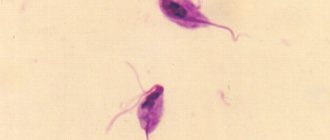
Discharge during urination can be a natural reaction of the body to changes in hormonal levels or be a symptom of a serious disease of the human genitourinary system.
When the discharge is a consequence of increased work of the endocrine system (during puberty, intimacy, ovulation and pregnancy in women or menopause), it is in the nature of leucorrhoea (clear or milky mucus in small quantities), which can be seen on toilet paper or underwear after the end. act of urination. These discharges do not require treatment and disappear after restructuring of the body; apart from them, nothing else bothers people, that is, there is no itching, pain or burning.
Pathological discharge is characterized by consistency and duration, they are accompanied by a number of specific signs characteristic of a particular disease.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the color of the discharge is yellow or bloody, your body temperature has increased, or you are bothered by pain and itching when urinating. Finding out the cause of the disease and prescribing the correct treatment can only be done after a thorough medical examination and examination.
Causes of male discharge
The mucous membrane produces the necessary amount of lubricant to protect the penis from infectious attack. If the integrity of the foreskin is damaged or pathogenic proliferation of microorganisms occurs, the amount of lubrication may increase.
Discomfort and wet underwear are a reason to consult a doctor. Perhaps an inflammatory or infectious process is developing in the body.
Among the causes of urethral discharge in men are the following diseases:
- prostatitis of acute and chronic type;
- venereal diseases;
- pathogenic fungal proliferation;
- spermatorrhoea.
However, in some cases, discharge is a normal indicator of the functioning of the mucous membrane of the genital organ. Deviations can be distinguished by accompanying symptoms and additional signs of the disease.
Prostate diseases
The most common cause of discharge from the penis is prostatitis. Inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system can provoke an increased amount of secretion. In the absence of adequate treatment for prostate diseases, there is a risk of decreased erectile function, up to its complete extinction, and difficulties with urination.
The nature of the discharge depends on the stage of development of prostatitis:
- Initial stage. The mucous secretion is released in the same volume, but the patient may experience additional difficulties with urination or pain in the pelvic organs.
- Acute form. Increased secretion of white (possibly with yellow spots) mucus from the penis. In the acute form, additional symptoms also appear. Urgent treatment is required.
- Chronic prostatitis. It can go into a remission stage, during which the symptoms of the disease practically do not appear. In advanced form, purulent or bloody spots appear.
Often the secretion is released during the treatment of prostatitis. This is a normal process that helps get rid of congestion in the prostate gland. After a massage or other physiotherapy, discharge is excreted along with urine.
White mucus from the vagina - normal or pathological?
Moderate vaginal discharge is normal. The question is when to sound the alarm.
Mucus discharge in women, like snot, is produced by the glands of the cervix
. If everything is in order, they have no odor, do not cause any unpleasant sensations and are released in moderate quantities, that is, not abundantly. The amount of mucous secretions depends on the phase of the cycle; this process is controlled by hormones produced in the ovaries.
In the first phase of the cycle there is a lot of transparent liquid mucus, and in the second it is transparent and viscous. Does it seem to you that the mucus is not as good as it should be, or there is too much of it? Perhaps there is cause for concern, since it is produced not only by the cervix, but also by the cervical canal and vagina. You should be wary if:
- an unpleasant burning sensation and itching appeared in the vagina;
- when urinating, there is a pulling or pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge is too abundant;
- clear mucous discharge gives way to thick white or yellow discharge.
Causes of clear vaginal mucus
Transparent mucus from the vagina in large quantities may begin to be released for the following reasons:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- very frequent washing, especially with the use of products that disrupt the acid-base balance of the delicate area;
- hypothermia;
- foreign objects entering the vagina;
- progression of cancer (of any organ);
- diabetes;
- entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the vagina during sexual intercourse;
- polyps.
Thus, the causes of abnormal mucus discharge may vary. Therefore, you need to take a smear and see what exactly is wrong.
