What are endometrial polyps and what are they?
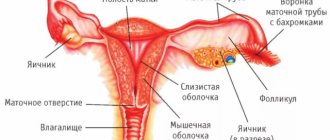
The inner surface of the uterus is covered with endometrium. It is to this that the fertilized egg should be attached, and it is this that is separated with the blood during menstruation if conception does not occur.
Normally, the endometrium is smooth. But sometimes growths appear on it the size of a sesame seed to a golf ball and even larger. These are Uterine polyps of the endometrium. They have connective tissue and blood vessels inside, so they do not disappear during menstruation and continue to grow.
One or more polyps may appear in the uterus. And they can look completely different. Some stretch out on a thin stalk and hang like a pear into the uterine cavity or extend into the vagina Uterine polyps. Others form a wide base and protrude into a mound.
Image: Marochkina Anastasiia / Shutterstock / Lifehacker
In addition, they may have different histological structures of Uterine Polyps. That is, some have the correct order of layers of normal cells, while others have tortuous vessels, disrupted tissue structure and cells that can degenerate into cancer.
Polyps can occur at any age, but Uterine Polyps are most common in women 40–50 years old.
What clinical picture is accompanied by uterine prolapse.
Uterine prolapse (look for a photo and description of the disease in the article) in the first stages may not manifest itself with any specific symptoms . Subsequently, as a rule, the following appear:
- mild, rare pain in the lower abdomen, as well as in the genital area (after lowering, the uterus begins to put pressure on neighboring organs);
- a foreign body is constantly felt in the vagina;
- Frequent urination is observed during the day;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movements and regular constipation;
- severe leucorrhoea between menses;
- during physical activity, air is pumped inside the vagina, in particular during intimacy;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Why do polyps appear in the uterus?
Scientists believe that the main endometrial polyps. Etiology and pathogenesis The cause of endometrial polyps is an increase in estrogen levels. If there are too many of them in the blood, this is absolute hyperestrogenism. But more common is relative, when estrogens are normal and progesterone is not enough. This is exactly what happens after 40 years: when ovulation stops, progesterone stops being produced.
Research says that hyperestrogenism, and therefore polyps, most often appear Uterine Polyps with:
- Overweight. Estrogen is produced not only by the ovaries, but also by adipose tissue. As long as there is little of it, the hormonal levels do not suffer. And when there is a lot, problems begin.
- Arterial hypertension. It, as a rule, Obesity and arterial hypertension: pathophysiological features, diagnosis and treatment, occurs in women with excess body weight.
- Taking tamoxifen. It is prescribed for the treatment of breast cancer. It blocks estrogen receptors in cells and prevents it from stimulating tumor growth. But the hormone remains in the blood, so it looks for other points of application and finds the endometrium in the uterus.
- Endometrial replacement polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment of hormonal therapy in postmenopause. In this case, estrogens are introduced into the body.
With chronic inflammation of the uterus, polyps may also appear due to the fact that endometrial cells begin to divide incorrectly.
Excitation of the uterus is a sign of an enchanting orgasm
Almost all of us know how to get sexual pleasure. Many people love it and would like to experience it again and again. But not everyone can feel a real orgasm. The difference between these two concepts is that we get pleasure from sex on an emotional level, and orgasm on a physiological level. That is why it is not difficult to understand what is what.
Orgasm is divided into several types: genital, breast and whole body orgasm. At the same time, genital orgasm is the most common among its kind. And although such an orgasm does not last long, nevertheless, the sensations after it leave a significant mark on your subconscious. In turn, genital orgasm is divided into three more subtypes: vaginal, clitoral and uterine, they are all interconnected, so we will consider all three.
Vaginal orgasm
The methods of arousal for experiencing this orgasm are associated with the muscle that is located in the lower part of the vagina. But an undeveloped muscle, which is typical for most women, negates the possibility of such an orgasm. Therefore, only a few can experience a vaginal orgasm. In order to become aroused, it is necessary to synchronize the contraction of the vagina and the lifting of the pelvis.
Clitoral orgasm
Clitoral orgasm occurs due to stimulation of the clitoris. In most cases, it is experienced by girls who masturbate. To do this, after they are left alone, they turn on a film containing scenes of a pornographic nature, and, being in a completely relaxed state, stimulate their clitoris. It is not so easy to get such an orgasm with a partner, since relaxation plays the most significant role, but with a man it is very difficult to be in such a state.
Uterine orgasm
For some reason, arousal of the uterus is not considered by doctors as thoroughly as other types of orgasm. However, many women experience it, so it is worth giving it the right to life. Strong arousal occurs as a result of the penis irritating the cervix, causing it to contract. But this is not always possible due to the fact that not every man has a penis that can reach the cervix, or it happens that during sexual intercourse it simply passes without even touching it.
