Reasons for missed periods - what are they?
One of the most common causes of delayed menstruation is diseases of the female genital organs. Even a seemingly harmless thrush can cause it. However, you should not self-medicate. A discharge similar to thrush symptoms may mask a more serious condition.
Delayed menstruation can be caused by the onset of menopause. This happens to every woman at different ages. The norm is considered to be the cessation of menstruation between the ages of forty-seven and sixty.
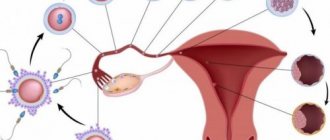
Endometriosis is the growth of uterine tissue - epithelium. There are many reasons for its appearance - from untreated sexually transmitted diseases to hypothermia and hormonal imbalance. Endometriosis can sometimes be very difficult to diagnose. One of its most common symptoms is constant delays in menstruation, as well as its abundance and pain.
A cyst or polyp in the uterus is another reason for missed periods. Often the disease is practically asymptomatic, and apart from constant disruption of the cycle, there are no additional manifestations. But an ultrasound and examination by a gynecologist will definitely reveal it.
Until the menstrual cycle is established, delays can occur constantly. Usually, complete hormonal changes take two to three years from the beginning of the first menstruation. If delays occur after this, you need to consult a doctor.
Stressful situations at work and at home can cause a delay in menstruation. This also happens with a sharp change in climate, with intense physical exercise, and in many cases when the body finds itself in an unfamiliar environment. If this is an isolated case, and then menstruation comes on the right days, there is no reason to worry.
Severe colds, flu, sore throat and other viral diseases often disrupt the menstrual cycle. It may take one to two months to recover. If after time it has not returned to normal, you should consult a doctor. Viruses could travel lower and affect the reproductive organs. Then additional treatment will be required.
Reasons for delayed menstruation with a negative test
A delay in menstruation and pain in the lower abdomen is a fairly serious reason for a woman to start worrying about her health and consult a doctor. Moreover, if this is accompanied by other painful or simply unpleasant sensations, such as headache, nausea, lethargy and depression, then there is no need to even doubt going to the doctor; this must be done without fail.
1 Pregnancy and cycle failure
First of all, this version comes to mind for a woman who is sexually active. And rightly so. You need to take a pregnancy test to be on the safe side. If the test turned out to be negative, reassured or, conversely, upset a woman who wants a child, then this is not yet a reason to deny the version of pregnancy and not consider it anymore at all. A negative test is not the ultimate truth. Of course, modern tests are of very high quality, they are able to determine pregnancy even in the earliest stages, but where is the guarantee that this particular woman did not get a defective test? Therefore, you need to go to a gynecologist and take a special hormone test. Only this test can accurately tell whether there is a pregnancy in the early stages or not. A negative test means practically nothing.
If the delay is more than 6 days, the pregnancy test was negative and the hCG test was positive, then there is a risk that an ectopic pregnancy is developing. Usually, the woman does not feel well. She has a headache, aches and pains in the lower abdomen, there is apathy, dizziness, weakness and bad mood. Usually women simply do not realize the seriousness of the situation and think that this is just a condition before the next menstruation, and wait for it, since the test showed a negative result. Finish
Source
Delay with a polyp in the uterus - Waiting for a stork
- Reasons for delay with a negative test
- Why is there a delay?
- Why is there a month delay in menstruation?
Reasons for missed periods - what are they?
One of the most common causes of delayed menstruation is diseases of the female genital organs.
Even a seemingly harmless thrush can cause it. However, you should not self-medicate. A discharge similar to thrush symptoms may mask a more serious condition. Delayed menstruation can be caused by the onset of menopause. This happens to every woman at different ages. The norm is considered to be the cessation of menstruation between the ages of forty-seven and sixty.
Endometriosis is the growth of uterine tissue - epithelium. There are many reasons for its appearance - from untreated sexually transmitted diseases to hypothermia and hormonal imbalance. Endometriosis can sometimes be very difficult to diagnose. One of its most common symptoms is constant delays in menstruation, as well as its abundance and pain.
A cyst or polyp in the uterus is another reason for missed periods. Often the disease is practically asymptomatic, and apart from constant disruption of the cycle, there are no additional manifestations. But an ultrasound and examination by a gynecologist will definitely reveal it.
Until the menstrual cycle is established, delays can occur constantly. Usually, complete hormonal changes take two to three years from the beginning of the first menstruation. If delays occur after this, you need to consult a doctor.
Stressful situations at work and at home can cause a delay in menstruation. This also happens with a sharp change in climate, with intense physical exercise, and in many cases when the body finds itself in an unfamiliar environment. If this is an isolated case, and then menstruation comes on the right days, there is no reason to worry.
Severe colds, flu, sore throat and other viral diseases often disrupt the menstrual cycle. It may take one to two months to recover. If after time it has not returned to normal, you should consult a doctor. Viruses could travel lower and affect the reproductive organs. Then additional treatment will be required.
Is pregnancy possible with a negative test?
A negative test is not a 100% guarantee of absence of pregnancy. It is possible that fertilization has occurred only a short time ago, and the level of the hCG hormone, which signals the presence of an embryo, is still too low. If there is no reason to fear for your health, but there is a possibility of pregnancy, you need to repeat the test on the eighteenth to twentieth day after the expected conception.
Reasons for delayed menstruation with a negative test
A delay in menstruation and pain in the lower abdomen is a fairly serious reason for a woman to start worrying about her health and consult a doctor. Moreover, if this is accompanied by other painful or simply unpleasant sensations, such as headache, nausea, lethargy and depression, then there is no need to even doubt going to the doctor; this must be done without fail.
1 Pregnancy and cycle failure
First of all, this version comes to mind for a woman who is sexually active. And rightly so. You need to take a pregnancy test to be on the safe side.
If the test turned out to be negative, reassured or, conversely, upset a woman who wants a child, then this is not yet a reason to deny the version of pregnancy and not consider it anymore at all. A negative test is not the ultimate truth.
