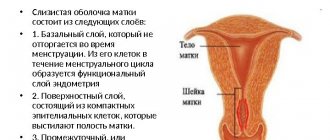
Diagnosis of gynecological diseases often requires intervention in the uterine cavity. This is not a doctor’s whim, but a necessity.
It is impossible to assess the condition of tissues without closely examining them under a microscope.
A procedure such as curettage allows not only to diagnose the condition, but also to carry out treatment.
Diagnostic curettage - what is it?
Partial removal of the mucous membrane of the inner uterine surface for histological examination is called diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
The technique is quite traumatic, so it is used according to strict indications.
Most often, a separate method is used: a scraping is made separately from the uterine cavity, and separately from the cervical canal. This is necessary for accurate detection of pathological changes. To improve the quality of diagnosis, before surgery it is necessary to perform hysteroscopy - a visual examination of the inner surface of the uterus using an optical instrument.
Indications for surgery
Against the background of leiomyoma, diagnostic curettage is performed in the following cases:
- menstrual irregularities with acyclic bleeding;
- heavy regular menstruation;
- detection of thickened endometrium by ultrasound during a normal cycle;
- suspicion of oncological pathology of the uterus;
- preparation for surgical removal of fibroids.
The main purpose of the operation is to eliminate the possibility of malignant degeneration of the endometrium. This must be done for every woman receiving drug treatment for leiomyoma, or having any type of menstrual irregularities. Before surgery to remove the uterus against the background of large fibroids, diagnostic curettage is required to select the extent of the operation: if the endometrium is normal, a conservative myomectomy can be performed, but if there is a high risk of a malignant tumor, the uterus must be completely removed.
Contraindications
- Infectious diseases of the reproductive system or general inflammatory processes.
- Chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, heart in the acute stage or decompensation.
- Suspicion of perforation of the uterine wall.
The procedure for removing uterine fibroids using the laparoscopic method: patient reviews. This article discusses the features of treatment of small uterine fibroids.
The link https://stoprak.info/vidy/zhenskix-polovyx-organov/matka/kogda-i-kak-delaetsya-abort-pri-miome.html describes the effect of abortion on fibroids.
Execution method
The operation of diagnostic endometrial curettage for fibroids is carried out in several stages.
Operation stages
| Operation stages | What will the doctor do? |
| Anesthesia | Any type of uterine surgery requires good anesthesia. Intravenous anesthesia is usually used to provide a short-term (15-20 minutes) anesthetic effect. |
| Vaginal treatment | Using special antiseptic solutions, the doctor treats the woman’s external genitalia and vagina to prevent infectious and inflammatory complications after surgery. |
| Cervical dilatation | Using special dilators, the doctor performs an operation to improve the patency of the cervical canal so that one can enter the uterus |
| Visual examination of the uterine cavity | A preliminary examination using hysteroscopy is not always carried out, but this method helps the doctor identify gynecological diseases (submucosal node, polyposis, areas of adenomyosis) and select the most suspicious area of the endometrium for curettage |
| Separate curettage | Using a special instrument, the doctor scrapes separately from the cavity and from the cervical canal. |
| Collection of received material | The tissues obtained as a result of scraping are collected in vessels with a fixing solution and sent to the laboratory |
Preparation
The procedure can be performed routinely or urgently. The amount of preparation for it depends on this. Planned intervention requires a minimal examination to assess general health.
- A general blood test reflects the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and the level of hemoglobin. A low rate will require taking iron supplements after surgery.
- A general urine test reflects the functioning of the kidneys and the condition of the bladder. Leukocytes and bacteria indicate the presence of inflammation, which may be a contraindication for planned curettage. In this case, you need to treat the infectious process and only then perform the operation.
- The ECG evaluates the state of the conduction system of the heart. The operation involves anesthesia, so an assessment of cardiac function is needed to make a prediction regarding the tolerability of the intervention.
- The coagulogram reflects the state of the blood coagulation system. In case of pathology, it is worth anticipating measures to stop bleeding.
- Blood type is necessary during any surgical intervention in case of emergency need for transfusion.
- Blood test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, C.
- Vaginal swab to assess cleanliness. Signs of inflammation require measures to sanitize the vagina. To do this, Ginezol and Terzhinan suppositories are placed for a week.
If the procedure is performed for emergency reasons (intermenstrual bleeding), then upon admission to the hospital they take a general blood test, urine test, coagulogram, blood group, and ECG. Tests for HIV and syphilis are also carried out, but their results are not awaited.
