How does the spiral work?
The spiral prevents the fertilized egg from attaching to the uterine mucosa, as a result of which pregnancy does not occur. In addition to this, the IUD has one more property. Copper particles produce a toxic environment inside the body (copper ions, enzymes and a huge number of leukocytes), which has spermicidal properties, having a detrimental effect on sperm.
Modern IUDs are manufactured in such a way that the body has a complex effect. Double protection appears, which today is recognized as one of the most reliable.
A high-quality coil can be installed for five to seven years. However, you should visit a specialist regularly for examination.
Can the spiral fall out?
Despite all the advantages of using an intrauterine device, there are disadvantages that you should be aware of. To avoid trouble, you should be attentive to your feelings, especially immediately after installation of the IUD by a specialist.
Under no circumstances should you install an intrauterine device yourself. Only a specialist can do this correctly.
A visit to the gynecologist should not be delayed if you begin to feel discomfort and pain in the vaginal area and the prolapse of the intrauterine device is accompanied by discharge.
Why does the intrauterine device fall out? Causes
The spiral may fall out involuntarily. The fact of loss is not always painful and, as a rule, does not harm the body. However, at this moment the woman is not protected from unplanned pregnancy.
Most often, loss occurs within a few hours after insertion of the contraceptive. However, there are cases when the IUD falls out a few months after installation. Sometimes the prolapse of the IUD may be unnoticeable and not cause discomfort to the woman.
There are several reasons for the spiral to fall out. The most common of them:
- incorrect installation by a specialist;
- cervical deformity;
- choosing the size and type of IUD that does not correspond to the individual characteristics of the body;
- great physical activity.
How to understand that the spiral is falling out? Signs
The woman herself can check whether the contraceptive is in place or not. Many female representatives ask the question: how to feel the antennae from the spiral? To do this, you need to independently examine the vagina. During the examination, it is necessary to pay attention to the length and location of the threads. If something has changed, you shouldn’t delay seeing a specialist. A change in the length of the antennae may also indicate that the IUD has shifted. In this case, its contraceptive effect is minimized. Most likely, in addition to a medical examination, you will be prescribed an ultrasound. Therefore, the following signs are cause for concern:
- you cannot feel the antennae from the spiral, or they have become shorter/longer
- the location of the threads (antennae) has changed;
- experience pain during sexual intercourse;
- There are painful sensations during menstruation.
Mirena: instructions for the spiral
According to the instructions for the Mirena spiral, it should be installed after an examination (ultrasound, colposcopy, blood tests, smears). Installation and removal takes place in a gynecological chair; this may cause minor pain. For engraftment, you should abstain from physical activity and sex for 10 days.
If there are signs of prolapse (bleeding, pain), or the threads (antennae) in the vagina are not detected, then you need to use a condom to protect against pregnancy and consult a doctor.
Preparing for installation
Before installing the spiral, preparation is required to identify possible contraindications and limitations:
- examination by a gynecologist and mammologist;
- vaginal smears;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood test: general, biochemistry with liver and kidney tests, coagulogram (clotting).
Based on the results of the study, the gynecologist can expand this list. As a result of the diagnosis, pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections should be completely excluded, and the cure of all inflammatory diseases should be confirmed.
What day of the cycle is it placed on?
In order to get a reliable contraceptive effect from the first cycle and eliminate the risk of possible pregnancy, it is necessary to insert the IUD 4-5 days from the start of menstruation. Most often, the doctor prescribes installation on the last day of bleeding.
If this time is missed, then the administration should be postponed to the next cycle, since, starting from days 10-13, there is a risk of ovulation and fertilization. Women who have completely stopped menstruation (natural or medicated menopause) can have the IUD inserted on any day.
Menstrual cycle
How is Mirena installed?
Mirena installation takes place at a gynecologist's appointment:
- after determining the expiration date and eliminating damage, the packaging is opened;
- the woman is on a gynecological chair, a speculum is installed in the vagina;
- the cervix is treated with an antimicrobial agent (antiseptic), and then with a local anesthetic.
- the intrauterine system moves through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity, and then it is imperative to lie down for another 30-40 minutes;
- the doctor conducts a control examination; if there are no signs of prolapse or displacement, then the procedure was successful;
- You must come back for your next examination in a month.
Installation of the Mirena coil
Is it painful to insert the IUD?
According to women, inserting the IUD does not hurt; it is reminiscent of taking vaginal smears. There may be discomfort and short-term pain. If there is a high sensitivity to pain, then additional painkillers are administered. After 2.5-3 hours, women’s pain completely disappears.
When, by the end of the first day, a woman notices unpleasant sensations, or while wearing the Mirena they arise during sexual contact or movements, it is important to immediately contact a gynecologist.
Watch this video about the benefits and harms of the intrauterine device:
What not to do after
During the first ten days (10 days) after installation, douching and other therapeutic or diagnostic procedures in the vagina should not be performed. Also during this period restrictions are introduced on:
- sexual contacts,
- hot bath,
- sauna,
- swimming,
- sports,
- lifting weights from 3 kg.
It is necessary to limit strength training and heavy lifting.
All these precautions are important, since the device must be well strengthened in the uterine cavity. After this period, as a rule, women do not feel the presence of Mirena at all. It does not interfere with sex or active movements, but its presence is considered one of the factors that increases the risk of inflammation. Therefore, for the entire period of wearing it is recommended:
- in case of casual sex, changing partners, use a condom to avoid sexually transmitted infections;
- carefully observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- If unusual symptoms appear (pain, itching, burning, bleeding, leucorrhoea, fever), immediately contact a gynecologist, visit him once a year, even if there are no complaints.