What kind of discharge can there be?
Mucus can be different. Based on color, volume and consistency, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis and distinguish the physiological norm from a deviation of an infectious nature. To accurately diagnose the disease, laboratory diagnostics will be required.
By color
Discharge can be divided according to the presence of odor, color and consistency. If lumps appear that look like cottage cheese, then candidiasis can be suspected. An unpleasant odor indicates the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
The following normal discharges are distinguished by color:
- Yellow. If there is no odor and a thickened consistency, this may be normal - these are urine residues.
- White. Sometimes with a touch of yellowness. This is prostate secretion. They have the smell of seminal fluid.
- Gray. At the same time, the shade is unobtrusive and light, the amount of mucus is small - this is smegma.
If there is a change in volume and consistency, as well as the main symptom - an unpleasant odor - an infectious process can be suspected. But with ureaplasma infections, for example, the amount of discharge may be scanty, so color and stringiness are another sign of infection.
Pathogenic colored discharge:
- White curds. They talk about increased activity of candida fungi, which can provoke swelling of the foreskin and redness of the glans penis. If there is a “curd” on the penis and a characteristic fishy odor, there is a possibility of thrush.
- Cloudy and liquid. A sign of sexually transmitted diseases, dark green blotches may also be present. At the treatment stage, swamp-colored pus is released. The mucus may also be clear.
- Bright green and yellow. This is a sign of gonorrhea, which also has a strong putrid odor. Associated symptoms are severe pain and burning during sexual intercourse and when urinating.
- Red or brown. These are bloody spots that may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the pelvic organs or an advanced type of infection. The appearance of blood is a dangerous symptom that requires immediate treatment. Characteristic of hematorrhea (mechanical damage to the urethra).
It is easiest to cope with the disease at the initial stage of its manifestation. Chronic and advanced forms are difficult to stop, and in some cases they cannot be treated. If you experience an unpleasant odor from the genitals, a burning sensation in the urethra or redness, immediately seek help from a doctor.
Why does mucus appear in urine?
The causes of mucus in the urine in women are inflammation of the urinary tract and kidneys
.
It is released when epithelial cells begin to be rejected from the inside of the urinary tract. It occurs as a result of injury to the tissues of the walls of organs after the passage of stones and sand or as a result of a bacterial infection. The cause of mucus in the urine may also be an autoimmune chronic inflammatory disease
or a long process of urinary retention, which provokes an increase in the functioning of the cells responsible for the secretion of mucus.
Were unusual inclusions discovered during laboratory tests? In this case, the problems lie both in internal inflammatory processes and in poor hygiene and improper collection of tests. Before collecting urine, you need to wash yourself and insert a tampon into the vagina. If this is not done, vaginal mucus will get into the urine, and correct diagnosis will become impossible.
Cystitis, pyelonephritis or urolithiasis?
If you collected urine correctly for analysis, but mucus was found in it, this could be:
- Cystitis
is a common female disease. Bacteria from the vagina enter the urethra, affecting the bladder and triggering an acute or chronic inflammatory process. - Pyelonephritis
– develops from advanced cystitis. Accompanied by inflammatory processes in the kidneys and mucus secretion. - Urolithiasis
– stones interfere with the free flow of urine and cause inflammation of the kidneys.
For cystitis, a woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs and proper drinking regimen. Folk remedies are also used, but with severe inflammation they will not bring quick relief. For kidney stones, surgical treatment is usually prescribed; antispasmodics and painkillers will help alleviate the condition during severe attacks of urolithiasis. Preparations that dissolve salts have low effectiveness.
Associated symptoms
Excretory processes accompanied by an unpleasant odor or the appearance of other symptoms may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted or inflammatory diseases. You can suspect trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, balanoposthitis, gonorrhea or urethritis.
