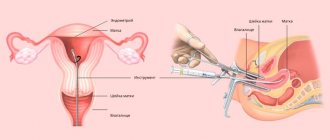
Indications for the study
A biopsy for erosion should not always be performed. Usually, for such a diagnosis, it is enough to take a Pap smear and undergo a colposcopy.
The study is prescribed only if, along with erosion or pseudo-erosion, so-called suspicious colposcopic signs were detected:
- areas not stained with iodine after the Schiller test;
- white areas after exposure to acetic acid solution.
A biopsy of the cervix during erosion confirms or refutes this diagnosis, and is also used to exclude precancer and oncopathology.
Indications
A diagnostic procedure during which the doctor takes a biopsy sample from the problem area for further histology is called a cervical biopsy. The purpose of the study is to identify oncology and other equally dangerous diseases. Shows accurate results. Not all patients with erosion are prescribed a biopsy.
Basic
The study is indicated when identifying HPV carriage, white areas after applying acetic acid, as well as in the presence of lesions that do not absorb iodine. These signs signal tumor or precancerous processes. It is in order to exclude pathologies that the doctor conducts a study on the recommendation.
Visual
The procedure is indicated for the following visible changes:
- cracks;
- areas with dead tissue;
- seals;
- ulcers.
There are true and false erosions in the cervix. The first type is characterized by the absence of outer epithelium, which is why the granulation layer appears on the surface. Against the background of such changes, the appearance of swelling and inflammation is noted. This defect heals on its own.
False erosion is characterized by protrusion of cells from the cervical canal (ideally, they should not come into contact with the vaginal environment). This pathology occurs secretly, exists for years, provokes inflammation and often degenerates into cancer. In order to obtain accurate information and differentiate the types of pathology, you need to examine the tissue under a microscope.
Features of the procedure
The biopsy is done on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle immediately after the end of menstruation. This is necessary for the wound to heal before the next menstrual bleeding begins. Otherwise, the risk of infection in the cervix increases, as well as the likelihood of developing endometriosis in the future.
Collection of material is possible only in the absence of infectious diseases. Therefore, preparation for a cervical biopsy includes a smear for microflora. If an infection is detected, the woman is first prescribed appropriate treatment, and after recovery, a biopsy is performed.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis within a few minutes.
Is it painful or not to perform a cervical biopsy in the presence of erosion?
This examination is painless because there are no sensitive nerve endings in the cervix, so it is performed without anesthesia. An unpleasant sensation may be associated with the insertion of gynecological speculum into the vagina. In addition, in response to the action of the instruments, the uterus may contract slightly, which causes short-term discomfort in the lower abdomen.
The biopsy should be performed under colposcopy guidance. The cervix is treated with Lugol's solution, while the pathological areas remain light. For more accurate sampling of the material, the cervix is examined under magnification using a colposcope.
Types of procedure
A biopsy for erosion is done in several ways. They differ in the tools used and the amount of material that needs to be taken. Sometimes the technique can eliminate the focus.
Circular
It is considered an extensive research method, as it captures part of the channel with surrounding cells. It involves taking healthy and problematic tissue. The material is taken with a radio wave or a regular scalpel. Anesthesia is used during manipulation. After taking a biopsy, discomfort and bleeding may occur.
puncture
This technique is used to study changes in the uterus if dysplasia or cancer is suspected. The material is collected with a needle. A small column of cells is sufficient for examination. The procedure is carried out quickly and does not hurt.
Anesthesia is not used during the manipulation. The doctor takes the material during the examination on the chair. The process feels similar to an injection. Its duration is 15 seconds. After the biopsy, bloody discharge may appear. After three days the symptom goes away.
Conchotomnaya
The sample is taken with scissors (forceps) or a conchotome. It is carried out similarly to sighting. The only difference is the volume of the biopsy. Since more material is taken during this study, local anesthesia is used. The method is not used for girls with unrealized motherhood.
Loop
The outer layer is removed using a loop with electric current. An anesthetic is pre-injected. Due to the large volume of sample taken, bleeding occurs at the end of the procedure. The manipulation is traumatic and involves the formation of a scar. The formation of a scar is fraught with disruption of pregnancy, impossibility of fertilization and problems with cervical dilatation. This biopsy is not prescribed for nulliparous patients.