Of course, modern tests are of very high quality, they are able to determine pregnancy even in the earliest stages, but where is the guarantee that this particular woman did not get a defective test? Therefore, you need to go to a gynecologist and take a special hormone test.
Only this test can accurately tell whether there is a pregnancy in the early stages or not. A negative test means practically nothing.
If the delay is more than 6 days, the pregnancy test was negative and the hCG test was positive, then there is a risk that an ectopic pregnancy is developing. Usually, the woman does not feel well.
She has a headache, aches and pains in the lower abdomen, there is apathy, dizziness, weakness and bad mood.
Usually women simply do not realize the seriousness of the situation and think that this is just a condition before the next menstruation, and wait for it, since the test showed a negative result. Finish
Source
Question: Why can there be a delay in menstruation and pain in the lower abdomen?
Periodically occurring short-term nagging pain in the lower abdomen is also characteristic of a normal pregnancy. The mechanisms of occurrence of this kind of pain syndrome are not fully understood. It is believed that the pain is associated with complex hormonal changes in the body, as well as with an enlargement of the uterus and stretching of its ligamentous apparatus.
We should not forget that the cause of pain in the lower abdomen against the background of delayed menstruation can be pathologies not related to early pregnancy or hormonal imbalance, such as, for example, acute appendicitis, acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, renal or intestinal colic, etc.
Pain in the lower abdomen during termination of an ectopic and normal (uterine) pregnancy
If you experience acute pain in the lower abdomen with delayed menstruation, you should first rule out ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening pathology that is the main cause of internal bleeding in women of reproductive age.
Many authors, both domestic and foreign, note a trend towards an increase in the number of cases of ectopic pregnancy in recent decades. You should be especially careful if there are factors that increase the likelihood of developing this pathology, such as:
An ectopic pregnancy is the abnormal implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity (in the vast majority of cases in the fallopian tube). Of course, such a pregnancy cannot develop normally and is therefore terminated.
Pain when the fallopian tube ruptures occurs acutely, for no apparent reason, is localized to the right or left in the lower abdomen, radiates to the rectum, under the scapula, in the hypochondrium, as well as to the sub- and supraclavicular areas on the corresponding side. Excruciating pain is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, not
Source
Menstruation with polyp 26
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that can appear in different parts of the uterus.
It rarely degenerates, but it can seriously complicate a woman’s life, negatively affecting her well-being and preventing her from getting pregnant. This is one of the main reasons why it is necessary to get rid of the tumor.
It is natural that menstruation after removal of the polyp takes on a different character, which means that many body functions are restored.
Polyps can reach a size of up to 3 cm. Their surface is porous and completely penetrated by blood vessels. The exact reasons for the appearance of tumors in women of different ages and even teenage girls are unknown. Experts assign a significant role to hormones in this.
Polyps in the uterus are located either on its inner surface or on the cervix. Sometimes nothing indicates their presence. But in frequent cases, a woman notices that her menstruation has become different.
Source: https://jduaista.ru/zaderzhka-pri-polipe-v-matke/
Questions
Question: Why can there be a delay in menstruation and pain in the lower abdomen?
Periodically occurring short-term nagging pain in the lower abdomen is also characteristic of a normal pregnancy. The mechanisms of occurrence of this kind of pain syndrome are not fully understood. It is believed that the pain is associated with complex hormonal changes in the body, as well as with an enlargement of the uterus and stretching of its ligamentous apparatus.
We should not forget that the cause of pain in the lower abdomen against the background of delayed menstruation can be pathologies not related to early pregnancy or hormonal imbalance, such as, for example, acute appendicitis, acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, renal or intestinal colic, etc.
Pain in the lower abdomen during termination of an ectopic and normal (uterine) pregnancy
If you experience acute pain in the lower abdomen with delayed menstruation, you should first rule out ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening pathology that is the main cause of internal bleeding in women of reproductive age.
Many authors, both domestic and foreign, note a trend towards an increase in the number of cases of ectopic pregnancy in recent decades. You should be especially careful if there are factors that increase the likelihood of developing this pathology, such as:
An ectopic pregnancy is the abnormal implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity (in the vast majority of cases in the fallopian tube). Of course, such a pregnancy cannot develop normally and is therefore terminated.
Pain when the fallopian tube ruptures occurs acutely, for no apparent reason, is localized to the right or left in the lower abdomen, radiates to the rectum, under the scapula, in the hypochondrium, as well as to the sub- and supraclavicular areas on the corresponding side. Excruciating pain is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, not
Source
Causes of hypomenorrhea
Among the main reasons for scanty periods are changes in the ratio of hormones in the body, which occurs as a consequence of natural processes (the formation and decline of sexual function), gynecological or endocrine pathologies, the use of hormonal drugs for treatment or contraception.
Recommendation: If hypomenorrhea occurs during the use of contraceptives for more than 2 months in a row, then it is necessary to select other means.
In addition, there are other reasons for scanty periods:
- Thyroid diseases. The hormones produced in this gland directly affect the formation of estrogen and the functioning of the reproductive organs. Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland cause the egg to not mature and be unable to leave the follicle (protective capsule). When estrogen levels are low, the uterine lining does not have time to develop. She is too thin for full periods.
- Excessive body weight or excessive thinness. Estrogen production occurs in adipose tissue, just like in the ovaries. In obese women, this accumulation leads to an excess of hormones. The lack of adipose tissue in women who are too thin leads to their lack. In both cases, hormonal disorders appear, which affect the condition of the reproductive organs.
- Scanty periods (up to complete disappearance) occur with anorexia. In addition, the cause of the pathology is sudden weight loss after a special diet or forced fasting.
- Anemia, vitamin deficiency. Without micro- and macroelements, as well as vitamins, the production of hormones in the body and normal metabolism are impossible. Hematopoiesis is disrupted. Exhaustion of the body inevitably affects reproductive abilities, leads to infertility, and the occurrence of cancerous tumors.
- Damage to the genital organs during childbirth, abortion, curettage, leading to changes in tissue structure that interfere with the normal course of the menstrual cycle. If, after cleaning the uterus, your periods become scanty and the discharge has an unpleasant odor, then sometimes you have to do a second curettage, since, most likely, particles of the lining remain in the uterine cavity or an infection has occurred.