Associated symptoms:
- difficulty urinating;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- the appearance of pain syndrome;
- unpleasant odor;
- the appearance of pus and blood spots;
- itching and burning in the urethra, on the head or in the foreskin;
- erectile disfunction.
If you experience difficulty urinating, lack of sexual desire, increased urge to go to the toilet and a feeling of incomplete emptying, prostatitis can be suspected. Pain, burning and itching are common symptoms characteristic of any disease. The smell indicates the proliferation of microorganisms on the mucous membrane of the penis.
Causes of pathology
Women's diseases - provocateurs include:
- urolithiasis disease;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis, etc.
Excessive mucus can also be found in women during pregnancy. This is due to the production of female hormones - progesterone and estrogen and most often does not represent a deviation from the norm. In men, a large number of epithelial cells can be detected in prostate adenoma (prostate).
Urolithiasis disease
This is an unpleasant and dangerous pathological process in which stones in the ureters and bladder can begin to move at any moment, causing unbearable, excruciating pain. In this case, the walls of the ureters are injured, microcracks appear. In addition to mucus, blood particles may be found in the urine. If the problem cannot be solved with medication, a radical method is used - surgery.
Cystitis
The structure of the female genital organs has its own characteristics. The entrance to the urethra is located close to the anus, so if you ignore the basics of personal hygiene and improper washing, infection with E. coli and staphylococci often occurs. The hemorrhagic form of cystitis is caused by viral pathogens.
The woman experiences frequent urge to go to the toilet, a burning sensation occurs in the external genital area, and the body temperature may rise. If the disease is not treated, the inflammatory process from the lower parts spreads further into the internal organs.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra, which is called urethritis, can be of infectious or non-infectious origin. A copious amount of mucus, which has a blue-greenish tint, may include an admixture of pus - this depends on the degree of development of the disease.
Non-infectious is provoked by congestion in the pelvis, obstruction of the urinary ducts (adhesions), injuries, etc. When the acute phase passes, the mucus, which has an unpleasant odor, may disappear. The person has a feeling of imaginary recovery. But in women, pathogenic microorganisms “hide” in the Bartholin glands and at the entrance to the vagina, waiting for the immune system to fail. Then the pathogenic bacteria are released and actively multiply, causing inflammation.
Pyelonephritis
Pathogenic flora, penetrating the urinary canal and rushing along the ascending path to the internal organs, become the cause of a serious disease - pyelonephritis. The inflammatory process affects the renal pelvis . The disease begins with an acute attack, which over time becomes chronic. Signs of pyelonephritis appear as a consequence of untreated urethritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, in which pathogenic microorganisms “expand their domain” by penetrating the kidneys.
When to see a doctor
It is recommended that men visit a urologist, venereologist and andrologist once a year, even in the absence of symptoms of disease. Many pathologies develop without symptoms. Detection of diseases at an early stage will eliminate long and difficult treatment.
Otherwise, there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic. If you notice any suspicious symptoms, contact a specialist immediately. With the normal development of men's health, underwear always remains dry.
When to see a doctor:
- when the color, consistency and volume of discharge changes;
- when an unpleasant odor appears from the genital organ;
- with a feeling of general discomfort and accompanying symptoms.
You can visit a specialist even after unprotected sexual intercourse, when there is a high probability of infection. The doctor will order a diagnostic test that will help determine the disease.
Testing for STDs: to take it or not
Mucusy, snot-like discharge in the middle of the cycle is normal. But if their consistency or color worries you, it would be better to take a smear to check for major STDs. Snot-like discharge from the genitals is characteristic of the following diseases:
- gardrenellosis
- copious, gray, mucous discharge, with a fishy aroma; - vaginal candidiasis
- the mucous discharge is quite thick, has a characteristic sour odor, and contains cheesy inclusions; - gonorrhea
- the discharge is also mucous, abundant, green or yellow (with purulent impurities); - genital herpes
– snot-like mucus is released from the vagina, and painful blisters form on the surface of the genitals; - chlamydia
– very profuse clear or white discharge; - trichomoniasis
- yellowish or greenish snot of a foamy nature.
