This entry was checked by Ekaterina Alekseevna Barashkova - obstetrician, obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, reproductive specialist
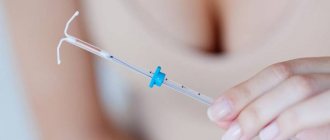
Is it worth or not to install a spiral? This question is asked by many women who choose a method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. An intrauterine device is a device (usually made of plastic with gold, copper or silver) that acts as a barrier to the attachment of an egg to the walls of the uterus.
What types of intrauterine device are offered today , what is better to choose, and what might be the risk of installation?
The IUD is not a fertilization blocker. Fertilization of the egg in women occurs in the ampullary section of the fallopian tube. And within 5 days, the already dividing embryo enters the uterine cavity where it is implanted into the endometrium.
The principle of any IUD device that does not contain hormones is the creation of aseptic inflammation, that is, unfavorable conditions, in the uterine cavity. There will always be fertilization, but there will not be implantation.
Complications and side effects of the IUD
Intrauterine contraceptives are generally well tolerated, so side effects are uncommon. In addition, unpleasant symptoms are most pronounced in the first three months of using the spiral, and then most often disappear completely.
Complications when using an IUD are also quite rare; their development is most often associated with the following unfavorable factors:
:
- underestimation of contraindications (use of the IUD by women at risk of developing inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, small or deformed uterine cavity, etc.);
- the woman’s failure to comply with the doctor’s recommendations;
- inexperience of the specialist installing the spiral;
- purchasing a low-quality spiral.
The most common complications when using an intrauterine device are pathologies such as (arranged in descending order of frequency of occurrence):
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- severe pain syndrome;
- spiral rejection;
- severe bleeding requiring drug therapy.
Other consequences of using the IUD that are dangerous to a woman’s health are extremely rare. For convenience, all complications associated with the use of IUDs are classified according to the time of occurrence.
:
- complications related directly to the installation of the spiral;
- complications that arise during the use of the spiral;
- complications that appear after removal of the coil.
Purpose and types of intrauterine devices
Purpose of application:
- prevents the entry of male germ cells into the cavity of the fallopian tubes;
- shortens the lifespan of the egg;
- reduces the number of active sperm;
- creates inflammation in the uterus that is harmless to the body, which prevents the embryo from penetrating through the wall of the uterus.
Advantages of different types of IUDs:
Copper and silver spirals are easy and safe to use, and, most importantly, quite durable: their shelf life is about 10 years. They are not suitable only for women who are allergic to these metals. The effectiveness of the IUD is 98%.
Today you can buy intrauterine devices containing levonorgestrel. Their action is based on the fact that a small amount of hormones is released, thereby reducing the risk of pregnancy. They are much more expensive and their shelf life is about 5 years, but the effectiveness of this product is 0.5% higher.
Perforation of the uterus
Perforation (perforation) of the uterus is an extremely rare complication and occurs more often in young, non-pregnant and/or nulliparous women, usually when the IUD insertion technique is violated.
Perforation of the uterus can be complete or partial. You can suspect a perforation of the uterus if characteristic symptoms occur
: severe pain syndrome occurring against the background of symptoms of intra-abdominal bleeding (drop in blood pressure, increase in heart rate, pallor of the skin).
In some cases, usually with incomplete perforation of the uterus, the pathology may manifest itself some time after installation of the coil with severe, unremitting pain in the lower abdomen.
If uterine perforation is suspected, hysteroscopy or ultrasound is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis. In case of incomplete perforation, it is possible to remove the device through the vagina and use conservative therapy.
If there is a complete perforation of the uterine wall, the spiral is removed through abdominal access, and the uterine defect is sutured. In this case, the laparoscopic method is most often used (an optical fiber is inserted through a small hole in the abdominal wall with a video camera that transmits the image to the monitor screen, and the instruments with which the operation is performed).
In extremely severe cases, they resort to amputation of the uterus.
Vasovagal reaction
Not life-threatening, but a very unpleasant complication. It occurs most often in nulliparous women with a narrow cervical canal, as an increased reaction of the vagus nerve to pain and emotional reaction to the procedure. It manifests itself as a sharp pallor of the skin, a drop in blood pressure and a slowing of the heart rate; in severe cases, fainting may develop.
