After 50 years, the functions of the appendages fade, and menopause occurs. For some medical reasons, women have to have their ovaries removed. But there is a fundamental difference whether appendage removal occurs after 50 years or at a young age.
Age characteristics
The operation of removing the ovaries before the age of 40 leads to forced menopause and a cascade of premature changes in the body. In this case, hormone replacement therapy is more often prescribed. If it is impossible, then the woman faces symptoms characteristic of menopause: hot flashes, heat, palpitations, heart rhythm disturbances, changes in blood pressure, worsening mood.
Removal of appendages after 50 years does not entail any changes other than those natural for menopause. By this age, reproductive functions have almost died out, and the body has already prepared for “retirement” metabolic processes. Therefore, the decision about such an operation is made easily by doctors.
Indications for surgery
After 50 years, removal of the uterus and ovaries is prescribed in the presence of severe diseases. In most cases, these types of pathologies pose a danger to the health and life of the patient, so surgical treatment is performed to eliminate the risk of complications.
Main indications:
- malignant processes in the genital organs or the risk of their occurrence;
- ectopia of the cervix;
- organ prolapse;
- uterine fibroids;
- cystic and tumor formations on the ovaries;
- uterine rupture during pregnancy, childbirth;
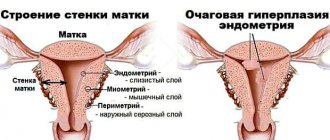
- progressive endometriosis;
- heavy uterine bleeding;
- ovarian rupture.
Removal of organs is prescribed only if other types of therapy are ineffective or impossible to carry out.
Autonomic disorders
According to statistics, more than 60% of women who experienced menopause after removal of the uterus are familiar with this problem. Lack of proper saturation of the body with sex hormones negatively affects the functionality of the autonomic system and contributes to the appearance of:
- decreased performance;
- increased fatigue;
- general weakness of the body;
- frequent headaches that develop into migraines;
- partial short-term numbness;
- tachycardia;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- neurological diseases.
Diagnostic measures
Before determining the treatment method, a complete diagnosis of the functionality of the genital area is necessary. To do this, a woman must undergo the following types of studies:
- gynecological examination - determination of the size of the genital organs, possible changes in their structure;
- colposcopy – assessment of the condition of the cervix and vaginal walls;
- biopsy - collection of biomaterial for further research on microflora, the presence of infections or determining the type of tumor;
- vaginal smear - analysis of the state of local microflora and the possible presence of infectious or fungal microorganisms;
- blood tests to study hormonal levels and identify inflammatory processes in the body.
If an infectious lesion of the uterus and appendages or acute inflammation is detected, the detected pathologies are initially treated. Surgery is performed after these conditions have been eliminated. Prescribing surgery during their course can aggravate the inflammatory process or lead to widespread infection.
Hormonal disorders
The sex hormone estrogen is responsible for moisturizing the mucous membranes of the vagina and fallopian tubes. Its insufficient quantity leads to disruptions in the functioning of the mucous membranes, during which they become thinner and dry out. The woman feels uncomfortable and prefers to completely refuse intimacy, since the lack of hydration causes pain. Against this background, conflicts in relationships with a partner and prolonged depression are possible.
Estrogen also has a huge impact on the functioning of the brain, especially disrupting cognitive functions and processes associated with them. Impaired cognitive functions cause:
- memory impairment;
- throughput of perception and assimilation of information;
- problems with remembering new information.
These manifestations can be further aggravated by the woman’s stressful state.
Types of surgical interventions
When removing the uterus and appendages after 50 years, three main surgical methods are used. The choice of type of operation is determined by the indications for its implementation.
Types of interventions:
- Radical. Removal of the uterus, its tubes and appendages, part of the omentum, a third of the vagina, and nearby lymph nodes. Most often, radical hysterectomy is performed in the presence of malignant processes in the genital organs.
- Total. Removal of the uterus and its cervix.
- Supravaginal. Surgery to amputate the body of the uterus.
These types of organ removal after 50 years can be carried out using various surgical methods.
Early symptoms of menopause
The natural decline of the reproductive system occurs smoothly. The female body manages to adapt to changes in hormonal levels, so the symptoms of menopause appear less pronounced and are harmoniously tolerated. At the same time, artificial and postoperative menopause after removal of the uterus occurs abruptly, and its symptoms are pronounced and have an increased negative impact on the normal functioning of the female body.
Three weeks after the operation, menopause appears after removal of the uterus. Symptoms are conditionally divided into four categories, based on the localization of the impact.
