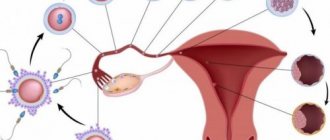
Uterine bleeding is any discharge of blood from the uterus that is not associated with the menstrual cycle. They can be of different frequency and intensity. Any bleeding, even minor, is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. The etiology of this pathology may be different, but in any case it is a sign of a gynecological problem.
What kind of blood discharge is normal?
Uterine bleeding is divided into functional (normal) and pathological. Normal physiological blood secretions in women include:
- Period. Their duration is 3-5 days, volume 50-80 ml. They occur regularly with a deviation of 2-3 days. The interval between them is 21-35 days. The color of the discharge ranges from red (at the beginning) to burgundy or dark brown (on the last day), the consistency is mucous with clots of coagulated blood.
- Minor spotting in the middle of the cycle. They occur when the follicle ruptures.
- Implantation bleeding. Appear if conception occurs. They are caused by slight damage to the endometrium at the time the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus. Scanty discharge of this kind appears on the 7th day after fertilization. If they intensify, this indicates detachment of the fertilized egg and the threat of miscarriage. If a woman is looking forward to pregnancy, then such discharge should alert her and force her to urgently go to the doctor.
- Obstetric – bleeding during childbirth.
It is important to know how to distinguish menstruation from pathological bleeding in order to take timely measures and begin treatment.
Addition: Any deviations from the norm, as well as increased pain in menstruation, are a pathology. In rare cases, deviations are due to the characteristics of the body and heredity. Most often the cause is serious illness.
More details about the types of bleeding
Dysfunctional
The main signs of this type of bleeding are heavy blood loss or prolonged bleeding. Adolescent girls and menopausal women are at risk. The provoking factor of the pathology is an excessive amount of estrogen or progesterone. To eliminate this pathology, hormonal therapy is used.
There are two types of dysfunctional blood loss:
- ovulatory. They are characterized by manifestations of an abnormal cycle, that is, over the course of a month, a woman experiences slight discharge of a scanty nature or, conversely, short menstruation that have an interval of more than one month;
- anovulatory. They are characterized by significant blood loss, cycle disruption, poor health, loss of appetite and a constant desire to sleep.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
It is important! Primary pathology can be determined using a gynecological examination, supplemented by ultrasound.
Video: Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Juvenile
May appear seasonally. This is explained by the fact that the corpus luteum does not form due to hormonal imbalance. If a teenage girl is diagnosed with neoplasms in the reproductive system, then juvenile bleeding cannot be ruled out.
Juvenile uterine bleeding
Breakthrough
A third of cases of breakthrough bleeding occur due to problems with the uterus, which are provoked by the intrauterine device. Bleeding can also be caused by the consequences of taking hormonal contraception. To prevent subsequent bleeding, it is recommended to remove the IUD and select the correct dosage of contraceptives.
Profuse
Profuse blood loss is difficult to distinguish from menstrual discharge, since it is also characterized by menstrual pain. The only symptom is increased blood loss, which is characterized by scarlet discharge. The exact period of occurrence is difficult to determine because it varies.
Is it dangerous! Profuse bleeding is difficult to diagnose and requires urgent hospitalization of the woman. In this case, surgical treatment in the form of uterine curettage is mandatory.
Video - How to distinguish menstruation from bleeding?
Bleeding and menopause
During menopause, a woman cannot exclude the risk of developing neoplasms of various types (fibroids, polyps). This is explained by a decrease in the level of estrogen, which is responsible for the normal menstrual cycle. It is distinctive that a woman will experience severe pain during sexual intercourse, as well as an interval between menstrual cycles of more than three months.
Blood loss during pregnancy
If a woman experiences any bleeding after conception, this is a direct threat to her life and to the fetus. If you notice a woman’s bright bloody discharge, you should immediately call an ambulance. The discharge is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The occurrence of severe pain in the lower abdomen, which resembles contractions.
- Nausea leading to vomiting.
- Increased level of sweating.
- The appearance of dizziness.
Note! The occurrence of bleeding during pregnancy is considered a dangerous sign that threatens life.
