The appearance of a cyst is possible at any age. Such a neoplasm may not bother a woman at first, but as it develops, the cyst can cause many unpleasant symptoms. It is believed that the presence of the disease can be recognized by irregularities in the menstrual cycle and the appearance of discharge from an ovarian cyst. But you need to understand that the characteristic vaginal secretion must be taken into account along with other symptoms, because spotting may be associated with other pathologies of the reproductive system.
General symptoms of cysts
A woman needs to pay attention to all changes in her body, because vaginal secretion with blood during a neoplasm may be completely absent or indicate another type of disease. The following symptoms exist:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- problems with the menstrual cycle (absence, delay of menstruation);
- bloody discharge from the vagina of a brown, brown color that occurs between menstrual bleeding;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- nausea and sometimes vomiting;
- frequent urination;
- a feeling of heaviness not only in the stomach, but also in the pelvis;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- high body temperature;
- hormonal imbalances (appearance of facial hair, decreased voice tone);
- general loss of strength and a sharp decrease in immunity;
- problems with conception;
- fluctuations in body weight (sudden weight loss or weight gain).
- dizziness, decreased ability to work.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should visit the hospital, because only a doctor can determine the presence of a tumor using an ultrasound. Naturally, the presence of such symptoms is not a 100% guarantee of a cyst, but if the problem is not detected in time, the threat to the woman’s life increases significantly, and there is also the possibility of loss of reproductive function.
Discharge from a neoplasm may vary depending on the type of cyst:
Follicular ovarian cyst Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary Endometroid cyst of the ovary Dermioid cyst of the ovary
Changes in the menstrual cycle and the risk of uterine bleeding
Before talking about pathology, it is worth getting an idea of the norm:
- The menstrual cycle in a healthy woman lasts from 21 to 35 days,
- Duration of menstruation - 3-7 days,
- Discharge during menstruation is moderate (on the days of the heaviest discharge, absorbent pads are changed no more often than every 2-3 hours),
- There may be minor discomfort, but there is no significant pain during menstruation,
- Menstruation comes regularly, no acyclic discharge is observed.
Any deviation from the norm should be considered as a sign of a gynecological disease. First of all, ovarian cysts should be excluded, as well as hyperplastic processes of the reproductive organs - the most common causes of cycle failure.
Hormone activity during the normal menstrual cycle.
The nature of the discharge during menstruation will depend on the form of the pathology:
- Follicular cysts lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle. There is a delay in menstruation for an indefinite period - from 3 to 30 days. After the delay, profuse and painful bleeding from the genital tract appears. This nature of menstruation is associated with excessive growth of the endometrium during this period and its subsequent rejection. Heavy periods can lead to uterine bleeding, requiring surgery .
- Luteal cysts are accompanied by a long delay in menstruation with subsequent bleeding. The pathology is successfully disguised as intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy. As with pregnancy, breast engorgement and other dubious signs of gestation appear against the background of a corpus luteum cyst. Luteal formation can also occur during a normal pregnancy,
- Endometrioid cysts lead to prolongation of menstruation and the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen. Menstruation usually comes on time, but becomes heavy.
On a note
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding occurs in 10% of women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome. Despite the similar name, this pathology has nothing to do with tumor-like formations of the appendages. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a severe endocrine disorder associated with changes in menstrual function and leading to infertility.
Main symptoms of PCOS.
Hormone-dependent neoplasms
Such neoplasms are called functional, because their appearance is associated with a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Older women are more susceptible to the appearance of cysts during menopause.
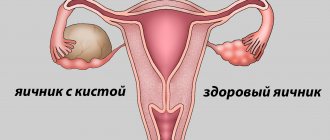
They most often disappear on their own, but sometimes hormonal treatment cannot be avoided. Without medical supervision, there is a possibility of several small cysts appearing, which cause a disease such as polycystic disease.
Polycystic ovary syndromeHealthy ovary
Follicular cyst
Its appearance is associated with compaction of the follicle capsule, from where the egg is released. In a normal situation, ovulation is accompanied by rupture of the follicle, but with hormonal problems this process does not occur, so an ovarian follicular cyst appears.