- Congenital abnormal development of the genital organs, partial removal of the uterus.
- Physiological processes associated with hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, lactation, menopause).
- Increased physical and neuropsychic stress, working with harmful chemicals, unfavorable environment.
Video: Reasons why scanty brown periods appear
Scanty periods during pregnancy
Pregnancy occurs if, after the egg has matured in the 2nd half of the menstrual cycle, it is fertilized. During the period of maturation, the ovaries produce the maximum amount of female sex hormones, estrogens. They are also responsible for preparing the uterus to receive the fertilized egg, the growth of the mucous membrane where it should take hold and develop.
After fertilization, the level of estrogen decreases, and another hormone, progesterone, begins to be produced, which preserves the structure of the mucous membrane and prevents its rejection. Therefore, menstruation does not normally occur during pregnancy.
In some cases, scanty periods still appear, which misleads the woman: she may not be aware of her pregnancy. There are several explanations for this.
Insufficient production of progesterone due to the physiological characteristics of the body. In this case, the mucous membrane is partially rejected. There is a danger that the fetus will be rejected at the same time, and the pregnancy will be terminated at the very beginning. If a woman has small periods for several months in a row, but pregnancy does not occur, she should consult a doctor and have a progesterone test done. Timely adjustment of its level will help preserve the next pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy. As a result of underdevelopment of the endometrium or pathologies, the implantation of the fetus occurs not in the uterus itself, but in the tubes. In this case, the woman experiences scanty periods due to the rejection of the underdeveloped mucous membrane.
Deviations in the development of the fetus, making its normal attachment impossible, can cause partial rejection of the endometrium along with the fertilized egg, and the appearance of scanty menstruation. If a woman immediately takes a test and consults a doctor, then at this stage it is sometimes possible to maintain the pregnancy.
endometrial polyp delays menstruation
Menstruation with polyp 26
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that can appear in different parts of the uterus. It rarely degenerates, but it can seriously complicate a woman’s life, negatively affecting her well-being and preventing her from getting pregnant. This is one of the main reasons why it is necessary to get rid of the tumor. It is natural that menstruation after removal of the polyp takes on a different character, which means that many body functions are restored.
Polyps can reach a size of up to 3 cm. Their surface is porous and completely penetrated by blood vessels. The exact reasons for the appearance of tumors in women of different ages and even teenage girls are unknown. Experts assign a significant role to hormones in this.
Polyps in the uterus are located either on its inner surface or on the cervix. Sometimes nothing indicates their presence. But in frequent cases, a woman notices that her menstruation has become different.
How and when is endometrial polyp removed?
Removal of the endometrial polyp is indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective. A benign neoplasm is usually called a polyp. His rebirth is possible, but this happens extremely rarely. More often, the presence of a polyp entails certain consequences for the female body in terms of poor health and the inability to become pregnant. Infertility is considered the main reason for which the uterine growth should be removed. It is significant that menstruation after removal of the endometrial polyp takes a different course, indicating that the reproductive function in the female body returns to normal.
The effect of polyps on the female body
The size of the polyp can be about 3 cm. Its surface is porous and dotted with blood vessels. The nature of the appearance of such growths in the uterus in women of different age groups and teenage girls is not completely clear. However, doctors are unanimous in the opinion that the leading role in this issue belongs to hormones.
The location of polyps on the uterus can be external or internal (in the cervix). Sometimes nothing reveals the presence of a polyp. Usually the signal is the fact that menstrual flow becomes somewhat different.
Having discovered changes in your monthly cycle and its nature, you should consider the relationship of such disorders with the presence of polyps in the uterus.
Important! With some formations, one observation and treatment of the main problem that caused their appearance is sufficient. And only the rapid growth of tumors can serve as a reason for radical treatment.
Endometrial polyps and menstruation
The ovaries, which produce hormones, sometimes do not function as they should. When the production of the hormone estrogen prevails, excessive growth of the endometrium is stimulated. Its parts did not come out
Source
Polyp coming out during menstruation: myth or truth
Among gynecological diseases, a common pathology of the genital organs in women is the proliferation of polyps. The neoplasm is classified as a benign tumor. The peculiarity of the disease is the high probability of transition to a malignant form.
The pathology is treated primarily surgically; according to experts, other methods are ineffective. However, women often have a question about whether a polyp can come out with menstruation.
To understand whether such a phenomenon is possible, you should understand in more detail the characteristics of the disease and methods of its treatment.
A polyp in the uterus can appear in any woman
How polyps affect the cycle
The formation of growths can greatly affect the functionality of the reproductive organ system. Depending on the location of the formation, a woman sometimes has no symptoms of pathology, or, on the contrary, signs of the disease begin to appear.
Most often, when a polyp forms and increases in size, deviations in the menstrual cycle are observed. Menstruation, as a rule, becomes irregular, accompanied by severe pain and varies in consistency and volume of discharge.
Note! The cause of the disorders is changes in hormone levels under the influence of pathological processes.
If a growth forms in the cervix or tube, it begins to interfere with the natural flow of menstrual flow. During menstruation, not the entire layer of rejected endometrium may be released, so after menstruation or before it begins, a woman periodically experiences scanty discharge with a strong unpleasant odor.
A polyp can affect the intensity of discharge
In cases where the neoplasm is located on the outer wall of the uterus, menstruation is more abundant due to damage to the affected tissues, which begin to become inflamed as a result of sexual intercourse.
Experts do not identify clear characteristic changes in the menstrual cycle with polyps. The main symptom is considered to be a delay in menstruation and the presence of discharge in its absence.
What are the causes of a polyp?
A polyp cannot appear in the genitals without a reason. The main provoking factor is hormonal imbalance, the consequence of which is the inflammatory process of endometrial tissue.