If the Mirena coil falls out, what should you do?
If the Mirena device falls out, then it is imperative to use means of protection against unwanted pregnancy - suppositories, vaginal tablets, a condom. It is recommended to immediately visit a gynecologist to rule out fertilization. Even if the IUD is displaced, there is a risk of cessation of contraceptive action.
Signs that may indicate prolapse are:
- pain;
- bloody issues;
- resumption of menstruation after cessation;
- increased menstrual bleeding.
Throughout the entire period of wearing the intrauterine system, it is necessary to periodically check the presence of antennae in the vagina.
When can an IUD be removed?
After five years or at the woman's request, the intrauterine device (IUD) can be removed at any time. This happens more often if complications or severe adverse reactions arise while wearing it (for example, abdominal pain, joint pain, headache, depression).
If the entire period of health remained normal, and for medical reasons the gynecologist recommends continuing to use Mirena, then after 5 years it will be changed to the next one. You must visit the doctor 1-2 cycles before the end of the period in order to undergo an examination before removal.
Removing the Mirena coil
If Mirena is removed as planned, and not due to urgent indications for removal, then the gynecologist often schedules a visit on the last day of menstrual bleeding (if it continues).
On the gynecological chair, after treatment with an antiseptic solution and anesthetic, the cervical canal is widened and Mirena is removed by the antennae. This may be accompanied by slight soreness and a brief episode of dizziness. At the same time, if necessary, the doctor installs a new IUD.
Removal of the IUD
Symptoms of intrauterine device prolapse
If changes begin to occur in the body, you should urgently consult a doctor. Symptoms of an IUD falling out may include:
- heavy menstruation, change in cycle length;
- flu-like symptoms;
- fever or chills;
- vaginal discharge;
- bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- constant headache.
These symptoms are an alarming signal that something has gone wrong in the body.
What to do if the spiral falls out?
If any of these symptoms or signs appear, you should immediately consult a specialist. Since only a doctor can answer the question of whether the intrauterine device fell out or not.
The IUD is one of the most modern and reliable ways to protect against unplanned pregnancy. If you master all the intricacies of its application, you don’t have to think about alternative methods.
Women say that the spiral is often displaced. How can you tell if the spiral is out of place? Is it possible, for example, to stick your hand in and try to feel the ends of the spiral (I read about this on the forums)?
Answered by Berezovskaya E.P.
First, there are rules that a doctor must adhere to. Each spiral has threads (tendrils), which after inserting the spiral must be cut to a length of 2 cm. No more and no less. Just by the length of the antennae you can know whether the spiral has shifted or not during the next inspection in the mirrors.
Secondly, a woman should be taught two rules: 1. control of sensations and signs - if there is aching or sharp pain, bleeding, discomfort, if during sexual intercourse a man complains of something stabbing inside the vagina, if inflammatory discharge (green) appears , yellow, purulent), you must consult a doctor.
checking the presence of antennae - after menstruation, you can insert two fingers into the vagina and try to feel the presence of antennae. This is not easy in some cases, because not everyone has long fingers, and a woman can also “skip” the antennae by inserting her fingers away from the cervix. If the antennae appear at the exit of the vagina or, conversely, they cannot be found, then you need to go to the doctor. It is important not to pull the antennae, because you can displace the spiral with your manipulations.
Preventing unwanted pregnancy can be achieved in different ways. One of the most reliable and relatively safe is . This method is suitable for most women, but still not for all. In order to understand whether this method of contraception is right for you, you will first have to exclude all diseases, then weigh the pros and cons. And then install the spiral.
After the IUD is placed, many women are faced with a dilemma - everything is fine, nothing hurts, but you can feel the tendrils of the IUD with your fingers; they can be easily felt from the vagina. Is this normal, women ask on forums? Should it be like this? But what about the partner, because he will notice by touch, and not only notice, whether the mustache will interfere with the partner? Or is something wrong? How should it be? Many questions arise.
How should the spiral be positioned?
The annotation for the spiral says that the antennae of the spiral should protrude from the cervix by 1-2 cm. When installing the spiral, the gynecologist must trim the long antennae to this length. By these antennae you can determine every month whether the spiral is in place. Therefore, feeling the tendrils of the spiral is completely normal. At first, the antennae are curled, then they unwind, and the woman can feel them herself.
It's another matter if a woman no longer feels her mustache. There may be several explanations for this. Firstly, perhaps the woman simply does not know where to look for a mustache. Secondly, the antennae broke off, while the spiral continues to remain in its proper place. Thirdly, the IUD fell out of the uterus. If you cannot feel the antennae, you need to visit a gynecologist and determine the real reason for this.
To the question of whether there are any restrictions on sexual intercourse with a protruding mustache and what these restrictions are, we can answer the following: there are no restrictions. Neither a woman nor a man should feel discomfort from the elements of the spiral during sexual intercourse under any circumstances. The IUD will not fall out during sexual intercourse unless, of course, the man makes special efforts.
After some time, the antennae usually retract. Sometimes gynecologists deliberately leave large mustaches for an unforeseen event. And the antennae are cut off when the spiral is at the very bottom of the uterus. With a retracted spiral and small antennae, the spiral is more difficult to reach if necessary.
Sometimes there are cases when the spiral is rejected on its own. In these cases, the woman may also feel the protruding tendrils of the spiral coming out. This happens just two weeks after installation.
: the antennae sank down, “fell”, and the spiral had to be removed.