At the beginning of the development of such a neoplasm, the woman feels practically nothing, and even her periods continue to occur as usual. The larger the cyst becomes, the more pronounced its symptoms. Most often, brown discharge occurs with this type of ovarian cyst. They appear in the middle of the cycle and disappear towards the end.
Bleeding during the development of complications and their dangerous consequences
Bloody discharge from the genital tract may be a sign of cyst rupture - a special case of apoplexy. This condition can be provoked by violent intimacy, sudden movements and turns, physical activity, sports and abdominal injuries. The likelihood of cyst rupture increases during pregnancy and after surgery.
The clinical picture will depend on the intensity of bleeding. With moderate discharge, the woman’s general condition does not suffer too much. Pale skin and cold sweat are noted. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and gluteal region. Bloody discharge usually stops as the pain subsides.
Excessive blood loss leads to tachycardia and decreased blood pressure. Dizziness, nausea and vomiting are noted.
Bloody discharge can also occur when the pedicle of the ovarian cyst is torsed - scant or moderate. Intense bleeding is not typical for this pathology.
Alarming symptoms:
- Gradual increase in vaginal discharge,
- Increasing pain syndrome
- A sharp decrease in blood pressure,
- Confusion and loss of consciousness.
Such signs indicate ongoing blood loss and require immediate medical attention.
Severe bleeding with an existing ovarian cyst requires emergency medical care.
Pathological neoplasms
The following cysts are considered more dangerous to health, since over time it is possible that they will turn into malignant neoplasms. That is why, if you have any characteristic symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, and not hope that the cyst will go away on its own.
Endometriotic
The main symptoms of this tumor are considered to be very long menstruation with painful sensations. Also very often there is a spotting secretion before and after the menstruation itself.
If the cyst is not diagnosed in time, it may rupture, which is accompanied by pain, a sharp increase in body temperature and blood pressure. In this case, the woman must be immediately hospitalized and undergo surgery.
Red-brown
Mucinous
Doctors have not fully figured out the cause of the mucinous cyst, and its symptoms, although they resemble general symptoms, can differ significantly in each individual case.
The main feature is the content of the remains of embryonic germ layers in the neoplasm. Doctors note that this cyst is practically not accompanied by hormonal disruptions, so menstruation can proceed in a normal rhythm without spotting in the middle and end of the cycle.
Dermoid
The main feature is the content of the remains of embryonic germ layers in the neoplasm. Doctors note that this cyst is practically not accompanied by hormonal disruptions, so menstruation can proceed in a normal rhythm without spotting in the middle and end of the cycle.
The absence of pathological secretion plays a cruel joke on a woman, because in this case it is extremely difficult to find the problem in time if there are no problems with menstruation. From this example, it becomes clear that you need to visit a gynecologist, even if you don’t feel anything. This increases the chance of identifying a tumor in time and taking appropriate measures.
Discharge after removal of an ovarian cyst
During the postoperative period, which proceeds without complications, bleeding in women appears in the first days after laparotomy.
This is considered normal, since as soon as the menstrual cycle is restored, the spotting disappears. If the amount of blood does not increase and there is no excessive mucus or pus on the pads, there is no cause for concern. But, if there are any changes in the nature of the discharge after removal of the tumor, it is important to inform the attending physician about this, because in case of tissue suppuration or suture dehiscence, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent the development of an inflammatory reaction and blood sepsis.
Note! If, after a laparotomy to remove the cyst, a couple of days after discharge, the discharge changes color and becomes more intense, consult a doctor immediately; ignoring this symptom is dangerous for women’s health, provokes the spread of a secondary infection and the development of inflammation in the ovaries and other genital organs.
For women with a history of cysts (of various forms and etiologies), it is important to carefully monitor the nature of the smear and menstruation. The slightest change in regulation should alert patients and motivate them to go to the clinic. There is no point in hoping that without treatment the cyst will resolve on its own and disappear. This happens in individual cases. In most cases, cystic formations require complex hormonal therapy or surgical removal.
Features of bleeding
The most dangerous thing in such a situation is bleeding, which can be internal or external. In this case, the woman’s skin turns pale, there is a sharp pain in the abdomen, she becomes dizzy, and possible loss of consciousness and vomiting. The temperature may also rise high, which cannot be brought down with medications. In this case, you must quickly call an ambulance for hospitalization, because only a doctor can help in such a situation.