A treatment regimen for gynecological diseases that cause the appearance of profuse snot-like discharge is prescribed by a venereologist or gynecologist - taking into account the causative agent of the infection, diagnosis, and clinical manifestations. For fungal infections, antifungal drugs and general-spectrum restoratives are prescribed; for genital herpes, antiviral drugs are prescribed. The most difficult and lengthy treatment is the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases; both partners must undergo it. During menopause, heavy discharge is usually caused by hormonal changes in the body.
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient needs to contact a medical center. During the initial examination of the penis, the doctor will assess the condition of the penis, foreskin, and identify the presence of a rash, deformation of the organ, swelling and other signs.
The urologist will also assess the condition of the lymph nodes using palpation. The size of the prostate and the presence of an inflammatory process in the glandular tissue is indicated using a rectal examination.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Finger examination. Used to assess the condition of the prostate gland. Rectal penetration is sometimes used as a method of treating prostatitis. The doctor feels the presence of lobes, tissue density and size.
- Laboratory research. General tests are prescribed. Elevated white blood cell counts are a sign of infection.
- Smears for microscopic examination and culture. At the same time, the accuracy of the study is high; mycoplasma, candida fungi and other pathogens can be detected on the mucous membrane.
- PCR method (polymerase chain reaction). The study helps to detect sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), pathogens such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, and detect gonorrhea, herpes or syphilis.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Helps detect inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Ultrasound reveals the exact size and condition of organs and the presence of tumors.
- CT scan. It is prescribed to confirm or refute an existing diagnosis. Usually indicated for complicated and severe diseases.
- Biopsy. It is prescribed if a neoplasm has already been detected on the prostate gland or other organ. The study helps determine whether cells are malignant or benign.
Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed. The more serious the problem with men's health, the more procedures you will have to undergo. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations in order to identify the disease in time.
Mucus in urine during pregnancy
Having discovered mucus in a urine test, most often the doctor will prescribe a repeat examination of a new portion of the material, since one of the reasons for a bad result may be non-compliance with the rules for collecting urine. What other factors could lead to a similar result?
Reasons for the appearance of mucus in urine during pregnancy:
- If all the rules for preparing for the analysis are followed, and the result of the analysis still shows an increased content of mucus, with a high degree of probability we can talk about a pathological process occurring in the body of the expectant mother. The disease can be either local or general in nature. The main reasons for the appearance of mucus:
- Infectious processes caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, trichomonas, gonococcus. Infection with these microorganisms poses a threat not only to the condition of a pregnant woman, but also to the health of the baby in her womb.
- A physiological increase in the load on the organs of the urinary system, as a result of which the latter fail.
- In late gestation, the enlarged uterus puts strong pressure on the kidneys, ureters and bladder. Compression of organs disrupts the normal outflow of urine and provokes stagnation. Such conditions are a good environment for the active growth of bacteria.
- Non-compliance with the principles of healthy eating - passion for sweets, fried and fatty foods. The latter helps increase cholesterol levels. As a result, the urine becomes cloudy, mucus and a pungent odor appear.
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed based on the diagnosis. Treatment methods can be divided into medicinal, conservative, folk and surgical. The latter are used only if other methods have not shown effectiveness.
Treatment of diseases:
- Candidiasis. Antifungal drugs are prescribed: Clotrimazole, Pimafucin or Exoderil. Tablets, gels and ointments are indicated for treatment. If thrush is detected, both sexual partners are treated.
- Prostatitis. It requires complex treatment, drugs from the group of alpha-blockers, herbal remedies and dietary supplements are prescribed. Among the popular ones are Prostamol Uno, Vitaprost, Omnic.
- Infections. White fluid from the urinary canal in men is treated only with antibiotics, which are prescribed depending on the pathogen. It is also recommended to additionally take medications to protect the liver (Essentiale), and douching with Chlorhexidine. Both sexual partners receive treatment.