If a vasovagal reaction occurs, it is necessary to pause the insertion of the IUD and reassure the patient. When symptoms of fainting begin, a cold compress is placed on the forehead, the head end is lowered, and the legs are raised up, thus ensuring blood flow to the head.
When fainting, the patient's head is turned to one side to avoid aspiration of stomach contents into the respiratory tract in case of vomiting. In case of severe pain, analgesics (analgin or ibuprofen) are administered.
Vasovagal reaction does not require drug treatment, but further observation is necessary to exclude the presence of such serious complications as uterine perforation.
To prevent a vasovagal reaction, it is advisable for women at risk to undergo local (paracervical) anesthesia when installing the IUD.
Side effects and complications that may occur when using any type of IUD
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs are one of the most common complications of the use of intrauterine devices and are observed in approximately 4-14% of cases of IUD installation.
As a rule, these complications arise when contraindications to the use of IUDs are underestimated, such as acute and subacute inflammatory processes in the female genital area at the time of installation of the device or an increased risk of developing sexually transmitted diseases due to the presence of several sexual partners.
According to a large-scale study of women with PID that developed due to the use of an intrauterine device, it turned out that in 65% of cases the causative agent of the inflammatory process was sexually transmitted infections, and only in 30% of cases - nonspecific microflora.
PID is dangerous due to severe complications such as
: chronic pelvic pain syndrome, ectopic pregnancy (occurs as a result of obstruction of the fallopian tubes), infertility. Therefore, if you suspect the development of infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvis, you should urgently consult a doctor.
The most common signs of PID are
:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying during or after menstruation;
- fever, nausea, vomiting (in acute process);
- dysuria (frequent urge to urinate, pain when urinating);
- purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Therapy for PID consists of prescribing antibacterial drugs based on the pathogen that caused the disease.
The development of acute PID is an indication for removal of the IUD, which is carried out against the background of antibiotic therapy.
About complications of an ingrown IUD
The most common complications of an ingrown IUD are: inflammation, bleeding, chronic endometritis. Normal and acceptable symptoms after surgery are:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding in small quantities;
- discomfort in the pelvic area;
- muscle spasms in the abdomen.
If symptoms do not go away after 5-7 days, you should seek medical help from your doctor.
If purulent or brown discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, body temperature rises, or health deteriorates after removal of the IUD, you should consult a gynecologist.
After conducting a series of studies and diagnostics, the specialist will be able to determine the reason for the deterioration in the woman’s well-being and prescribe a course of therapy.
Expulsion
Expulsion (rejection) of the IUD is also a relatively common complication (5-16% of cases when using copper-containing IUDs and 5-6% of cases when using the Mirena hormonal intrauterine system).
Young nulliparous women are most susceptible to this complication. With age, as well as with an increase in the number of pregnancies (including those that ended in abortion), the likelihood of expulsion decreases.
Most often, this complication develops in the first days or first three months after installation of the IUD. Often, especially in the first days and weeks after installation, expulsion is accompanied by intense cramping pain in the lower abdomen, which is practically not relieved by analgesics and antispasmodics.
In such cases, differential diagnosis with other complications is necessary, such as inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, ectopic pregnancy, and interrupted physiological pregnancy.
If intense pain that cannot be relieved by analgesics and antispasmodics occurs in the first days after installation of the IUD, it may indicate an incorrect position of the IUD, a mismatch between the IUD and the size of the uterine cavity, or such a serious complication as uterine perforation.
To clarify the causes of pain, ultrasound or hysteroscopy is usually prescribed. In case of IUD expulsion, the woman is advised to choose another method of contraception.
However, the IUD can fall out relatively painlessly, so women using an IUD should regularly (after every period) check for the presence of the IUD tendrils at the cervix.
In cases where the antennae of the spiral cannot be felt, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. As a rule, an ultrasound is prescribed to determine the location of the spiral. If the study shows that there is no IUD in the uterus, you should either insert a new IUD or choose another method of contraception.
Intrauterine device: pros and cons of this method of contraception
It may be time for you to ditch condoms and birth control pills and try something new.
