due to the fact that the uterus is enlarged before menstruation, the girl feels pain when trying to self-examine. In this case, you should not expose yourself to unpleasant sensations, and it is better to postpone the procedure until the end of menstrual bleeding.
Is it possible to warm up with cystitis?
Many people know that with cystitis, heat helps relieve pain. Moreover, some consider this method a universal remedy for cystitis. But are there any contraindications? From this article you will learn how heat and cystitis relate: is it possible to bask in the bathtub, is it possible to apply a heating pad, steam your feet, warm up and steam in a bathhouse.
Is it possible to heat cystitis at all?
Local dry heat helps relieve spasm of the urethra and lower bladder, thereby reducing cramping pain. In addition, heat dilates blood vessels and improves blood circulation, which helps reduce inflammation and speed up recovery.
However, warming up will not completely solve the problem. It should be used as an additional component to antibacterial therapy.
In addition, there are contraindications. The procedure cannot be performed at elevated temperature, weakness, poor health, blood in the urine, or during menstruation. In pregnant women, thermal procedures are also strictly contraindicated, as this can provoke an increase in uterine tone and even spontaneous miscarriage.
Is it possible to warm up in the bathroom if you have cystitis?
This is absolutely contraindicated. The fact is that the cause of cystitis is the proliferation of bacteria, and an increase in temperature around the pelvis and lower back will create favorable conditions for the penetration of microbes into the kidneys. Warming up cystitis in a bath often leads to a complication – pyelonephritis. Moreover, often the cause of inflammation in the kidneys is improper behavior during cystitis.
So, remember, the answer to the question is it possible to take (sit, lie down) a hot bath with cystitis - there is only one answer and it is “no”.
Is it possible to heat with a bottle or a heating pad if you have cystitis?
This method is the most preferable. Dry heat in the form of a warm bottle or heating pad is applied to the lower abdomen and lie there for about 25 minutes, covered with a blanket. You need to use a heating pad with a water temperature of no more than 40 °C to avoid causing burns. In addition to water, the bottle can be filled with heated sand or salt.
Is it possible to heat the lower abdomen if you have cystitis?
Yes, you can warm your stomach, subject to the conditions described above. In this case, it is better to warm the area above the pubis, where the bladder is located, with dry heat. Warming the lower back is contraindicated due to the risk of spreading infection to the kidneys.
Is it possible to soar your feet if you have cystitis?
If there is no fever, hovering your legs is not contraindicated, but it is somewhat pointless. Blood, warming in the veins of the lower extremities, flows upward to the pelvic organs, including the bladder. If the spasm of smooth muscles is relieved by such heat, it will be very weak. It will not affect the infection in any way. It is better to warm your feet with warm socks.
Examination of a pregnant woman
When carrying a child, the size and functional activity of all organs of the female reproductive system change. During pregnancy, the obstetrician-gynecologist carefully monitors the condition of the uterus to prevent isthmic-cervical insufficiency and other pathologies. In the first months, the cervix lengthens, is located high, and has a dense consistency. The cervical canal must be closed. As it approaches childbirth, the organ descends and shortens, the opening of the pharynx takes on a rounded shape and expands.
The structure of the female reproductive system
The internal reproductive organs in women include:
- The vagina is the canal that connects the cervix (lower part of the uterus) to the outside of the body. It is also known as the birth canal.
- The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the “home” for the developing fetus. The uterus is divided into two parts: the cervix, which is the lower part that opens into the vagina, and the main organ of the uterus, called the corpus or body of the uterus. The housing can easily expand to support a developing baby. The canal through the cervix allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit.
- The ovaries are small oval glands located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones.
- Fallopian tubes: These are narrow tubes that attach to the top of the uterus and serve as tunnels for eggs from the ovary to the uterus. Conception, the fertilization of an egg by sperm, usually occurs in the fallopian tubes. The fertilized egg then moves to the uterus, where it is implanted into the mucous wall.
