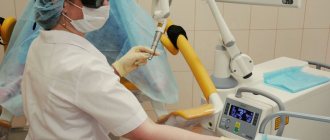
A biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that involves removing a small area of pathological tissue for histological and cytological examination. This examination is the most common and reliable way to establish a final diagnosis of oncology. In the event of a malignant neoplasm, microscopic analysis is considered a mandatory procedure, which makes it possible to determine not only the presence of a tumor, but also to diagnose its histological identity, as well as the stage of cancer.
Highly accurate non-invasive diagnosis of tumors using MRI
Early diagnosis is a priority in modern oncology. Even cancer that is detected before the seeding of atypical cells into the lymph nodes and distant organs can be cured, achieving long-term remission of the process. The advent of magnetic resonance scanning techniques has opened up new perspectives in the diagnosis of tumors.
Magnetic resonance scanning is used for the initial detection of cancer, planning surgery, as well as assessing the results of radiation or chemotherapy or surgical treatment over time. An experienced specialist knows well what a tumor looks like on pictures in various scanning modes, and based on these data, it is possible to state with a certain degree of probability what kind of tumor we are dealing with.
When describing an MRI, the doctor makes a conclusion about the nature of the tumor based on indirect signs. A definitive diagnosis of cancer or benign formation is possible only on the basis of a biopsy.
In most cases, benign neoplasms have smooth and even borders, which indicates their expansive growth (they push the surrounding tissues apart and push aside those nearby structures). Fuzzy and uneven contours characteristic of malignant neoplasms reflect infiltrative growth.
Benign formations have a homogeneous structure, so they most often look like shadows of uniform density. Malignant - contain areas of necrosis and calcifications, so the density of their image is heterogeneous.
- Degree of vascularization and contrast uptake.
The doctor can see the structure of blood vessels using an MRI with intravenous enhancement. In benign neoplasms, the vessels are arranged linearly and do not intertwine with each other; they accumulate more contrast than the surrounding tissues, but less than malignant ones. A cancerous tumor contains many highly branched capillaries that actively anastomose with each other.
Only a biopsy - a microscopic examination of its fragment - can finally differentiate the nature of the formation. The higher the qualifications of the doctor who conducts the scan and gives an opinion, the less likely it is to confuse a benign process with cancer. However, there are tumors that appear benign on imaging but turn out to be malignant on biopsy.
Features of the procedure
After the procedure, performed in any of the above ways, it is important for a woman to remain under the supervision of doctors for two to three hours. This is necessary to provide timely assistance when bleeding begins.
The recovery period lasts from several days to a month, depending on the type of biopsy, the presence of complications, the individual characteristics of each woman’s body, etc. At this time, the patient is subject to a number of restrictions that will help avoid unpleasant consequences:
- in the first two weeks you must refrain from sexual activity and physical activity;
- you cannot take hot baths, visit baths and saunas;
- It is prohibited to use tampons;
- It is not recommended to do douching without a doctor's prescription.
Even such a minimal surgical intervention requires bed rest in the first days after the procedure. Since there is a high risk of bleeding during this time, you should not exercise. It is better to lead a passive lifestyle for some time and not neglect all the doctor’s recommendations.
To speed up the healing process, you may be prescribed auxiliary therapy.
Your doctor should warn you about the possible consequences of taking tissue from the cervix. Tell him or her about any unusual symptoms in a timely manner. It is better to play it safe once again than to miss the moment of development of the inflammatory process or other complication.
After the procedure, a repeat colposcopy procedure or appropriate therapy for cervical dysplasia (cellular abnormalities in the tissues of the cervix) may be necessary. The decision about the need for additional procedures is influenced by the result of the biopsy. If treatment for dysplasia is still required, the following types of therapy are most often used:
- radio wave coagulation, in which part of the tissue is removed from the surface of the cervix through the use of special attachments to which radio wave radiation is transmitted. The radio wave knife simultaneously cuts through tissue, disinfects and coagulates the opening vessels. The tissues are restored very quickly after its use, there are no scar changes or deformations of the cervical walls.
- non-contact argon plasma coagulation;
- cryotherapy - the procedure is the freezing of the affected area of the uterine cervix and leads to the destruction of cells of an abnormal nature;
- laser therapy - involves getting rid of cellular abnormalities using a laser.