- Spermatorrhoea. Leakage of seminal fluid is a dangerous pathology. It cannot be cured on its own; serious treatment is required. Most often, surgical treatment is prescribed. In some cases, exploratory surgery is performed followed by treatment.
- Oncology. If a cancerous tumor is detected, the patient will be offered several treatment methods: chemical castration, surgical removal of the affected organ, or radiation therapy. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and is prescribed depending on the location of the tumor and the stage of the oncology.
Any deviations require immediate treatment. Traditional recipes can only be used as additional therapy. Do not take medications or use alternative medicine methods without a doctor's prescription. Self-medication can aggravate the disease and cause complications.
Features of the appearance of mucus
Epithelium in the urine that appears in representatives of different sexes can be due to various reasons. So, in women, the causes of excess mucus may be:
- Incorrect urine collection. This phenomenon is observed when washing before the procedure is not thorough enough, the sample is submitted to the laboratory more than two hours after urine is excreted, or the use of a non-sterile container.
- The development of pathological processes - urolithiasis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and other problems.
- The appearance of cystitis - in women, this disease occurs quite often, and the result is inflammatory processes in the mucous layer of the bladder.
- Another of the many reasons for the appearance of mucus in the urine can be autoimmune inflammatory processes.
Pregnancy deserves special consideration, in which OAM helps to assess the course of diseases and identify possible abnormalities much earlier. If a woman urinated to check the tests while carrying a child, the indicators should not exceed 1+. If there are no other pathological results during the examination, level 2+ falls into the list of moderate and acceptable indicators.
When mucus appears in the urine of pregnant women, leukocytes or bacteria appearing in parallel should cause special concern. Such indicators indicate an infectious lesion, which is dangerous for both the woman and the fetus. In this case, bacteriological culture is required, which will identify the causative agent of the pathology, and sometimes PCR is used as an additional research method.
What to do?
If you are concerned about unusual, too abundant, unclear color or mucous discharge in the urine, you first need to find out the cause of this condition. You should not start treatment on your own, as this can only worsen the situation. In addition, you need to find out whether the problem is with the urinary tract or reproductive system.
The main methods of treating mucous discharge:
- douching;
- use of vaginal suppositories;
- antibiotic therapy.
Self-medication in this case is dangerous, since you can muffle the symptoms and decide that everything is fine, and the disease will progress inside the body.
Urinalysis: in what cases and how to take it correctly
If you suspect an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, your doctor will refer you for a urine test. Its results allow:
- identify pathology of the genitourinary system;
- assess the general condition of the body;
- control the course of the disease;
- diagnose diabetes mellitus;
- analyze the consequences of intoxication of the body as a result of poisoning.
Even a healthy person who is not worried about anything should regularly undergo a general urine test. And if something bothers you, then you definitely need to do it. To accurately find out the levels of mucus in your urine, buy a special container at the pharmacy, and before collecting the analysis, wash your genitals (it’s best just with warm water, without soap). The day before the test, do not eat foods with coloring elements - greens, beets, carrots.
. Avoid taking medications, alcohol and coffee. It is very undesirable to take a urine test during your period. Have you collected the material in a container? Try to get it to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Mucus in urine during pregnancy
From the second trimester, foreign impurities may appear in the urine. This is due to the fact that the fetus puts pressure on the kidneys, uterus and other organs, the bladder does not empty normally, and mucus accumulates in it. What should I do and should I do it at all? The doctor will be able to tell you this after the examination.
Consequences
Any disease, if left untreated, can cause problems with other organs. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, other unpleasant symptoms associated with urination or erectile function may appear.
Consequences:
- transition of the disease to a chronic type;
- spread of infection to other organs of the genitourinary system;
- chronic pain syndrome;
- the appearance of neoplasms;
- erectile disfunction;
- development of infertility;
- cancer.