Dysfunctional bleeding
This is uterine bleeding that occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance associated with impaired functioning of the ovaries, pituitary gland and adrenal glands. Depending on the nature of the manifestation, they are divided into the following types:
- Menorrhagia. This is the name for regular, long and heavy periods with a short gap between them. The bleeding continues for more than a week. During this time, blood loss is 100-150 ml or more, which leads to anemia.
- Metrorrhagia. This is irregular bleeding between periods. They have nothing to do with the processes of the menstrual cycle. Their duration and volume are variable.
- Menometrorrhagia. Irregular long periods.
- Polymenorrhea. Frequent periods less than 21 days apart.
Causes
There are functional, organic and iatrogenic causes.
Functional. These include diseases of the ovaries, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, which lead to disruption of hormone production. These include inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, ovarian dysfunction, hypothyroidism and others.
Organic. Associated with diseases in which not only the production of hormones is disrupted, but also the structure of organs (tumors, cysts, polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, endometriosis, fibroids, uterine cancer, as well as liver cirrhosis, pyelonephritis, hematopoietic disorders).
Iatrogenic. The reasons are medical manipulations or taking medications (hormonal drugs, antidepressants, anticoagulants).
Types of dysfunctional bleeding
Factors such as emotional stress, physical overload, poor living conditions, and poor nutrition contribute to the occurrence of dysfunctional bleeding. In addition, an important factor is the age and general condition of the body, its functioning.
Video: Uterine bleeding. Types and reasons
Juvenile bleeding
It occurs in girls during puberty, when hormonal levels become established. The development of reproductive organs in adolescents is influenced by living conditions, emotional and physical stress, and nutritional patterns. The appearance of unusual uterine blood discharge is promoted by malnutrition, vitamin deficiency, abnormalities in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Puberty and reproductive health are also affected by previous infectious diseases (measles, mumps, whooping cough, rubella), and the presence of diseases of the liver and other organs. Juvenile bleeding is anovulatory and may be distinguished by the fact that it occurs primarily in winter and spring.
Dysfunctional bleeding of the reproductive period
They occur in women of reproductive age with endocrine disorders, heart and vascular diseases, in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, endometriosis or uterine tumors, as well as as a result of stress and physical fatigue. This group also includes bleeding that occurs only in women who are sexually active.
Ovulatory. They appear during menstruation. In this case, ovulation occurs. Characteristic fluctuations in the intervals between menstruation. They are abundant and long lasting. The cause is usually inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, the formation of adhesions. Often, in addition to heavy periods, a woman also experiences spotting brown discharge before and after them. Such discharge is associated with impaired ovarian function, leading to an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone. They are typical for young women.
Anovulatory. Cycles without ovulation occur when there is insufficient progesterone and excess estrogen. This leads to pathological growth of the endometrium (hyperplasia, endometriosis), the appearance of benign and cancerous tumors. Such bleeding is characteristic of menopause and also occurs in adolescents. At the same time, menstruation comes with a delay. The intensity of blood loss may be too great, and the duration of menstruation exceeds 7 days. This affects the woman’s well-being, as anemia occurs.
Breakthrough bleeding. It occurs as a result of taking hormonal oral contraceptives. Usually, spotting and spotting appear in the first months after starting to take the pills due to the body’s adaptation to changed hormonal levels. They can be scarce. Their volume may increase if the drug is abruptly stopped. If the patient complains of breakthrough bleeding, the doctor changes the dose or recommends another contraceptive.
Profuse bleeding. This is the most dangerous type of internal or external heavy bleeding. It can occur both during and between periods. Leads to anemia, hemorrhagic shock (acute blood loss). Occurs due to injuries to the genital organs (for example, during curettage, removal of fibroids). Often, such bleeding can only be eliminated through surgery.
Video: How dysfunctional bleeding occurs
How to stop bleeding
Since it leads to iron deficiency anemia, in addition to the enormous inconvenience experienced by a woman who is forced to constantly change tampons and pads, urgent measures are needed.
The method to stop the bleeding will be chosen depending on its cause. Earlier in the article, we briefly reviewed them, as well as the measures that doctors take.
Let’s summarize everything point by point and add additional information.