In extremely rare cases, a wedge resection of the cervix or a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary after a biopsy.
The main task of a biopsy is to identify the presence of atypical pathological cells in the tissues of an organ. The following deviations may be the reason for ordering an analysis:
- dysplasia or ectopia of the cervix;
- oncology;
- precancerous conditions;
- infertility;
- papilloma virus;
- polyps or condylomas of the cervix.
An invasive diagnostic method is carried out in the first period of the cycle, 3-6 days after the end of menstruation. It is forbidden to do a biopsy at the time of maturation of the corpus luteum. In this case, the woman’s body will not have time to recover by the beginning of the next cycle.
The gynecological procedure itself lasts no more than half an hour under general or local anesthesia. Most often it is done on an outpatient basis. After the procedure, the patient needs to rest for 20–40 minutes, then she can go home.
In some cases, when it is necessary to take a large piece of tissue for analysis, the woman may be asked to go to the hospital for several days.
If the patient has had a cervical biopsy in the past and is planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to warn her doctor about this.
Typically, patients notice discharge after a cervical biopsy. Is this the norm? As a rule, this is a fairly common phenomenon and should be treated not as a pathology, but as a healing process.
The discharge may vary in color and intensity and continue until the next menstruation. There is no need to worry too much about this.
Usually after a cervical biopsy the discharge is bloody. In this case, the patient notes a slight nagging painful sensation in the lower abdomen. According to doctors, this can last 5-10 days. As the tissues heal, the discharge becomes more scanty. After menstruation, the cervix is completely cleared and bleeding stops.
It is not uncommon for a patient to notice yellow discharge after a cervical biopsy. This is also normal and does not require seeing a doctor.
If the bleeding becomes profuse and becomes threatening, we can talk about the development of a complication such as bleeding. It is necessary to immediately contact a gynecologist if you have the following ailments:
- The discharge is not very intense, but lasts more than 3 weeks.
- Severe bleeding of a bright color appeared.
- The temperature rose to 38 °C.
- The discharge has acquired a foul odor.
Such symptoms indicate the development of an infection and require immediate medical attention. The doctor must identify the cause of the complication and prescribe treatment.
A biopsy is performed on days 5-7 of the cycle, after menstrual bleeding has stopped. It is possible to collect material for research only in the absence of infection, therefore, before the biopsy, the vaginal flora must be examined. If an infection is detected, the woman is first prescribed treatment and only after good test results are obtained, a biopsy is performed.
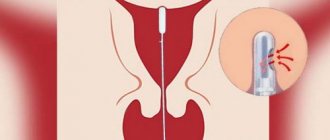
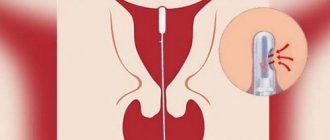
Cervical biopsy is a painless, short procedure, performed without anesthesia: there are no painful endings on the cervix, and during the procedure the woman feels only light stretching - this is the uterus contracting in response to the touch of the instruments. In order to reduce contractions, just relax.
To collect material, a scalpel, a radio knife, biopsy forceps, and an electric loop are used.
A biopsy is performed under the control of a colposcope, a device similar to a microscope, and Lugol's solution is used as a dye to mark the altered area of the epithelium.
What does it reveal and show?
Of course, only a doctor should decipher the results of histological examination.
But most patients want to know everything and understand the nuances of their illness.
Sometimes misinterpretation of medical formulations leads a person to neurosis and depression.
Therefore, before you start to panic, you need to understand what this or that term that is indicated in the analysis results means.
As soon as the histological examination is carried out and the result is already in hand, you can proceed to deciphering:
- If the phrase “nodular goiter” is written, this means that it is possible to say: the formation in the thyroid gland is benign and not dangerous. The accuracy of this conclusion is 98%.
- If the conclusion says “colloid” or uses the term “follicular epithelium”, this indicates benignity with a probability of 95%.
- Possible interpretations are “a nodule with symptoms of proliferation of the follicular epithelium and atypia” or “difficulty in differentiating adenoma and carcinoma,” here we are talking about follicular neoplasia. This pathology allows one to suspect a malignant neoplasm with a probability of 50%.
