Women often face the problem of being unable to conceive a child. This can be caused by various chronic or inflammatory processes in the genital organs. However, what to do if a woman is absolutely healthy, but childbearing is not carried out. The cause may be an abnormal position of the uterus. Bend of the uterus is diagnosed quite often today; this pathology does not have characteristic symptoms. This means that a violation of the location of the cervix and body of the uterus can be detected only with careful diagnosis. With this diagnosis, there is some difficulty in getting pregnant on your own. So, if the organ is deviated anteriorly or posteriorly, then there is a significant difficulty in the flow of sperm to the mature egg. But this does not mean that a patient with such a diagnosis should despair; today there are many techniques that help eliminate uterine bending. Let's take a closer look at this problem and determine the best methods to solve it.
Displacement of the uterus - left, right
More often, displacement of the uterus is one of the individual variations of the normal location and does not cause problems.
In the absence of gynecological diseases, this displacement does not affect the woman’s health. Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease. The site provides reference information.
Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications.
Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
Normal position of the uterus
The uterus is located between the bladder and rectum, in the center of the pelvis. The normal position of the uterus is tilted forward, towards the pubic joint.
An open angle of 70 to 100 degrees is formed between the cervix and the body of the uterus.
The uterus is in this position due to the muscles, vaginal walls, and ligaments that attach it to the pelvis on all sides. When the intestines and bladder are filled, the uterus can freely move towards the direction of least resistance. This allows you to avoid discomfort and a feeling of fullness when these organs are overfilled.
Ligaments and muscles can weaken, as a result, the uterus can shift in either direction - towards the right or left ovary. The elasticity of the supporting structures of the small pelvis ensures the mobility of the woman’s internal genital organs.
The following may be subject to displacement:
- Uterus,
- Ovaries,
- The fallopian tubes,
- Bladder.
Only 2 positions of the displaced uterus have pronounced consequences, moving backward, or regression, and moving down, or prolapse.
Uterine displacement - different options
With age, the tissues of the internal genital organs and ligamentous apparatus undergo atrophic changes. In older women, the internal genital organs - the uterus along with the appendages - are located lower, i.e. Set deep in the pelvic floor. The angle between the cervix and the body of the uterus increases, it seems to lean back.
There are 4 offset options:
- Left,
- Right,
- Forward,
- Back.
A problematic pathology is organ torsion around a vertical axis and prolapse, i.e. Excessive downward displacement.
Variants of displacement occur with a sharp loss of body weight or after traumatic injuries to the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvis.
Reasons for displacement
With age, changes in the anatomical position of the organ occur due to characteristics, as a result of various diseases or injuries. The causes are inflammatory processes of the appendages. Factors provoking its displacement:
- Severe bruises in the sacrum or tailbone;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Adhesive process of the small pelvis,
- Operations;
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- Weakening of the pelvic ligaments after pregnancy and childbirth;
- Lifting, carrying heavy objects before or during menstruation, too soon after childbirth;
- Weak pelvic muscles;
- Chronic spasm of the muscles of the lower back, sacrum.
At risk are women who are underweight and, conversely, those who are overweight.
In the first category, weakness of the perineal muscles and ligaments is observed. In obese women, displacement occurs due to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
https://www..com/watch?v=dDkHE_8rySw
Symptoms of changes in organ position
Symptoms of displacement depend on which direction and how many degrees the uterus deviates. There are general signs of changes in the position of the uterus and individual ones inherent in each option.
General signs:
- Pain in the lower back before and during menstruation, when the uterus increases in volume;
- Painful or irregular periods;
- Dark brown discharge at the beginning and end of menstruation;
- Recurrent vaginal infections;
- Painful sexual intercourse.
When displaced towards the rectum, constant pressure occurs on this organ.
With pronounced deviation of the uterus backwards, the following is observed:
- Periodic back pain
- Chronic constipation,
- Varicose veins on the legs,
- Fatigue and numbness in the legs.
If the uterus moves forward, there is constant pressure on the bladder. Women are concerned about:
- Urinary incontinence;
- Frequent urination;
- Urinary infections.