Discharges may indicate to a woman certain health problems, but they are not a reliable diagnostic method. The right decision is to regularly visit a gynecologist and it is necessary to remember that any disease, if detected in a timely manner, has a greater chance of rapid treatment without consequences.
Diagnosis of the disease
The pathological process in a woman is diagnosed using the following methods:
- An examination by a gynecologist and a questioning of the patient allows us to determine the degree of enlargement of the appendages and the painfulness of the process of cyst formation.
- Ultrasound clearly determines not only the presence of formation, but also its type and degree of development;
- Laparoscopy also makes it possible to determine methods of treating the formation.
When an ovarian cyst is diagnosed, a woman needs to take a pregnancy test (this rules out ectopic pregnancy).
The patient also undergoes a CT or MRI - these studies make it possible to determine the benign quality of the formation and its fairly accurate characteristics.
Such diagnostic methods are often carried out before surgery.
Approaches to diagnosis and treatment
If bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, you must:
- Contact a gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor will assess the nature of the discharge and conduct a bimanual examination. An ovarian cyst is defined as a mobile round or oval formation in the projection of the appendages. Pain on palpation indicates a rupture of the capsule or torsion of the pedicle of the formation,
- Conduct an ultrasound examination. On ultrasound, tumor-like formations of the ovaries are clearly visible. When the cyst capsule ruptures, free fluid is detected in the pelvic cavity.
Further tactics will depend on the results of the examination and the identified pathology.
Follicular and luteal cysts are prone to spontaneous regression, so in the absence of complications, gynecologists are in no hurry to operate. Dynamic observation for 3 months is indicated. After the specified period after the next menstruation, a control ultrasound is performed. With a high degree of probability, the functional formation will go away after menstruation, and the unpleasant symptoms will stop.
This is what a follicular ovarian cyst looks like on ultrasound.
Regarding drug therapy for functional ovarian formations, gynecologists have not reached a consensus. Two options are allowed:
- Observation without the use of medications. Justified for asymptomatic small cysts or against the background of the appearance of minor acyclic discharge from the genital tract, moderate pain in the lower abdomen,
- Hormonal therapy for 3 months. For treatment, combined oral contraceptives are used - drugs that inhibit the growth of the cyst and lead to its regression.
If the cyst does not go away within three months and the symptoms of the disease persist, surgical treatment is indicated. Either cyst removal or ovarian resection is performed. In advanced situations, when there is no healthy tissue left, removal of the entire organ is indicated - oophorectomy. If technically possible, all manipulations are performed laparoscopically. In other situations, abdominal surgery (laparotomy) is performed.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cyst.
First aid for bleeding due to an ovarian cyst:
- Provide the woman with complete peace,
- Put cold on your stomach: a heating pad or a bottle of ice water, ice cubes wrapped in a cloth. Exposure should not last more than 15 minutes. Cold promotes vasospasm and stops bleeding,
- Offer fluids as needed. Eating is not recommended - bleeding may be an indication for surgery under anesthesia.
If heavy bleeding from the genital tract appears, you must call an ambulance. It is not recommended to take any medications before the team arrives. Hospitalization is carried out on a gurney. Further treatment will be carried out in the gynecological department after the examination.
In the hospital, the following drugs help stop bleeding:
- Hormonal agents. Combined oral contraceptives are used in high dosages with a gradual dose reduction. This tactic is more often used for juvenile bleeding (in adolescents),
- Hemostatic drugs: Vikasol, Dicynone, calcium gluconate, etc. In the first days, hemostatic agents are prescribed by injection, then switched to tablet form.
In cases of severe uterine bleeding in women of reproductive age and menopause, therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is indicated. During the procedure, excess endometrium is removed and the discharge ends. The resulting material is necessarily sent for histological examination to the laboratory. Sometimes the cause of bleeding is not an ovarian cyst, but a concomitant pathology of the uterus.
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it bleeds? For moderate discharge, conservative therapy is acceptable. If symptoms increase, you should not refuse surgical treatment: the consequences of bleeding can be unpredictable. Only timely therapy can avoid the development of complications and preserve the woman’s health.