Possible reasons:
- ovarian dysfunction;
- hyperestrogenism;
- excess weight or, conversely, anorexia;
- chronic sexual infections;
- injury to the uterus;
- surgical abortion;
- endometriosis curettage;
- long-term use of intrauterine devices;
Malfunction of the ovaries leads to the formation of polyps
- thyroid disease;
- severe stress;
- diabetes;
- age-related changes after 45 years;
- weakened immunity.
Medicine has not established the exact causes of the disease. As a rule, pathological neoplasms appear when several provoking factors are combined.
Can a polyp come out with menstruation?
There are many myths that a growth can resolve on its own, or that a polyp will come out during menstruation.
Important! The neoplasm attaches to the tissues of the organ and, under the influence of drug therapy, rejection occurs in exceptional cases.
Spontaneous release of a small tumor is allowed if there has been trauma to the tissue at the site of its attachment. However, there is a high probability of tumor detachment without attachment. In this case, after some time, a relapse occurs in the form of multiple growths.
This pathology requires examination and treatment.
According to doctors, polyps do not resolve on their own and do not leave the body either under the influence of drug therapy or under the influence of folk remedies.
What is the conservative treatment for polyps?
Beginning treatment for polyps involves conservative therapy. Taking medications is also required after the operation.
In case of painful sensations, a woman is prescribed medications that have an analgesic effect:
- Paracitamol;
- Ibuprofen;
- Diclofenac;
- Analgin.
To prevent the development of a bacterial infection, douching with drugs is prescribed:
- Potassium permanganate;
- Septadine;
- Collargol.
Additionally, hormonal medications can be prescribed, but only on an individual basis, taking into account the level of estrogen in the body.
What other treatment options are there?
It is impossible to limit yourself to drug therapy alone for polyps. Depending on the characteristics of the tumor, the method of surgical intervention is selected. The operation makes it possible to prevent relapses and eliminate the likelihood of developing cancer.
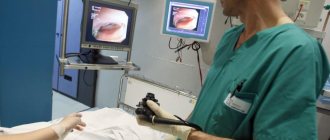
Hysteroscopy is performed to remove the polyp.
The operation can be performed using three methods:
- curettage - cleansing endometrial tissue manually (a painful method, often leading to relapse);
- hysteroscopy is a diagnostic procedure during which growths are removed using ultrasound;
- laser removal is a non-traumatic and effective method of removing polyps using laser beams.
The choice of treatment method depends on the capabilities of the clinic and the patient herself, as well as the presence of possible contraindications. Most doctors no longer perform curettage, but use more modern methods.
Is it possible to remove polyps during menstruation?
Surgery for polyps can be carried out both during menstruation and at another period. However, some experts recommend performing the procedure during menstruation. This is due to the fact that removal of a polyp during menstruation reduces the risks of complications arising from trauma to the endometrium of the uterus.
While menstruation is ongoing, it is not recommended to remove polyps
There are natural difficulties that make it difficult to remove a polyp during menstruation - discharge containing endometrial particles and mucus can impair the patency of the hardware tube, the frequency of access to the lesion site and visibility. These disadvantages often lead to the reappearance of growths.
Note! If the polyp is located in the cervix, or the woman has bleeding (during menstruation), then the operation is performed during menstruation.
If the tumors are removed as planned, the procedure is scheduled for 2 or 3 days after the end of menstruation. The endometrial layer, which has not yet grown, allows for good visualization while maintaining free access
When will your period start after surgery?
The menstrual cycle changes after treatment. The reason for this is trauma to the uterine endometrial layer, taking medications and restoring hormonal balance after tumor removal.
Menstruation after removal of a polyp with normal rehabilitation begins on average 40 days later. If after removal of the polyp there are no periods for more than two months, you should consult a gynecologist. Complications may develop, or during the operation, not only the upper layer of the uterus was damaged.
After watching this video, you will learn about the treatment of polyps:
Menstruation after polypectomy is often heavy, but its duration should be limited to 7–10 days. Longer periods may indicate insufficient cleaning of the uterus.
Polyps are a dangerous disease, regardless of their location. The growths can migrate, grow and develop into a malignant tumor. You should not try to treat the disease with traditional methods or refuse surgery. Incorrect treatment can have life-threatening consequences.
Source: https://mesyachnie.com/informacija/polip.html
All about menstruation after polyp removal
A woman's menstrual cycle is the main indicator of health. In diseases and pathologies, it tends to go astray. For example, when diagnosed with an endometrial polyp, menstruation acquires the following properties:
Because of these symptoms, the woman undergoes surgery to remove polyps. However, menstruation after polyp removal also has its own characteristics. Which ones? Read what the article says and get your answer.
How does the menstrual cycle go after removal?
After the woman has decided to remove the tumor, doctors plan the day of the operation. This usually happens 2-3 days after the next period ends. The operation is carried out in several ways:
After surgery, the patient goes through a postoperative period, which includes taking antibiotics, painkillers and vitamins.
But when will your next period start? It depends on which part of the organ the polyp was in. If the removal took place in the cervical canal, then menstruation will begin quickly. This will happen due to the fact that the body has received less stress. Discharge from the blood usually begins immediately after removal of the polyp from the cervical canal and can last up to 10 days. After healing, menstruation will come, which may be quite scanty. But it normal. After a full recovery everything will be fine.
If a polyp was found in the uterine cavity itself, then the operation was most likely performed using the curettage method. This is a lot of stress for the body. In this case, your period will come 30-40 days after the intervention. The delay directly depends on the latitude of curettage. The more affected endometrium is removed, the longer the period will be delayed. Delays are also caused by antibiotics, which are prescribed without fail after removal of a polyp in the uterus. Immediately after the operation it will be necessary
Source
Tribestan is an over-the-counter drug and is freely available without a prescription. Information for doctors and patients.
How to get rid of a polyp
Even if the neoplasm is small, it can cause significant health problems: from cycle irregularity to persistent infertility. Treatment of polyps and menstruation normalizes and stops uterine bleeding between them. And most importantly, it helps restore fertility. If a polyp is detected at an early stage, they try to eliminate it with hormones:
- Oral contraceptives, if its value is less than 10 mm, the patient is under 35 years old, bleeding and cycle failure are observed. These drugs are prescribed for 2-3 weeks;
- Antibiotics if the cause of polyp growth is determined to be a chronic infection. Before the appointment, it is necessary to do a flora analysis;
- Preparations containing progesterone (Duphaston, Utrozhestan), if endocrine disorders are detected;
- Iron supplements, vitamins for frequent bleeding;
- Diferelin, if the woman is over 35 years old.