When the organ is displaced to the right or left, periodic nagging pain on the side of the deviation is added to the general symptoms.
This is due to tension in the ligamentous apparatus and irritation of nerve endings. Deviation from the normal location of the organ provokes chronic venous and lymphatic stagnation. This adversely affects tissue nutrition and can disrupt the normal functioning of the organ.
Possible complications of pathology
The pressure of the displaced uterus on neighboring organs (bladder, rectum) gradually causes dysfunction of these organs. The displacement of the organ to the right or left is provoked by inflammatory processes in the ovaries or tubes. It is attracted to the side where inflammation occurs.
Since the main reasons for displacement to the right or left are inflammatory changes in the appendages, a change in position in their direction causes the formation of adhesions, connective tissue cords that fix the organ to each other.
The process of organ adhesion is fraught with some loss of mobility, then with natural movement during bowel movements or urination, the patient may experience discomfort or pain on the affected side.
If the uterus has moved down or prolapsed, dysfunction of the bladder and intestines occurs. Weakened ligaments are unable to hold organs in a fixed position. Gradual sagging of the ligaments provokes urinary or fecal incontinence. Options for displacement are subject to surgical treatment.
Exercises and surgical treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on how much the displaced position of the organs causes disruption of their function. Since changes in the position of the uterus are caused by various pathologies, they are treated with medication and physiotherapy.
In the initial stage, when the patient has not yet begun to be bothered by severe pain or urinary incontinence, they are limited to local procedures and gymnastics:
- Douching with a decoction of oak bark;
- Kegel exercises;
- Exercises according to Yunusov.
With small degrees of deviation from the norm, these methods help return the uterus to its original position.
In case of pronounced downward displacement or prolapse, when other pelvic organs are displaced after the uterus, surgical treatment is indicated.
Plastic surgeries are performed aimed at restoring the ligamentous apparatus. In case of complete organ prolapse, the uterus is removed followed by pelvic floor plastic surgery.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Several methods are used to diagnose this pathology:
- Examination by a gynecologist. This is the very first stage, which allows you to notice that the uterus is displaced. The patient lies down on a gynecological chair, and the gynecologist, by palpating the abdomen and inside the vagina, can determine the displacement of the organ. If the fingers rest against the body in the posterior fornix of the vagina, this means that the uterus has moved back. When palpation is carried out above the womb, you can notice a forward displacement of the organ. The diagnostic method is also effective for other locations of the uterus.
- Hysterosalpingography. Such a study is aimed at determining the patency of the fallopian tubes, their condition, the position of the uterus, and the presence of problem areas in the pelvic area. With the help of a contrast agent that is injected orally, which moves through the fallopian tubes, any abnormalities can be detected using x-rays or ultrasound.
- Colposcopy. Such a study may show a downward shift of the uterus. To carry out this procedure, no anesthetic is used; everything is done using a special device - a colposcope. In addition to displacement, it can also show other diseases of the uterus, for example, neoplasms or dysplasia.
The presence of such a pathology is detected using traditional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis and vagina;
- A blood test that helps identify any inflammatory processes;
- Taking a smear to determine the presence of any infections or viruses;
- X-ray, which can be used to see the displacement of an organ.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the help of a gynecologist and other specialists is required: proctologist, urologist. This is necessary to notice any changes that accompany the displacement.
Help from folk remedies
Traditional methods help with displacement of the uterus, but before carrying out the procedures you should consult with a specialist so as not to aggravate the condition of the disease.
Douching with medicinal infusions is effective for this pathology:
- To prepare, mix sweet clover, marshmallow leaves and chamomile in equal quantities. Pour one spoon of the resulting mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave covered for half an hour. Strain, syringe twice a day, a quarter cup.
- Douching with an infusion of St. John's wort and cinquefoil effectively helps with displacement. To prepare, pour 2 liters of water into a container, put it on the fire, when it boils, add 4 tablespoons of chopped St. John's wort, cook for half an hour. Then add a spoonful of bloodroot and boil for another 5 minutes. Strain and use twice a day.