Photo https://www.onclinic-ryazan.ru/lechebnyj-tsentr/gynecology/intrauterine-device/
What is an intrauterine device and how does it work?
Intrauterine devices are contraceptives, a means of controlling the onset of pregnancy. Their effectiveness is very high: when used correctly, they protect against pregnancy by 99%. They are even used for emergency contraception after unprotected sex.
Externally, most of the spirals that are now used resemble the letter T with different tails. But there are intrauterine implants of other forms.
Spirals are divided into two large types:
1. Copper intrauterine device
The principle of operation is this: copper supports aseptic inflammation in the uterus. Aseptic means that it does not happen due to microbes and does not threaten anything. But the action of copper changes the composition of cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to penetrate the uterine cavity. In addition, copper prevents the egg from attaching to the wall of the uterus.
2. Intrauterine device with a hormonal component
These are plastic coils that contain progesterone, an analogue of the human hormone that prevents pregnancy. They also interfere with sperm and egg implantation, and at the same time also suppress ovulation in some women.
How long does an intrauterine device work?
Spirals from different manufacturers and with different compositions are installed for a period of three to ten years.
An intrauterine device costs quite a lot: from several thousand rubles (including the installation procedure). However, it quickly pays for itself and is one of the most affordable methods of contraception for women who have regular sex life.
How to install a spiral
Only a doctor can install any type of spiral, and the same can remove it. Therefore, you cannot do without consulting a specialist who will help you choose a product (with copper or hormones) and decide on the installation.
This is usually a simple procedure, but an extremely rare complication is uterine perforation. Sometimes the spiral may fall out. Therefore, in the first three months you need to regularly visit the gynecologist; the doctor himself will prescribe a schedule.
After installation, the spiral is not felt, only two short antennae are released from the cervical canal (from the cervix). These are threads that help make sure that the spiral is in place. Subsequently, they will help the gynecologist remove the IUD.
These same mustaches do not interfere in everyday life, including during sex.
Sometimes after installation a woman may feel discomfort and dizziness, but they pass quite quickly. The procedure itself is not very pleasant, but not much worse than a regular examination by a gynecologist.
What are the advantages of an intrauterine device?
The main advantage is the reliability of contraception. Nothing here depends on the woman, her partner or a host of external factors. Condoms break, you can forget about the pill, but the coil stays in place and doesn’t go anywhere.
In addition, the IUD can be used by breastfeeding women who cannot afford, for example, hormonal contraceptives.
In most cases, women do not notice the spiral at all.
Contrary to popular belief, the IUD can be installed in women who have never given birth or become pregnant before (but it is better to use the IUD after 20 years, when the internal organs are fully formed). IUDs have a reversible effect, and you can get pregnant literally in the first month after removing the IUD.
In addition, IUDs do not increase the risk of cancer and can be combined with any medications.
When should you not insert an intrauterine device?
There are not many contraindications:
- Pregnancy. If you want to use the IUD as emergency contraception, you need to hurry.
- Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs (including sexually transmitted diseases or those associated with complications after termination of pregnancy). That is, we first treat infections, then introduce the IUD.
- Oncological diseases of the uterus or cervix.
- Vaginal bleeding of unknown origin.
- There are additional restrictions for the IUD with hormones, just like for taking hormonal contraceptives.
What side effects may there be
Apart from complications when installing the IUD, the most common side effect is changes in the menstrual cycle. As a rule, periods become heavier and last longer. This is especially noticeable in the first months after the installation of the spirals.
Sometimes bleeding becomes too heavy and long, bleeding appears between cycles - in any case, this should be discussed with your doctor. Sometimes you have to abandon this method of contraception.
IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections, and in some cases increase the risk of an ascending genital tract infection. Therefore, with a new partner you need to use additional methods of contraception.
What happens if you get pregnant while on the IUD?
Although the IUD is one of the most reliable methods, pregnancy is rarely possible. If a woman decides to keep the child, they try to remove the IUD at an early stage so as not to damage the amniotic sac and cause a miscarriage.
