Progesterone is a steroid hormone. It is produced in organisms of both sexes in the ovaries and testicles, respectively. A small amount of it is produced by the adrenal glands. Its function is mainly related to the genital area.
It is often referred to as a pregnancy hormone: it prepares the endometrium of the uterus for the implantation of an egg after its fertilization and the subsequent bearing of a child.
What is the hormone progesterone produced in women responsible for?
- It helps the egg to strengthen in the uterine cavity after fertilization;
- Stops menstruation after conception;
- Does not allow the muscles of the uterus to contract, stimulates its growth;
- Increases sebum production;
- Increases blood pressure.
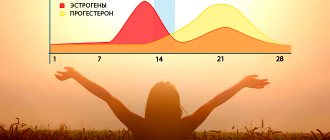
Norm at different periods of the cycle
- During menstruation (follicular phase) it is produced in low quantities.
- Around the period of ovulation, its level begins to rise.
- After the follicle bursts and an egg comes out of it, ready for fertilization, the luteal phase begins: the burst follicle becomes the corpus luteum and begins to produce this substance. At the moment, its level in the blood is increasing.
A high concentration is a signal that it is necessary to prepare for pregnancy.
If a woman does not become pregnant, its level gradually decreases, after about 10-14 days the corpus luteum dies and the menstrual cycle repeats. If by the time of menstruation its level is low, we can assume a phenomenon such as a hormonal imbalance that requires treatment.
If pregnancy has occurred, then it must be high to maintain it. Otherwise, its deficiency can lead to spontaneous abortion in the early stages. In the healthy body of the expectant mother, the concentration of this substance increases significantly. From 4 months it is produced by the placenta.
The role of the hormone
The element is produced by the ovaries, the adrenal cortex, and the placenta during gestation. Its role in relation to the female body is enormous. The substance helps regulate the menstrual cycle.
The hormone is also responsible for the ovulation process, prepares the organ (uterus) for conceiving a baby and prevents miscarriage. The deficiency of this component must be replenished immediately.
A similar task can be accomplished in different ways. For this purpose, it is recommended to use products containing progesterone or special preparations.
Symptoms of lack or excess of progesterone in women
When there is a deficiency or, conversely, excessively high production, the following phenomena are observed:
- breast tenderness;
- menstrual cycle disorders;
- vaginal bleeding;
- bloating;
- mood swings.
To determine the violation, it is necessary to undergo an appropriate analysis. Since the level of this substance increases in the second half of the cycle, it is recommended to take the test after ovulation.
To find out the time of the last one, you can use a special test. As a rule, the doctor prescribes a test approximately 3 weeks after your period (if the cycle lasts exactly 28 days). When the cycle is longer, the study is carried out later, for example, on the 28-29th day with a 35-day cycle.
In any case, the doctor will prescribe a referral for the test, and he will also determine on what day it is best to take it.
With regular menstruation, it is taken a week before the start of the last one. When the cycle is irregular, several studies are required at a certain interval. It is easier for a woman to navigate when she measures her basal temperature. In this case, blood must be donated a week after the increase.
Blood is donated at least 8 hours after a meal. It is recommended to do this in the morning on an empty stomach. The same applies to tests for all other hormones.
Norm of progesterone in women
The level of this substance is measured in nanograms per milliliter of blood (ng/ml) or nanomoles per liter (nmol/l).
To convert the former to the latter, you need to multiply the result in milliliters by 3.18.
- If the body produces the hormone in sufficient quantities, then the norm fluctuates in the following values: follicular phase - 0.32-2.23 nmol/l; ovulatory – 0.48-9.41; luteal – 6.99-56.63;
- After menopause, its level does not exceed 0.64;
- As already mentioned, this substance is largely responsible for the course of pregnancy. Its norm during gestation varies in the following values: in the first trimester - 8.9-468.4; in the second – 71.5-303.1; in the third – 88.7-771.5.
If a pregnant woman is taking any medications, she must inform the doctor or laboratory assistant about this. This is necessary for the latter to correctly decipher the indicators.
As you can see, the hormone is released with varying intensity throughout pregnancy. This indicates that its concentration in the blood may fluctuate. In addition, norms may vary slightly in different medical sources.
Using Herbs
Medicinal plants will also help normalize hormonal levels. There are many herbs in nature that promote the synthesis of progestogens and components that are converted into hormones in the body. The following plants help increase the production of this substance:
- Fruits from the Abraham tree;
- Vitex sacred twig;
- Potentilla gossamer;
- Common cuff grass;
- Raspberry leaves;
- Taiwanese pseudo-Japanese yam;
- Dioscorea knotweed shrub.
Healers use the grains of the Abraham tree to reduce sexual desire. The fruits activate the production of progesterone and also suppress the level of estrogen in the blood simultaneously with prolactin.
Herbalists are confident that this remedy is a natural source of progesterone, so they recommend taking the fruits in the form of tincture and extract. The fruits of the Abraham tree are prohibited for use by pregnant women or those planning to conceive.