- Pour a glass of water into a container, add a spoonful of crushed oak bark. Boil over low heat for 5-10 minutes. After straining, dilute a little with cold water. Use half a glass every day for 2 weeks.
- Mix 2 servings of St. John's wort, one each of horsetail and chamomile. Pour a spoonful of the mixture into a glass of water and place on low heat. After 15-20 minutes of boiling, turn off and let sit for half an hour. Strain, take a quarter glass three times a day.
- Dilute a teaspoon of tannin in 200 ml of warm boiled water and take half a glass twice a day.
Often, displacement of the uterus is associated with inflammatory processes.
To get rid of unpleasant symptoms you can use the following recipes:
- Mix chamomile, peppermint, and valerian root one spoon at a time. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over one spoon of the resulting mixture and let it brew for 1-2 hours. Drink before meals three times a day.
- Pour 4 tablespoons of chamomile into a glass of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour, strain, drink half a glass twice a day. You can wash yourself with this infusion, it gives a good result.
- Make an infusion of plantain leaves, it will help relieve inflammation and pain. pour a spoonful of crushed, dried herbs into two glasses of boiling water, leave for 20-30 minutes, strain, drink a teaspoon three times a day.
- If spasms occur in the pelvic area, an infusion of prickly plum flowers will help. Pour 2 tablespoons into a glass of boiled cold water and leave overnight. Afterwards, strain, take half a glass three times a day.
- A decoction of acacia flowers effectively relieves pain. Pour boiling water over a spoonful of flowers, leave for 30 minutes and drink before eating.
With the help of such herbal preparations you can douche or take a bath. They effectively fight inflammation and help relieve pain.
Features of dietary nutrition
With this pathology, you do not need to adhere to special diets. You need proper and balanced nutrition, which will help the body restore its functionality, increase the level of the immune system in order to prevent the ingestion of dangerous viruses that can aggravate the condition.
You need to eat as many fruits and vegetables as possible, preferably fresh or steamed. Drink plenty of liquids and freshly squeezed juices.
Do not consume in large quantities:
- Fatty and fried foods;
- Spicy dishes;
- Alcohol.
To prevent displacement, consume as many vitamins and microelements as possible. A huge amount of which is found in sea fish, seaweed, and cereals.
No need to neglect dairy products. They saturate the body with necessary substances that increase immunity. It is healthy and important to eat a lot of nuts and dried fruits, especially prunes. It cleanses the body of toxins and prevents frequent constipation.
Prevention of organ displacement
To prevent displacement it is necessary to take preventive measures. It is most effective to start doing this from early childhood, so as not to give such a pathology a single chance.
The most well-known and effective methods of preventing such pathology are:
- Do not lift or carry weights exceeding 10 kilograms.
- During pregnancy, you should carefully monitor its correct course.
- Protecting the genitals from germs, bacteria or damage.
- Avoiding frequent constipation and following a diet aimed at preventing it.
- Regular exercise to maintain a healthy body. Regular exercise helps strengthen all muscles and prevent uterine displacement.
- Taking hormonal therapy, which helps restore blood circulation and strengthen the ligaments of the organs in the pelvic area. You should only take medications after consulting a specialist.
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Avoid prolonged colds.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor
Source: https://FeedMed.ru/bolezni/reproduktivnoy-sistemi/smeshchenie-matki.html
Cervical length at 38 weeks of pregnancy
How the cervix changes before childbirth at 38 weeks of pregnancy
The cervix prepares for childbirth starting at 32 weeks of pregnancy. The beginning of this process is indicated by softening of the edges; the area around the cervical canal remains dense. Next, the tone of the uterus appears, the woman can feel training contractions, it is they that ensure the softening of the lower segment, the myometrium becomes denser. The fetus descends, its head is adjacent to the pelvic region, and under the applied pressure, opening is ensured.
As the neck opens, it shortens; a couple of days before maturity, it smooths out and allows more than 2 fingers to pass through. A soft neck is considered ideal. After it softens, the mucous plug comes off. During pregnancy, the cervix is tilted posteriorly, and at 38-39 weeks it should turn forward, before labor begins, the cervical canal is located directly in the center of the pelvic organs.