Operation methods
The surgical method is determined by the type of operation prescribed, the patient's condition and the need for emergency intervention. Basic surgical methods for removing the uterus and appendages:
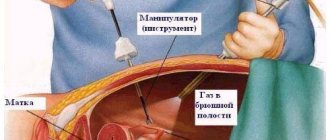
Laparotomy
Abdominal surgery performed by making an incision in the anterior abdominal wall. It is often used for radical removal of organs or when emergency intervention is necessary - in case of rupture of the uterus or ovaries, intense internal or uterine bleeding.
Preoperative preparation
During preparation for surgery, the patient undergoes a basic list of examinations. These include ECG, blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests and hormone determination. The blood type and Rh factor are determined, express diagnostics of syphilis, viral hepatitis and HIV infection are carried out, and fluorography is performed. An important component of the examination is preoperative ultrasound.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia in a clean operating room. The patient is hospitalized in a gynecological hospital the day before the planned intervention or urgently according to indications.
Consequences of the operation
Removal of the uterus and appendages after 50 years does not leave its mark on the body. Changes occur in a woman’s emotional state and well-being. For complete rehabilitation with a minimum number of consequences, the patient requires the help of several specialists.
Psychological disorders
After such surgery, young women are most susceptible to depression. Emotional depression is also possible in patients over 50 years of age - this condition is considered absolutely normal. Life after organ removal seems gray and dull to a woman, and a feeling of inferiority appears. At this time, her closest people provide her with the greatest support - they restore faith in herself and contribute to the emergence of a new surge of strength.
In order to avoid depression, the patient is recommended to do what she loves or acquire a new hobby. This will distract her from the treatment experience and improve her mood. At this time, you should pay more attention to your family and take care of the well-being of loved ones.
In severe cases, the help of a psychologist is required, but you can contact him immediately after the operation - this will speed up the process of emotional recovery.
Loss of reproductive ability
Women over 50 years old should not be concerned about the lack of reproductive function. This does not have a negative psychological effect on patients of this age, so it is not considered a problem. This fact significantly affects the emotional state only in women under 30-40 years of age.
Deterioration of health
Removal of the ovaries, which previously produce hormones, significantly affects the condition of the body. When menopause occurs before surgery, the effects of treatment are less pronounced.
Possible consequences of removal of the uterus and ovaries for the patient’s health after 50 years:
- vascular atherosclerosis - prevented by taking special medications;
- weight gain is a consequence of hormonal imbalance;
- swelling and heaviness of the limbs – present after removal of lymph nodes;
- chest pain - occurs when the genital organs are removed before menopause, often painful sensations occur on the days when menstruation was supposed to begin;
- hot flashes;
- state of fatigue, increased drowsiness;
- irritability, mood swings.
During the first time after surgery, a woman has pain in the lower abdomen and bloody discharge from the vagina - this is considered normal.
These symptoms are considered temporary and disappear within a few months after treatment. To prevent them, preventive medications are prescribed.
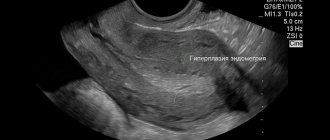
Treatment of ovarian cysts in Moscow
At the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, specialists diagnose and treat various types of ovarian cysts in women. The modern technical base and professionalism of the oncologists who provide assistance and accompany patients at every stage of treatment make it possible to carry out the necessary procedures.
Oncology clinic specialists regularly interact with patients, monitor how postmenopausal ovarian cysts develop and respond to treatment. As part of the treatment of ovarian cysts at the Yusupov Hospital, treatment of concomitant pathologies can be carried out. Women who have undergone surgical removal of a tumor undergo rehabilitation under the guidance of highly qualified oncologists, rehabilitation specialists, and exercise therapy instructors.
Comfortable conditions for patients are an important part of successful treatment. The cozy wards of the Yusupov Hospital have created the necessary conditions for a comfortable stay. For the convenience of patients and their loved ones, parking is equipped on the territory of the Yusupov Hospital.
The development of the Yusupov Hospital is taking place in accordance with global trends, current norms and regulations in the field of medicine. The staff of the medical institution maintains the tradition of attentive and friendly attitude towards each client. To get a consultation with an oncologist, you need to choose a convenient time and make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Rehabilitation
Depending on how long ago the operations were performed, the recovery process takes place differently. To speed up its progress, there are some rules developed for each period.
Early rehabilitation
Immediately after the operation, the woman is in a hospital setting. The early recovery process takes place in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. To do this, the following procedures are performed:
- taking medications in the form of tablets and injections - painkillers, antibacterials, anticoagulants;
- processing of surgical sutures, dressings;
- monitoring the patient’s condition - monitoring possible deterioration of health, wound suppuration, the occurrence of blood clots, bleeding;
- provision of nutrition - in the first days after treatment, the patient consumes only light soups, cereals, fruit drinks, etc.