Gestagens and gonadotropins are taken for up to six months. After this time, it becomes clear whether the therapy helped or whether other methods will have to be used.
Those taking drug treatment are interested in whether a polyp can come out with menstruation. This happens with small tumors. A woman can also mistake pieces of endometrial tissue found in menstrual fluid for a polyp. You should not stop therapy on your own. If it seems that the polyp came out with menstruation, it is necessary to be examined after this and, if possible, provide the material to the gynecologist, preserving it in saline solution.
Surgery
If drug treatment fails, surgical removal of the polyp will be required. It is done using a hysteroscope, simple curettage or laser. There are different opinions about whether it is possible to remove a polyp during menstruation. On the one hand, at this stage the endometrium is already being renewed, so the manipulation will take place with the least consequences for the woman. Such an intervention is more physiological, since it does not violate the time frame and stages of the cycle. On the other hand, menstrual flow and the thickness of the endometrium can prevent the equipment and the doctor from seeing the tumor and efficiently removing it. And in this case, it is possible that it will grow again in the same place. The material that specialists receive during such an operation is not informative enough, since the cells of the upper layer of the endometrium are already dying. That is, it will not give an idea of whether any of them are malignant. The polyp is removed during menstruation if curettage is necessary to stop bleeding. If it is located on the cervix, this option is also possible. The cervical canal at this stage is so open that the neoplasm on the pedicle is clearly visible and can be easily grasped with an instrument.
When, after menstruation, is it advisable and most often performed to remove a polyp in the uterus? If we are talking about a planned operation, they prefer to do it 2-3 days after the end of menstruation.
The functional layer of the uterus is at its thinnest at this time, so the neoplasm is clearly visible with the help of a hysteroscope.
What happens to the cycle after treatment
The first thing that concerns a woman who has undergone surgery is when her period begins after the removal of a polyp. Without complications and with normal recovery, this occurs in a month or a little more. But here the individual characteristics of the body are important, which can increase this period.
Menstruation after cervical polyp
Menstruation after removal of a polyp of the cervical canal normalizes faster, since the organ experiences less stress. Usually the first menstruation is scanty. This is the effect of antibiotics, which are prescribed to avoid postoperative inflammation. Bleeding between periods stops, but slight discharge is observed immediately after removal of the polyp, which lasts quite a long time, up to 10 days. Their early completion occurs due to spasm of the cervical canal, which is treated by no-shpa. This cannot be tolerated, since fluid that does not come out in time can become a source of inflammation.
Delay of menstruation. Reasons for delayed menstruation.
The reason for a delay in menstruation (for a period of 5 or more days) can be not only pregnancy. Stressful situations, sudden fluctuations in weight - weight loss or, conversely, obesity, can cause a delay in menstruation or even absence of menstruation, amenorrhea.
Often, a delay in menstruation occurs in female athletes - due to high physical activity, as well as a low content of adipose tissue, various endocrine disorders can occur in the body.
Women! The normal content of adipose tissue in the body is 18-25 percent. Fat is part of a complex chain of hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle. Reduced fat content - less than 15 percent - leads to suppression of menstrual function and the first is a delay in menstruation. This is a good warning to those who want to achieve model size at any cost.
Delay of menstruation. Rule one.
You should not consider as the norm (provided that you do not know what is the norm for everyone in this case) the cycle to which you are already accustomed, even if it has been characteristic of you from the very beginning of your menstruation, and even if you, despite due to its peculiarity or irregularity, you manage to get pregnant and give birth.
The beginning of the cycle should be counted from the first day of (for example, these) menstruation to the first day of the next menstruation, and not from the last to the first.
Normally, the cycle should be equal to the full cycle of the moon - 28 days (this has been considered the norm from time immemorial, for all women on earth), plus or minus 3-5 days. And if you have it, for the most part, more or less (I’m not talking about irregularity in general), then this is a reason to consult a doctor.
1. moderate (if you are “filled up”, and then in
Source
What is hypomenorrhea
The volume of blood that is released during the entire period of menstruation is normally 50-150 ml. Menstruation is considered scanty when less than 50 ml is released. This condition is called hypomenorrhea. It is usually accompanied by oligomenorrhea (decreased duration of menstruation). If menstruation normally lasts 3-7 days, then with oligomenorrhea this period is reduced to 2 days, sometimes less.
Hypomenorrhea in some cases (for example, during menopause) may precede the complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea). Scanty periods are considered a natural physiological state in girls during puberty, when the cycle has not yet established (in the first 2 years after appearance), as well as in women during premenopause, when the functioning of the ovaries is impaired due to aging. A decrease in estrogen levels leads to the fact that the uterine mucosa does not have time to develop sufficiently, so the volume of menstruation decreases.
In women of childbearing age, such periods most often indicate diseases of the genital organs. An examination is necessary to determine the cause.
Menstruation with polyp 28
A polyp is a benign neoplasm that can appear in different parts of the uterus. It rarely degenerates, but it can seriously complicate a woman’s life, negatively affecting her well-being and preventing her from getting pregnant. This is one of the main reasons why it is necessary to get rid of the tumor. It is natural that menstruation after removal of the polyp takes on a different character, which means that many body functions are restored.
Why does a polyp interfere?
Polyps can reach a size of up to 3 cm. Their surface is porous and completely penetrated by blood vessels. The exact reasons for the appearance of tumors in women of different ages and even teenage girls are unknown. Experts assign a significant role to hormones in this.
Polyps in the uterus are located either on its inner surface or on the cervix. Sometimes nothing indicates their presence. But in frequent cases, a woman notices that her menstruation has become different.
The neoplasm often provokes the development of anemia and infertility. Therefore, it is important for women of any age to know what polyps are, symptoms and treatment. With menstruation with changed characteristics, there is reason to look for the cause of the ailments in this.