- If they write “malignancy cannot be excluded,” this indicates the presence of cancer cells with a probability of 70%.
- If there is a 90% probability of carcinoma, they write “suspected carcinoma.”
- If the analysis indicates the word “carcinoma,” then this is already an alarming sign, since the result indicates that the node is almost one hundred percent malignant, and surgery is inevitable.
Whatever the wording, in any case, an accurate diagnosis can only be determined by the attending physician after a comprehensive examination.
Therefore, even if the histological examination has a poor prognosis, you should not make a diagnosis yourself, since the possibility of an erroneous result always exists.
The purity of the study, of course, can be influenced by the human factor - the professionalism of the specialist who collected the drug for the study, and the level of knowledge of the specialist who directly carried out the histological examination itself.
In addition, the correct result directly depends on the storage of the resulting material, its quantity and quality, as well as strict adherence to all standards of sterility and sanitation.
If after the histological examination there are still questions or, taking into account other components, the diagnosis is called into question, then it is better to repeat the analysis.
Next, the doctor looks under a microscope at the structure and position of cells in the tissue. Each tissue in the body must have its own order and arrangement of cells. In addition, they must have their own structure, size and structure. If there is any deviation, this may indicate disease, inflammation or oncology.
In addition to histology and histological examination, there is so-called cytology. Many patients confuse these two concepts and do not know what the difference is between cytology and histology.
Cytology is a field of medical science that studies the structure of a single cell, its nucleus, functioning, as well as other organelles. The tissue collection is the same. Usually the doctor looks and checks the structure of the tissue.
During diagnosis, he observes that the structure is not of the correct shape and there are atypical cells (these are cells that are very different in structure from healthy ones). For example, they have an enlarged nucleus or are irregularly shaped.
Now we need to determine the degree of malignancy and whether these cells are cancer. The fact is that atypical cells, or those that differ from healthy ones, may not always be cancer. Benign tumors have the same tissue abnormalities.
This is precisely what histology shows the structure and type of cell. The doctor examines the structure of the atypical cell under a stronger microscope and determines the degree of its malignancy.
Answers to the most typical questions from patients about the method of puncture biopsy of the thyroid gland:
Does a thyroid biopsy hurt?
The sensations experienced by patients during a thyroid biopsy are similar to the sensations during an injection into the buttock, with the only difference that during a biopsy the injection is made in the neck, which frightens the patient much more.
However, a thyroid biopsy is called a fine-needle biopsy for a reason - needles with a diameter of 23-25G are used to puncture the thyroid gland, i.e.
thinner than those usually used for intramuscular injections, therefore you should not expect any special pain, and you will not remember anything special about the day when you had a puncture of the thyroid gland. It shouldn't hurt at all in good hands.
“Will the needle hit somewhere else instead of the knot?”
An ultrasonic device is used to ensure precise guidance of the needle onto the node. When performing a puncture of the thyroid gland, an endocrinologist surgeon sees exactly where the needle is going - this completely eliminates the possibility of it hitting other organs.
“Will a thyroid biopsy cause the tumor to spread beyond the nodes?”
No, that won't happen. Numerous studies of nodes removed during surgery after fine-needle biopsy of nodes show that the tumor does not spread from the node after biopsy.
“They say: “Don’t touch it, there won’t be any problems.” Will the node grow faster after a biopsy?
No, that won't happen either. Fine needle biopsy does not cause changes in the growth of nodes. If the node had a tendency to grow before the biopsy, it will continue to grow after this study. If the nodule has not grown, it will not grow only because a thyroid biopsy was performed.
“How to prepare for a thyroid puncture?”
In principle, a biopsy does not require any preparation. The only thing I would like to recommend to patients is not to fast before this study. A thyroid biopsy is not a blood test; refusing to eat on the day of the biopsy will not change its results, but it may add extra dizziness and a feeling of weakness before the puncture...
“How often should the biopsy be repeated?”
Fine-needle biopsy is a method for diagnosing thyroid diseases, and not a method for monitoring the patient. If an informative answer is obtained during the initial study, then the biopsy does not need to be repeated.