Uterine displacement: causes, symptoms, treatment features, rehabilitation
In its normal state, the uterus is a mobile organ, which in its structure is similar to a pear. In a nulliparous woman, its size usually reaches 8 centimeters. As a rule, it can move in different directions without any difficulty.
This movement is ensured by the work of the abdominal muscles and ligaments that attach the uterus to the walls of the pelvis. Under normal conditions, the uterus is slightly tilted forward. Difficulty in mobility may indicate the presence of a pathological condition called uterine displacement.
It can be either acquired during life or congenital.
Displacement is quite often a consequence of inflammatory processes. Women who are underweight or overweight are at risk. You will learn more about the consequences and causes of uterine displacement to the left or right from the article.
Causes
The main reasons due to which the uterus shifts to the right or left include:
- weakened pelvic muscles after childbirth;
- passive lifestyle;
- previous surgical operations;
- physical activity during the postpartum period;
- presence of gynecological diseases;
- excess body weight;
- injuries received during childbirth;
- oncological tumors;
- hormonal disorders;
- damage to ligaments and muscles.
Symptoms
There are many symptoms that indicate a changed location of the uterus. There are cases when this pathology is asymptomatic and is discovered only when a woman complains of infertility.
In general, cervical displacement is accompanied by the following obvious symptoms:
- problematic ovulation;
- increased pain in the menstrual cycle;
- cycle disruption;
- pain during intimacy;
- decreased libido;
- lack of orgasm;
- vaginal dryness;
- obstructed venous outflow;
- infertility;
- exacerbation of inflammation of the uterus and its appendages;
- frequently recurring spontaneous miscarriages and abortions;
- migraine;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Depending on the side to which the uterus has shifted, other symptoms may be added. When the uterus deviates forward, there is pressure on the bladder, as a result of which the woman may have trouble urinating.
She is bothered by frequent urges, cystitis and urinary retention may appear.
In almost every case, the symptoms are sufficiently severe, making it possible to suspect the onset of pathology in the uterus and seek medical help.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are often performed in 3 stages. Moreover, to determine an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a gynecologist, urologist and proctologist. Often this pathological condition of the main reproductive organ is accompanied by other abnormalities that occur in the urinary system and intestines.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor palpates the abdomen and the uterus itself by inserting fingers into the vagina. If the uterus tilts back, the fingers will press against the arch at the back. Forward deviation can be felt above the pubis. When it deviates to the side, its insufficient mobility and gravity in a certain direction are revealed.
Hysterosalpingography and colposcopy are the next stages of the examination. Hysterosalpingography makes it possible to identify the level of tubal patency, assess the general condition of its cavity and make sure that no adhesions have developed. To perform this, a substance flowing through the tubes is injected into the uterus.
The entire process is controlled by x-rays and ultrasound. Colposcopy is used to determine downward deviation of the uterus. The procedure is carried out with a colposcope, and in this case there is no need to use an anesthetic drug.
Thanks to this method, it is also possible to additionally detect various neoplasms, the onset of cancer, dysplasia and pathologies of the cervix.
Traditional methods
This group of methods for diagnosing uterine displacement includes various tests:
- microflora smear;
- which help detect atypical cells;
- ultrasound examination;
- general blood and urine analysis.
An ultrasound is also indicated to help determine the position of the uterus. Treatment of uterine displacement is carried out in 2 stages. Usually there is an inflammatory process, as well as the formation of adhesions.
First stage of treatment
At this stage, the main task is to eliminate inflammation and restore blood supply to organs that are not well nourished due to pinched blood vessels. For this, different methods are used. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for therapy:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Nurofen";
- "Ibuprofen."
If an infection occurs, the use of antibiotic courses may be indicated. Physiotherapeutic procedures: the use of UHF and other methods for treatment that help relieve inflammation, resolve adhesions, improve lymphatic metabolism and blood supply, which significantly improves the general condition of the body.