Radio wave
It is considered the most modern technique because:
- the procedure does not injure the neck and adjacent tissues;
- does not provoke complications;
- no need to use anesthesia;
- no bleeding occurs.
Since the radio wave technique for erosion on the cervix is not associated with the risk of scar formation, it is often prescribed to nulliparous patients.
Laser
This biopsy method requires hospitalization and the use of general anesthesia. The method is non-traumatic and does not provoke complications. Within five days after a cervical biopsy, pink or brown discharge may be present if erosion is present.
Wedge-shaped
The biopsy sample is taken with a knife. A wedge-shaped sample is cut out from the mucous membrane of the neck so that healthy tissue enters it. It is performed only under general anesthesia. Discomfort and discharge are present for two weeks.
Scraping
After the administration of anesthesia, the tissue located in the cervical canal is removed. Indicated for girls with the following pathologies:
- proliferation of the endometrium;
- dysplasia;
- HPV with high oncogenic risk;
- polyps.
The procedure is performed even when the changed area is located in the lumen of the cervix, during tumor processes.
Preparing for the study
2 days before the biopsy, you must stop using vaginal tampons and replace them with sanitary pads. It is recommended to wash yourself every evening with warm water and soap, avoiding douching. Suppositories and vaginal tablets can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. 2 days before the procedure you should abstain from sexual intercourse.
Shaving the perineum is usually not required, but this issue can be clarified with a gynecologist.
Before the biopsy, tests are taken to exclude an infectious process in the vagina and nearby organs:
- general blood analysis;
- flora smear (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis);
- tests for mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, HIV infection, syphilis, hepatitis.
Blood clotting is checked using a coagulogram test.
Before the biopsy, it is necessary to perform a colposcopy to determine the location of the material collection.
The study is not carried out for acute inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, during menstruation, or during pregnancy. Erosion is not such a dangerous condition as to risk the health of the unborn child.
Before the intervention, you need to inform your doctor about the following facts:
- a list of medications taken, primarily for blood thinning;
- allergies to medications or food;
- blood diseases in family members or the patient herself;
- concomitant diabetes, hypertension or ischemic disease;
- suffered deep vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism.
Procedure options
Material for microscopic examination can be obtained in different ways. How to take a cervical biopsy for erosion:
- most often, special forceps (conchotome) are used to take pieces of tissue from different parts of the cervix - in this case, a spray with lidocaine is applied to the surface of the organ for pain relief;
- a puncture biopsy is performed using a needle, into which an area of altered tissue enters;
- it is possible to obtain biopsy material during treatment of erosion with the Surgitron apparatus using radio waves (radio wave biopsy); after such a procedure, there are practically no scar changes in the cervix, which allows the use of a radioknife in young women; however, the quality of the resulting material is not always good;
- other options - laser and loop biopsy - are used less frequently; the laser is well tolerated, but requires intravenous anesthesia; after loop electroexcision, scars may remain on the cervix, which subsequently interfere with bearing a child;
- The most reliable way to obtain tissue for examination is to excise the suspicious area using a scalpel.
In the latter case, the study is prescribed to women who have already given birth and do not plan to have children. This manipulation is performed under local or intravenous anesthesia and, in some cases, is performed in a hospital.
Conclusion
A biopsy is prescribed for girls with cervical erosion to select a treatment method, and also to exclude degeneration into cancer. The procedure is painless and, if carried out and prepared correctly, does not cause complications. The safest method of research is considered to be radio waves. It is performed even on nulliparous girls, since after the manipulations there are no scars left that could interfere with pregnancy.
Practitioner. She graduated with honors from Vitebsk State Medical University in 2012 with a degree in general medicine. She was awarded a certificate of honor for her achievements in her work.
Ask a Question
How is a biopsy performed?
In case of erosion, a biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, in the gynecologist's office. The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair for examination. Using speculums, the doctor dilates the vagina and takes a good look at the cervix. The mucous membrane is cleaned with a cotton swab soaked in sterile saline solution. At this stage, colposcopy with a Schiller test can be performed.