Planned curettage is carried out several days before natural menstruation . This makes it possible to evaluate the condition of the endometrium and the degree of its hyperplasia during histology. During menstrual bleeding, diagnostic curettage is not informative, since necrotic changes occur in the cells.
If a polyp is present, it is scraped out a few days after menstruation so that a thin layer of the endometrium allows its location to be assessed.
The night before a planned operation, a woman takes a light dinner. In the morning, she is given a cleansing enema to prevent feces from narrowing the vagina. Eating breakfast and drinking is prohibited. She takes a shower, shaves her crotch hair.
An anesthesiologist is consulted. The doctor finds out what operations the patient has previously had, what anesthesia was given, and how she endured it. The presence of allergies to medications and chronic diseases must be clarified.
Before the operation, a speculum examination is performed. A venous catheter must be installed. The woman is asked to urinate.
Postoperative period
After diagnostic surgery, a woman must be under the supervision of a doctor for at least 2 hours. If after this time there are no complications, then you can go home.
Given intravenous anesthesia, a woman should not drive on this day.
It is advisable that one of your relatives or friends help you get home. On the day of surgery, the following unpleasant sensations are possible:
- nagging pain in the abdomen;
- scanty bleeding;
- nausea and dizziness.
There are serious complications during and after surgery, but this happens very rarely, especially if all the rules are followed during the preparation stage.
Complications
Dangerous complications during and after surgery are the following situations and conditions:
- an acute inflammatory process that occurs in the endometrium, which is most often caused by infection from the vagina;
- chronic endometritis, which appears as a result of traumatic effects on the inner surface of the uterus;
- necrosis of the myomatous node due to impaired blood flow;
- perforation of the uterus with an instrument;
- uterine bleeding caused by impaired contractility of the muscle wall.
Complications after diagnostic curettage occur extremely rarely. Most often, the causes of problems after surgery are the individual characteristics of the pelvic organs or non-compliance with the rules for preparing for scraping. Feedback from women shows that in most cases, discomfort occurs immediately after the anesthesia wears off, but if the doctor’s recommendations are followed, they stop soon after the operation.
Rehabilitation
In order to prevent purulent-septic complications, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed for 5 days. This is especially true if the smear is inflammatory in nature and there are chronic infectious processes in other organs.
A few hours after the procedure, you can get up and be sure to urinate. For 4-10 days, vaginal discharge will continue , which will change from bloody to bloody, and then to mucous.
If they are not there, but your stomach hurts, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. A possible reason is cervical spasm and impaired blood outflow, causing hematometra. To prevent it, drotaverine is prescribed for 3-5 days.
You should not forget about hygiene, but under no circumstances douche. You can enter into intimate relationships no earlier than a month after curettage. If you neglect this recommendation, then there is a high risk of infection entering the uterine cavity and the development of endometritis.
Options for histological results
10 days after surgery, the doctor will receive the result from the laboratory. The following options are possible:
- normal endometrium corresponding to the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- glandular endometrial hyperplasia;
- glandular cystic hyperplasia;
- endometrial polyposis;
- atypical hyperplasia (precancerous changes in the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity);
- endometrial cancer.
Depending on the result, the doctor will choose treatment tactics for uterine leiomyoma.
Choice of treatment method
If asymptomatic small uterine fibroids are detected and the endometrium is normal, treatment is not required: regular observation and ultrasound examination once every 3 months are sufficient.
The combination of leiomyoma with any type of benign endometrial hyperplasia requires mandatory long-term treatment using courses of hormonal medications. According to indications, the doctor will suggest surgical removal of the submucosal or subserous node. Possible options include uterine artery embolization or FUS ablation.
If atypical hyperplasia or endometrial cancer is detected, it is necessary to undergo surgery to remove the uterus. Hysterectomy is the only guaranteed cure for cancer.
Curettage of the uterine cavity for fibroids is one of the important diagnostic studies included in the complex of preparatory examinations before starting conservative or surgical treatment.
The main goal of the method is to timely identify cancer pathology. After curettage, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations and begin a course of treatment for uterine leiomyoma. We advise you to learn about menstrual irregularities due to uterine fibroids.
Why histology for uterine fibroids?
Depending on the clinical picture of the disease, patients with uterine fibroids are conventionally divided into 2 groups:
In the article “Types of uterine fibroids” you can learn more about the characteristic features of various tumors.
This is a small tumor. It grows slowly, and a woman may not know about its existence for a long time. It is detected during a pelvic ultrasound as an incidental finding. It does not give any symptoms for a long time, and after the cessation of menstruation, when the woman moves into a new stage of her life - postmenopause, she may even undergo reverse development.