Source
We try very hard to find the most useful things for you and are very happy about every like))) Subscribe to us, we always have a lot of interesting things)))
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5af039c548c85e9c0f6ce062/vnutrimatochnaia-spiral-pliusy-i-minusy-etogo-metoda-kontracepcii-5b02eb237ddde8be6c50b808
Prolonged and/or heavy bleeding
According to WHO recommendations, prolonged bleeding can be said when it lasts more than 8 days, and heavy bleeding can be said when it is twice as strong as usual.
Prolonged and/or heavy bleeding when using copper-containing IUDs most often occurs in the first months after installation of the coil. As a rule, they do not require special therapy.
However, in case of severe and/or profuse bleeding, you should consult a doctor, since it may be a symptom of a pathology, for example, an ectopic pregnancy, uterine perforation, or a spontaneously terminated physiological pregnancy.
If more than three to six months have passed since the installation of the IUD, and bleeding continues to be prolonged and/or heavy, so that signs of iron deficiency anemia appear, then it is better to remove the IUD and choose another method of contraception.
If a woman wishes, the copper-containing IUD can be replaced with a hormonal system, then the gestagens entering the uterine cavity will help reduce menstrual blood loss.
Indications for removal of the intrauterine device
There are a number of symptoms that may occur in women who have inserted the IUD. Thanks to them, even before examination using an ultrasound or gynecological examination, it is possible to determine that the spiral has grown into the wall of the uterus. These may be the following indications:
- pain of varying strength in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, pelvis and bladder;
- severe weakness;
- pallor;
- tachycardia;
- bleeding.
Serious signs such as bleeding and severe pain are extremely rare in women. Therefore, to prevent these symptoms, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist in time.
Procedure for removing an ingrown IUD
How the operation to remove an ingrown IUD into the wall of the uterus will be performed largely depends on its location. If the contraceptive is located close enough to internal organs or the walls of large vessels, then removal will be quite difficult and time-consuming.
The operation takes place in several stages:
- A hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity.
- Using laparoscopic forceps, the doctor removes the spiral, making his way to it from the abdominal cavity.
- If most of the spiral is located in the thickness of the walls of the uterus, then the doctor is forced to perform a laparotomy.
- Hysteroscopic forceps can be used to remove an ingrown intrauterine device if only a small part of it has entered the uterus.
Rehabilitation period
There is no need to follow any special regimen after the procedure to remove a contraceptive that has grown into the uterus. A few hours after the operation, the patient can go home. She must comply with the following recommendations:
- carefully monitor personal hygiene;
- limit physical activity.
Cramping pain in the lower abdomen
Cramping pain in the lower abdomen often bothers women during the first three months after installation of the IUD. This side effect is more common in young, non-pregnant and/or nulliparous women.
If the pain syndrome reaches a high intensity, you should consult a doctor to rule out pathologies such as ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous termination of a physiological pregnancy, IUD rejection, uterine perforation, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, etc.
However, clinical experience shows that in most cases, severe pain is an unpleasant side effect of a copper-containing IUD.
If the pain is very severe and/or continues to bother the woman three to four months after the installation of the IUD, then it is better to replace the copper-containing IUD with a hormonal system, or remove the IUD and choose another method of contraception.
Reviews from women and specialists
Feedback from patients and specialists allows us to conclude that the intrauterine device is a highly effective means of contraception, which has been used abroad and in domestic practice for decades.
In recent years, the IUD has become affordable. It is easy to install, the procedure itself takes no more than 15 minutes. The process is painless if there are no contraindications, and it is carried out by an experienced specialist.
An additional advantage is that installation of this product is possible at any age. Some women in their reviews say that they had the IUD for almost the entire period of their reproductive years.
A natural occurrence when placing the IUD inside the uterus is discharge. As a rule, they are brown and have no foreign odor. Depending on the cause, such bleeding lasts from several days to six months.
Victoria, 42 years old: “As long as I have been sexually active (since I was 17 years old), I have been wearing the IUD for as long. All my life she protected me from conception. When my husband and I decided to have a child, as planned, the specialist removed it, and after two menstrual cycles I was able to get pregnant. After giving birth, this wonderful invention was placed again. I didn’t notice any special discharge; as a rule, it was a slight spotting for about a week, and in the first days after the installation I felt a slight tug in my lower abdomen.”