A repeat biopsy is possible only in cases where the first study revealed a benign nature of the node, but subsequently there is a constant growth of the node or the occurrence of “suspicious” symptoms (hoarseness, cough, difficulty swallowing and breathing).
“I am being offered a thyroid biopsy without ultrasound guidance. Agree?"
In no case! “Blind” biopsy (i.e., biopsy performed by touch, under the control of fingers) has already become a thing of history. Ultrasound-guided biopsy and non-ultrasound-guided biopsy are completely different research methods. The reliability of ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy is many times higher than the reliability of a “blind” biopsy.
“The biopsy response is uninformative. Remake?
Necessarily! Both you and your doctor can gain valuable information from a fine-needle biopsy. If the primary material does not contain enough information to make an accurate diagnosis, the biopsy should be repeated.
An uninformative examination usually cannot be considered a consequence of low qualifications or an error by the specialists who performed the biopsy, however, in most clinics, a repeat examination is carried out free of charge and out of turn - simply to maintain their reputation and ensure your convenience.
“After the second biopsy, the answer is also uninformative. What to do?"
This situation requires a more careful assessment. There are nodes from which it is not possible to obtain informative material even with repeated research. If you completely trust the clinic where the test was performed, repeat the biopsy again.
The experience of our medical center convincingly demonstrates that nodes with repeated uninformative biopsy findings most often end up being benign.
Therefore, insisting on the mandatory removal of a thyroid nodule upon repeated uninformative findings is fundamentally wrong.
“I was given a response that included a diagnosis of follicular adenoma. They say that this is a benign formation. Is this answer reliable?
No, this conclusion usually indicates insufficient qualifications of the cytologist who conducted the drug study in diagnosing thyroid tumors.
It is impossible to distinguish follicular adenomas (benign tumors) from follicular carcinomas (malignant tumors) based on fine-needle biopsy data. All that a cytologist has the right to write is a conclusion like “Follicular tumor, probably an adenoma,” i.e.
the cytologist has the right to express his opinion about the essence of the process in the node, but this opinion can never be considered sufficient to establish a final diagnosis. Only complete removal of the node followed by histological examination can reliably exclude malignancy in nodes of the follicular structure.
If you receive a similar answer after a biopsy, pick up glasses with cytological preparations at this institution and contact a specialized endocrinology center for a consultation with a cytologist.
Source: //thyroidcancer.ru/patients/articles/thyroid/diagn/fna/index.htm
Source: //hospit.med.cap.ru/novie-tehnologii/novie-tehnologii/punkcionnaya-biopsiya-schitovidnoj-zhelezi/otveti-na-naibolee-tipichnie-voprosi-pacientov-o-me
Advantages of magnetic resonance diagnostics for cancer patients
- High resolution - it is possible to detect tumors ranging in size from 0.1-0.3 mm, that is, detect cancer before the formation of metastases. Reproducibility of the result: based on two images taken at different times, the doctor can give an opinion about the change in the state of the tumor over time. Using MRI with contrast, it is possible to assess the growth pattern of the formation and determine its vascularization, which is especially important when a biopsy before surgery is impossible. Harmless to the body - the magnetic field does not potentiate tumor growth, so the examination can be carried out many times without fear of aggravating the process.
Discharge after cervical biopsy
Bleeding after a cervical biopsy is a fairly common occurrence and is not considered a complication, but rather a natural healing process. During this period, a woman may experience unexpressed nagging pain in the lower abdomen, as during menstruation. As healing progresses, spotting after a cervical biopsy gradually becomes scarcer, the wound becomes scarred, and after five to six days the patient can return to her normal routine. After a cervical biopsy is performed, discharge may persist for quite a long time. To avoid complications, it is enough to follow the rules of personal hygiene and medical recommendations:
- use sanitary pads;
- do not use a syringe;
- do not visit the swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna;
- exclude heavy physical activity;
- refuse intimate relationships (the period will be indicated by the doctor);
- do not take medications that contain aspirin (aspirin thins the blood and bleeding may increase).
Every doctor is obliged to warn his patient: when a cervical biopsy has been performed, the discharge may be bloody, scanty and not last for a long time. Although discharge after a cervical biopsy may be of a different nature depending on the type of biopsy: for example, discharge after a cervical biopsy by conization is more abundant and prolonged. But discharge after a cervical biopsy using the radio wave method can be extremely scanty and short-lived. Bleeding after a cervical biopsy is always less pronounced with more gentle techniques.