Some women report that the antennae sometimes come off. Cases are described when only one tendril came off, which was found by the husband two years after installation. The woman went to see a gynecologist, and the doctor determined that the IUD was in place normally and decided to leave the IUD. She stood there for another five years after that.
So, feeling the spiral is normal. If the spiral begins to fall out, this moment can hardly be missed - the woman will feel cramping pain, and then she must definitely go to the doctor.
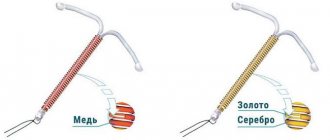
Intrauterine devices
(IUD) is a small contraceptive device made of flexible plastic. It is inserted into the uterus, where it provides safe, highly effective and long-term contraception.
The most common among women are the non-hormonal coils "Multiload" and "Nova-T" (the principle of action of which is based on the prevention of egg implantation through the spermicidal effect of the coil caused by the oxidative reaction of the copper with which the devices are wrapped), as well as the hormonal coil "Mirena" (active ingredient - the hormone levonorgestrel, which suppresses ovulation, thickens the mucus in the cervical canal and thins the endometrial layer in the uterus, thereby making pregnancy almost impossible).
The effect of coils with copper winding is from three to five years, and the effect of Mirena is at least five years. All three types of spirals are T-shaped and about 1.5 cm in length. The coils can be removed at any time at the woman’s request.
IUDs are a good choice for women who want a highly effective, long-term, yet easily reversible method of contraception. IUDs are also well suited for those women who do not want (or who are contraindicated) to use certain hormonal methods, such as birth control pills or. Keep in mind that the IUD does not protect against reproductive tract infections (STIs).
The average cost of an IUD ranges from $20 to $500 plus the cost of installation. Of course, if you opt for Mirena, which costs about $300, then this amount may seem simply enormous! But do the math: the effect of the IUD lasts about 5 years, which means that you spend about $60 a year on contraception, which is much cheaper than birth control pills.
Where can I have an IUD installed?
If you decide to install an IUD, contact your gynecologist. Before performing the installation, the doctor will make sure that you are not pregnant and that you do not have any infections or inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. During a gynecological examination, your doctor will determine the position of your uterus and make sure that you do not have any medical contraindications for having an IUD installed.
If the gynecologist considers it possible to install an IUD in you, he can do it immediately, during the examination. If you are scheduled for additional tests, the installation of the IUD will be postponed until the results are received.
How do IUDs prevent pregnancy?
The operating principle of copper IUDs is based on preventing sperm from fertilizing an egg. The IUD releases a small amount of copper into the uterus, and oxidative processes make copper a kind of spermicide.
As for Mirena, its principle of action is to release the hormone progestin (in the form of levonorgestrel) into the uterus. This hormone primarily blocks the onset of ovulation. But if ovulation does occur, it also leads to thickening of the cervical mucus, so sperm cannot reach the egg ready for fertilization.
In the unlikely event that the egg is fertilized, it will still not be able to implant in the uterus, since its mucous membrane (endometrium) will be greatly thinned under the influence of progestin.
IUD after childbirth and during breastfeeding
If you've just given birth, you'll have to wait about six weeks after birth for your uterus to return to its pre-pregnancy state. Some clinics install an IUD in the first week after birth, but it is better to refuse such an idea - the probability that the IUD will be expelled is more than 90%.
IUDs can be used during breastfeeding - they have absolutely no effect on the quality or quantity of breast milk.
IUD effectiveness
Intrauterine devices
are one of the most reliable forms of contraception. Only 2 out of 100 women using copper IUDs became pregnant within five years of using them. Among women using Mirena, the figure was just 7 out of 1,000 women over five years.
This means that IUDs are as effective as . But unlike sterilization, the IUD is a reversible method of birth control, and you become fertile again soon after the IUD is removed.
In practice, it has been proven that the effectiveness of the IUD is 22% higher than any other method of contraception (except sterilization), where the human factor can play a role (for example, they forgot to take a pill or change the patch on time). Using an IUD virtually eliminates the possibility of human error. All you need to do is check every time after menstruation to make sure the IUD is in place and see a gynecologist every six months.
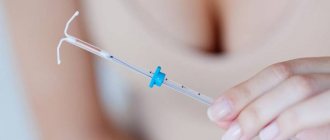
How is the IUD inserted?
Before inserting the IUD, the gynecologist places speculum in the vagina and treats the vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution.
He then uses a dilator—an instrument to widen the cervix—which may cause mild but sharp, short-term pain. This instrument straightens the cervical canal and moves the uterus closer to the vagina so that the doctor can measure the depth of the uterine cavity.
The doctor then inserts the IUD using a narrow applicator tube. Most women at this moment feel a painful, but not prolonged, spasm in the lower abdomen.
Once the IUD is in place, the applicator is removed and the IUD's T-shaped legs are opened. The entire IUD installation procedure takes only a few minutes.
It may seem strange that you have a piece of plastic inside, but you should not feel it if the coil is inserted correctly. The two tendrils attached to the end of the IUD will stick out slightly from your cervix, but your gynecologist will trim them so that you won't notice them.
You may experience abdominal cramps or back pain for several days after the procedure. Take ibuprofen as needed to reduce discomfort. If you are used to using tampons during your period, then there is no reason to change your habits! You can use tampons from the first day after inserting the IUD.
Your doctor will likely give you a follow-up appointment after the end of your next cycle to make sure the IUD is in place and that you have no signs of infection.
You will need to have a routine gynecological examination regularly, approximately once every six to nine months, to check the IUD, because it may partially fall out of the cervix (or even be completely expelled) without you even noticing.