The development of complications depends on the diagnosis. Along with chlamydia, urethritis or pyelonephritis may develop, and the functioning of the liver and kidneys may be impaired. At first glance, harmless discharge can cause significant harm to men's health.
Features of discharge from the urethra in women
The urethra is the urethra. This organ belongs to the genitourinary system and performs the function of removing water-soluble waste products of the body from the bladder . The urethra of the fair sex is significantly different in size from that of men: it is shorter, but has a larger diameter. For this reason, pathogenic microorganisms attack a woman’s urethra in greater numbers, and accordingly, inflammatory processes occur more often.
The female genitourinary system constantly produces various secretions that perform important functions. The secretion produced by the glands and uterus varies depending on the course of the menstrual cycle.
Since the organs in the intimate area are located quite close, and the urethral canal fits tightly to the vagina, the mucous secretion from the urethra mixes with the vaginal secretion at the exit. That is why it is difficult for a woman to determine the nature of their occurrence. In this case, if you notice changes in the discharge, you should first visit a gynecologist.
Test for kidney problems
You can find out the cause of white urine using a 3-glass test. After thorough hygiene of the genitals, you need to urinate in 3 transparent containers. If the first portion is cloudy but the others are relatively normal, the problem may be an infection in the urethra. The white sediment in the last sample is a likely symptom of an inflamed bladder, usually accompanied by cutting and burning when emptying it.
A home test helps understand the causes of incontinence and changes in urine color, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
How to recognize the disease yourself?
First of all, men need to pay increased attention to going to the toilet in the morning. During the night, discharge can accumulate in the canal, and in the morning it is much easier to detect it. In addition, you should carefully monitor your underwear. There may be traces of discharge on it, which should alert any member of the male population. And the most important method of self-diagnosis for the presence of a disease is pressing on the genital organ, which brings a painful sensation.
Factors of occurrence
When white mucus appears after urination, this means that inflammatory processes are definitely present in the body. Depending on the disease, the discharge varies in color and consistency. What diseases can cause the appearance of atypical discharge that causes discomfort?
The most common disease is inflammation of the urethra, or urethritis. The glands begin to secrete white mucus in large quantities, which can be seen in the urine. Thus, the urethra tries to fight the infection that has entered it.
Penile cancer may also present with discharge due to inflammation of the urethra. Discharge with blood may indicate the presence of pathological prostate diseases.
In addition, sexually transmitted diseases are causes. If strange discharge and discomfort appear after unprotected sexual intercourse, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication in such cases can have disastrous consequences for health.
The cause of atypical discharge is an unhealthy diet, if the food is too spicy or contains a lot of spices. Abuse of alcoholic beverages also affects the change in color of male discharge.
If a man has a weakened immune system, pathogenic microorganisms can enter the genitourinary system. In addition to weak immunity, this can be caused by non-compliance with intimate hygiene rules and previous injuries.
Purulent, white or other discharge often indicates the presence of inflammation in the male reproductive system. Only an experienced specialist can make a correct diagnosis, but before that he must prescribe a series of tests.
What does the color of the discharge indicate?
If epithelial cells are present in large numbers in the discharge, then they will have a gray color.
Yellow or green discharge indicates the presence of leukocytes in the area of inflammation.
Thrush doesn't only affect women. Therefore, if a man has white curdled discharge, he should think about treating this disease.
The color of urine in the male half of the population often changes. This occurs under the influence of many external factors. For example, medications and dietary changes can affect the color of a man's urine.
Often, white urine indicates that a man has some kind of disease. Diabetes mellitus can have this effect on the male body. In this case, urine may become almost colorless, and its amount increases sharply.
Increased urine density, or hyperstenurea, is characterized by white discharge from the male genital organ. The root cause of such a disease may be disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system or a disorder in the functioning of the kidneys.
Under no circumstances should you delay a visit to the doctor if white urine is also accompanied by discharge in the form of flakes or with traces of pus. Any foreign inclusions in male urine require serious consultation with a specialist.