You can read more about the signs of pathology in the article: “Symptoms of uterine fibroids.”
Since fibroids usually begin asymptomatically, they can be detected accidentally during an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
This is an active type of tumor. Progresses very quickly, gives pronounced clinical symptoms:
- Pain. Appears when the fibroid leg is twisted or necrosis occurs and nutrition in the node is disrupted;
- Uterine bleeding or irregular spotting. Pathological bleeding is the most characteristic sign of fibroids;
- Dysfunction of neighboring organs. Occurs if the uterus with nodes reaches a large size;
- Severe iron deficiency anemia – is a consequence of intense bleeding;
- Impaired fertility and infertility. Myoma can create an obstacle to the movement of the egg through the tube and interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg, causing miscarriages and premature birth.
With rapidly growing uterine fibroids, pathological bleeding is often observed.
Such fibroids not only do not decrease during menopause, but, on the contrary, may even increase. Its growth often accelerates during pregnancy.
You can read about how quickly fibroids can grow and how to stop their growth here.
Time favorable for diagnostic curettage
Diagnostic curettage is the removal of the superficial functional layer of the endometrium (that which is normally rejected on its own during menstruation) along with the pathological formations located in it using a surgical instrument - a curette. The operation is carried out for diagnostic, therapeutic and treatment-diagnostic purposes.
After cleaning the uterus, the resulting material must be sent for histological and cytological examination to the laboratory for close examination under a microscope. Based on the histology conclusion, the doctor can judge the condition of the inner lining of the uterus and choose the right treatment tactics. The examined scraping may indicate:
- About the presence of polyps;
- About endometrial hyperplasia;
- About adenomyosis;
- About the inflammatory process in the uterine cavity;
- About malignant degeneration of the endometrium.
"Tell me, doctor...
1. Can bleeding occur after curettage for uterine fibroids?”
This phenomenon is rare, but possible. Occurs in those patients who have abnormalities in the blood coagulation system. Therefore, if after curettage you experience heavy bleeding, an urgent visit to the doctor is indicated.
2. When will menstruation begin after curettage?”
The day of curettage is considered the first day of the menstrual cycle. The next period after surgery should normally begin exactly as many days as your cycle lasts. But if the first period after the “cleaning” came with some delay, do not worry, this is allowed.
3. How long after curettage can you get pregnant?”
Curettage itself does not affect pregnancy in any way. It may occur as soon as you resume sexual relations. In most cases, gynecologists recommend waiting 3 months before conceiving a child, or at least until the first menstruation after curettage.
Curettage of the uterine cavity for fibroids is performed for diagnostic purposes. Knowing the condition of the endometrium, the doctor will determine possible treatment options and, if necessary, perform a conservative myomectomy, preserve the uterus and give the woman a chance to get pregnant.
It is necessary to clarify the condition of the endometrium using curettage not only in young women, but also in postmenopausal patients with uterine fibroids in order to recognize a malignant endometrial tumor in time.
For anovulatory bleeding, a scraping is taken several days before menstruation.
For menorrhagia, curettage is performed on days 5-7 of the cycle.
In case of infertility, scraping is taken before menstruation, but not in the very last days.
Acyclic dysfunctional bleeding requires curettage in the first days of bleeding.
Amenorrhea is a reason for repeated 4 line scrapings at weekly intervals.
A scraping for hormones is taken between the 17th and 24th day of the menstrual cycle, and to identify tumors, scraping can be done at any time.
Curettage should be carried out carefully, without making hasty movements, so that the result is large fragments of tissue. For this purpose, the doctor removes the curette from the cervix after each passage along the uterine wall. Small pieces of tissue make research difficult, since it is not always possible to restore the structure of the endometrium.
The most informative method of taking tissue for histology is curettage. It allows you to obtain high-quality, large enough material for research.
The professional training of a laboratory assistant is of priority importance, since the pathologist is required to know the characteristics of tissues depending on the phase of the cycle.
When is the procedure really necessary?
Diagnostic curettage allows you to obtain material from the uterine cavity, namely the surface layer of the endometrium, and evaluate its condition. But this manipulation does not provide any information about the condition of the myomatous nodes.
Sometimes you hear that curettage is prescribed in order to “remove nodes from the uterus” or in order to “determine the benignity of the tumor.” This is fundamentally wrong.
Only pedunculated submucosal nodes can be accessed for removal during diagnostic curettage.
Progressive uterine fibroids almost never occur in isolation. It is often combined with polyps and other hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, heavy acyclic uterine bleeding, and prevents a woman from becoming pregnant and safely bearing a baby.