If necessary, an anesthetic is injected into the cervical area or sprayed in the form of a spray. Then a small piece of tissue is excised from the suspicious area using any of the methods listed above. It is placed in a sterile solution and sent to the laboratory.
Recovery period
In most cases, the procedure is safe and does not cause complications. Within 3-5 days there may be scanty bleeding from the vagina, which gradually stops.
Risk factors for complications after biopsy:
- excess weight;
- long history of smoking;
- elderly age;
- high blood sugar;
- renal and liver failure;
- high blood pressure;
- chronic lung diseases;
- malnutrition and anorexia;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- autoimmune diseases;
- immunodeficiency.
If a woman has one or more of the listed factors, she may have the following negative consequences of a cervical biopsy when diagnosing erosion:
- bleeding lasting more than a week;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- changing their color;
- stomach ache;
- increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees or more;
- bad feeling.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a gynecologist.
These signs do not occur if the woman follows all the doctor’s instructions: it is not recommended to use douching or vaginal tampons. During the same period, sexual intercourse is not recommended.
At this time, you should not lift objects weighing more than 3 kg, visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna or take a hot bath.
If you experience mild aching pain in the abdomen, you can take a regular painkiller, for example, Paracetamol or No-shpu.
The doctor may prescribe some medications that speed up the process of mucosal restoration:
- vaginal suppositories Terzhinan for the prevention of infection;
- Metronidazole tablets orally for the same purpose;
- rectal suppositories Genferon, which improve local immune defense and accelerate wound healing;
- vaginal suppositories Betadine, which effectively act not only on bacteria, but also on fungi and viruses.
From the 10th to the 20th day after the procedure, medications are prescribed that improve tissue regeneration processes and prevent the formation of scars:
- vaginal suppositories Depantol;
- vaginal suppositories with an immunostimulating effect Galavit.
After a biopsy for erosion, the woman is usually able to work the next day. Only if a significant portion of the cervix is removed with a knife in a hospital setting, the period of incapacity for work can be several days.
After a knife biopsy, a small scar may remain on the mucous membrane. Sometimes it interferes with fertilization by deforming the cervical canal. In other cases, scar tissue does not stretch well during labor, making it difficult for it to proceed naturally. However, with erosion, the volume of biopsy material is very small, so gross scar changes do not occur.
Symptoms of complications
If all the doctor’s recommendations are not followed or incorrectly followed during the healing period, complications are possible, which can be identified by several symptoms:
- Body temperature rises above 37.5.
- A burning pain appears in the lower abdomen.
- The discharge of blood is profuse and does not go away for more than seven days.
- Blood clots are observed in the discharge.
- Yellowish discharge with a pungent odor.
If one or more symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor immediately.
results
Why do they take a cervical biopsy for erosion?
The main goal of this study is to exclude concomitant precancerous conditions or cervical cancer. Based on microscopic examination of cells, the doctor can determine the following changes:
- dysplasia of varying severity;
- atypical or simple leukoplakia;
- malignant tumor;
- polyps;
- inflammation;
- erosion.
The study is necessary for carriers of oncogenic types of viral human papillomatosis for timely recognition of early precancerous changes. Thus, test results normally do not indicate the presence of cervical intraneoplasia. In case of complications due to ectopia (pseudo-erosion) or true erosion (ectropion), the decoding includes data on CIN degrees I-III. This is already a precancerous condition.
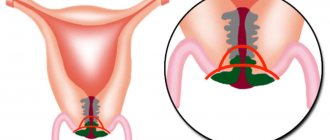
True erosion during biopsy is characterized by the appearance of a defect (damage) in the multilayered epithelium lining the surface of the cervix. At the bottom of the eroded surface, granulation (connective tissue) grows and leukocytes accumulate. There is congestion of the arteries and swelling of the superficial layers of the mucous membrane. True erosion often heals on its own.
Pseudo-erosion occurs when the cylindrical epithelium from the cervical canal extends beyond the external uterine os and forms a circle on the vaginal part of the cervix. Ectopia, or pseudo-erosion, can be of three types:
- Glandular.
- Papillary.
- Immature squamous.