Doctors' opinion
Gynecologists believe that there is no point in conducting routine self-examination. Many women have difficulty determining the difference in the consistency and position of the cervix before menstruation, during ovulation and on other days of the cycle, so the information content of the method is low.
With problems and complaints, you should contact a doctor who will conduct an expert diagnosis using not only physical, but also laboratory and instrumental research methods.
What is it for
During the first half of the menstrual cycle (from the first day of menstruation to approximately day 14), the uterus is restored and at the same time the dominant follicle matures. From about the 14th day of the cycle, the follicle is determined and begins to prepare for possible pregnancy.
In order to be ready to “receive” a fertilized egg, its inner layer must be thick and loose. Then this same egg will be able to penetrate the wall of the uterus and attach itself there. After this, the body receives a signal about pregnancy, and the egg continues to develop in the wall of the uterus. And since the newly born embryo initially has practically no nutrients, it receives them directly from the uterus. To do this, it must be filled with nutrients and “feed” the embryo until a full-fledged placenta grows. Thus, enlargement of the uterus is necessary for two reasons - consolidation and nutrition of the fertilized egg, and therefore to maintain a possible pregnancy.
If pregnancy does not occur, then the uterus gets rid of the “extra load” by.
Pros and cons of self-diagnosis
The only positive aspect of self-examination is the ability to suspect some diseases in order to see a doctor in time. Considering that it is difficult for a girl to distinguish a normal cervix from a pathologically altered one, the examination has low diagnostic value. Sometimes women use palpation of the organ to determine the day of the cycle with the calendar method of contraception, but there is a high probability of errors.
There are many more disadvantages to such a procedure. Here are the main ones:
- Traumatization. Without knowing the anatomy of the genital organs, a woman can accidentally damage the mucous membrane of the cervical pharynx, especially if it is low on the eve of menstruation. When menstruation is delayed due to cervical erosion, inaccurate examination often ends in bleeding, which the patient mistakes for the beginning of her period.
- Introduction of infection. Together with your fingers, you can introduce microbes into the cervical canal, which can result in inflammation of the endometrium (endometritis) and serious consequences. At home, it is difficult to monitor compliance with sterility, so this complication of self-diagnosis is often observed.
- An imaginary feeling of security. A woman who has palpated the cervix and is convinced that “everything is fine” may not visit a gynecologist for routine examinations for a long time. This is fraught with the latent course of diseases of the genital area and the development of complications, including infertility.
Other causes of uterine enlargement
Other reasons for an enlarged uterus may be:
1. Possible pregnancy. The reasons for its increase are the same as before menstruation. 2. Various diseases - fibroids, adenomyosis and others.
It should be taken into account that in those who have given birth, the uterus is always larger than in those who have not given birth.
Sources:
- About progesterone
- Why does my stomach swell before my period?
Uterine cancer in most cases develops from endometrial cells, the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the uterus. Most often, this disease occurs in mature or elderly women. The chances of recovery, if the tumor is detected in a timely manner, are quite high.
Instructions
Scientists have still not been able to figure out the reason why uterine cancer occurs. According to one of their assumptions, a significant role in this is played by the increased level of estrogen in the body - female sex hormones. The amount of estrogen usually increases in the following situations: - growing up too early; - before the onset of the last menstruation; - long-term use of estrogen-based medications.
In addition, others may be a risk factor, for example, metabolic syndrome. At the same time, if a woman has been pregnant several times during her life or has taken oral contraceptives that are suitable for her for a long period, her risk of developing uterine cancer is reduced.
The first sign indicating the possible development of uterine cancer is vaginal bleeding, which cannot be confused with normal bleeding, because it occurs in older women months, or even years, after the end of menstruation. If the woman is still of fertile age, the disease may manifest itself as irregular heavy bleeding that occurs regardless of the monthly cycle.
A doctor can detect the presence of a tumor using a conventional ultrasound examination. If doubts or suspicions arise, he may prescribe a diagnostic curettage. Tissue analysis will with 100% probability confirm or deny the presence of a malignant tumor.