Marina, 25 years old: “After the implantation of the IUD, my period lasted for another two weeks. As it turned out later, it was discharge against the background of endometrial detachment, the vessels of which are quite weak. This is how the specialist explained it to me. Now my menstruation is going differently. There's a lot more blood. But it doesn't make me uncomfortable. The main thing is that I am reliably protected from an unwanted pregnancy.”
Thus, the IUD is an excellent, highly effective contraceptive. When placed correctly and all rules of use are followed, it gives the highest results among means of protection and does not cause harm to the body. IUDs were invented for those women who keep up with the times and value their health.
Similar article - Asparkam for prevention
I got the Mirena IUD 2 months ago. My weight is normal, pimples on my face have begun to appear less frequently (there used to be more), my hair is not falling out, my libido is fine. In short, there are almost all advantages, but there is one big MINUS - bloody discharge that has not stopped for almost 2 months. For some reason I cannot consult my doctor right now (she is away). Please share your experience: how did the spiral take root for you? and whether there was bloody discharge for as long as mine. What did you do in this case?
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Glinchikova Elena Viktorovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Slobodyanik Marina Valerievna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Zinovieva Natalya Yurievna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Dyachenko Elena Vladimirovna
Psychologist, Gestalt therapist in training. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Nikulina Marina
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Sheludyakov Sergey
Psychologist, Clinical psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Trifonova Maria Anatolyevna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Gundertailo Yulia Danilovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Vyacheslav Potapov
Psychologist, consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is a fairly common side effect of using a hormonal intrauterine system. The absence of menstrual bleeding in such cases is explained by reversible atrophy of the uterine epithelium.
A woman using a hormonal IUD should know that amenorrhea that develops while using the IUD is completely reversible and does not pose a threat to life or reproductive health.
However, immediately after the development of amenorrhea, you should consult a doctor to rule out pregnancy (including ectopic).
Doctor's recommendations
Doctors' opinion about the intrauterine device is positive if all contraindications to this contraceptive are taken into account before installation. Gynecologists recommend that you undergo a preliminary examination to exclude infectious diseases and do an ultrasound of the pelvis. If a woman does not have fibroids with deformation of the uterine cavity or inflammatory diseases, she can safely use this method of protection. Premenopausal women will benefit from an IUD with hormones; it will stabilize the endometrium and reduce blood loss.
Symptoms of systemic action of gestagens
In the first three months of using a hormonal intrauterine device, symptoms of systemic action of gestagens may appear, such as
:
- engorgement and tenderness of the mammary glands;
- acne (adolescent acne);
- attacks of headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- back pain resembling sciatica;
- decreased sex drive;
- increased nervousness;
- deterioration of emotional state up to the development of mild depression.
The severity of these symptoms, as a rule, gradually decreases. If, after three months from the installation of the IUD, unpleasant symptoms persist, this indicates poor tolerability of gestagens. In such cases, it is better to remove the hormonal IUD and choose another method of contraception.
Complications that appear after removal of the coil
In most cases, long-term use of an IUD does not harm a woman’s health, with the exception of cases when inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs develop due to the use of the IUD.
Acute infectious processes in the pelvis can lead to the development of a tubo-ovarian abscess (purulent melting of the uterine appendages), peritonitis, or become chronic (chronic adnexitis, etc.).
In such cases, after removal of the IUD, ectopic pregnancies may develop due to obstruction in the fallopian tubes deformed by inflammation. Often, infertility or chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a consequence of pelvic inflammatory diseases.
anonymously
Hello, my name is Katya. I’m 32 years old. I wore the IUD for a long time for 13 years (without knowing about it) because 13 years ago I had a miscarriage for 6 months. The doctor installed it without my knowledge. Our village is small and there are no good specialists. I couldn’t stand these unbearable things anymore. pain in the lower abdomen. unstable menstruation happened 2 times a month. I had the same complaints. but since we don’t have an ultrasound. they diagnosed inflammation of the uterus and stuffed them with antebiotics. and that’s it. this year I went to Syktyvkar myself so that I could be there They also looked at a pelvic ultrasound and found a speral. They pulled it out, seemingly without any problems, prescribed treatment. Drink Wobenzin. Hexicon. Viferon. The pain seemed to have gone away, but not completely. Questions - how long will the treatment last? If there are no main problems, how soon will pregnancy occur? Is there a threat infertility after someone has been wearing the IUD for a long time? Thank you, I'm waiting for an answer.