The first type is characterized by the presence of glandular formations under the epithelium. The branching glandular ducts are lined with high columnar epithelium. Around such glands, microscopic signs of inflammation are expressed. With papillary ectopia, expanding papillae are formed, formed by the underlying connective tissue and covered with columnar epithelium.
The difference in the microscopic picture allows one to distinguish between true and false erosion. These conditions have different causes and treatments.
After receiving the results of the biopsy, it is necessary to discuss with your doctor further steps to treat the detected erosion. If the material reveals signs of cervical intraneoplasia, this will require in-depth diagnostics.
If the colposcopic picture and biopsy of a woman with erosion are within normal limits, her risk of developing cervical cancer is low. It is recommended that such a patient undergo regular Pap smears. If the Pap test, colposcopy and biopsy show different results, another biopsy test is prescribed to remove more tissue.
The biopsy result may be provided to another doctor to form a so-called “second opinion”. This will not only reduce the likelihood of diagnostic errors, but will also help the treating gynecologist formulate the correct treatment plan for the patient. A “second opinion” based on the biopsy results can be obtained in various clinics, including foreign ones, by sending samples by mail.
Results of histological examination
The research results are divided into four types:
- No pathology is observed.
A negative analysis indicates that the patient is absolutely healthy. The tissues taken for analysis do not have atypical or altered cells.
- Minor changes.
This analysis result indicates that the cells have a slightly changed shape. This may be a consequence of an inflammatory process.
- Benign changes.
This result can be obtained in the presence of diseases that do not threaten the health and life of the patient and are treatable. It is possible to identify diseases such as: endometriosis, endocervicitis; and benign formations such as polyps and papillomas.
- Precancerous condition.
The analysis shows the presence of diseases that need urgent treatment. If such a pathology is left unattended, over time, it can turn into a cancerous tumor.
- Cervical cancer.
The test reveals the presence of cancer cells.
Modern medicine makes it possible to successfully combat cervical cancer. If a woman with chronic cervical erosion is regularly examined by a gynecologist, this makes it possible to early detect the presence of atypical cells.
Detecting cervical cancer in the early stages allows not only successful treatment, but also maintaining the opportunity to have children.
Video: cervical biopsy
Cervical biopsy. Not to look nervous.
How is a cervical biopsy performed for erosion? Contraindications and complications
To clarify the nature of cervical pathologies, a biopsy may be prescribed. Not knowing the intricacies of the procedure, the patient begins to worry that it will be painful and assumes that her illness is severe, since she was prescribed such a complex examination. However, it is necessary to understand that this is only an important diagnostic method that makes it possible to choose the most effective treatment. Carrying out a biopsy of the cervix during erosion is necessary in order to recognize the earliest signs of possible diseases and prevent serious consequences.
- Complications after the procedure
Consequences of a biopsy
After the procedure, slight bleeding with a brownish tint may be observed for several days. Often the procedure is well tolerated by women, the effects disappear within two days. You should contact your doctor in the following cases:
- The presence of discharge of normal color and consistency, which does not go away for more than two days.
- The occurrence of pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increased body temperature.
- The appearance of yellow discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Deterioration in general health.
The specialist determines the cause of the consequences and prescribes the necessary treatment. To speed up the healing process, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or suppositories.
Biopsy for erosion is the most informative research method, which helps to establish not only the presence of pathologically altered cells, but also other pathologies. The procedure is safe and does not cause serious disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Purpose of biopsy
The procedure involves taking a small piece of tissue from an area of the cervix where damage was detected during colposcopy. After the biopsy, the sample is examined under a microscope and it is determined whether there are cells of an atypical structure (that is, a precancerous condition is observed) and whether the pathology is malignant.
In what cases is a biopsy prescribed? Contraindications
Such a procedure is indicated if, during an examination for inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis), ulceration, areas of necrosis and keratinization of tissue, and cracks are found on its surface. In this case, suspicions arise about the presence of leukoplakia, cervical dysplasia of varying degrees, the occurrence of polyps, and cancer.
A biopsy is prescribed based on the results of an extended colposcopy. At the same time, the reaction of tissues to treatment with special substances is checked. When the surface is lubricated with a 3% solution of acetic acid, the damaged areas look pale against the background of healthy epithelium. After applying Lugol's solution (iodine), they remain uncolored. Taking and examining a sample of the material is necessary to confirm or refute the presence of erosion and other pathologies.