In order to prevent this from happening and the stimulation of the uterus still causes a storm of emotions in you, you need to know a few secrets. The first and very simple way is to simply change your position. The pose will especially help when you lie on your back, the man is on top of you, and at the same time your legs are pulled up to your stomach. Another position that allows you to feel the excitement of the uterus is when a man, lying on his back, holds a woman sitting on him with her legs tucked in by the waist.
Another reason why it is impossible to experience a uterine orgasm is that the uterus is not positioned correctly in your body. But that’s not scary either. To keep the uterus in place, you need to change your position again. This time it is best for the woman to lie on her stomach or side.
Another way that guarantees 100% uterine orgasm is anal sex. But for some reason, many females refuse it, considering such sex to be something vulgar and unacceptable.
To understand how uterine arousal occurs, it is necessary to have a very good understanding of human physiology. Changes occur with very strong sexual arousal. The increased blood flow contributes to the swelling of the uterus almost twice. Such an orgasm is especially noticeable and is remembered for a long time, since the sensations in the uterine area resemble cramps.
Signs of girls' excitement appear not only externally, but also internally. So, for example, if a girl is calm, then the vagina has a maximally narrowed gap, which during arousal increases in all directions by more than half. In this case, the body of the uterus and cervix take on a slightly elongated shape. Also in the upper part of the vagina, which increases by almost 3 cm when aroused, a place for sperm appears next to the cervix.
Love - and feel in seventh heaven!
Why are endometrial polyps dangerous?
Most often, an endometrial polyp is a benign formation. It cannot grow into surrounding tissues, does not metastasize, and its cells do not differ in structure from the rest of the mucous membrane. But there is always a risk of complications:
- Degeneration into cancer. According to statistics Atypical Endometrial Polyps and Concurrent Endometrial Cancer: A Systematic Review, transition to a malignant tumor occurs in 5.6% of women with atypical endometrial polyps. This is a type of formation in which the cells have an immature structure, an altered nucleus and an incorrect location in the tissue layers.
- Chronic anemia. Polyps cause uterine bleeding. If it is repeated frequently, the level of hemoglobin in the blood decreases.
- Infertility. It is believed that polyps can prevent sperm from entering the fallopian tube or prevent the embryo from implanting into the wall of the uterus. Infertility is associated with Endometrial polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment with polyps in 3.8–38.5% of cases.
What symptoms can you use to recognize polyps in the uterus?
Often polyps do not cause any inconvenience at all; they are accidentally found during examination. But sometimes symptoms of Uterine polyps appear, in which you need to consult a gynecologist:
- The menstrual cycle has gone wrong: a different number of days pass between periods each time, the cycle has become more than 35 or less than 21 days.
- Between menstruation, spotting or heavy bleeding appears.
- I've been through menopause for a long time, but suddenly there was blood on my underwear.
- Menstruation has become noticeably heavier, and you have to use more pads or tampons.
- Attempts to get pregnant are unsuccessful.
Urgently go to the gynecologist or call an ambulance if the pad overflows and leaks in less than 2 hours. This is a sign of severe uterine bleeding, which can be life-threatening.
How are endometrial polyps diagnosed?
The polyp is almost impossible to notice during a gynecological examination. The exception is if it is large and comes out of the cervix. Therefore, special diagnostics of Endometrial polyps are needed: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment:
- Transvaginal ultrasound. It is done on the 10th day of the menstrual cycle. The research method is quite simple, but not always accurate: a polyp can be overlooked or confused with fibroids. Therefore, additional examination is needed.
- Dopplerography, or color Doppler mapping. A special ultrasound mode that shows blood flow in the vessels in blue and red colors. Helps to find the artery feeding the polyp.
- Sonohysterography. An ultrasound method in which saline solution is pumped into the uterus. The liquid expands the cavity, helps to distinguish a polyp from a fibroid and to see even small formations: they will sway with the movement of water.
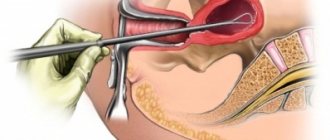
- Hysteroscopy. Under anesthesia, a flexible tube with a video camera is inserted into the uterus of a woman. The method helps to examine the polyp and the entire uterus, do a biopsy - take some tissue for examination under a microscope. During diagnostic hysteroscopy, the polyp can be removed.
It is possible to accurately say about the structure of a polyp and assess the risk of degeneration into cancer only after studying its tissues during a histological examination.
Basal temperature from A to Z
Pap smear - or more simply, a cytological smear.
These two photographs were taken while a smear was taken for cytology on a 25 year old woman 6 weeks after giving birth. The smear can detect potentially precancerous changes (called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical dysplasia), which is usually caused by the sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV). The test can also detect infections and disorders of the endocervix and endometrium.