Copper spirals begin to work immediately after their installation. The effect of the progestin IUD (Mirena) begins after a week, so after its installation it is recommended to use an additional non-hormonal method of contraception for seven days.
How to remove an IUD?
Usually removal of the intrauterine device
occurs in three cases:
- for medical reasons (for example, if inflammation or infection has developed around the IUD, or if a woman becomes pregnant while using the IUD);
- at the request of the woman (for example, if you decide to become pregnant or use another method of contraception);
- upon expiration of the spiral.
Removal of the IUD begins in the same way as its installation: the gynecologist inserts speculum into the vagina and treats the cervix and vagina with an antiseptic.
After this, he grabs the antennae of the spiral with small tweezers and, using an expander, opens the cervical canal. He then gently pulls the tendrils of the IUD and the IUD is released from the uterus. The procedure takes about 10 seconds.
Although the spirals are made of flexible material, nevertheless, while the spiral passes through the cervix, you will feel mild cramps in the abdomen. If you want to continue using the IUD, your doctor can fit you a new one right away.
The IUD can be removed at any time (even during your menstrual cycle) if you want to try to conceive. After the IUD is removed, you can start trying to get pregnant right away, in the same cycle. Typically, fertility is restored within a few days after the device is removed, and it remains the same as it was before the IUD was inserted.
The effect of the IUD on menstrual periods
If you opt for a hormonal IUD (such as Mirena), then in the first three to six months you may notice that your periods become very irregular. But after six months, your cycles will become established, they will become shorter and lighter than they were before, and if you suffered from painful periods, then you will remember it like a nightmare. Moreover, for many women, after a year of using the IUD, menstruation becomes very rare, and for some, it stops completely.
Copper IUDs may also cause irregular menstrual bleeding during the first few months. Your cycles may become longer and heavier, especially in the first three to six months after insertion. Over time, they may become lighter, but most women complain that before the introduction of the IUD, their periods were lighter and less painful.
If you have very heavy periods after having the IUD installed, you will need to take hemostatic medications and iron supplements to prevent anemia. If you continue to experience very heavy bleeding three months after having your copper IUD inserted, you will likely need to have the IUD removed. But if you want, you can install a progestin-containing IUD instead of a copper one.
Side effects from using an IUD
IUDs cause virtually no serious side effects.
A small percentage of women using the progestin IUD report side effects such as:
- acne;
- headache;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- depression.
But in most cases, these side effects gradually go away over time.
Additionally, many doctors recommend hormonal IUDs for women who suffer from heavy, long, or painful periods because it not only makes their periods easier, but can also stop them altogether. This causes women to lose less blood, making them less likely to develop iron deficiency anemia, which can cause chronic fatigue and serious health problems.
Dangerous symptoms when using an IUD
Dangerous symptoms indicating problems associated with the installed coil are:
- sharp or severe pain in the pelvic area or lower abdomen;
- fever for no apparent reason;
- unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge;
- the appearance of ulcers on the genitals;
- pain during sex;
- bleeding or spotting after sexual intercourse or between periods;
- heavy or prolonged periods or any vaginal bleeding;
- persistent or severe headaches and migraines (when using hormonal IUDs);
- the appearance of signs of jaundice - yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin (when using hormonal IUDs).
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the symptoms above, or if you have any signs that you may be pregnant, such as:
- missed menstrual cycle (using a copper IUD);
- pain in the mammary glands:
- morning sickness.
If you are using a hormonal IUD, it is also best to consult your doctor to rule out pregnancy the first time you miss your period. After this there will be no need for this as the spiral will take full effect.
Also see your doctor if:
- you cannot feel the spiral;
- the spiral seems shorter or longer to you than usual;
- you feel the coil during intercourse (or your partner feels it);
- you think you may have contracted an STD even if you have no symptoms;
What happens if you get pregnant with an IUD?
The first thing your doctor will do is check that you do not have an ectopic pregnancy. To do this, you will need to undergo blood tests, a vaginal gynecological examination and an ultrasound examination.
If your pregnancy is not ectopic, you can choose to terminate it or continue with it. If you decide to continue, your doctor will remove the IUD if possible. The doctor can remove the device without invasive intervention in the cervix by pulling the spiral by the antennae. Of course, there is a small risk that removing the IUD may cause pregnancy loss, but you are much more likely to lose the baby and jeopardize your health due to infection if you leave the IUD inside the uterus.
In the unlikely event that the IUD
impossible, but you still decide to continue the pregnancy, you will be under very careful monitoring. In addition, if pregnancy occurred while an IUD was installed, or if the IUD was not removed, then you are a woman at increased risk of premature birth.
Source: edema-club.ru
The spiral has grown into the uterus, consequences. Indications for removal of the intrauterine device
Doctors advise women to install an IUD for a period of no more than 5 years. With modern spirals you can walk for up to 8 or even 15 years. To prevent complications, it is necessary to periodically visit a gynecologist to monitor the position of the spiral.
The indication for removal is the end of the contraceptive's useful life. There are several types of IUDs: copper (duration of use from 3 to 5 years), silver with hormones (suitable for 5 to 7 years), gold (worn for 10 to 15 years in the absence of contraindications).
Other indications for removal: the onset of menopause (a year after the last menstruation, the device is removed from the internal organ due to uselessness), pregnancy (while using a contraceptive in women, in rare cases, ectopic conception of the baby may occur), displacement of the device or its partial loss (removed old and a new one is installed).