Contraindications to a cervical biopsy are the presence in a woman, in addition to erosion, of acute or chronic inflammatory processes in the genital organs. If a vaginal smear shows that there is an infection in the body, the procedure is postponed.
A biopsy is also not performed if a woman has blood diseases (coagulation disorders), vascular pathologies or heart failure.
Features of the biopsy
The biopsy is performed the day after the end of menstruation (approximately on the 7th day of the cycle), so that by the beginning of the next menstruation the wound at the site of sampling has time to heal. In this case, the risk of infection during the next period is reduced. In addition, menstrual blood entering an unhealed wound on the cervix can lead to the development of genital endometriosis.
The duration of the procedure is usually several minutes. Depending on the technique used, the biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis (if local anesthesia is used) or in a hospital (when tissue sampling is performed under general anesthesia).
The procedure is controlled using a colposcope, a device that makes it possible to optically magnify and illuminate the surface of the vagina. The selected material is placed in a formaldehyde solution and sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
Is the biopsy procedure painful?
Since there are no nerve endings in the cervix, severe pain does not occur during the collection of material due to erosion. Depending on the biopsy method and the extent of the erosion site from which the sample is taken, the procedure is performed without anesthesia or with local anesthesia (lidocaine injection is given). Contractions of the uterus, which reflexively occur when the cervix is affected, can cause slight discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Video: Why is a biopsy prescribed and how is it performed
What does the biopsy show?
Examination of altered tissues reveals:
- inflammation;
- dysplasia;
- cervical erosion without atypia;
- simple leukoplakia.
A biopsy before cauterization of the erosion reveals precancerous conditions that require immediate treatment.
Validity of results
For the treatment of ectopia, the use of radical, destructive techniques, including cauterization of erosion, is often prescribed. This treatment promotes the rejection of altered cells and the formation of healthy epithelium. Before surgery, a biopsy is indicated. The result is considered valid for a month.
For girls who have undergone extensive examination, cervical erosion is not cauterized, since the entire problem area was removed during the biopsy. The mucous membrane heals within three months.
Features of decoding results
The biopsy is sent to the laboratory for a comprehensive histological examination. After receiving the answers, the doctor gives the girl a diagnosis.
Table - Biopsy Finding Categories
| Result | Decoding |
| Negative or "−" | There are no pathologies |
| Minor deviations | Consequence of inflammation in the form of changes in shape in several cells |
| Benign disorders |
|
| Prerequisites for oncology | If treatment is not started, the risk of malignancy will increase |
| Cervical cancer | |
Detection of atypical cells and tumor markers contributes to the early diagnosis of a malignant process. Adequate therapy guarantees recovery.
Types of biopsy
The following methods of sampling from the surface of the cervix are used:
- conization - cutting out a separate piece of tissue in the shape of a cone using a laser beam, scalpel or other device;
- excisional biopsy (puncture) - pinching off a piece of tissue from an erosion site using medical forceps (conchotome);
- endocervical biopsy, when a small amount of material is scraped from the surface of the cervix using a special device (curette), which is then examined histologically;
- trepanobiopsy - sampling for erosion from several areas of the cervix.
Depending on what devices are used to perform conization during a cervical biopsy when diagnosing erosion, there are several types of such a procedure.
Simple biopsy. The material is collected using needles of various diameters. It is possible to extract it in the form of a column, which contains cells located at different depths.
Knife biopsy. Cutting out a small piece of tissue during erosion is done using a scalpel. The most effective, but painful procedure, which is performed under general anesthesia.
Radio wave biopsy. It is carried out using the Surgitron device, which allows for a bloodless cut of tissue with a radio knife (a special electrode emitting high-frequency radio waves). The disadvantage of this method is the cauterization of tissue, which somewhat reduces the quality of the sample taken and the accuracy of the results obtained.
Laser. The fabric is cut using a laser beam.
Loop. The cutting of material during erosion is carried out by an electrode in the form of a thin metal loop through which a weak current is passed.