In the top photo you can see a metal reflector used to open the vagina (a speculum) and a wooden spatula used to collect cell samples from the cervical canal. Use a spatula to clean the area around the cervical canal in a circular motion to collect the cells. In the bottom photo you see how the brush was inserted into the CC of the cervix. The cells are collected with a brush and applied to a glass slide with a spatula and examined in the laboratory or under a microscope.
Cervix after abortion. 26 days after the abortion was performed. This woman is 29 years old. She gave birth twice (6 and 10 years ago). At 7 weeks pregnant, she had some bleeding and went to the hospital for an ultrasound. Specialists didn't see a fetus in her uterus, so her doctor prescribed her a drug to clean out her uterus after what they thought was an incomplete miscarriage. They later learned that it was a misdiagnosis, but the drug she was prescribed was too toxic to continue the pregnancy, so the doctor was forced to perform an abortion. The doctor gave her an IUD after the abortion (note the black strings) because he advised her not to get pregnant again for at least 3 more menstrual cycles.
Colposcopy Colposcopy is a method for diagnosing diseases of the female reproductive system. It is carried out with a special device called a colposcope. These photographs were taken during a colposcopy on a 33-year-old woman. She also underwent a procedure to remove the transformation zone, which is also called LLETZ electrosurgical excision. She hasn't given birth and you can see her CB is round. Her smear came back with abnormal results due to HPV. At the next appointment, acetic acid/iodine was applied to the cervix to better highlight the abnormal cells. The tissue sample came back very bad, so she returned to the clinic again for the LLETZ procedure (photo below). This was performed with local anesthesia. This photo of the cervix is a colposcope view (on the TV screen) as the procedure begins. This photo shows how after applying acetic acid and iodine solution to the cervix, the solution temporarily stains the cervix and helps visualize any abnormal cells in the transformation zone (where many precancerous and cancerous lesions often occur). White areas indicate atypical cells. She experienced slight discomfort when the tissue was cut out with a loop. But the sensation disappeared after a moment, and she no longer felt the cauterization itself. She said she smelled something burning. Additional cauterization will stop the bleeding. If you look closely, you can see a small blue flame above the instrument on the cervix. This is a sample of abnormal tissue in a jar. The biopsy showed CIN2 (precancerous) without clear outlines (however, since the edge of the tissue was burned, they could not see the true field). Later that evening she had some minor cramping but no pain afterwards. She had slight bleeding for about 5 days. She was given antibiotics for inflammation. She was required to abstain from sex, tampons, swimming, hard work, tension, etc. She had a smear test 6 months after the procedure, which fortunately came back normal. The CC hole is now larger than it was.
Before and during colposcopy. This is the cervix of a 23-year-old woman who has no history of STDs and has never been pregnant. A speculum is inserted and the doctor uses a colposcope to illuminate and magnify the inside of the vagina and cervix so he can see what the naked eye cannot see. Sometimes vinegar or iodine is applied. The doctor may also take a biopsy, or tissue sample, from the surface of the cervix and cervical canal to send to a laboratory for further testing. During colposcopy.
This photo was taken during a colposcopy after abnormal cells were found in her Pap smear results. A biopsy confirmed the presence of abnormal cells, etc.
Two months after the procedure, she received an IUD.
How are polyps in the uterus treated?
Differently. The gynecologist will remove the tumor, prescribe medications or suggest waiting for Uterine polyps. Some studies of Endometrial polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment say that a polyp up to 10 millimeters that does not bother you can simply disappear within a year. You just need to see a doctor regularly.
Polyp removal
Scientists have not yet decided Endometrial polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment, whether it is necessary to remove all endometrial polyps. But in case of bleeding, pregnancy planning, cycle disorders, doctors recommend removing even small tumors. This will help The clinical significance of small endometrial polyps return normal menstruation.
There are three methods for removing a polyp:
- Curettage of the uterus. Under anesthesia, using a special metal loop, the entire mucous membrane of the uterus is removed and sent for histological examination. The method is suitable for small polyps.
- Hysteroscopy. This is the main treatment method. The doctor can see the location of the polyp, carefully remove the polyp using an electric loop, and cauterize its base. After surgery, some bleeding may persist for 1–2 days.
- Uterus removal. Uterine Polyps: Management and Treatment is used if malignant cells are found in the polyp. This will protect you from cancer and death.
Drug treatment
Gynecologists prescribe Uterine Polyps: Management and Treatment hormones in tablets or injections or install a hormonal coil Endometrial polyps: Pathogenesis, sequelae and treatment. The goal is to reduce the production of your own estrogens or block their effect on the endometrium.
But the effect of all this is temporary. Uterine polyps. While the woman receives hormones, the size of the polyps decreases, the symptoms disappear, and as soon as she stops, everything returns to normal.
Therefore, medications are prescribed if it is necessary to postpone surgery for several months or immediately after removal of a polyp in order to reduce the risk of relapse.