✓ Article checked by doctor
For each woman, the process of menstrual bleeding is completely individual, depending on the characteristics of the female body. The average duration of the menstrual period is determined to be up to five days. At the same time, if there are any atypical discharges, then it is worth thinking about pathology. However, bleeding should not be ruled out, which can easily be confused with menstruation. Therefore, to provide timely assistance, it is necessary to have an understanding of the distinctive features.
How to determine bleeding or menstruation?
Bleeding during menopause
After 40 years, women experience a gradual decrease in the level of sex hormones. Hormonal imbalances increase the risk of tumors and other pathologies in the uterus. It is important for women to know exactly how to distinguish between menstruation and bleeding during this period.
Any bleeding that occurs after you have not had a period for 1 year cannot be menstruation because the ovaries have stopped functioning. Bloody discharge now acts only as a sign of the disease. The sooner a woman sees a doctor, the greater the chance of avoiding serious complications.
Video: Features of blood discharge during menopause
Self-treatment before visiting a gynecologist
If there is heavy uterine bleeding, you must urgently call an ambulance. Before her arrival, you can take the following measures to reduce discharge:
- Lie down so that your legs are higher than your torso.
- Provide plenty of fluids.
- Apply dry ice to the groin area of the abdomen.
After hospitalization and relevant studies and tests, doctors will decide whether the patient should see a gynecologist. Perhaps the symptom requires the intervention of other specialists.
Medications are often used to reduce blood loss: Tranexam, Vikasol, Dicynon. Taking each of these drugs requires consultation with a gynecologist, careful reading of the instructions for use and strict adherence to dosing rules.
How to distinguish menstruation from bleeding, when bloody vaginal discharge is normal, and when it is pathological and requires medical attention, possibly urgent?
To understand this, it would be correct to consider the most common situations as a result of which such questions arise.
- too short a period from the beginning of the last menstruation, less than 21 days, when there were no gynecological manipulations, surgeries, or taking hormonal medications;
- heavy periods lasting more than 7 days and with blood loss of more than 120 grams (you need to change pads more often than once every 2-3 hours, they get wet through), starting on time or with a delay - this should be regarded as bleeding. This is where the difference lies.
Exactly the same signs distinguish cyclic spotting from bleeding in women during menopause. After the onset of menopause (this is the absence of menstruation for 12 months), there can be no menstruation. The ovaries are gone. And all spotting is uterine bleeding, most often associated with precancerous or cancerous diseases.
Discharge after an abortion or miscarriage can be considered menstruation and a new cycle can be counted from this day. The next critical days will be in about 1-1.5 months.
How to distinguish menstruation from pathological blood loss
There are signs that will indicate how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding of a pathological nature:
The nature of the discharge helps to distinguish bleeding from menstruation after childbirth. When several weeks have already passed after the cessation of lochia and bright red profuse discharge appears again (while the woman is breastfeeding), this is not menstruation.
Uterine bleeding and menstruation: main differences
In order to identify pathology, you should interview the patient, who can easily characterize the typical menstrual flow that is characteristic of her. Therefore, any changes should alert the woman. The nature of menstruation can change dramatically, therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the following warning signs:
- The volume of menstrual flow increases significantly.
- The release of blood does not occur in batches, but occurs almost continuously.
- The outgoing discharge is characterized by a too liquid consistency.
- There are no blood clots.
- The color of the discharge becomes deep red.
- There is no specific odor characteristic of blood.
- Signs of anemia are observed.
- There is severe weakness.
- Possible pain in the lower abdomen.
- Before the onset of menstruation, sexual intercourse may cause pain.
What is the difference between menstruation and bleeding?
Carefully! If the above symptoms are observed, then you should not hesitate to visit a specialist.
What to do if there is heavy or suspected bleeding
If signs of blood loss are detected, a woman should definitely consult a doctor; if there is severe bleeding, call an ambulance.
Before the doctor arrives, you need to lie down and remove the pillow from under your head. Your feet should be higher than your head. Ice should be placed on the lower abdomen. You can drink a decoction of nettle or yarrow, which have a hemostatic effect.