Second stage and stabilization
Next, final relief from inflammation is required in order to move on to the final stage of therapy. Anti-inflammatory treatment is performed with the same agents that were used at the previous stage of therapy. It is important to completely cure the inflammatory process, since without this it is impossible to perform gynecological massage - a key element in the treatment of uterine displacement.
Physiotherapy is intended to improve blood circulation in the uterus and finally relieve inflammation with the help of safe anti-inflammatory drugs. The organ tissues will respond better to treatment, becoming more elastic. Subsequently, the adhesions will dissolve, and the massage will stretch them.
Massage helps strengthen the fascia and ligaments of the pelvic organs. Also, the uterus will gradually move to its normal physiological position. Ligaments strengthened by massage will tightly fix the uterus in a physiological state.
The duration of treatment performed will depend on the complexity of the uterine displacement. However, massage must be carried out at least 15 sessions lasting no more than 10 minutes. With the right approach and quality treatment, uterine displacement can be eliminated, and the woman will be healthy!
Rehabilitation
As a rule, if the treatment is successful, the woman is discharged after 3 days. But the full recovery period is a month. However, restrictions on a number of loads remain in place for several months.
Depending on the operation and the accuracy of following the doctor’s recommendations, an improvement in the condition can be observed within a week, and if the operation was performed on a large area of the uterus, after 2 weeks. A faster recovery period occurs when a support mesh is installed.
After the operation, the sick leave is valid for another month, this is very important for those women who lead a sedentary lifestyle, since being in a sitting position for a long time after the operation is dangerous.
During the rehabilitation period, the following restrictions apply: you cannot have an intimate life for 2 months until the stitches are completely dissolved. You can't lift weights for six months. You are not allowed to visit the pool for 2 months.
Also, you should not engage in active physical activity for 2 months. After surgery, the hospital will usually prescribe painkillers to help you get through the first stage of recovery.
This is usually quite enough, but if inflammation begins, antibiotics are also prescribed.
Additional measures
If the operation was performed vaginally, it is also recommended during the rehabilitation period:
- Watch your diet. It is important that the stool is liquid at first; you should not strain your lower abdomen when visiting the toilet.
- You can sit only 3-4 weeks after surgery.
- You can take a shower only after 5-7 days, and you will need to follow the instructions given by your doctor. You cannot visit the sauna, bathhouse, or take a bath for 2 months.
- If bleeding occurs, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- After the operation, examination is carried out a week later, and then a month later.
Consequences of uterine displacement
The uterus, if displacement occurs, begins to put pressure on the rectum and bladder. It happens that the uterus shifts to the left or right, usually caused by inflammatory processes in the ovaries or tubes. In this case, the organ shifts in the direction where the inflammation occurs.
The displacement of the uterus to the side leads to the formation of adhesions, the connective tissue that secures the organs is stretched and weakened. Organs are displaced and adhesions form between them. As a result, some organ mobility is lost.
When visiting the toilet, a woman may experience pain or discomfort in the side where the adhesion occurred.
If the uterus moves downwards and descends, problems begin with the functioning of the bladder and intestines, as the uterus begins to put pressure on these organs.
The ligaments are weakened, as a result of which the organs cannot be fixed in the desired position. Further weakening and sagging of the ligaments leads to urinary and fecal incontinence. In this case, surgical intervention is required.
As a result of displacement of the uterus in one direction or another, the following consequences may occur:
- Development of cystitis, problems with urination.
- Constipation, lower back pain.
- Numbness of the limbs, development of varicose veins, neuralgia of the sciatic nerve.
Pregnancy during displacement
Uterine displacement (uterine bending) is a diagnosis that gynecologists make for almost every fifth woman. Minor displacement of this female organ is not a clinical pathology and occurs in many both parous and nulliparous women.
Experts consider only strong deviations from the established norm to be pathologies, but they are quite rare. If the displacement of the uterus is not significant and the woman’s health is in order, then pregnancy is quite possible.
However, it must be taken into account that the stronger this deviation, the more difficult it will be for sperm to enter the uterine cavity. Therefore, according to the advice of gynecological specialists, when conceiving, it is necessary to choose certain positions that will simplify the advancement of the seed, for example, the knee-elbow position.