Some tumors only require observation. And only with their growth may the need for radical measures arise.
The hormone-producing ovaries do not always function correctly. If estrogen predominates in the total amount of hormones they produce, this provokes excessive growth of the endometrium. Some of its cells, instead of being released with discharge during menstruation, remain inside the uterus. If this happens over several months, growths form at the points where the endometrium accumulates. Gradually they fill with blood vessels and connective tissue. This is a finished polyp. See it if it is localized inside an organ
Polyp is a growth of tissue over the mucous membrane of an organ. They can form anywhere - in the stomach, intestines, as well as in the uterine cavity and cervical canal. Their danger lies in the fact that only after their removal and histological examination can the possibility of its malignant degeneration be excluded.
The effect of a polyp on menstruation
When endometrial particles accumulate in one place, a growth is formed. Due to a significant increase in the tumor, various symptoms and pathological transformations may be observed. Since the appearance of a growth is affected by progesterone deficiency, hormonal imbalance is reflected in the menstrual cycle.
The neoplasm prevents the release of the endometrium from the uterine cavity, which entails the development of inflammation and pathological conditions. Therefore, a woman can observe bleeding outside her period, because the exfoliated endometrium could not completely leave the uterus. It is also possible to experience brown discharge with an unpleasant odor before menstruation.
When a neoplasm appears on the outside of the uterus, the girl is faced with an increase in the intensity of her periods, since there is regular injury and irritation of pathological tissues. Such conditions manifest themselves during sexual intercourse and the use of intrauterine contraceptives. If damaged, the growth becomes inflamed, a purulent infection develops, and a viscous dark brown vaginal discharge appears.
Menstruation with a polyp
If a woman has a polypous neoplasm, she may observe the following changes:
- heavy periods, which mainly consist of blood, which provokes the development of anemia;
- inconsistency of menstruation, which provokes the appearance of spotting between regular periods. This is a clear sign of the presence of a neoplasm in the uterine cavity;
- due to the proliferation of endometrial tissue, the duration of menstruation also increases;
- severe pain appears due to increased contractions of the uterus.
In most cases, due to the neoplasm, there may be delays in critical days. They are caused by hormonal changes, and regular bleeding makes it difficult to track the dynamics of the menstrual cycle.
What is a polyp
It is the growth of tissue over the mucous membrane of an organ. Polyps can form anywhere - in the stomach, intestines, as well as in the uterine cavity and cervical canal. Their danger lies in the fact that only after their removal and histological examination can the possibility of its malignant degeneration be excluded. Polyps in the uterine cavity and cervix are the causes of cycle disorders, heavy and clotted periods.
The following types of polyps in the cervix and cervical canal are distinguished:
- glandular - grow from glands and produce mucus;
- epidermalized - more dense in structure;
- decidual - occur against the background of hormonal changes during pregnancy.
In the uterine cavity, uterine polyps can be of the following nature:
- glandular - formed from cells that produce glandular secretions, more often than others prone to malignant degeneration;
- fibrous - are dense growths, in most cases they occur in menopausal women, are not prone to malignant growth and are less likely to recur after removal;
- glandular-fibrous - combines the characteristics of the previous two;
- adenomatous - occupy a middle position between glandular polyps and adenocarcinoma of the uterine cavity, therefore their detection is an indication for surgical removal;
- placental - occur after pregnancy and childbirth, abortion, miscarriage, if the remnants of placental tissue (chorion) were not completely removed.
The appearance of polyps is associated with various problems. First of all, hormonal imbalance plays a role - an excess of estrogens against the background of an absolute or relative deficiency of gestagens leads to uncontrolled growth of the inner lining of the uterus and the formation of similar growths.
It is believed that polyps often form against the background of chronic endometritis and cervicitis. This fact proves that such growths on the cervix more often occur in the presence of erosion and ectopia.
Polyps of the cavity and cervix are more often formed in women with various endocrine disorders - problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, as well as cardiovascular diseases.
And here is more information about why spotting appeared after an examination by a gynecologist.
Polyps in the uterus can cause cancer and bleeding | University Clinic
Polyps and tissue hypertrophy (proliferation) belong to the group of hyperplastic processes, since they have common causes and treatment methods.
Endometrial polyp
A polyp is a benign neoplasm in the form of a growth on a “pedicle”. The presence of numerous polyps is called polyposis.
These formations are divided into several types:
- fibrous - dense, round in shape. They have a thin “leg” through which feeding vessels pass.
- glandular - spongy, soft, often multiple.
- glandular-fibrous - the growth contains connective and glandular tissue.
- adenomatous - the structure of the formation contains altered glands.
All types of polyps are benign in nature. However, any growth should be examined in a laboratory to rule out the presence of cancer cells. The size of polyps varies from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. Large lesions can block the cervical canal connecting the uterus and vagina, preventing the flow of menstrual blood and fertilization.
Causes of polyps
Hormonal theory - the growth and rejection of the endometrium is regulated by female sex hormones: estrogens and progesterone. Excessive amounts of estrogen lead to the appearance of glandular polyps.
Infection - polyps are formed as a result of penetration into tissue and active reproduction of the genital herpes virus or human papillomavirus. A number of researchers believe that the growth of polyps can be triggered by any infection, and the longer the chronic inflammatory process, the higher the likelihood of polyp formation.
Injuries to the inner surface of the uterus. Excessive growth of the endometrium can occur as a result of damage to the walls of the uterine cavity during abortion, curettage and other interventions.
The development of polyps is also promoted by:
- obesity;
- carrying out hormone replacement therapy;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- age-related changes.
Symptoms of endometrial polyps
These formations appear at any age, but more often it occurs at 40-50 years of age. Small polyps do not manifest themselves for a long time, becoming an accidental finding on ultrasound.
When pathology occurs, the following are observed:
- spotting in the middle of the cycle, before or after menstruation;
- excessively heavy periods;
- the appearance of spotting several years after menopause;
- infertility;
- frequent spontaneous miscarriages;
- unsuccessful IVF attempts, when the transplanted embryos cannot be implanted into the uterine lining;
- contact bleeding, in which spotting appears after sexual intercourse.