After a cervical biopsy has been performed, the discharge should not cause concern to the patient. Usually, a cervical biopsy does not have any consequences, and it is better to do it in the first half of the cycle. It is known that it is during this period that tissue regeneration is highest. After a cervical biopsy is performed, discharge is an indicator of health. The likelihood of complications increases if the patient does not follow medical recommendations. Consequences obtained after manipulation of a cervical biopsy may occur if the biopsy was performed during menstruation. If a cervical biopsy is planned, menstrual bleeding may require postponing the procedure.
Why is differentiation needed?
If the cell is cancerous, you need to find out the degree of differentiation - that is, how different it is from healthy cells. Usually there are several types:
- Highly differentiated - cells are slightly different from healthy ones. This pathology does not develop quickly, and the cancer is not so aggressive.
- Moderately differentiated - more different from healthy tissues. Average speed of growth and aggression.
- Poorly differentiated is a very aggressive form of oncology.
- Undifferentiated - pathological cancer cells cannot be distinguished from healthy ones.
As is clear from the definition, the doctor must know how dangerous the tumor is and how quickly it develops in order to roughly calculate the treatment strategy and know how much time the patient has.
Also, based on the degree of differentiation, it is possible to determine which chemotherapy drug will be most effective. Often the most aggressive types of tumors are more sensitive to strong chemicals and radiation.
Dangerous symptoms after the procedure
The biopsy diagnostic method is used very often in gynecology. And since it does not require hospitalization of the patient, every woman should have a clear idea of what symptoms may indicate the development of pathological conditions in order to promptly seek medical help and avoid negative consequences in the future.
If you have any questions related to pain and the amount of discharge, you should consult a specialist.
Especially if the following symptoms are observed:
- prolonged discharge;
- heavy bleeding;
- burning and itching;
- elevated temperature;
- change in color and nature of discharge;
- abdominal pain;
- intense and prolonged periods;
- delay of menstruation.
Prolonged discharge
- bleeding of bright scarlet or dark color with clots; increased body temperature above 37C; unpleasant odor of discharge; severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen; slight nausea.
Why is MRI used in oncology?
- Diagnosis of the tumor process at an early stage.
With the advent of magnetic resonance scanning, the diagnostic capabilities of oncology have expanded significantly. Thanks to its high resolution, it is possible to detect lesions with a diameter of 0.1 – 0.3 mm. The examination is prescribed as a screening examination in the presence of risk factors, and when specific and nonspecific symptoms of tumor growth appear.
- Evaluation of treatment results.
The magnetic field is harmless to the body, so patients undergoing radiation therapy for cancer do not have to worry about increased side effects. At the same time, it is possible to obtain a reliable picture of changes in the tumor after treatment.
- Planning for surgery.
MRI shows not only the presence of a tumor, but also provides reliable information about its size, shape and relationship with nearby vessels, nerves and internal organs. Based on the obtained images, a three-dimensional reconstruction of the area under study is created, which actually allows the surgeon to see the surgical field at the stage of planning the operation.
- Monitoring the state of the neoplasm over time.
Removing a tumor located near vital structures can pose a serious risk to the patient. Therefore, in the absence of aggressive growth, they try to control such neoplasms conservatively. In this case, magnetic scanning is the optimal method of periodic monitoring, informative and harmless to the body.
Indications for use
In particular, it is almost always prescribed in order to more accurately know the nature of the cancer. This is especially decisive in the first stages, when it is impossible to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Histological examination helps:
- Make an accurate diagnosis;
- Monitor treatment and screening after surgery, radiation and chemotherapy;
- Speed of the pathological process;
- Degree of differentiation;
- The presence of a malignant tumor.
Biopsy
This is a procedure where the doctor takes a piece of suspicious tissue for histology and cytology. Several options can be used for this. If the tumor is in a reachable area, they can simply excise a piece with a scalpel. Otherwise, an incision or surgery may be performed.