After sexual intercourse, a woman needs to lie down for a while in the “birch tree” position. These methods increase the likelihood of pregnancy.
In case of critical displacement of the uterus, this pathology must be eliminated, which can subsequently lead to infertility. During pregnancy, this disease can be expressed in the form of frequent urination and back pain.
In most cases, at the beginning of the second trimester, the fetus begins to grow rapidly, the uterus increases in size and returns to its proper place in the woman’s pelvis.
Only a posteriorly displaced uterus can interfere with examination or ultrasound.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/404769/smeschenie-matki-prichinyi-simptomyi-osobennosti-lecheniya-reabilitatsiya
Signs of backward bending of the uterus
There are no exact symptoms of retroflexion; its presence can be suspected by the following signs:
- Periodic pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- Painful menstruation;
- Changes in the volume and nature of menstrual flow (presence of clots, bleeding and scanty flow);
- Violation of the menstrual cycle;
- Feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen before and after menstruation;
- Urinary retention;
- Leucorrhoea;
- Intestinal dysfunction (frequent constipation);
- Impossibility of conception;
- Problems of bearing a fetus;
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, etc.
The listed signs are rarely a direct symptom of a bend of the cervix along the posterior wall. These are most likely symptoms of pathological processes occurring in a woman’s body, which cause the formation of a posterior bend.
Causes and consequences of uterine deviation
Having heard from a friend a diagnosis of “uterine displacement,” I became interested in the problem and began studying medical sites. It turns out that it means a deviated state of the organ to the right or left, depending on the cause of the pathology.
Conclusion
Displacement of the uterus to the right or left is associated with:
- with diseases;
- injuries;
- surgical interventions.
Timely identification of the abnormal condition will help prevent the development of complications and infertility.
The uterus and its normal location
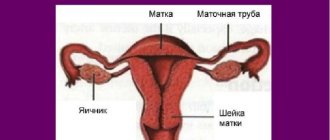
A hollow organ consisting of muscle tissue is called the uterus. Normally, it is located between the bladder and intestines in the pelvic space; the fallopian tubes extend from it to the right and left, through which the uterus is connected to the ovaries.
A healthy organ is located deviated from the symphysis pubis; an angle of 70-100 degrees is formed between the body and the neck. The position of the uterus is ensured by a complex of muscles and ligaments that are highly elastic.
Due to them, it takes a deflected position forward, backward, right or left - when filling the bladder and intestines.
Offset Options
Uterine displacement is divided into:
- to horizontal – back, left or right;
- vertical - with drooping, eversion or prolapse.
Symptoms of position change
A deviated position to the right or left when the uterus is displaced often has no manifestations and is determined when attempts at conception are unsuccessful. In other variants the problem is expressed:
- pain during menstruation or cycle disorders;
- intestinal dysfunction, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- discomfort in the lumbar region, pain during sexual intercourse;
- dryness of the vaginal mucosa, loss of sexual desire.
Consequences
The deviated position of the uterus to the right or left when displaced causes:
- difficulty conceiving;
- heavy menstruation or lack thereof;
- infertility, organ loss.
Pathology during pregnancy
If the uterus remains mobile, then the deviated position does not become a problem with conception. During gestation, the organ straightens as the fetus grows; in some patients, a significant displacement to the right or left can cause serious complications.
The pronounced pressure of the organ on the bladder and intestines becomes a source of development of congestion and problems with their release. Prolonged compression provokes inflammation of the kidneys, septic peritonitis, gangrene of the bladder, and spontaneous abortion.
Diagnosis and treatment
Confirmation of uterine displacement to the right or left is carried out:
- gynecological examination;
- colposcopy;
- ultrasound examination;
- taking a smear for infection.
X-ray helps to identify the deviated position of the organ.
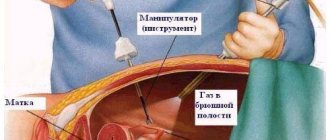
Surgical intervention
The operation is recommended for prolapse or displacement of other pelvic organs. Plastic surgeries help restore the ligamentous apparatus and return it to its original position. Complete prolapse requires excision of the uterus and pelvic floor plastic surgery.