The IUD is also removed at the request of the patient if she wants to conceive a child or this method of contraception is not suitable for her. Medical indications for removing the IUD: pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding, the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the uterine cavity and ovaries, the development or growth of tumors and neoplasms.
Contraceptive penetration (ingrowth of the IUD into the muscular wall of the uterus) is a complication that is an indication for removing the IUD. When an IUD is used longer than necessary, it begins to grow into the organ tissue. This can also occur due to improper installation of the contraceptive.
Symptoms indicating the ingrowth of a spiral: deterioration in a woman’s well-being, constant fatigue, internal bleeding, heart rhythm disturbances, dizziness and fainting, pale skin, pain in the lower abdomen.
Causes of pain in the lower abdomen after installation of the IUD
The intrauterine device prevents the fertilized egg from attaching to the lining of the uterus. As a result, pregnancy cannot fully develop.
Hormone-containing IUDs are also popular. They not only mechanically prevent normal conception, but also affect a woman’s hormonal levels.
The likelihood of complications after the introduction of a foreign body into the uterus is reduced.
The hormonal drug Mirena is widely used, but side effects may occur from the use of such devices. If your lower abdomen hurts after installing the Mirena coil, it is possible that inflammation of the genital organs is developing.
Immediately after installing a contraceptive device, mild discomfort in the lower abdomen and minor spotting are considered normal. If there is heavy bleeding or severe nagging pain is observed for more than two days, you should contact your gynecologist again.
The duration of abdominal pain after the installation of coils should not be long. After injection, the foreign body “takes root.” This means that the lining of the uterus adapts to the new material.
As a rule, unpleasant symptoms disappear completely within a week. However, the entire adaptation process can take up to three months. Nagging pain often appears in the first days of menstruation.
Alarming symptoms
The IUD is a device that is not suitable for everyone. This method of contraception can only be used by women who have given birth. Contraindications include:
- malignant tumors in the uterus;
- underdevelopment of the reproductive system organs;
- the presence of fibroids or polyps in the uterus.
It is strictly forbidden to install a spiral if you have diseases of the pelvic organs or the presence of sexually transmitted infections. Before introducing a foreign body into the uterus, the doctor conducts a visual examination and prescribes a series of tests.
Even if the study has been carried out and no contraindications to the installation of the IUD have been identified, side effects may develop. The female body does not always perceive a foreign body well. As a result, an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa develops - endometritis. The disease in the acute period will manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the pubic bone;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor (mixed with blood or pus).
If such signs develop, you should immediately seek medical help. Refusal of therapy will lead to inflammation spreading to other organs. There will be a serious threat to the woman's life.
Uterine bleeding (metrorrhagia) is another complication that can develop immediately after installation of the IUD. Seek immediate help if the pad fills completely within an hour. Metrorrhagia often leads to serious blood loss.
Ways to eliminate pain
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
If your stomach hurts slightly after installing the Mirena coil or other similar device, you can relieve the unpleasant symptoms with the help of medications. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used.
The gynecologist will recommend a suitable medicine. The drugs Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Panadol relieve pain well. Medications are recommended for use in extreme cases, when pain prevents you from coping with everyday responsibilities.
Warmth will help relieve nagging pain in the lower abdomen. All you need to do is lie down to rest and place a heating pad on the pubic bone area. You can replace the heating pad with a bag filled with warm salt.
Rest in the correct position will also help to alleviate the condition in the first few days after installing the spiral. You need to lie down in a ball and pull your bent legs to your chest. The fetal position helps relax the muscles in the lower abdomen.
As a result, pain sensations are not so pronounced.
It is not advisable to massage the abdomen if pain occurs. It must be remembered that there is a foreign body inside the uterus. Intense mechanical stress can damage the endometrium.
If mild discomfort develops into severe malaise, you cannot postpone a visit to the doctor. It is possible that the spiral was installed or selected incorrectly. A specialist can always recommend another effective method of contraception.
How likely is the IUD to come out?
The categories of women who are associated with a higher risk of IUD failure are detailed below.
Recent women giving birth
In 2021, American scientists conducted a study involving 162 women who had intrauterine devices inserted immediately after natural birth. It turned out that during the first 6 months of using the coils, 8% of the study participants experienced complete withdrawal, and 16% experienced partial withdrawal.
Girls
Another study by US experts showed that girls aged 14 to 19 years also have an increased risk of IUD release. This risk decreases after girls turn 19.
Women after medical abortion
There are some scientifically proven facts on the basis of which doctors recommend postponing the use of IUDs for women who have recently undergone a medical abortion.
The study, published in the European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health, found that women who start using intrauterine devices within the first two weeks after a medical abortion are associated with a higher likelihood of IUD failure compared with women who are inserted after three weeks. weeks after termination of pregnancy or later.
However, scientists did not record a significant difference. During the first six months after a medical abortion, the IUD came out in 6.7% of women who waited two weeks or less to insert the IUD, and in 3.3% of study participants who waited longer than three weeks.
High, long-lasting and completely reversible contraceptive effect
Modern copper intrauterine devices are one of the most effective contraceptives.
The chance of pregnancy within 1 year of wearing a copper IUD is 0.6 to 0.8% (see the article Guide to Contraception and Birth Control for the effectiveness of other contraceptives).
The contraceptive effect of the copper IUD is completely and quickly reversible.
A woman’s ability to conceive a child is restored, on average, a few weeks after removal of the IUD (after the onset of her next menstruation).
Wearing a copper IUD does not increase the likelihood that, after stopping use of this product, a woman will experience difficulties conceiving a child (including those associated with obstruction of the fallopian tubes).
The copper IUD can be used by almost all women who wish to provide long-term contraception, regardless of their age and whether they have given birth in the past or not.
Symptoms of release and displacement of the intrauterine device
When the doctor places the intrauterine device in the uterus, he explains to the woman how to monitor the threads of the device.
If the IUD comes out or becomes dislodged, a woman may notice at least one of the following changes when checking the strings:
- the threads become shorter than usual;
- the threads seem uneven;
- the threads change location;
- there are no threads.
Women may also notice that they cannot feel their IUD.
In some cases, a dislodged or prolapsed IUD can cause physical symptoms. These symptoms include the following:
- severe bleeding;
- acute spasms;
- deviations in the nature of vaginal discharge.
Sometimes, when the coils come out, there are signs of infection, such as fever and malaise.
If a woman experiences the listed symptoms, then she needs to visit a gynecologist.
Mirena: side effects
Side effects of Mirena include:
- loss (expulsion) with cessation of therapeutic and contraceptive effects;
- perforation (perforation) of the wall of the uterus, cervix;
- increased bleeding, lack of menstruation;
- backache;
- ovarian cysts;
- hair loss;
- depression.
Expulsion
Expulsion is the loss of a spiral. Mirena has a T-shape, which in 98% of cases is securely fixed in the uterine cavity. But when the muscle layer contracts (menstruation, physical stress, breastfeeding), it can move out of the uterus, especially in women with a wide or deformed cervical canal.
Signs of expulsion are pain in the lower abdomen and the appearance or increase of bleeding. Even a displacement of the IUD can lead to a decrease in the contraceptive effect.
Expulsion
Therefore, you should regularly check for the presence of antennae near the cervix (for example, when taking a shower). If they cannot be found, or you can feel the edge of the spiral with your fingers, then it is important to urgently contact a gynecologist for examination and ultrasound. For a while, you should either avoid sexual intercourse, or use a condom or suppositories.
Perforation, penetration
Perforation is the formation of a hole, and penetration means the growth of a spiral into the walls of the uterus or cervix. These complications completely disrupt both the therapeutic and contraceptive effects of the IUD. It needs to be removed. Women are at risk after childbirth and during breastfeeding, as well as when the uterus is bent backwards. If penetration or perforation is not detected in time, the following will develop:
- adhesions between organs in the pelvis;
- obstruction, intestinal perforation;
- inflammation in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis);
- ulcers (abscesses) or injury to the bladder or rectum.
Perforation during IUD installation
Weight gain
Although, according to official data, Mirena does not affect body weight, but, according to reviews of women who installed it, it may increase it. This effect is caused by the restructuring of the body, recovery after prolonged bleeding. Most often, after 3-6 months the weight returns to normal. In most patients, the weight remains the same, and sometimes even decreases.
Joint problems after Mirena
After the introduction of Mirena, a number of patients noted the appearance or intensification of pain in the back, problems with the joints (poor mobility, crunching, pain when moving). The exact connection between articular syndrome and the spiral has not been established, so this effect has not yet been included in the official instructions.
Back pain is considered a common undesirable consequence when installing Mirena due to endometrial hyperplasia and for its prevention during bleeding. If symptoms are severe, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesulide, Ibuprofen).
Backache
Hair loss
Hair loss is a reaction to the Mirena coil. If such a symptom appears, you must contact a trichologist or dermatologist to prescribe treatment. It is necessary to exclude all factors that increase hair loss: stress, lack of protein, vitamins and microelements in the diet, thyroid diseases.
Bleeding with Mirena
The most noticeable changes with Mirena affect uterine bleeding - they may intensify in the first months, then gradually decrease in volume and frequency. Spotting of blood, rare periods or their complete cessation are possible. After removing the IUD, menstrual function is restored.
Ovarian cyst
Cysts may appear during the use of the Mirena coil, as the follicle grows and its reverse development is delayed. Therefore, a cavity forms in the ovary, which on ultrasound looks exactly the same as a cyst. This complication occurs in 7% of women. Most often there are no symptoms, but pain in the lower abdomen is also possible during sexual intercourse.
As hormonal levels change, cysts disappear without treatment, usually within 2-3 months. If spontaneous resorption does not occur, then surgery is prescribed.
Heavy menstruation after removal
For most women, after removing the Mirena coil, menstruation is delayed or scanty, and heavy discharge is rare. The reason for this is a sharp change in hormonal levels, increasing the sensitivity of the inner layer to estrogen. Therefore, this consequence occurs when their production by the ovaries is high. It should be noted that in the first 5-7 days, mild bleeding is normal.
Other
Side effects of Mirena include:
- headache, migraine;
- engorgement and tenderness of the mammary glands;
- increased blood pressure;
- depressed mood;
- acne;
- growth of dense hair on the face and limbs;
- itching, darkening of the skin, jaundice;
- increased risk of reproductive system infections;
- fluctuations in blood sugar in diabetes.
In case of severe neurological manifestations (constant headache, attacks with loss of vision), depressive disorders, early removal of Mirena is indicated.
Watch this video about the side effects of Mirena:
How does the release of an intrauterine device affect the risk of pregnancy?
If the intrauterine device falls out or becomes dislodged, the risk of unwanted pregnancy increases.
If the IUD remains in the uterus during pregnancy, it can lead to health problems for both the mother and her baby. In particular, the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy will increase.
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg begins to develop outside the uterus. This usually occurs in the fallopian tubes.
An ectopic pregnancy is a problem that requires emergency medical attention.
Due to the increased risks, the doctor will pay special attention to a woman who becomes pregnant while having an IUD in the uterus.
Mirena therapeutic spiral: indications for installation
Indications for installation of the Mirena therapeutic coil are fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, endometriosis, estrogen therapy for menopause. In all these cases, the intensity of uterine bleeding decreases. If you have a polyp, you must first remove it, examine it for cancer, and after eliminating it, insert an IUD.
For fibroids
For fibroids (tumors growing in the muscle layer of the uterus), Mirena helps get rid of the main symptom – uterine bleeding. For 2-3 months you can expect their volume to decrease, and then they are usually completely absent. This effect is the most important, but at the same time the sensitivity of the uterus to the action of estrogen and progesterone also decreases, slows down the growth of existing nodes and prevents the formation of new ones.
Types of fibroids
Not all types of fibroids can be treated with a spiral - it is contraindicated for a tumor that is located in the submucosal layer, that is, the direction of its growth is the uterine cavity (submucosal). Installation is not recommended for cervical fibroids, as well as for node sizes exceeding 2.5-3 cm. In the latter case, it is possible to first reduce its volume by creating an artificial menopause (with drugs).
For endometriosis
When the endometrium grows outside the uterine cavity (endometriosis), the introduction of Mirena helps:
- stop feeding the lesions, they gradually decrease, then die and are replaced by connective tissue;
- reduce blood loss;
- prevent iron deficiency anemia;
- relieve pain in the lower abdomen;
- prevent the emergence of new areas.
During menopause
A gynecologist may recommend Mirena upon the onset of menopause due to age or after surgery to remove the ovaries for:
- prevention of endometrial thickening while taking estrogen (replacement therapy);
- reducing bleeding, normalizing blood composition after anemia;
- preventing cancerous changes in the inner layer of the uterus.
For endometrial hyperplasia
Mirena, due to the content of levonorgestrel, has a positive effect on the growth (hyperplasia) of the endometrium: its cyclic changes stop, blood flow decreases - the vascular networks become empty, the arteries thicken and become clogged with blood clots. This leads to a gradual thinning of the inner layer and stopping bleeding.
The same effect is observed with long-term use of female sex hormones (estrogens), so the IUD is placed in women, among other things, to prevent hyperplasia.
For polyps
A polyp is a growth inside the uterine cavity. If it is present, Mirena cannot be installed. This is why it is so important to undergo a full examination before using the IUD. If such a formation is suspected, a diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is prescribed. If, according to histology (tissue examination), cancer is excluded, then the hormonal IUD is allowed to be used; it can prevent the re-formation of the polyp.
Is the IUD used as a contraceptive?
The Mirena spiral as a contraceptive is recognized as the most reliable. It prevents pregnancy both mechanically and hormonally. The risk of fertilization over 5 years does not exceed 0.7%. This is almost 80 times higher than that of suppositories and condoms.
The use of Mirena has an advantage over tablets, since the penetration of levonorgestrel into the blood is minimal. In the absence of restrictions on its use, it is successfully used as a contraceptive, but this method is not recommended for women who have not given birth.
Can it be installed and worn during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Mirena cannot be used during pregnancy, but it is not contraindicated during breastfeeding . When using a spiral, it is important for women to consider:
- this is a reliable means of contraception, but there is a risk of prolapse from the uterine cavity;
- while wearing the IUD, there may be no bleeding, and the effect of the progesterone analogue is often accompanied by symptoms of conception (nausea, pain in the mammary glands), if these symptoms arise suddenly, and if there is any doubt, you should consult a gynecologist;
- if pregnancy has occurred and the IUD remains in the uterine cavity, then it must be removed; if this is not done, then miscarriage, premature birth, infection, blood poisoning may occur;
- during the period of removal of the IUD, spontaneous abortion often occurs;
- pregnancy with Mirena will occur with the threat of excess hair growth in girls; the possibility of other pathologies cannot be excluded, since there are very few such cases.
When breastfeeding, you can neglect the amount of hormone that penetrates into the blood and then through breast milk to the baby. You should regularly check the presence of the device, since during sucking the released oxytocin provokes uterine contractions. This increases the risk of Mirena falling out.
Watch this video about contraception during breastfeeding:
When should you see a doctor?
A woman should see her doctor if she suspects that the IUD has come out or become dislodged. The specialist will likely perform a gynecological examination or suggest an ultrasound examination to check the correct placement of the IUD.
In addition, a woman should consult a doctor if she becomes pregnant while having an IUD inside the uterus, since in such situations the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy increases.
A visit to the hospital is also necessary if a woman experiences one of the following symptoms:
- severe cramps;
- severe bleeding;
- fever;
- deviations in the nature of vaginal discharge;
- constant pain in the uterus or persistent discomfort.
The listed symptoms may indicate that the displacement of the spiral can lead to serious complications.
Hormonal intrauterine device Mirena: changes in the body
The hormonal intrauterine device Mirena causes irregular or increased menstruation in the first 3 cycles. Bloody discharge is normally possible in the first 3-5 days after installation and removal.
How is your period going?
In the first three months, there is a gradual decrease in the formation of hormones, so during this period there are different types of bleeding:
- irregular,
- reinforced,
- meager,
- between the next menstruation.
After 3 cycles, blood loss should decrease as the layer that is shed (the endometrium) becomes thinner. For many women, menstruation disappears completely. The gynecologist usually warns about this effect; it is considered normal.
Seeing a doctor is necessary if after 4-5 months the bleeding remains heavy or there is intermenstrual bleeding.
Discharge after installation of the Mirena coil
Since a foreign object is inserted into the cervix and uterine cavity, discharge may be brown or red after Mirena installation, but it is usually spotty and goes away on its own within 3-5 days. Signs of complications (infection) are:
- unpleasant odor;
- discharge of scarlet or dark blood, as during menstruation;
- blood clots;
- the appearance of pus.
At the same time, body temperature may rise and pain in the lower abdomen may increase.
If Mirena bleeds after removing the IUD
After the IUD is removed, Mirena may bleed for the first 3-5 days. The discharge is normally not intense, spotting, and painless. As a rule, normal menstruation returns from cycle 3-4. Uterine bleeding rarely occurs in the first months, since the endometrium grows gradually. Such a reaction is possible if, instead of the prescribed 5 years, Mirena was in place for much longer. Any bleeding due to pain or fever requires clarification of the cause from a gynecologist.
Can the spiral move?
In medical practice, there are often cases when the IUD moves or falls out completely. Most often this happens after menstruation. Excessive bleeding and rejected tissue, coming out, can cause displacement. In some cases, the IUD is dislodged immediately after insertion. As a rule, this is due to the unskilled work of the doctor who installed it.
Spiral displacement. Symptoms
Pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse, bleeding - these are the main signs of displacement of the spiral. Incorrect placement of the IUD significantly reduces its contraceptive effect. Therefore, if the above symptoms are detected, it is very important to use additional methods of birth control. For some women, the incorrect position of the IUD does not cause any pain, i.e. is asymptomatic. To detect a defect in time, you must follow some recommendations:
- You need to independently control the length of the threads coming out of the cervix. How can you tell if the spiral has shifted? If the antennae have disappeared or become significantly shorter, this may indicate that the device has fallen out. Most often this happens unnoticed when visiting the toilet. In this case, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and check for pregnancy. Elongated strands indicate helix displacement.
- You should visit a gynecologist's office once a year and perform an ultrasound diagnosis. Following these simple rules will allow you to identify the incorrect position of the IUD in time and avoid unplanned conception.
Negative consequences
If the spiral has become dislodged (moved), in addition to heavy menstruation and pain in the abdominal area, more serious consequences are possible. In 15% of cases, women are diagnosed with damage or injury to nearby organs, especially the intestines.
Treatment
An ultrasound examination should determine the position of the device in the uterine cavity. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the IUD needs to be removed. After this, you can install a new one or choose a different method of protection. The device cannot be reused. If no inflammatory processes occur during wearing, removal is almost painless. It is very important that the procedure is performed by a specialist and takes place under sterile conditions. This will avoid damage to the uterine mucosa and infection. Typically, the IUD is removed during the menstrual cycle.
Doctors have found that women who have had a vaginal birth have virtually no complications associated with the use of such a contraceptive method as the intrauterine device. Displacement is most often observed in women with suspected adenomyosis.
Reviews and comments
Leave a review or comment
Source: www.zppp.saharniy-diabet.com
Mirena spiral: features of the IUD
Mirena is a spiral that releases a hormone similar to natural progesterone. It inhibits the growth of the inner layer of the uterus, reduces bleeding, prevents the growth of fibroids and unwanted pregnancy. Set for 5 years, price 12-12.8 thousand rubles, 1.9-2.3 thousand hryvnia.
What does it look like
Mirena looks like a white letter T about 3 cm in size. This is the main part of the hormonal device that is placed in the uterine cavity. On the white polyethylene body there is a reservoir for the hormone; it is gradually released through the membrane at a pre-calculated rate. A loop and threads are attached to the T-shaped base, through which Mirena is removed. The second part of the system is an insertion device (tube, piston, slider, handle).
Compound
Mirena contains levonorgestrel. It is similar in action to the female sex hormone progesterone. Due to it, two processes occur simultaneously - treatment of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterus) and strengthening of the contraceptive effect of the IUD. The total amount of levonorgestrel is 52 mcg. It is released at a rate of 20 mcg per 24 hours, but after five years the release into the uterine cavity drops by half.
All other components are auxiliary:
- polymer core with high elasticity (flexibility) and viscosity;
- shell made of polymer material with silicon dioxide;
- plastic housing with barium sulfate;
- thin brown threads (antennae).
We recommend reading about how menstruation occurs during and after the IUD. From the article you will learn about the effect of the IUD on the reproductive system, installation of the IUD, and the timing of the onset of menstruation with the IUD.
And here is more information about treatment options for hyperplasia without curettage.
Action of Mirena
The action of Mirena occurs simultaneously in two directions - therapeutic and pregnancy prevention. The first is manifested in the following changes:
- the thickness of the inner layer - the endometrium - decreases, its nutrition deteriorates, cell division is inhibited, the response to female hormones (estrogens, progesterone) decreases;
- uterine bleeding decreases by 95% after a year, and may disappear while the device is in the uterus, this helps restore the composition of the blood;
- prevents further growth of tumors (fibroids) of the muscle layer.
The contraceptive effect is provided by several processes at different levels:
- pituitary gland (gland of the brain) – the production of luteinizing hormone decreases, it is responsible for the process of release of the egg from the follicle;
- endometrium - Mirena prevents its cyclical changes, reduces its thickness, which prevents the fertilized egg from attaching;
- cervix – sperm motility decreases, mucus becomes thicker;
- fallopian tubes - relaxes the walls, reduces the speed of movement of the egg.
As a result, either ovulation (and, accordingly, conception) does not occur at all, or the spiral interferes with the attachment of the fertilized egg.
Manufacturer
The manufacturer of the original Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is the Bayer Schering Pharma concern. Its factories are located in Germany and Finland.