Menstruation is a regular natural process in the body of a woman of childbearing age. Monthly discharge may have an individual character, but in general they have a number of common features. As a rule, menstruation occurs at the same time, natural bleeding lasts no longer than a week, and during menstruation the woman experiences unpleasant but tolerable sensations. If the bleeding differs significantly from the characteristics described above, you need to sound the alarm. It is extremely important to recognize the signals and be able to distinguish alarming bleeding from ordinary menstruation, since the former is a very dangerous factor for women's health.
The nature of discharge during menstruation
The menstrual cycle is individual for all women, but on average it lasts 21-35 days, and menstruation lasts for 3-7 days. Menstruation begins with slight discharge, by the second or third day it becomes more intense, then its amount decreases to spotting, and it gradually stops. The blood at the beginning of menstruation is bright red, after which it turns dark red or brown. Dark blood clots are normal. The total amount of discharge ranges from 60 to 120 ml.
The above symptoms are considered normal. Deviations require medical intervention to determine whether bleeding is a threat.
To distinguish menstruation, which is normal, from uterine bleeding, you should listen to your body every period and keep a menstrual calendar, which will help determine the exact cycle. You need to monitor your sensations before and during your period, and it would also be useful to know what other discharge can be considered normal, in addition to regular menstruation.
Other types of discharge, such as implantation bleeding or postpartum lochia, which are not dangerous in themselves, are often confused with menstruation.
Implantation discharge can occur when an egg is fertilized and attaches to the wall of the uterus. Microdamage to blood vessels provokes the release of pink or light brown blood, which can be released for several hours and has a spotting character. Very often this phenomenon is confused with normal menstruation, however, implantation discharge can indicate pregnancy earlier than the hCG test. This completely normal process is not accompanied by pain or discomfort.
Other blood losses in gynecology are considered a pathological phenomenon and can threaten the health and life of a woman. In order to prevent serious consequences, you should know how to distinguish dangerous uterine bleeding from menstruation, and what measures to take first.
Menstruation is a normal occurrence for every girl or woman. But when it doesn’t proceed as usual, then...
Treatment methods for cervical erosion, their advantages and disadvantages.
If erosion is detected together with a latent infection, the doctor may prescribe a course of drug therapy, which will be aimed at suppressing the detected causative agent of the disease. Treatment in this case can be carried out by taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Elimination of defects in the mucous membrane of the cervix is carried out after menstruation in the first stage of the menstrual cycle. Among the methods for eliminating ulcers on the surface of mucous membranes, chemical and surgical methods can be distinguished.
Coagulation under the influence of chemical components
The method involves influencing an area of the mucous membrane that has a pathology with the help of the drug Solkovagin, the composition of which is based on nitric acid and zinc nitrate. The additional components include a group of organic components represented by acetic and oxalic acids. An alternative to Solkovagin is treating the injury site for 1-1.5 weeks with tampons containing Vagotil. The advantages of the method include ease of implementation, absence of pain, and low cost of the drugs used. The main disadvantage, which significantly limits the scope of application of the methods described above, is the possibility of using them only to eliminate minor damage.
Consequences of coagulation under the influence of chemical components
The effect of the method is based on the fact that at the site of damage, a crust is formed containing coagulated particles of blood and rejected material, which is eliminated after a few days. The full course of restoring tissue integrity takes 1.5-2 months.
Radio wave removal
The method is widely popular and is prescribed for the treatment of benign and oncological structures in the organs of the female reproductive system. To carry out the procedure, the Surgitron device is used, the operating principle of which is based on receiving radio waves when converting electric current. Cauterization of cervical erosion with radio waves can be performed in any phase of the monthly cycle, with tissue regeneration occurring within 14-21 days. The disadvantages of this method include the need for local anesthesia and the lack of special equipment in a significant part of antenatal clinics.
Consequences of radio wave removal
The resulting radio waves are directed through the electrode to the area where the affected area is located. The method does not involve contact with the damaged surface of the mucous membranes, since the electrode does not touch the tissue and is not heated to a temperature at which thermal damage can occur. Under the influence of waves, fluid evaporates from the cells of pathological formations, after which their destruction occurs. The method is 100% effective, there are no scars on the surface of the mucous membranes, and bleeding with this treatment is practically excluded.