Exercises
At the initial stage, with minimal pain, the patient is prescribed to perform Kegel and Yunusov exercises. These techniques allow you to return from a deviated state to its original position.
Prevention
Preventing drift to the right or left begins with the following recommendations:
- prohibition on lifting and carrying heavy objects weighing more than 10 kg;
- daily hygiene procedures - to avoid the development of inflammation;
- timely treatment of diseases of the reproductive department;
- giving up a sedentary lifestyle;
- exclusion of hypothermia, frequent change of sexual partners;
- regular check-ups with a gynecologist.
A shift to the right or left can be caused by both physiological and pathological sources.
Periodic diagnostic checks will prevent the transition of the abnormal condition into a chronic course with prolapse, cure existing pathologies, and restore the normal position.
Yulia Olegovna Hello! My name is Yulia Olegovna. I am the head of the endometriy.com project. I graduated from the Faculty of General Medicine (Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy (Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy), completed an internship in the specialty "Obstetrics and Gynecology". I will be glad if our materials help you understand your ailments. Remember that all articles on the project are intended for informational purposes only; if you have any suspicions or signs of illness, you should immediately contact your doctor.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Causes and consequences of uterine deviation Link to main publication
Source: https://endometriy.com/matka/smeshhenie
Retroflexion and pregnancy
The pathological location of the uterus posteriorly is in no way the cause of a woman’s infertility and the difficulty of bearing a child. As a rule, a woman cannot conceive a child due to adhesions formed in the abdominal cavity, which prevent fertilization and form an abnormal position of the uterus.
Compliance with preventive measures and timely treatment of organs located in the abdominal cavity can prevent pathological retroflexion.
Retroflexion is a fairly common problem that involves a backward bending of the uterus. Such an abnormal phenomenon can lead to a fairly large number of problems, both when conceiving a child, and during pregnancy or childbirth. Why the uterus is bent backwards, causes and consequences - there are quite a lot of questions, but only a doctor can give answers.
Displacement of the uterus: right, left
A slight deviation of the uterus to one side is only a physiological feature of a woman’s body. Usually it does not cause any discomfort and does not affect the course of menstruation or pregnancy.
Sometimes pathological displacement of the uterus is observed, caused by a number of reasons. What could be the consequences and methods of treating such a deviation is of concern to all women who encounter it without exception.
The uterus and its normal location
The uterus is a hollow organ whose walls are made of muscle fibers. In its normal position, it is located in the pelvic space, between the lower intestine and the bladder. The fallopian tubes extend from it to the right and left, connecting it with the ovaries.
Normally, the uterus is located at a slight inclination to the symphysis pubis. And between her body and the neck an angle is formed, the value of which can vary from 70° to 100°.
The spatial position of the uterus is provided by a whole complex of muscle fibers and ligaments. The elasticity of these structures allows for deviation to the right, left, anterior or posterior, caused by the pressure of a full bladder or intestine. Both the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes can be displaced.
A slight deviation from the usual location, both to the right and to the left, is the absolute norm.
What is uterine retroflexion
The bend of the uterus (posterior deviation) is an anomaly in the position of the organ, in which the deviation from the normal position in the pelvis is permanent. It can be congenital or acquired.
The congenital form usually does not cause significant discomfort or problems in a woman’s adult life. More often, the posterior location of the uterus is found in women of asthenic physique, characterized by low weight, thinness and an elongated chest. Often, the causes of retroflexion include a hereditary factor.
Secondary (acquired) posterior bending of the uterus is a consequence of various pathological processes occurring in a woman’s body, which lead to loss of elasticity of the ligaments or to their weakening. The most likely causes of the formation of a bend in the cervix and uterus, according to most obstetricians and gynecologists, are inflammation of the internal genital organs, infections, including some sexually transmitted diseases, surgical interventions “for gynecology” and traumatic childbirth.
Displacement of the uterus to the right causes and consequences
Having heard from a friend a diagnosis of “uterine displacement,” I became interested in the problem and began studying medical sites. It turns out that it means a deviated state of the organ to the right or left, depending on the cause of the pathology.