In most cases, treatment of uterine cancer comes down to surgical removal of the uterus itself; if metastases grow in neighboring reproductive organs, removal of the ovaries, as well as further operations, may be required. Possible tumor remnants can be easily removed through radiation or chemotherapy.
Only removal of this organ will help protect you from uterine cancer 100%, but for the purpose of cancer prevention, it is unlikely that at least one doctor will agree to do it. However, if the uterus was removed for some other reason, you no longer have to be afraid of this type of oncology. For everyone else, regular visits to the gynecologist are recommended, which, even if it does not prevent the occurrence of the disease, will still help to detect it in time and begin timely therapy. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the patient’s chances of recovery.
In addition, every woman should be well versed in the calendar dates of her menstrual cycle and be attentive to unexplained vaginal bleeding.
Video on the topic
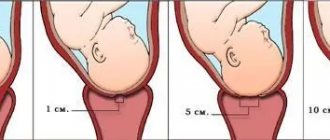
Before childbirth, the cervix changes significantly, preparing for the main moment: delivery. Doctors closely monitor her condition during the entire birth process.
Features of the cervix during gestation
During pregnancy, the cervix rises as high as possible in the vagina; upon examination, it can only be felt with a fingertip. It will be very hard and dense, and the hole will look like a small flat slit. Knowing what the cervix is like before menstruation, you can compare whether it is prepared for the start of the cycle.
During pregnancy, the length of the cervix also increases (becomes more than 2.5 cm). If it begins to decrease before the appointed time, it means that the risk of premature birth or spontaneous abortion increases.
Examination during pregnancy
During pregnancy, an examination allows you to determine the likelihood of a miscarriage, since the cervix during this period should be long and dense, but if its length becomes less than 2.5 cm, the doctor should prescribe additional examinations or hospitalization of the pregnant woman to prevent premature birth or miscarriage.
Shortly before childbirth, examination of the cervix allows you to determine the readiness of a woman’s birth canal for the start of labor. At this time, the neck should be shortened, smoothed and allow 1-2 fingers into the pharynx.
The cervix before menstruation and during pregnancy has its own characteristics that allow doctors to determine a woman’s condition without conducting additional examinations, if they are not currently possible. The doctor can make a final conclusion only after a complete examination of the body.
Vaginal infections
Vaginal infections occur when bacteria, fungi, or viruses grow in and around the vaginal area. Anything that reduces the acidity of the vagina can cause a vaginal infection, while some other infections are sexually transmitted. No one is safe from them.
What are some causes of vaginal infections?
Some types of bacteria live inside the vagina naturally. They produce acid that helps keep the environment at a certain pH level to help the body fight infections. However, hormonal changes and even the use of soap to cleanse the genital area can change the acid levels in the vagina.
This can cause bacteria that lives naturally inside the vagina, which usually doesn't cause problems, to grow erratically and cause harm. A foreign body, such as a forgotten tampon, can also stimulate bacterial growth and cause infection. This can lead to life-threatening complications known as toxic shock syndrome, but this is usually rare. Vaginal infections can also be caused by unprotected sex.
What happens to the uterus
All hormonal changes during a cycle in a woman’s body have a direct impact on the state of the organs of her reproductive system. Next, we will look at what happens to the structure and appearance of the cervix at different periods of the menstrual cycle.
Before menstruation
In normal condition, the cervix should be firm and dry. During the period of ovulation, when a mature egg leaves the ovary, the surface of the organ becomes looser, and the pharynx opens slightly, preparing for conception. If the sperm does not reach its final goal or there is no sexual intercourse at all, fertilization does not occur and menstruation begins.
Shortly before the regulus, the uterus begins to descend, so the cervix is low. During the release of the egg and during pregnancy, the cervix becomes softer and moist, and the pharynx begins to open slightly. Thus, the appearance and structure of the organ before the critical days and in the early stages of pregnancy are completely different. Another symptom of pregnancy is the bluish color of the uterus, this color is given to it by blood vessels, the number of which increases significantly after conception.