Chasteberry is also used to normalize hormone levels. Take it for a long time under the supervision of a naturopath. The diagram looks like this:
- Capsules should be taken at a dosage of 900–1000 mg per day;
- Alcohol tinctures should be consumed 60–90 drops per day.
You can make tea from this product. Take 1 tbsp. l. dried herb and pour 250 ml of boiling water over it, infuse and take. The decoction has an unpleasant taste, but the effect is excellent. Health measures through this plant must be carried out for at least 6 months.
The use of Potentilla anserina for low progesterone is also appropriate. This remedy has a positive effect on the pituitary gland and also stimulates the production of luteinizing hormone, which, in turn, promotes the production of the sex hormone. To prepare the drink you need to take 1 tsp. seeds and a glass of boiling water. Boil the mixture for about 5 minutes over low heat. Strain the tea, cool and drink 0.5 cups in the morning and evening.
Common cuff is one of the herbs that has progestogenic activity. The plant promotes the production of sex hormones, which ensures the onset of gestation and the further successful course of pregnancy. The herbal remedy is recommended for use during the luteal phase, from day 10 during the 15–25 day menstrual phase.
The decoction is prepared as follows: combine 1 tbsp. l. the main component, the bark of plants such as peppermint and cinnamon, black pepper in the amount of 2 peas. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the ingredients. Place the drug on low heat and simmer for 5 minutes. Use the composition throughout the day in the form of tea.
The method of using a drink made from wild yam and raspberry leaves to eliminate progesterone deficiency is very simple. The medicinal components must be combined in equal proportions and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Be sure to leave the decoction for about 2 hours. It is recommended to take three times a day before meals in small volumes (15 ml).
Reasons for decreased progesterone levels
If a woman becomes pregnant, but the concentration of this substance is low, it means that the body does not receive a signal to prepare. Accordingly, a new cycle begins and the fertilized egg is rejected. That is, hormone deficiency can lead to early miscarriage.
The deficiency is often observed when the luteal phase is insufficiently long, when less than 10 days pass from the moment of ovulation to menstruation.
The duration of this phase can be calculated using basal temperature.
When the level does not increase after follicle maturation, we can talk about hormonal imbalance.
The reasons for this may be hidden in the following conditions and phenomena:
- Insufficiency of the placenta or corpus luteum;
- Miscarriage;
- Intermenstrual uterine bleeding;
- Post-term pregnancy;
- Chronic inflammation in the genital organs;
- Taking a number of medications;
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
How can you increase progesterone in women?
Such conditions require progesterone therapy in dosage form. This drug can cause side effects, including vaginal bleeding, liver dysfunction, and breast tumors. It is taken with caution for diabetes, impaired renal function, heart failure, migraine attacks, bronchial asthma and epilepsy, depression, ectopic pregnancy, lactation.
- The concentration can be increased using the drug in injections or tablets. Which form to choose is determined by the attending physician.
- It is worth noting that intramuscular or subcutaneous administration of the drug is more effective.
The injections will help restore hormonal balance, for example, restore the normal menstrual cycle. If there is a threat of miscarriage, injections of the drug will help save the fetus.
Diagnostics
To determine the concentration of progesterone, it is necessary to donate venous blood. During the collection of biological material, the patient must inform the nurse about the following data:
- Cycle day:
- Presence of menopause;
- Week of pregnancy;
- Taking medications that affect hormonal levels.
Based on the test results, the doctor determines:
- Cause of infertility;
- The presence of ovulation;
- The presence of an ectopic or pathological pregnancy;
- How does the fetus develop?
- Are there any complications?
This study determines the effectiveness of recommended hormone injections for maintaining pregnancy in the first trimester. If necessary, the doctor will recommend products that increase progesterone.
Causes of excessively elevated progesterone in women
The concentration of this substance normally increases in the middle of the cycle, when the body prepares for pregnancy. An increase in level is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Increased progesterone is observed in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- renal failure;
- intermenstrual uterine bleeding;
- disruption of placental development;
- amenorrhea;
- taking a number of medications;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- lack or excess of hormones produced by the adrenal glands.
Microelements and vitamins
A lack of valuable substances leads to an imbalance in a woman’s body. It is important to consume foods that support the synthesis of natural hormones. Pay attention to food that also contains:
- Magnesium
- regulates the function of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of progesterone. You need to take 320 mg of magnesium per day. - Vitamin C
- eliminates free radicals, increases immune defense, promotes hormone production. 85-200 mg of ascorbic acid is needed per day, sometimes the dose is increased to 500 mg. - Vitamin B6
is a vital component for those who want to get pregnant and carry a child to term normally. The recommended daily dose is 50-100 mg.
The body also needs zinc, which is also involved in the production of a substance valuable for women. It is recommended to consume 15-254 mg of the substance per day. Don't forget about vitamin E, as well as L-arginine. The latter substance is found in turkey breast, chicken breast, pumpkin seeds, and peanuts.