Note: When choosing the method of performing the procedure, the degree of development of cervical erosion and the age of the patient are taken into account. For nulliparous women, knife, conchotomy and loop biopsies are not recommended, since a scar remains on the cervix. This reduces the elasticity of the wall, which can subsequently complicate childbirth.
Treatment methods for cervical erosion
2 treatment approaches:
- conservative;
- surgical.
The first involves drug therapy. The second is cauterization. Often medications and hardware treatment are combined.
Electrocoagulation of erosion
Electrosurgery for cervical erosion is prescribed based on the results of a preliminary examination; usually combined with a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs. The procedure is outpatient. The optimal time for this is 8-9 days of the cycle. Compliance with the deadline guarantees better recovery and lower risk of complications. When preparing for manipulation, douching for cervical erosion is prohibited.
Electric is a type of cauterization of cervical erosion that does not require general anesthesia. The sequence of how cauterization of cervical erosion is done:
- placing the patient in a gynecological chair;
- local anesthesia;
- treatment of diseased tissues with an antiseptic;
- location of the passive electrode on the thigh, sacrum;
- conducting an active current with a spark to the diseased area.
The event lasts about 20 minutes. After completion of the procedure, the patient is observed for several hours. If the condition is satisfactory, they are sent home. Complete healing requires 1.5-2 months. The special smell after cauterization of cervical erosion does not bother you, but weakness, soreness, and discharge with ichor are possible. Since there is a risk of scar formation, which complicates childbirth after cauterization of cervical erosion, electrosurgery is not recommended for nulliparous women.
Electrocoagulation of cervical erosion. Photo: doctorvera-kaluga.ru
Cryodestruction of erosion
Cryosurgery involves local exposure to low temperatures. Cauterization of cervical erosion with nitrogen is accompanied by the destruction of pathological tissues. The method is more widespread than electrosurgery, since it leads to complications less often. During manipulation, the painful area is cooled to a temperature of 90-150 degrees below zero. Before the procedure, the doctor will tell you how long cauterization of cervical erosion lasts: the active phase takes only 2-5 minutes. When choosing how to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous girls, a cryosurgical approach is recommended.
Advantages:
- painlessness;
- minimal harm to healthy tissues;
- complete recovery due to activation of the immune system;
- minimal risk of complications;
- point impact;
- maintaining the elasticity of tissues of the reproductive system;
- outpatient implementation.
Cryosurgical treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous and parous women occurs without bleeding due to vasospasm and thrombosis.
Cryodestruction of cervical erosion. Photo: mioma911.ru
Laser vaporization of the cervix
Laser destruction of cervical erosion is a modern, safe, reliable method of treatment. The method is minimally invasive, bloodless. Indicated for benign, borderline gynecological diseases. Laser cauterization of cervical erosion is recommended if conservative therapy does not produce results.
It is available to all age groups and is recommended for nulliparous women. Before the procedure, colposcopy, histological examination, and microflora analysis are performed. If pathological microorganisms are identified, before laser treatment of cervical erosion, a course of antibiotics, antiviral, and immunomodulatory drugs is taken.
Laser treatment of cervical erosion involves exposing the pathological area to a laser beam. Strong heating provokes evaporation of diseased tissues. The duration of the procedure is less than half an hour. Upon completion, the patient is sent home.
The best moment for the event is day 8-9 of the cycle.
Rehabilitation - up to a month. At the end of the procedure, the doctor will explain what is not allowed after cauterization of cervical erosion:
- carry heavy loads;
- overheat the lower body.
It is important to know! Sex after cauterization of cervical erosion until the mucous membranes are restored is prohibited.
A follow-up visit to the doctor is required a month after the intervention. Since repeated erosion of the cervix after cauterization is possible, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist 2 times a year for early detection of relapse.
Radiosurgical treatment of erosion
Radiosurgery of cervical erosion - excision of diseased tissue with a radio wave scalpel. This is a safe, painless procedure that does not cause bleeding. The sensations after cauterization of cervical erosion, as with other methods, are not very pleasant, but pass quickly; discomfort is mild.