However, such symptoms occur with various gynecological and endocrine diseases, so when they appear, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Why are polyps dangerous?
Risk of developing a malignant tumor
. For the most part, polyps are benign neoplasms and only in 0.5% of cases contain altered or cancerous cells.
To eliminate the risk of developing cancer, all polyps are necessarily sent for histological examination.
Such a study does not take much time, is inexpensive, but at the same time allows you to determine the nature of the tumor with 100% accuracy.
Infertility
– polyps located in the area of the corners of the uterus can block the entrances to the fallopian tubes and interfere with the process of conception. Formations often lead to implantation failure and spontaneous miscarriages.
Pain and bleeding
– large polyps often provoke the appearance of uterine bleeding of varying degrees of intensity.
Diagnosis of polyps
- Ultrasound -
during a transvaginal ultrasound performed through the genital tract, one can only suspect the presence of a formation. Its type can be definitively determined only after removal. - Ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy (USGSS) –
use of a contrast solution to visualize tumors in the uterine cavity.The picture obtained with ultrasound examination is clearer, which allows one to suspect the presence of large neoplasms with a greater degree of certainty than with ultrasound.
- Hysteroscopy -
during this procedure, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity, allowing you to examine its inner surface and remove the polyp. - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
is recognized as a fairly accurate method. Its average sensitivity was 79% and specificity was 86%.
Treatment of endometrial polyps
Hormone therapy –
in young patients, polyps may disappear when adequate hormonal therapy is prescribed.
If there is no effect, hysteroscopy with possible simultaneous removal of the tumor is indicated. In all other cases, there is no need to postpone the operation.
This is especially true for patients 40 years of age and older, who have an increased risk of developing cancer.
Surgical method of treatment.
The most effective method for removing polyps is hysteroresectoscopy - removal of growths through the dilated canal of the cervix. The risk of complications is minimal, since the doctor monitors the performance of all manipulations using the camera of the optical system of the hysteroresectoscope.
Removing a polyp surgically is not enough. For complete cure, maintenance hormonal therapy is required.
Cost of minor operations by a gynecological surgeon at the University Clinic
| Price | price, rub. |
| Diagnostic hysteroscopy with anesthesia, biopsy of the endocervix and endometrium and histological examination | 18200 |
| Therapeutic hysteroscopy with anesthesia (hysteroresectoscopy, polypectomy, histological examination of the endocervix and endometrium) | 18200 |
| Removal of the intrauterine device under anesthesia in the absence of wire threads under hysteroscopy control | 12000 |
| Removal of vaginal cysts, including anesthesia or general anesthesia | 18500 |
| Vacuum for frozen pregnancy (up to 12 weeks) with anesthesia and histological examination | 12000 |
| Separate diagnostic curettage with anesthesia and histological examination under hysteroscope control | 12000 |
The endometrium is the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, sensitive to the action of hormones. Its functional layer comes out during menstruation with menstrual blood and grows again every month.
Normally, in menstruating women in the middle of the cycle, the height of the mucous layer is 10 mm, before menstruation - 12 mm. During menopause, the normal endometrial thickness is 4 mm. Exceeding these indicators is called hyperplasia.
Reasons for the development of hyperplasia
The pathology occurs in women of all ages - from adolescence to menopause.
Promote the development of endometrial hyperplasia:
- hereditary predisposition;
- polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS);
- injuries to the genital organs during diagnostic curettages and abortions;
- hormonal disorders - excess estrogen and lack of progesterone;
- the presence of concomitant diseases such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the ovaries, thyroid gland, parathyroid, mammary glands, adrenal glands.
Normally, estrogens cause endometrial growth, and progesterone provokes its rejection during menstruation. Excess estrogen and lack of progesterone lead to the fact that the uterine mucosa is not rejected and continues to grow indefinitely, leading to a delay in menstruation. Subsequently, when the hyperplastic layer is rejected, profuse and prolonged bleeding occurs.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation.
- The appearance of bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
- Menstrual dysfunction - delays, prolonged amenorrhea, subsequently accompanied by heavy bleeding with large blood loss.
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back
Without treatment, these symptoms lead to significant blood loss and anemia (anemia). In addition, in the overgrown uterine layer, the appearance of cancer cells and the occurrence of uterine cancer is possible.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be made using ultrasound. The screen shows a thickened endometrium, sometimes containing dense and loose inclusions.
A diagnostic and at the same time therapeutic procedure is separate diagnostic curettage. The method allows you to remove the layer of hyperplastic epithelium and free the uterine cavity from the contents, which leads to a quick stop of bleeding.
In very young patients, instead of diagnostic curettage, an aspiration biopsy using a Pipel probe may be performed. This method makes it possible to obtain tissue samples for histological examination with the least damage.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Removal of the overgrown endometrium is performed surgically in a hospital or specialized medical center. In case of massive bleeding, surgery is performed according to emergency indications.
After removal of the hyperplastic mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, the material is sent for histological examination. Based on the results of the cellular analysis, drugs are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels and prevent relapse.
Oral contraceptives and other hormonal agents are prescribed as anti-relapse therapy. Treatment is selected taking into account the patient’s age, her state of health, the initial level of hormones in the blood and a number of other factors.
Read articles on the same topic
Source: https://unclinic.ru/polipy-v-matke-mogut-vyzyvat-rak-i-krovotechenija/
How do menstruation change with a polyp?
The nature of menstruation and possible cycle disruptions depend on the location of the growths and their size.
If it's in the cavity
Polyps in the uterine cavity interfere with the normal contraction of the myometrium during menstruation, thereby causing heavy discharge. In addition, they may cause the following:
- spotting outside of menstrual days;
- spotting before and after menstruation, as well as after sexual intercourse;
- heavy menstruation and the appearance of clots;
- cycle disruptions - a woman is already lost in where her menstruation begins and where it ends;
- cause pain in the lower abdomen, more often during menstruation, but they may also appear on other days of the cycle.