- All forum topics “About Everything” (29126)
- New statement: Milana Kerzhakova announced that she is going to rehabilitation (20)
- “You lie down and think if you could wake up”: Alla Pugacheva spoke about her age (55)
- Turmeric – anti-cancer spice (2)
- The media reported the closure of a criminal case against the mother of a seriously ill child for the resale of drugs (76)
- Unforgettable rhythms of pure Arabica with the new coffee collection from NESCAFÉ Dolce Gusto (0)
- How to get rid of back pain (1)
- First formula with immune-boosting human milk oligosaccharides (2)
- Nicole Kuznetsova, who has undergone almost 300 operations, told how she lives after getting rid of a tracheotomy tube (9)
- Five facts about childhood cancer that every parent should know (0)
- Open meeting for people with eating disorders (7)
- An Australian woman almost went blind after using mascara that had been stored for 20 years (12)
- An insider spoke about the illness that forced MakSim to leave the stage (18)
- The heart of Jaha McMath, who officially died 5 years ago, stopped beating (40)
- Cancer patient Ed Matsaberidze reported that he felt better (5)
- A British man born without a genital can finally lose his virginity at 44 (12)
- Diego Maradona spoke about his health and hospitalization after the Argentina-Nigeria match (5)
- Singer MakSim leaves the stage due to deteriorating health (64)
- “Culture of Health” - an accessible way to manage your well-being (0)
- Three of our own, five of strangers: an American woman became a “serial surrogate mother” because she loves being pregnant (8)
Carnosine: a geroprotector that prolongs youth (0)
All articles in the “About Everything” section (2688)
Published:
18 Aug 2014,
14:33
Of all the methods of contraception, the IUD is the most reliable and popular. The application of this technique includes strict adherence to operating rules, one of which is the shelf life of the spiral, the presence of contraindications or restrictions.
As for how long the spiral is placed, it depends on the manufacturer of the product and the materials used in its manufacture. The hormonal IUD lasts 6 years (plus or minus a couple of years depending on the manufacturer), the copper-containing version is less regulated - the IUD lasts 10 years without the need for replacement. Considering that the contraceptive is actually a foreign body, a woman should carefully monitor how long the IUD is placed and not exceed it, as this can lead to serious side effects.
What is a spiral used for?
Many women consider it necessary to protect themselves in various ways through contraception. The IUD is one of the types of contraception that is the most effective compared to other methods of contraception. However, there are contraindications and disadvantages of this method.
Materials from which products can be made:
- copper;
- silver;
- gold.
The presence of fibroids can cease with the introduction of intrauterine contraceptives into the woman’s body, which have a therapeutic effect with the help of hormones. Contraceptive products are reliable because they protect women from unwanted pregnancy for 6-7 years, without the need for additional intervention to prevent pregnancy.
Advantages of the spiral:
- there are no changes in the woman’s hormonal background;
- no negative impact on internal organs;
- reliably protects against pregnancy for about 7 years;
- the girl spends ordinary everyday life and does not limit herself in anything.
However, there are not only positive aspects, but also negative ones, which the fair sex should not forget about.
IUD installation
The IUD is inserted by the gynecologist approximately 3-4 days after the start of menstruation, since it is at this time that the cervix is slightly open, which makes the procedure easier. In some cases, the best time will be 5-9 days after the end of your period. The doctor will determine the best option.
During the first days after installation, minor bleeding is possible. After 1-1.5 months, you need to visit the gynecologist again for examination. You should immediately contact a specialist in the following cases:
- unusual pain, particularly after sexual intercourse;
- severe bleeding;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen;
- absence of menstruation;
- inability to detect contraceptive threads;
- palpation of the hard part of the contraceptive;
- product loss;
- if you use a spiral whose validity period has already expired;
- other atypical symptoms.
When can I remove the intrauterine device?
Painful periods?