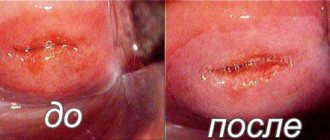
Radiosurgery is one of the best ways to combat ectopia. It is indicated for superficial and deep forms of pathology. Radio wave treatment of cervical erosion does not lead to burns, necrosis, or scar formation. As a result of the manipulations, the lesion disappears, the anatomy and functionality of the organ is restored. It is known what the cervix looks like after cauterization of erosion: the mucous membrane is evenly colored, the tissues are elastic, and the dimensions are normal.
Advantages of radiosurgery:
- efficiency;
- safety;
- applicability before birth;
- bloodlessness;
- painlessness;
- fast recovery;
- no scars.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Contraindications after cauterization of cervical erosion include:
- overheat;
- heavy loads;
- swimming;
- intimate contacts;
- hypothermia.
Radiosurgical treatment of cervical erosion.
Photo: afgsm.ru Surgical treatment methods
You can treat cervical erosion with folk remedies, but conservative and minimally invasive intervention is considered more reliable. Surgery is rarely required. During the event, diseased tissue is radically removed locally. The work is accompanied by injuries and is absolutely not suitable for nulliparous people planning a pregnancy. Surgical treatment is a last resort method.
Treatment of cervical erosion with folk remedies
Treatment of cervical erosion with folk remedies is practiced using:
- mumiyo;
- honey;
- sea buckthorn;
- celandine;
- Luke;
- propolis;
- homeopathic preparations.
Doctors recommend a home remedy for cauterizing cervical erosion from mumiyo. Before the procedure, douche with warm soda water. Soda is diluted at the rate of 1 large spoon per 1 liter. Then a tampon is soaked in the mummy, inserted deep into the vagina, and left for 12 hours. Treatment lasts 2 weeks, then a pause is required (5 days). The course is repeated until complete recovery.
Homemade suppositories for the treatment of cervical erosion are made with honey. 1 large spoon of liquid honey is combined with a glass of warm water. Douche with the solution 2 times a day. In the evening after the procedure, a honey suppository is inserted deep into the vagina. To prepare it take:
- honey (5 large spoons);
- butter (150 g);
- propolis (5 g).
The ingredients are heated in a water bath, mixed, poured into a candle mold, and cooled in the refrigerator. Doctors, explaining how to cure cervical erosion without cauterization (with honey suppositories), recommend using them for 7-10 days in a row.
Sea buckthorn oil is often used to treat cervical erosion. A sterile cotton swab is moistened in it and inserted deep into the vagina, pressing it against the cervix. The preferred time for the procedure is the evening, before going to bed. Treatment of cervical erosion with sea buckthorn suppositories lasts 10 days. A repeat course is carried out after a seven-day pause.
Preparing for a biopsy
Before prescribing the procedure, studies are carried out to determine blood clotting, as well as tests of blood, urine and mucus from the vagina and cervix to detect infections and inflammatory processes. In this case, the following is carried out:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test for sugar, urea, liver enzymes;
- coagulogram (blood test for clotting);
- smear for microscopic examination of the composition of the vaginal microflora;
- blood tests for syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections, as well as for HIV and hepatitis viruses.
If there are no contraindications to the biopsy, a day for the procedure is scheduled. In this case, a week before its implementation, it is necessary to stop taking blood thinning medications (aspirin, warfarin, ibuprofen). The day before the procedure, you must stop using tampons, douching, and the use of vaginal tablets and suppositories for erosion.
Before starting manipulations, a woman must warn the doctor about the presence of any drug or food allergies, hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, or vascular pathologies. You should also report on previous operations to remove the appendix, gallbladder, and, in particular, any complications that have arisen.
In some cases, at the request of the patient or if the area of the cervix is too large, a biopsy is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital. In this case, you must stop taking food, liquids and any medications 12 hours before it starts.
Does it hurt?
Many women believe that after collecting material for analysis, pain occurs. Actually this is not true. There is no prolonged pain after the procedure is completed. The sample is taken under general anesthesia if conization is performed, or with local anesthesia, since pain manifests itself precisely at the moment of capture of part of the epithelial tissue.
The duration of the procedure is no more than 15-20 minutes. After the anesthesia wears off, pain may appear in the lower abdomen. That is why the woman is given pain relief at the end of the procedure and can go home. In this case, sick leave is issued for 2-3 days.