Psychological disorders
No matter how emotionally prepared a woman was before the operation, after removal of the uterus, menopause and severe stress begin. Patients experience inferiority complexes and prolonged depression. Against this background, there arise:
- excessive impulsiveness;
- increased anxiety;
- severe irritability;
- bright outbursts of unreasonable anger;
- prolonged depression;
- lack of excitement;
- tearfulness;
- annoying fears.
The psychological problems that arise do not allow the body to adapt normally to the new condition and, in combination with other consequences of menopause, can develop into chronic pathologies. These problems should be solved immediately, because only by improving the psychological state can a woman feel healthy and again experience all the joys of her old life. Returning to your previous routine should be done gradually. Excessive fatigue and external pathogens can provoke a recurrence of symptoms.
Pros and cons of removing female genital organs
Over the age of 50, there are slightly fewer negative aspects than among young women. Basically, they are conditions of the body that worsen general well-being and increase the risk of complications:
- severe pain in the first days after treatment;
- presence of a scar on the abdomen;
- disruption of the pelvic organs;
- rapid onset of menopause;
- failure of the cardiovascular system;
- risk of developing osteoporosis;
- temporary ban on sexual intercourse;
- psychological discomfort.
Positive aspects of the intervention:
- end of menstruation;
- impossibility of pregnancy - for women at this age this is a definite plus;
- reducing the risk of developing cancer.
The advantages of removing the uterus and ovaries after 50 years are few, but they are considered significant. At the same time, all possible treatment deficiencies are easily eliminated or the intensity of their manifestation is reduced by introducing preventive therapy.
Modern methods of removing the uterus
If the diagnosis is checked and made, and a decision is made to remove the uterus, you need to understand that the body needs preparation. Perhaps psychological as well. The fact is that for most women, such a loss of the uterus is also a loss of femininity, a feeling of being deprived of the main attribute of their gender.
Many women are sure that with the removal of the uterus, their body will begin to wither sharply - the signs of aging will be more pronounced, and concomitant diseases will literally fall on the body that has experienced such deprivation. To get rid of fears, doubts, anxieties, several meetings with a psychologist or psychotherapist will be more than useful.
On the very day before the operation you cannot eat or drink, the intestines need to be cleansed. Contact lenses cannot be worn during surgery; makeup and manicure are also removed. Most likely, the woman will have repeated urine and blood tests on the same day.
The operation itself is carried out in several ways:
- Cavity removal of the uterus is used less and less, as this is the most traumatic method;
- Laparoscopic - the uterus is removed through small incisions in the abdominal wall;
- Vaginal – the uterus is removed directly through the vagina.
Today, the most acceptable and effective method is combined uterine amputation. In this method, vaginal access is combined with laparoscopic assistance. In this case, the operation will be very fast and as accurate as possible, and the stitches after restoration will be almost invisible.
Reduced risk of postoperative complications
Possible risks should be prevented immediately after operations. Prevention of complications consists of following all rehabilitation rules and doctor’s instructions:
- wearing a postoperative bandage for 1-2 months – reducing the likelihood of hemorrhoids, urinary disorders, reducing pain;
- regular preventive examinations - they must be carried out to monitor recovery and timely adjustment of therapy;
- performing therapeutic exercises – relieves swelling, preventing the formation of blood clots, strengthens the muscles of the pelvis and peritoneum;
- maintaining sexual rest for up to 2 months allows the organs to fully recover and the sutures to heal;
- refusal of a bath, sauna, steam bath - failure to comply with this rule is fraught with inflammatory processes, suppuration of the sutures, and increased stress on weakened blood vessels;
- using pads instead of tampons;
- proper nutrition – ensures the normalization of intestinal function.
If you have chronic diseases, you should inform your doctor about this before surgery - this will avoid exacerbations by prescribing additional preventive methods of therapy.
An operation to remove the uterus and ovaries after 50 years has few negative consequences for a woman. This is due to the lack of need for further reproductive capacity and the low number of possible complications. For a full and rapid recovery, it is necessary to follow all the rules of rehabilitation - they will reduce the risk of negative health consequences.
What awaits a woman after amputation?
Consequences can be divided into early, associated with postoperative complications, and late, caused by hormonal imbalance and pelvic organ prolapse.
In the near future after surgery it is possible:
- Infection and suture dehiscence;
- Painful sensations;
- Violations of the act of defecation;
- The appearance of adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- Bleeding associated with suture failure or the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome;
- Impaired bladder emptying, pain during urination;
- Development of peritonitis;
- Vascular thrombosis.
During the manipulation, the bladder, blood vessels and intestines are injured, which causes bleeding and causes the development of urinary incontinence and the release of feces from the vagina.