This natural remedy will 100% relieve pain during menstruation! If you guess what it is, you will get rid of it forever!
Regardless of the type and age of the device, it must be removed under sterile conditions by a gynecologist after a preliminary examination. You should not do this on your own, as there is a risk of damaging the uterine mucosa and introducing infection into the body.
If there were no complications or infections during the use of the IUD, then the removal process will be quick and completely painless. If it is impossible to find the threads of the product or other complications arise, hysteroscopy is performed to obtain a more complete picture of the location of the intrauterine contraceptive. The removal process consists of two main stages:
- Inspection and assessment of the condition in which the intrauterine device is located, the period of use of the product at the moment, etc.
- Delete. The optimal time to remove an IUD is during menstruation. This is done using local anesthesia. If we are talking about hysteroscopy, then anesthesia is used. In some cases, in particular, if the service life of the intrauterine device is significantly exceeded, it is impossible to remove the product through the cervical canal, so the contraceptive is removed through the abdominal cavity.
As for when you can remove the intrauterine device, this can be done before the expiration date:
- at the personal request of the woman;
- with partial rejection of the drug by the body;
- when the IUD is displaced, which can be determined by the device’s antennae, which have become either longer or shorter;
- in the presence of acute inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- very heavy bleeding;
- cancer diseases;
- the onset of menopause;
- pregnancy;
- other pathologies.
If the IUD remains in place for longer, there is a possibility that the device has become tightly attached to the walls of the uterus or even grown in. That is why women who use this type of contraceptive should undergo regular examination by a gynecologist, which helps to detect the problem in the early stages. There are cases with patients whose IUD lasts for 20 years or even more. Removal of the product under such circumstances is quite difficult and is usually carried out in a hospital setting.
Removing an IUD is a common procedure that can be done no matter how old the IUD is. In the absence of infection and complications, the process is easy and painless. If there are difficulties with removal, the contraceptive is examined and removed in a hospital setting. The cause of complications can be both the characteristics of the body and failure to comply with operating conditions. In order to protect yourself, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist and take into account how much a particular type of IUD is placed.
Pain during menstruation?
This remedy relieved all Chinese women from menstrual pain! It will help you too! You stick it on the groin and forget about the pain!
Removing an ingrown helix
One of the most popular means of protecting against unwanted conception of a child is the intrauterine device (IUD). This contraceptive is very effective, easy to use and has a long service life. Despite the numerous advantages, sometimes there is a need to remove the coil.
Indications for removal of the intrauterine device
Doctors advise women to install an IUD for a period of no more than 5 years. With modern spirals you can walk for up to 8 or even 15 years. To prevent complications, it is necessary to periodically visit a gynecologist to monitor the position of the spiral.
The indication for removal is the end of the contraceptive's useful life. There are several types of IUDs: copper (duration of use from 3 to 5 years), silver with hormones (suitable for 5 to 7 years), gold (worn for 10 to 15 years in the absence of contraindications).
Other indications for removal: the onset of menopause (a year after the last menstruation, the device is removed from the internal organ due to uselessness), pregnancy (while using a contraceptive in women, in rare cases, ectopic conception of the baby may occur), displacement of the device or its partial loss (removed old and a new one is installed).
The IUD is also removed at the request of the patient if she wants to conceive a child or this method of contraception is not suitable for her. Medical indications for removing the IUD: pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding, the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the uterine cavity and ovaries, the development or growth of tumors and neoplasms.
Contraceptive penetration (ingrowth of the IUD into the muscular wall of the uterus) is a complication that is an indication for removing the IUD. When an IUD is used longer than necessary, it begins to grow into the organ tissue. This can also occur due to improper installation of the contraceptive.
Symptoms indicating the ingrowth of a spiral: deterioration in a woman’s well-being, constant fatigue, internal bleeding, heart rhythm disturbances, dizziness and fainting, pale skin, pain in the lower abdomen.
The essence of diagnosis
A specialist can diagnose an ingrown helix after performing a hysteroscopy. The study helps determine the condition of the contraceptive and the degree of its growth into the walls of the uterus.
Microsurgical intervention allows you to choose the tactics for removing the IUD and determine its location. If the spiral is located near other internal organs and large vessels, surgical intervention will be risky.