Polyps of the uterine cavity are often combined with endometrial hyperplasia; the clinical picture of these two pathologies is similar; diagnosis can only be made after curettage of the uterine cavity or hysteroscopy and subsequent histological examination of the obtained material.
Symptoms that accompany scanty periods
With a decrease in the volume of menstruation and its short duration, the discharge may be lighter than usual or have a brown tint, resembling only traces of blood. Moreover, they occur on time or with a delay, and the duration ranges from several hours to several days.
If a woman has not previously had pain and other unpleasant symptoms during menstruation, then when their volume decreases, headaches, nausea, aching pain in the lower back, chest, and indigestion appear.
Scanty dark discharge from infectious or inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs has an unpleasant odor. There is nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Every time you have your period, you may experience nosebleeds.
Video: In what cases do scanty periods require attention?
https://youtu.be/sFyRtTBRalQ
Drug treatment
Polypoid growths of the cervix and cervical canal should always be removed. Further treatment depends on the background: if there is erosion - cauterize it, cervicitis - anti-inflammatory treatment, etc.
For endometrial polyps, there are two possible options for starting drug therapy:
- after examination, but without curettage of the uterine cavity;
- after diagnostic curettage and the results of histological examination of the obtained material.
Diagnostic curettage
The second option is preferable, since under the mask of an ordinary polyp, atypical formations with a high risk of malignant degeneration may be hidden in the cavity. Treatment with drugs in this case will only contribute to the development of the disease.
Close attention and appropriate therapy are necessary in the following cases:
- with recurrent polypous growths of the endometrium;
- for glandular, glandular-fibrous, adenomatous.
The list of medications used for treatment in both cases is the same. The essence of therapy is to suppress excess growth of endometrial tissue, establish hormonal balance, and eliminate provoking factors, most often inflammation.
Among hormonal drugs, gestagen analogues are prescribed. Schemes can be different - in women under 35-40 years of age, doses are most often prescribed from 10 to 25 or from 15 to 25 days of the cycle, at a later age - continuously throughout the entire cycle.
The following medications are used:
The course of treatment lasts on average about three months, after which ultrasound monitoring or diagnostic curettage is carried out.
For young girls, oral contraceptives can be prescribed according to a standard regimen for a course of 3-5 months with subsequent monitoring.
If polypous growths continue to form, more serious and expensive drugs may be prescribed, for example, Buserelin, Zoladex and others. They act at the level of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus of the brain, suppressing the secretion of sex hormones and bringing the body into a temporary state of artificial menopause.
If a woman is about 50-55 years old, she may be offered the option of medicinal menopause - suppression of ovarian function through the sequential administration of androgens and then gestagens.
Anti-inflammatory therapy may also be included in the regimen, since it is believed that polyps form against the background of chronic endometritis. In addition to this - vitamin therapy, enzyme therapy, physiotherapy.
Surgical removal of polyps
Can be done in several ways:
- Diagnostic curettage . This is the familiar “cleaning”, which is carried out under anesthesia. In this case, the doctor, using special curettes and dilators, inserts instruments into the uterine cavity and carefully scrapes out all the walls one by one. The entire procedure is carried out blindly - only under the control of the doctor’s sensations. So it’s easy to skip the polyp, leaving its stalk or part of the endometrium.
The material is sent for histological examination, and after receiving the result, a plan for further treatment is drawn up.
- Outpatient removal of polypous growths . Possible only for those located on the cervix. The polyp is removed with a regular clamp without anesthesia, and the place where it begins to grow is cauterized with an iodine solution. The procedure is quick and not painful, however, due to the fact that the “polyp leg” may still lie deeper in the cervical canal, there is a possibility of regrowth.
The “golden” standard for removing polypous growths in the uterine cavity and cervical canal is hysteroscopy. This is a technically simple operation that requires intravenous anesthesia - the woman falls into deep sleep and does not feel pain.
The doctor places a special instrument - a hysteroscope - into the cervical canal and then into the uterine cavity. Inside it there is a camera that displays the entire image on the monitor screen, as well as manipulators for removing polyps and cauterizing areas. Using a hysteroscope, the doctor clearly determines the location of polyps, their number, and removes them in a targeted manner.
If necessary, complete or partial ablation (cauterization) of the endometrium can be performed, after which the functional layer stops growing altogether.
In some cases, polyps of the uterine cavity are an indication for removal of the uterus. For example, in such situations:
- multiple recurrent polyps;
- lack of effect from conservative treatment;
- adenomatous polyps;
- a combination of polyps and symptomatic uterine fibroids (with frequent anemic bleeding, pain).
Menstruation after polyp removal
After removing polyps on the cervix and eliminating the problem that led to its formation, spotting and other similar troubles disappear. Resumption of symptoms is an indicator of relapse of the pathology. Moreover, polyps on the cervix can reappear after 6-12 months and even after several years.
Removal of polyps in the uterine cavity has a more obvious result - women stop bleeding constantly, periods become average, pain and discomfort disappear, and the menstrual cycle normalizes. If treatment is not suitable or polyps form again, the symptoms remain.
And here is more information about intermittent periods.
Polyps of the uterine cavity and cervix are a consequence of serious disorders in the body. All such formations are subject to careful observation or removal (depending on the clinical situation). Under the mask of an ordinary polyp, a malignant tumor or a high risk of its formation may be hidden.
Useful video
Watch this video about how to treat polyps in the uterine cavity:
Ideally, your period should begin within 1-3 days after Utrozhestan. Deviation per week is allowed. However, for longer delays, it is advisable to see a doctor.
Under a number of certain diseases, as well as during pregnancy, adolescence and before menopause, intermittent periods may occur. It is important to diagnose the condition promptly and begin treatment if necessary.
It happens that after an examination by a gynecologist, a woman discovers bloody discharge in her underwear. The reasons for their appearance can be either completely harmless (for example, when taking a smear from the cervix, pregnancy), or indicate a disease.
Often, periods with the IUD are the same as without it. However, sometimes an individual reaction may be the opposite - bleeding will begin. When is the best time to remove the coil? What are the normal periods?