For example, in the case of a neoplasm in the uterus, a special device is used to penetrate the organ and take a sample of the endometrium. Based on the degree of atypicality, one can observe whether it is cancer or endometrial hyperplasia. The tissue sample is placed in a special tube in a sterile environment.
Next, in the laboratory, the section is impregnated with paraffin. After which it can be stored for quite a long time. Before examining the material under a microscope, it is necessary to perform a microtomy - that is, make a small section so that it is convenient to examine it under the microscope.
Afterwards it is covered with glass, and it can be stored this way under any conditions. The histological glass can be taken and stored at home. Patients often do this so that they can go to other clinics.
After a biopsy, the lower abdomen feels tight
Hello, I am asking you for help. On March 17, I had a biopsy of the cervix and was prescribed Methyluracil suppositories.
I put the candles on as they said, two weeks of sexual rest, etc., but now for five days now I have been pulling my lower back and have pain in my lower abdomen, the temperature is 36.9 and yesterday it was 37 in the evening. The discharge is light yellowish in color, just a little bit. What could it be? Help me please. Thank you in advance. Chronic diseases:
Bronchitis
On the Ask a Doctor service, you can consult a gynecologist online on any problem that concerns you. Expert doctors provide consultations around the clock and free of charge. Ask your question and get an answer immediately!
If you have a similar or similar question, but you have not found the answer to it, get your 03 online consultation from an expert doctor.
If you want to get a more detailed consultation with a doctor and solve the problem quickly and individually, ask a paid question in a private personal message. Be healthy!
Source of the article: https://sprosivracha.com/questions/234776-posle-biopsii-tyanet-niz-zhivota
Limitations of the method and possible errors
The diagnostic capabilities of MRI depend on the resolution of the device and the professionalism of the doctor. The minimum thickness of the object visualized in the image depends on the power of the device’s magnetic field. Images obtained using low-field MRI systems do not have sufficient diagnostic accuracy for the early detection of tumors.
Certain limitations exist in the diagnosis of diseases of the lungs and skeletal system using MRI, but they do not apply to the detection of oncological processes. Lung and bone tumors can be detected using magnetic resonance.
Examination of the lungs and skeletal system has its own characteristics, but this has nothing to do with the diagnosis of tumors:
- Lungs: due to high airiness and low fluid content, broncho-alveolar tissue is poorly visualized on MRI, so diseases accompanied by its diffuse changes are better diagnosed using CT. Benign tumors or lung cancer, like other focal formations, are clearly visible on magnetic resonance images. Bone is low in water, and therefore itself gives a weak signal on MRI, unlike the bone marrow it contains. With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor can detect any changes in the structure of the bone marrow and tumor tissue other than bone.
Consequences of the procedure
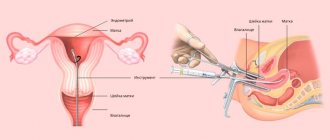
In the diagnosis of sexual diseases, cervical biopsy plays a very important role. Sometimes it is difficult for a gynecologist to identify the causes of diseases, bleeding, erosion or infections with a simple examination on the chair. Therefore, for a more accurate diagnosis of cervical pathologies, a biopsy is prescribed.
During a biopsy, a sample of the most altered area of the cervix is taken and sent for histological examination. The tissue is taken with special forceps, which pinch off a few millimeters of uterine tissue.
Tissue collection is done without the use of general anesthesia. This is a plus for those who find it difficult to tolerate anesthesia.
There are some possible consequences after a cervical biopsy. To avoid them, you need to follow several rules.
First, before the biopsy you need to pass the necessary tests. This includes cytology, ultrasound of the pelvic area, and blood tests. Consultation with a gynecologist regarding a biopsy is required. The procedure itself must be carried out with the help of a colposcope, which helps to determine the most affected areas of the cervix and make the most accurate diagnosis based on the results of tissue examination.
It is better to carry out the procedure itself immediately after menstruation, since before the onset of the next menstrual cycle, the wound must heal completely so as not to cause complications. After a biopsy, a wound is formed that may bleed. It is treated with hydrogen peroxide and a substance that stops the blood. If the bleeding intensifies, then you have to put stitches or cauterize the wound.
The consequences of a cervical biopsy vary from person to person. The most common are:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen that lasts up to five days. Sometimes they have the nature of contractions
- Severe bleeding, in which case you should immediately consult a doctor to get stitches in the cervical area.