Cervical biopsy
If the results of gynecological studies such as Pap test and colposcopy show the presence of pathology in the patient, the doctor prescribes a tissue analysis of the cervix. This organ is located between the intestines and the bladder. It is important to understand how a biopsy is performed and what it is. Using the procedure, the doctor accurately diagnoses the presence of cancer in a woman and selects effective therapy. A cervical biopsy is the removal of one small or several pieces of tissue for further research.
Indications for biopsy
The procedure is often prescribed for dysplasia, erosion and ectopia. Most clinics use the cauterization method exclusively after collecting biomaterial. If the results of the Pap test and colposcopy cytology are positive, there is no need to take a puncture. An oncology test is done if there is a suspicion of any negative changes in the organ. Indications for a biopsy may include:
- hyperkeratosis;
- condylomas;
- polyps;
- suspicious changes in the organ during colposcopy, for example, iodine-negative zones (areas that did not turn brown after treatment with iodine), acetowhite tissue, atypical vessels, and others;
- negative smear cytology results.
Contraindications
The list of reasons why women may be contraindicated to take the test is limited. Contraindications are due to the presence of pathologies of the reproductive system and the patient’s body. The main prohibition against performing a biopsy is poor blood clotting. Removing tissue from the cervix is a minor surgical procedure, but the procedure can cause severe uterine bleeding. This reaction of the body is due to the presence in the organ of a large number of small vessels, such as the endometrium (uterine lining). A biopsy is not performed:
- in the presence of acute inflammation in a woman’s body;
- patients with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, HPV, others);
- during pregnancy.
Types of biopsy
The best outcome of the procedure is the complete removal of suspicious tissue of the cervix (if the lesion occupies a small area of the organ). In other cases, it is necessary to take punctures from different parts of the organ, which means cutting out 2-3 samples during one procedure. Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the doctor uses one of the existing types of biopsy:
- Sighting (colposcopic). Using a special colposcope instrument, which is a pair of tweezers, a small piece of tissue is taken. The wound heals completely within 4-5 days after the procedure.
- Loopback (radio wave). A painless method of taking an analysis, which is carried out using a special apparatus. The patient does not require further rehabilitation.
- Knife (cononization). The tissue is taken through a hardware wedge-shaped excision of a tissue fragment. The method is used not only for diagnosis, but also for the treatment of pathological areas (their removal).
Biopsy: what is it?
What is a biopsy? This is the collection of part of the biological material for subsequent laboratory study in order to identify cancer cells. It is not indicated for all women, but only in cases of suspected degeneration of the disease into a malignant tumor.
The procedure is carried out using special instruments. The wound that forms after taking the material does not require stitches, and the patient can go home after thirty minutes. Biopsy for erosion is a safe procedure, and complications arise in exceptional cases.
Preparing for the study
A biopsy of the uterine cervix requires a preliminary series of tests (blood for HIV, RV, hepatitis, smears for infections). If there are no contraindications to the procedure, the woman signs consent for the operation. The patient must tell the doctor about her allergic reactions to iodine, medications, latex, if any. In addition, you must notify your doctor about your pregnancy. To reduce the risk of complications after the procedure, you should use the recommendations of gynecologists:
- do not inject any medications into the vagina 2-3 days before surgery;
- abstain from sex a couple of days before the test;
- do not use tampons, avoid douching;
- take a shower the day before the procedure;
- do not eat anything 8-10 hours before the procedure;
- wait until 7-13 days of the menstrual cycle (counting starts from the first day of menstruation) - this is the most favorable time to take a puncture.
Erosion research
The largest number of diseases of the cervix is erosion of this organ. However, the doctor must make sure that the diagnosis is correct, eliminating the possibility of simple focal inflammation, which is often found on the surface of the uterine cervix. Patients must remember two basic rules: examination (primary examination) must be carried out exclusively through a colposcope, and incorrect diagnosis and inappropriate treatment lead to the development of cancer.
Sources:
https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/biopsiya-shejki-matki-pri-erozii.html https://prosto-mariya.ru/kak-provoditsya-biopsiya-shejki-matki-pri-erozii-protivopokazaniya-i -oslozhneniya_1834.html https://sovets.net/4122-biopsiya-sheiki-matki.html