Tatyana Ostroverkhaya, gynecologist-endocrinologist. Editor A. Gerasimova
Normally, this organ is located between the rectum and the bladder. This arrangement is not accidental: the uterus is surrounded by free space, so it is not disturbed by neighboring organs, including during pregnancy.
A change in the normal position of the uterus (disposition) leads to various consequences - infertility, miscarriages, difficult childbirth, compression of nearby organs (bladder and rectum), so such pathologies must be treated.
How and where the uterus moves
The uterus can move to the side, change the angle of inclination, descend, rise and twist. The consequences depend on the type of pathology:
- Retroversion
is a displacement back towards the rectum. - Anteversion
is a deviation forward towards the bladder. - Lateroversion
- tilt to the side (to the left - sinistroversion, to the right - dextroversion). - Prolapse of the uterus
is called prolapse. It can be complete or incomplete: the organ can extend beyond the genital opening or remain inside. - Moving upward
(elevation). The uterine fundus is too high and the cervix is raised.
Changing the inclination angle:
- Hyperanteflexion
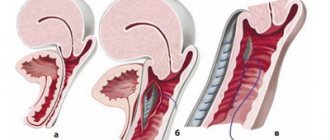
is an anterior bend in which the body and neck form an acute angle - Retroflexion (retrodeviation)
is a position in which the uterine body deviates backward and the cervix deviates forward. Intestinal pressure leads to prolapse and prolapse of the uterus. Retroflexion can be mobile or fixed. In the first case, the uterus can be returned to its physiological position, but in the second, it is not.
When the uterus is torsioned, its cervical part remains in place, and the body turns left or right; when turned, the entire organ turns.
Causes of uterine displacement
Uterine displacement can be congenital or acquired. All pathologies are associated with weakness, ruptures or defects in the muscles and ligaments that support the organ, with laxity and pathologies that increase the weight of the uterus itself.
Causes of uterine displacement to the left, right, back:
- congenital anomalies and underdevelopment (infantilism) of the genital organs;
- polyhydramnios, multiple births, multiple births, large tumors, sprained muscles and ligaments;
- inaccurate operations on the internal genital organs, abortions, complicated childbirth, leading to thinning of the walls of the uterus, injuries to muscles and ligaments;
- weakness of the pelvic floor muscles caused by heavy physical labor, sports activities, obesity, sudden weight loss;
- tumors and inflammation of neighboring organs, compressing the uterus, severe constipation;
- aging of the body - in this case, tissues lose tone due to poor blood supply and hormonal changes.
What does a woman feel when the uterus is displaced: symptoms of anomalies in the location of the organ
Symptoms of abnormal position of the uterus depend on the severity of the pathology, the location of the organ and the diseases that caused this condition.
- The lower abdomen almost always hurts and pulls during sexual intercourse (except for the elevated position of the uterus). With prolapse and prolapse of the uterus, intimate life is impossible.
- The second sign is menstrual irregularities, too scanty or heavy periods. When the uterus is displaced, women often complain of painful periods.
- With the disposition, problems arise with conception and pregnancy.
- When the uterus bends forward, pressure on the bladder makes urination difficult, more frequent, and may be painful or uncontrollable.
- When the uterus bends back, it puts pressure on the rectum, which leads to constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (you constantly want to go to the toilet), pain in the sacral region, and damage to the sciatic nerve.
Source: https://ugri-net.ru/smeshhenie-matki-vpravo-prichiny-i-posledstvija/
How to treat a posterior bend of the uterus?
When diagnosed with a posterior bend of the uterus, treatment can be carried out in a variety of ways. Among the features of treatment, we note the following points:
- First, you should consult a doctor. If the problem with conception lasts for a long time, then it makes sense to contact qualified centers.
How to correct a posterior bend of the uterus is a very common question. It should be borne in mind that after conceiving a child and before giving birth, the woman should also be observed. Childbirth takes place by caesarean section or after preparing the uterus by taking a large number of drugs that make it more flexible.