- It is also possible that an infection may develop, especially if it has not been completely cured before the biopsy. In such cases, antibiotics are taken.
There is a list of complications for which you should definitely consult a gynecologist: fever, heavy discharge, heavy bleeding and blood clots separating from the genital tract.
Hardware biopsy not only avoids bleeding, but also prevents the formation of scars that can lead to rupture of the cervix during childbirth.
No votes yet
To identify various unpleasant diseases, doctors use a research method such as a biopsy. It has also become widespread in gynecology, to detect, for example, cervical cancer.
But many women try to avoid this procedure, fearing various complications.
The consequences of a cervical biopsy, as well as any other minor surgical procedure, can be as follows:
- Bleeding. Sometimes a suture must be placed to stop it;
- Development of infection in the wound from which tissue was taken for analysis.
But it is worth noting that these consequences of cervical biopsy occur only in 0.5% of cases during this procedure. This is a minor complication compared to the number of diseases identified and prevented using this analysis.
Diagnostic procedure
Often, the same tests are performed for all cases of oncology. We will try to explain how important histology is.
- A possible patient comes to the doctor with complaints, or it may be a routine examination.
- The doctor palpates, examines and interviews the patient.
- If there is a suspicion of cancer, then he is sent for tests - a general and biochemical blood test and stool.
- If there are abnormalities in the tests, the patient is referred to an oncologist.
- An X-ray and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are performed.
- If the patient has clear symptoms, then the diagnosis of a specific organ begins.
- If a pronounced tumor is present, a sampling is made.
- And then a biopsy is performed and a piece of tissue is sent for histology.
- Afterwards, a CT or MRI may be performed. This is necessary to determine the degree of invasion - how much the cancer tumor affects nearby healthy cells and tissues.
Only after a thorough diagnosis does the doctor make a final diagnosis and come up with a strategy to combat the disease.
Prostate biopsy
A prostate biopsy is an outpatient procedure performed to diagnose prostate (prostate) cancer and its stage.
During the procedure, the urologist receives biopsy material (samples of prostate tissue), which is sent to histological and cytological laboratories, where an analysis will be made and a conclusion will be given.
If the presence of prostate cancer is confirmed, treatment tactics are selected based on the results of the biopsy.
Indications for primary biopsy
A primary biopsy of the prostate gland is prescribed by a urologist in case of suspected prostate cancer. Indications for primary biopsy are:
detection of a hypoechoic zone in the prostate gland during ultrasound. Ultrasound examinations can be performed through the abdomen (transabdominal) or through the rectum (transrectal);
the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level is above the normal limit, i.e. above 4 ng/ml;
the presence of a node or compaction in the prostate gland during digital rectal examination.
Indications for repeat biopsy
A repeat prostate biopsy is performed if the results of the initial biopsy are negative, as well as with the following indicators:
- continued rise in PSA levels;
- persistently elevated PSA levels;
- PSA density more than 15%;
- the ratio of free to total PSA level is less than 10%;
- detection of high grade PIN (prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia) during primary biopsy;
- insufficient amount of material.
Note that PSA is a prostate-specific antigen, which is a marker for the presence of prostate cancer (only if the concentration is exceeded).
Contraindications for biopsy
Almost any procedure has contraindications, and prostate biopsy is no exception. Relative contraindications include:
- the patient is taking anticoagulants;
- bleeding from the rectum;
- active inflammatory process in the rectum;
- acute prostatitis;
- presence of feces in the rectum.
An absolute contraindication is the patient's refusal to undergo the procedure.
Preparing for a biopsy
In order for the prostate biopsy to take place without inflammatory complications, you should properly prepare for the procedure and adhere to the following recommendations:
- When visiting a doctor, you must bring the results of examinations: general urine test, general blood test, urine culture for flora;
- If you are taking anticoagulants, you should notify your doctor and stop taking the medications seven days before taking them. If this is not possible, the biopsy should be performed in a hospital setting;
- it is necessary to inform the doctor about existing chronic diseases and diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- it is necessary to warn the doctor about drug intolerance;
- In the evening before the procedure, it is better not to have dinner, and in the morning - a light breakfast.