Diathermocoagulation
To soften the effect of the procedure, it is practiced before the onset of menstruation. This measure is necessary to ensure that the blood released during the cycle irrigates the crust, facilitating its easy rejection. Among the positive properties of the method, one can note its low cost and ease of implementation.
Consequences of diathermocoagulation
The method has practically fallen out of use, since its implementation is based on the impact of high-frequency currents on mucous surfaces, which can result in blood after cauterization of erosion. Carrying out cauterization of the cervix in this case is characterized by pain during its implementation, bleeding can appear both during and after the procedure. Tissue regeneration using this method lasts 1 month, however, in some cases it can take up to 1.5 months. If, after eliminating erosion using diathermocoagulation, a black crust forms on the surface of the affected area, which indicates a local burn. The use of this method involves the appearance of scars on the surface of the cervix; therefore, it is not prescribed to women planning children and nulliparous girls.
Among the pathological conditions that most often occur after cauterization, inflammatory processes that occur in the area of the structure remaining after cauterization should be highlighted. Such consequences are very rare; if they occur, you must immediately seek qualified help. This is a necessary measure, since at this stage of the pathology it significantly increases the risk of re-development of erosion and bleeding. Significant bleeding may be associated with damage to the structure of one of the large vessels. The appearance of scars in the area of the cervical canal and the associated narrowing of this area. Among the complications associated with this course of the postoperative period, gynecologists cite a high probability of developing endometriosis, premature birth, miscarriage during pregnancy, and difficulty conceiving.
Cryodestruction
The method is based on treating the affected area cooled to 150-170°C with nitrogen or nitrous oxide sprayed through nozzles. When exposed to the treated area, liquid crystallizes inside the cellular structures of pathological formations with further destruction of damaged cells. The procedure lasts 15 minutes, during which time the structure becomes white and there is a loss of sensitivity.
Consequences of cryodestruction
Partial regeneration occurs a week after the procedure, complete healing lasts for 1-1.5 months. The advantages of the method include ease of implementation, high efficiency, reaching 97%, no damage to the cervical structure, and minor pain during the procedure. Among the disadvantages of the method, gynecologists note a large number of cases when, after its implementation, the cervix bleeds. In addition, when performing cauterization, partial destruction of pathological structures cannot be ruled out, which increases the risk of recurrence of the disorder in the future.
Laser processing
The method consists of influencing the area of localization of pathology in a non-contact manner, using a directed laser beam. Before performing the procedure, the gynecologist wipes the cervix with diluted acetic acid to determine the area of pathological structures. After this, the surface is treated with iodine solution to delineate the boundaries of the damage. The principle by which erosion is cauterized is the effect of a laser beam on the surface of damaged cells, as a result of which the liquid contained in them turns into steam, which causes their further destruction. Among the disadvantages of the procedure, gynecologists note the high cost of implementation and the need to use special devices. These disadvantages limit the availability of the method and increase the coverage area of healthy cells compared to the radio wave processing method.
Consequences of laser treatment
The method is highly effective, has a low degree of pain and does not form scars in the area of treatment. The listed properties allow us to recommend it for use by nulliparous women.
What is the difference between menstruation and pathological bleeding?
Symptoms will help identify the problem in a timely manner. Abnormal bleeding usually differs from menstruation in the following ways:
- discharge occurred prematurely or with a significant delay;
- their duration exceeds a week;
- the amount of blood lost during discharge is more than 120 ml, there is a need to change hygiene products hourly;
- the blood is bright red, liquid, without clots;
- uncharacteristic smell of discharge;
- constant thirst;
- weakness, dizziness, pain in the lower abdomen, headache, excessive sweating, fainting, nausea, fever;
- pale skin, brittle nails;
- bleeding after sexual intercourse is also a pathology.
Other types of bleeding that can be confused with menstruation
All possible bleeding is divided into three types:
- Normal – monthly menstruation.
- Conditionally normal include implantation bleeding and postpartum lochia.
- Pathological – caused by diseases, neoplasms, blood clotting disorders.
There are several types of pathological discharge, which are easy to identify, since they differ from bleeding during regular menstruation in profuseness, protracted nature and irregularity:
- Dysfunctional – associated with hormonal imbalance. Such a deviation can occur due to problems with the adrenal glands, ovaries, and pituitary gland.
- Juvenile - so-called seasonal bleeding often occurs during adolescence. These discharges are not particularly painful, but lead to anemia. They are due to the fact that the uterus has insufficient contractility.
- Profuse - accompanied by menstrual pain. They differ from menstruation due to heavy blood loss and scarlet color. Profuse bleeding poses a serious health threat and requires hospitalization and surgery.
- Breakthrough - most often provoked by taking hormonal contraceptives or the uterine device. This bleeding signals that the IUD needs to be removed, and the birth control pills should be replaced or a more appropriate dose should be selected.
- Menopausal heavy bleeding occurs due to neoplasms (polyps, fibroids), which often occur during this period. A sign of pathology is pain during sexual intercourse and long delays.
- Discharge during pregnancy is also abnormal and poses a serious threat to both the fetus and the mother. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance. Only prompt action will help save the unborn child.
Classification of discharge
Experts classify uterine bleeding into three types.
| Bleeding | Short description |
| Normal | Every cycle a woman experiences menstrual flow, which is considered to be a natural norm for the body. |
| Conditionally normal | Discharge occurs in the preovulatory or postovulatory period. Implantation bleeding is also included in the conditionally normal type of bleeding |
| Pathological | These bleedings can occur at any age - during menopause, during the period of reproductive activity, adolescence. They can be divided into subtypes: functional. Bleeding occurs due to problems with the endocrine system or disruption of the pituitary gland; organic. If a woman is diagnosed with neoplasms (polyps and others) or illnesses (for example, endometriosis), then bleeding often occurs; systemic. Most often triggered by autoimmune diseases or chronic pathologies |
Nature of the discharge
Possible causes of formation
Unlike menstruation, uterine bleeding has pathological causes associated with serious disorders or diseases. First, you need to distinguish between relatively normal bleeding, such as implantation bleeding, and regular menstruation. If heavy discharge is still pathological in nature, you should consult a doctor and find the main reasons, as they can cause various diseases, discomfort in everyday life, painful sexual intercourse and other abnormalities:
- ovarian pathology;
- endometriosis;
- various neoplasms;
- bleeding disorders;
- infection and inflammation of the reproductive system;
- vitamin deficiency and iron deficiency;
- hormonal imbalance;
- abortion;
- eating disorders (strict diets);
- intense physical activity;
- depression, constant stress.
A gynecologist can identify the exact cause through an examination and, if necessary, refer you for an ultrasound and additional tests. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment is selected. Most often it is conservative in nature, but in some cases surgical intervention may be required. The main thing is to listen to your body in order to identify the problem in time, then treatment will go much faster.
How to distinguish uterine bleeding from menstruation
Any blood loss, except that which develops during critical days, can be dangerous for the female body. Uterine bleeding has pathological causes, menstruation has physiological causes. However, it is not always easy to determine whether we are facing bleeding or menstruation.
On critical days, a small amount of blood is released every day. At the beginning of the cycle, the discharge is bright and liquid, towards the end it is dark and thick.
In addition to the blood itself, menstrual discharge contains mucus and particles of dead endometrium. All this gives them a specific aroma, reminiscent of the smell of meat.
Thus, if a woman is interested in how to determine whether she has heavy periods or bleeding, she needs to start from the nature of the discharge.
A more accurate definition is based on the study of such signs of uterine bleeding as duration, cyclicity and volume of blood loss.
Duration
During menstruation, blood flows from the uterus from 3 to 7 days, depending on the individual characteristics of the female cycle. Periods lasting more than 7 days may be a sign of uterine bleeding. In addition to the duration, their character is also different. So, to determine whether menstruation or bleeding has appeared, you need to know that:
- During menstruation, in the first days the discharge is insignificant, spotting, and in subsequent days it is portioned; in case of pathological bleeding, it is continuous.
- Discharge on critical days has a strict duration - from 3 to 7 days, uterine bleeding can be one-time or bother the woman for more than one week. In this case, blood is released in small quantities.
Cyclicality
Menstruation has a certain cycle. It usually lasts 28 days, but fluctuations of 1 week in both directions are also considered normal. Accordingly, vaginal discharge detected outside the cycle makes it clear that this is most likely not menstruation.
It will be typical if “menstruation” occurs on a day that differs from the expected one by one week or more.
Volume of blood loss
The main difference between bleeding and menstruation is the volume of discharge. A physiological phenomenon is considered to be the loss of 50 ml of blood per cycle.
Also a variant of the norm are heavy periods, during which 80 ml of blood is released during the critical days. A single blood loss of 50 ml or a total of more than 100 ml is considered bleeding and requires immediate medical attention.
The characteristics of blood secretion are well illustrated by the amount of hygiene products that a woman has used per day. As a rule, during menstruation this number does not exceed 4 (depending on the abundance). This suggests that the volume of secretions falls within the physiological framework. If there is uterine bleeding, a woman can use more than 10 pads per day.
Thus, it is very important to distinguish heavy menstruation in a woman from blood loss that has pathological causes. Otherwise, there is a risk of iron deficiency anemia.
Opinion of gynecologists
If irregular bleeding is associated with pathology, it is necessary to pay attention to the problem in time. To do this, it is important to know how to distinguish menstruation from implantation bleeding, what signs indicate abnormal discharge. A gynecologist will tell you about this, and you need to visit him several times a year and consult about any problems that have arisen. Only timely detection of violations will help avoid illness.
If discharge appears during pregnancy, you should call an ambulance, as this may pose a risk of miscarriage. Copious blood loss of a profuse nature also cannot be ignored. To avoid blood loss during uterine bleeding, doctors recommend lying down, applying a cold heating pad to your stomach (this must be done very carefully, no longer than 15 minutes, so as not to catch a cold), and drinking a lot of water.
To prevent heavy bleeding during menstruation, you should avoid intense physical activity, visiting a sauna, taking a hot bath, spend more time in the fresh air, balance your diet, give up bad habits and strong coffee, and in case of any deviations, seek the help of a doctor. Only a specialist can prescribe the correct treatment for uterine bleeding; independent actions and ignoring the problem can harm your health.
How to help
What to do if you have heavy periods
First of all, it is necessary to minimize all physical activity. Then review your diet and include beef, offal (liver), and foods high in iron.
If a woman begins to experience heavy blood loss, she urgently needs to lie down in a position so that the pelvis is slightly elevated. To do this, you can place a pillow or slightly raise your lower limbs. In this way, loss of consciousness can be avoided and symptoms can be reduced.
To reduce bleeding, you will need to apply a cold compress so that the vessels of the uterus constrict and the muscle layer of the uterus contracts.
You should not ignore any pathological discharge, because it can be a sign of a serious illness. A specialist will tell you about the causes of uterine bleeding in a video commentary. Read about the difference between menstruation and bleeding on our website.
conclusions
Uterine bleeding carries a certain danger, which can be avoided by knowing the signs and causes of pathological discharge. The amount of blood, its color, consistency, and how long the discharge lasts will help determine whether it is menstruation or abnormal dangerous bleeding. It is very important to be able to distinguish conditionally normal discharge from menstruation, which includes implantation bleeding and postpartum lochia. But most importantly, if a problem arises, you need to consult a doctor, then many complications can be avoided and you can live a full life.
For the female body, discharge is a healthy and normal phenomenon. Thanks to them, the body removes bacteria and dead cells and protects the vagina from infections.
Progesterone and estrogen, the hormones responsible for female fertility, have the greatest impact on the female body. They are the ones who change the color and amount of discharge in the menstrual cycle. When pregnancy occurs, menstruation stops, but the discharge does not always disappear. By correctly determining the patient’s diagnosis, analyzing the color, consistency and amount of fluid released, you can not only assess the woman’s health, but also notice a dangerous disease in time.
Brown discharge as a symptom of pregnancy
Pregnancy always manifests itself and proceeds differently. However, brown discharge is most often a sign of early pregnancy. They are one of the very first responses to changes in a woman’s hormonal background. However, you should take a closer look at the discharge in any situation.
If your period is delayed and brown discharge appears instead, you are pregnant. At the beginning of pregnancy, they talk about the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. Typically, the discharge begins on the seventh day after fertilization and lasts 3-4 days, and its color varies from pink to dark brown.
Minor bleeding may also appear - this is the blood that was in the womb before fertilization. Bleeding may be accompanied by small cramps in the lower abdomen - these are muscle cramps of the uterus. Gynecologists note that excessive bleeding and very severe pain may be a signal of a possible miscarriage.
If you only had colored discharge instead of menstruation, and a few days later full menstruation began, this is a sign of hormonal disorders. In this case, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist to normalize hormonal levels.
Blood after obstetric manipulations and operations
With any invasive gynecological procedure associated with penetration into the tissue of the cervix or body of the uterus, vagina, there will be bleeding due to the formation of a wound surface. But in different ways.
Cervical biopsy
After this procedure, bloody or bloody discharge occurs for 2-5 days, but in volume no more than menstruation. It is carried out in a hospital setting and the woman is left under observation for several hours. If heavy bleeding suddenly opens up, this happens if a large vessel is touched, it is coagulated (“cauterized”) or the woman is given a hemostatic sponge (to stop bleeding). There is no need to remove it; it dissolves itself into the vagina. But on top of the sponge, so that it holds better, insert a cotton swab. You need to get it yourself after a few hours.
Danger to pregnancy
The discharge itself is safe and even beneficial. Healthy discharge does not have an unpleasant odor, is uniform in consistency and is not accompanied by pain.
An unpleasant odor is the first sign of inflammation. Do a mucosal test (smear) and consult a gynecologist. Any inflammation threatens the health and development of the embryo.
Other dangers include lumpy discharge, escaping pieces of tissue, and a bright scarlet color. Dizziness, fainting, severe pain, vomiting. In these cases, call an ambulance immediately. These symptoms indicate serious complications: ectopic pregnancy (the fertilized egg did not reach the uterus), molar pregnancy (the embryo does not develop correctly), frozen pregnancy (the embryo has stopped developing), miscarriage.
Discharge as a threat of miscarriage
Once pregnancy is confirmed, do not stop monitoring your menstrual cycle.
With a confirmed pregnancy (positive test and hCG analysis), discharge instead of menstruation takes on a tinge of danger. This means that a woman’s body cannot produce enough hormones to carry an embryo.
The period of menstruation is most dangerous for the embryo in the early stages. When the body has not yet had time to switch to pregnancy “mode,” the concentration of progesterone decreases greatly, and the uterus can remove the supposedly unfertilized cell. There is a high risk of miscarriage.
Diseases manifested by brown discharge
Brown discharge is usually harmless, but it can also be a sign of serious illness. Please note if you have satellites such as:
- Severe itching;
- Unpleasant odor from discharge;
- Tingling;
- Swelling or pain in the vagina;
- Painful sensations during sex.
You need to immediately contact a gynecologist. These may be sexually transmitted diseases, which are usually treated with antibiotics; uterine polyps - they can be treated with hormonal drugs (or in case of complications - with surgery to remove the uterus); cervical cancer.
Also, spotting may be a response to inflammation. The easiest way to get inflammation of the mucous membrane is to stay at a low temperature for a long time. The appendages, uterus, and cervix are at risk.
In addition, brown discharge instead of menstruation may be a signal of menopause or atrophic vaginitis (hormone deficiency that accompanies menopause). Menopause cannot be cured, but the symptoms of age-related changes in the body can be stopped.
Recommendations from experts
If brown discharge appears instead of menstruation, it is recommended:
- Change gaskets regularly throughout the cycle;
- Do not use tampons during pregnancy;
- Wear cotton underwear of the appropriate size;
- Do not wash the vagina! This will disrupt the natural flora and cause infection.
To correctly determine the cause of the discharge, it is first necessary to find out whether the patient is pregnant - this is what determines the choice of treatment.
During pregnancy, any deviation from the norm should be taken seriously. Here, not only the health of the expectant mother, but also her child may suffer.
Although pregnancy and menopause are common causes of brown vaginal discharge, you should not neglect your health. Contact your gynecologist as soon as you feel any unusual sensations.