The patient is warned about all possible risks before the procedure.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy include: inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, uterine bleeding, pregnancy, cervical cancer or stenosis, vascular and heart diseases, renal and liver failure.
Features of removing an ingrown helix
You cannot remove the IUD yourself; to do this, you should contact a qualified gynecologist. Before the procedure, the specialist will examine the patient in a gynecological chair and refer her for tests. Laboratory tests that a woman must undergo before manipulation:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood analysis;
- microflora smear;
- bacterial culture.
An ultrasound examination of the uterus and colposcopy should also be performed. After the doctor is confident that the IUD has grown into the patient’s organ, the doctor sets the time and day of the operation.
Extraction is carried out in stages using local anesthesia. Intimate organs are sanitized: the woman’s genitals are treated with antiseptic medications. Dilators are installed in the cervix to facilitate access to the uterine cavity. Next, a hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix, with which the gynecologist can examine the muscle walls in detail.
After the specialist detects the IUD, it is removed with sterile forceps or a curette. In cases where most of the contraceptive grows into the abdominal cavity, laparoscopy is prescribed.
If the coil is located near the bladder, urinary tract and large vessels, laparotomy is indicated. At the end of the procedure, the doctor scrapes out the overgrown mucous layer. The duration of the operation varies from 15 to 30 minutes.
If the IUD threads come off during surgery, the gynecologist will pull it out using a special hook. It is advisable to carry out further removal of the IUD under ultrasound control.
If an ingrown intrauterine contraceptive cannot be pulled out through the cervical canal (due to occlusion or atresia), then a specialist removes it through the abdominal cavity.
In this case, extraction occurs using laparoscopic methods under general anesthesia.
After surgery, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the doctor gives a referral for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
When is the best time to perform the procedure?
The operation is most often performed during menstruation, since during this period the external os of the cervix of the internal organ is slightly open and removal of the IUD will be more painless and gentle. The most favorable days for the procedure are the first or last day of menstruation, when there is a minimal amount of bleeding.
If the patient is bothered by discomfort or discomfort due to the contraceptive, it can be removed any day. Some experts recommend removing the IUD on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle.
Pregnancy after an ingrown contraceptive
The contraceptive method does not affect the subsequent conception of a child. After a recovery period (2-3 months), a woman may think about becoming a mother. During this time, the mucous membrane (mucosal layer) will be completely restored and the microflora will be normalized.
If the patient experiences complications, such as endometritis, due to wearing a contraceptive, she should refrain from conceiving until the disease is cured. After a successful course of therapy, you can get pregnant safely. If a woman feels well and does not have any contraindications, pregnancy can occur immediately after removal of the IUD.
About complications of an ingrown IUD
The most common complications of an ingrown IUD are: inflammation, bleeding, chronic endometritis. Normal and acceptable symptoms after surgery are:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding in small quantities;
- discomfort in the pelvic area;
- muscle spasms in the abdomen.
If symptoms do not go away after 5-7 days, you should seek medical help from your doctor.
If purulent or brown discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, body temperature rises, or health deteriorates after removal of the IUD, you should consult a gynecologist.
After conducting a series of studies and diagnostics, the specialist will be able to determine the reason for the deterioration in the woman’s well-being and prescribe a course of therapy.
Postoperative care
After removing the ingrown IUD, the woman must follow simple rules; complete sexual rest is recommended for 3-4 days. You cannot play sports or lift weights for 1-2 weeks; you must follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
In addition, you should avoid visiting baths, saunas, solariums and swimming pools for 1-2 months. The use of tampons is prohibited, and douching cannot be used as a method of treating diseases of the genital organs. The recovery period can take from 3 to 14 days.
The presence of a foreign body in an internal organ and wearing it for a long time can have a negative impact on a woman’s body. These are not only possible complications, such as the growth of a contraceptive into the wall of the uterus, but also inflammatory and infectious diseases and even rupture of the cervix.
The female body can react to an IUD in different ways, so at the first feeling of discomfort and pain, you should visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Source: https://FoodandHealth.ru/meduslugi/udalenie-vrosshey-spirali/