Anesthesia for biopsy
A prostate biopsy is usually a painless procedure and is performed without anesthesia. However, for some patients, anesthesia is used, but this can cause complications.
The most appropriate is the use of local anesthetic gels.
Biopsy techniques
1. Blind biopsy or digitally controlled prostate biopsy. In this case, the patient is placed on his right side and asked to tuck his legs toward his stomach, after which local anesthesia of the rectum is performed. Under finger control, a puncture needle is inserted into the rectum and 4-6 punctures are made.
The disadvantage of this method is insufficient needle control and limited material sampling. Today, the blind biopsy method is practically not used.
2. Ultrasound-guided multifocal (polyfocal) prostate biopsy is the most common method. The material for the study is taken from 12 points.
3. Saturation prostate biopsy is the most advanced technique in which a tissue sample is taken from 24 points, resulting in a more accurate examination.
Complications after prostate biopsy:
- blood in urine and stool;
- temperature increase;
- acute orchiepididymitis (inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis);
- acute urinary retention;
- difficulty urinating;
- sepsis;
- loss of consciousness during the procedure.
These complications are extremely unlikely, but if one of the complications occurs, you must notify your doctor.
The urological clinic of the European Medical Center has modern equipment and uses progressive and effective techniques. The professional team of doctors at the Urology Clinic will do everything possible to maintain and restore the health of patients.
Source: //www.emcmos.ru/articles/biopsiya-predstatelnoy-zhelezy
Do you know any cases where the cancer diagnosis turned out to be wrong?
They found lymphoma. For some reason the doctor mumbles and tells her she needs to think. I can't believe it myself. Of course, I will go further for examination, but again it will take a lot of time. Are there cases when a diagnosis of cancer is made based on a biopsy, but further research shows that it was an erroneous diagnosis?
My friend had a tumor on her neck, they went through the best doctors in Russia, all of them unanimously claimed that it was oncology. But she didn’t believe it, went to Germany, where they told her that it was because of wisdom teeth, and it’s good that they hadn’t done chemotherapy yet, otherwise they often come from Russia after chemotherapy, but there was no trace of oncology. A friend had her wisdom teeth pulled out and everything went away.
My mother's tests were mixed up and they announced that she had cancer. Then everything became clear.
I know. From the godbrother. They said it was a tumor in the brain. I was examined through a pressure chamber, everything turned out to be clean.
My aunt was diagnosed with stage 3 breast cancer, stage 3-4 is practically a death sentence, they only made a mistake with the stage, the breast was removed, but she is alive and well, this was 12 years ago.
My late mother-in-law said this. Not just one doctor, either. He was treated with chemotherapy. the truth was revealed only during the autopsy. It turned out to be Crohn's disease. I don’t know how this could be mixed up. But the morgue didn’t want to talk. They have an agreement with hospitals - they “don’t burn” doctors. I had to try very hard and promise not to sue so that the truth would be told.
And I know of cases (there are many of them) when the breast was removed, but it turned out that it was not cancer. And vice versa, the puncture showed that there was a benign formation in the breast, and then histology determined that it was cancer. True, stage 1
Cases of pseudo-diagnosis are now practiced. Absolutely healthy people are diagnosed with cancer in order to extract money for treatment. Look for information on the Internet, there are a lot of such cases. My mother’s colleague was once diagnosed with breast cancer. She did not go to other clinics to retake tests and make sure that everything was fine with her. As a result, the breast was removed, and then it turned out that there was no trace of cancer.
I know many cases of breast cancer where a healthy breast was removed. For doctors, everything is simple: if you have breasts, there is a problem, if you don’t have breasts, there is no problem. And how many were then poisoned with chemicals! I once overheard a conversation in a hospital where it was not definitely determined whether a woman had cancer or not. The doctor was on vacation and they suggested to her: well, if you want (.), we will remove your breast.
It happens, of course, but these cases are rare, mostly the stage can be mistaken. It’s a terrible thing, my husband died of stage 4 stomach cancer. They diagnosed gastritis and stomach ulcers, and then cancer developed! They didn’t operate on time and burned out within 2 months!
5. The biopsy shows what cells the tumor consists of. Unfortunately, it is impossible to mix up the cells