Therefore, there are usually two reasons for diagnostic curettage for uterine fibroids:
- Existing concomitant disease (polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, uterine bleeding);
- The need to exclude endometrial cancer. This is especially important for making a decision before removing fibroids, when you need to decide: to save the uterus and remove only the nodes or, given the malignancy of the process, to perform a hysterectomy - complete removal of the uterus.
The operation is performed on the first day of menstruation or 1-2 days before menstruation. During menopause - on any convenient day.
Venue: small operating room at a antenatal clinic or gynecological hospital, gynecological chair.
Anesthesia - intravenous anesthesia or local anesthesia in the form of injection of the cervix with an anesthetic solution.
Duration – curettage surgery for uterine fibroids takes 5-10 minutes.
Operation stages
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure. After an intravenous injection of a narcotic drug, the woman falls asleep and does not feel anything. And the doctor at this time:
- Conducts a vaginal examination to determine the position of the uterus and its size;
- Treats the perineum with an antiseptic solution;
- Opens the vagina with gynecological speculum and fixes the cervix with special forceps - bullets;
- The uterine probe determines the length and direction of the uterine cavity;
- Expands the cervical canal with medical dilators;
- Performs curettage of the uterine cavity with a special spoon with a long handle, called a “curette.” The doctor’s movements should be careful and unhurried in order to cause minimal trauma to the walls of the uterus. The doctor collects all the material in a tray, then places it in a container and sends it for examination;
- He removes the forceps from the neck and removes the mirrors.
Diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is performed with a curette - a special tool in the shape of a spoon with a long handle.
The operation is completed. A woman wakes up after anesthesia.
For two hours she is under the supervision of medical personnel, who monitor her condition: measure her pulse, blood pressure, body temperature and monitor her discharge.
In the first hours after surgery, the discharge may be bloody with small clots, which then become insignificant, mucous-sacral or brown.
As a result of intravenous anesthesia, a woman may experience weakness or drowsiness, which goes away on its own after a few hours. Moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen may occur. The pain persists for several hours after curettage, then subsides.
If there are no complications during the observation period, she is sent home.
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse for 1 month;
- Taking antibacterial drugs prescribed by a doctor in the postoperative period;
- Do not use vaginal tampons or douches;
- Baths and saunas are prohibited;
- Perform hygiene procedures only in the shower;
- Do not take medications that thin the blood and cause bleeding.
Preparing for the study
2 days before the histological examination, you should refrain from sexual intercourse. Toilet the genital organs without using cosmetics, and also avoid douching and baths.
The use of any medications is possible only with the permission of the attending physician, since this may affect blood clotting and also conflict with some medications used during manipulation.
Before histology, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination:
- vaginal smear for flora;
- coagulogram and general blood test;
- examination for infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis);
- cytology;
- tests for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV;
- colposcopy.
If inflammation or infection of the genital organs is detected, curettage is postponed until cure.
So, when can curettage of the uterus be performed for fibroids:
- Prolonged, painful menstruation with clots;
- Random spotting;
- Acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- Frequent and painful urination or constipation;
- Weakness, dizziness, decreased hemoglobin;
- Bleeding in menopause;
- History of infertility or miscarriage.
- Asymptomatic small uterine fibroids;
- Infectious diseases or inflammatory processes of the genitals.
Curettage of the uterus is, of course, an operation, albeit a minor one. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination for its successful completion. What tests need to be taken?
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- Blood coagulation studies;
- Blood for HIV infection, syphilis and hepatitis;
- General urine analysis;
- Vaginal smear for pathogenic microflora and sexually transmitted infections;
- Electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Before surgery, it is necessary to pass all general clinical tests.
Before the procedure, a therapist must be examined to identify somatic pathologies and contraindications for anesthesia. The day before the operation, the woman is examined by an anesthesiologist.
On the eve of the procedure, the following conditions must be met:
- Sexual abstinence;
- Do not use douching, vaginal suppositories or tablets;
- Carry out intimate hygiene only with running water;
- Be sure to shave the hair from the external genitalia;
- Cleanse the intestines;
- Take a shower;
- In the evening - light dinner.
On the day of surgery, do not drink or eat. Bring a clean shirt, slippers and a supply of sanitary pads. Before starting the procedure, empty your bladder.
What are the complications?
Negative consequences after curettage:
- Perforation (puncture) of the uterus with medical instruments;
- Inflammatory process of the genital organs.
After the procedure of curettage of the uterine cavity, if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, an inflammatory process may begin under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms.