The intrauterine device is a modern method of contraception that allows you to avoid unwanted pregnancy; the simple and effective principle of the IUD is to mechanically prevent the maturation of the egg. The installation of an intrauterine device is carried out by a doctor at the final stage of menstrual flow.
The consumer is presented with a wide range of spirals made in Russia and abroad, which makes it very difficult to choose. Based on competent advice on choosing a spiral, you can evaluate the advantages of each type and choose the most suitable option.
How to choose the right one
It is important to remember - you should not choose this contraceptive at your own discretion. Only a gynecologist is required to select on an individual basis after a gynecological examination.
When making a decision regarding choice, it is important to consider the following points:
- did the woman give birth or not, if so, how many times and whether the birth was natural or was it a caesarean section;
- whether at the time of installation there is an inflammatory process in the uterine cavity, diseases of the appendages, if any - how often do exacerbations manifest themselves;
For chronic inflammation, an IUD is not placed!
- what is the nature of menstruation - is it scanty discharge or, on the contrary, abundant;
- whether diseases such as fibroids or endometriosis are observed, and the anatomical dimensions and structure of the uterine cavity are also taken into account.
Why is it worth having an IUD installed at SM-Clinic?
- We employ experienced gynecologists;
- you will not encounter rudeness or inattentive attitude - we value our reputation;
- all necessary examinations can be completed right on the spot and at a time convenient for you;
- We use only high-quality products from world brands that have passed strict safety controls;
- you are under the constant supervision of a doctor, and if necessary, you can contact him immediately.
You can find out complete information about the cost of the procedure, ask any questions or sign up for a consultation by calling the numbers provided or on the clinic’s website. “SM-Clinic” is a medical center in Moscow where the price is affordable for most, and the quality of services is not inferior to the highest world standards.
Pros and cons of the spiral
Before you decide to put in an intrauterine device, you should weigh all the pros and cons of the product.
Regarding the advantages of the latter, doctors highlight the following points:
- Affordability and the ability to forget about contraception for several years, while not requiring the woman and partner to strictly adhere to the principles of protected sex.
- After removal, the woman’s reproductive functions are restored quickly, and the effect of contraception is achieved immediately after its installation.
- Indicated as a remedy for heavy menstruation and fibroids, intrauterine adhesions, and other pathologies.
- There are no adverse reactions when selected correctly and is suitable as a means of contraception during the postpartum period.
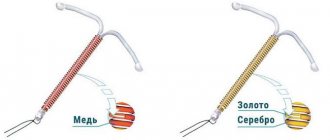
- It can be combined with many medications and alcohol, and has an anti-inflammatory effect due to the silver or gold contained in the intrauterine device.
Disadvantages include:
- The risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases significantly; the drug may spontaneously fall out of the uterine cavity.
- Increases the duration and heaviness of menstruation several times and increases the risk of contracting STDs.
- There is a high probability of damage to the uterine cavity if the intrauterine device is inserted incorrectly, and at the same time you have to constantly check whether the contraceptive is in place.
- Selects and installs only a gynecologist.
Introduction
The levonorgestrel intrauterine device (levonorgestrel IUD) creates a very reliable, stable and long-lasting contraceptive effect. In addition, the results of numerous studies confirm the high effectiveness of the intrauterine device with levonorgestrel:
- in terms of reducing blood loss during menstruation;
- in terms of solving the problem of irregular and/or heavy bleeding in women with uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, as well as in women approaching menopause, and in women with disorders of the blood clotting system;
- in terms of relieving menstrual pain and pelvic pain associated with endometriosis;
- in terms of reducing the risk of developing endometrial cancer and endometrial hyperplasia, as well as in terms of regression of endometrial hyperplasia in women who have already been diagnosed with this condition.
Many women who are faced with the problem of excessive bleeding choose the levonorgestrel intrauterine device as an alternative to hysterectomy.
To maintain the contraceptive and therapeutic effect of the levonorgestrel IUD, after its administration, no action is required on the part of the woman.
The contraceptive and therapeutic effects of the levonorgestrel IUD last for 3-5 years or a little more (depending on the brand of the device).
Among all hormonal contraceptives, the levonorgestrel intrauterine device has one of the highest safety profiles. Thanks to this, almost all women of any age can use it.
Given the high effectiveness and safety of levonorgestrel intrauterine devices, current guidelines for specialists (see Sources) recommend that doctors offer the installation of these IUDs to all women who need reliable and long-term contraception, regardless of their age or whether they have given birth in the past or not.
This article complements a number of guidelines that have presented conclusions regarding the advisability of using a levonorgestrel intrauterine device in various situations:
- Guide to Contraception and Birth Control - which provided information regarding the use of the levonorgestrel IUD as a contraceptive and how it compares to other contraceptives.
- Menstruation and Spotting, a Guide for Women - Provides information regarding the use of a levonorgestrel IUD to address the problem of heavy and/or prolonged periods and irregular vaginal bleeding in women of all ages. This article also provides information on how to address irregular bleeding in women using a levonorgestrel IUD.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome, a guide for women - a guide that provides information regarding the advisability of using a levonorgestrel IUD in women with PCOS to reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and/or cancer.
- Endometrial hyperplasia. Women's Guide is a guide that provides recommendations regarding the appropriate use of a levonorgestrel IUD for the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia.
- Uterine Fibroids, a Comprehensive Guide for Women - A guide that recommends the use of the levonorgestrel IUD to relieve bleeding in women with uterine fibroids.
- Endometriosis, a Comprehensive Guide for Women - Provides information regarding the use of the levonorgestrel IUD to relieve or eliminate menstrual pain and chronic pelvic pain associated with endometriosis.
- Adenomyosis of the Uterus, Answers to Basic Questions - provides recommendations regarding the advisability of using a levonorgestrel IUD to relieve various symptoms associated with adenomyosis (severe pain during menstruation, chronic pain in the pelvic area, heavy and/or irregular vaginal bleeding).
Women who, based on the recommendations presented in the guidelines outlined above, have come to the conclusion that the levonorgestrel IUD may be an appropriate solution to their problem will then find evidence-based answers to the following sets of questions:
- What is known about the possible negative and positive effects that a levonorgestrel IUD may have on various aspects of a woman's health in the short and long term? In particular, what is known regarding the possible positive and negative spirals:
- the likelihood of developing various types of cancer;
- on the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases;
- on the likelihood of developing osteoporosis and the risk of fractures in old age;
- on the emotional and psychological state of a woman;
- for various symptoms:
- pain during menstruation, chronic pain in the pelvic area,
- excessively heavy or prolonged menstruation,
- irregular bleeding from the vagina.
- on the development of various gynecological diseases:
- uterine fibroids,
- endometriosis,
- endometrial hyperplasia.
- What complications and side effects may be associated with insertion, wearing, and removal of a levonorgestrel intrauterine device, and what can be done to eliminate or alleviate these side effects?
- What recommendations should women follow to ensure maximum effectiveness and safety of wearing the levonorgestrel IUD:
- before starting to use this product;
- during the period of use of this product.
***
In addition to intrauterine devices with levonorgestrel, there is another type of device - copper IUDs.
Copper IUDs differ significantly from levonorgestrel IUDs in their principle of action and their effect on various symptoms and are therefore discussed in a separate article: Copper intrauterine device. Information for women.
We believe that the ability to safely, effectively and comfortably use modern contraceptives to plan pregnancy and improve quality of life by alleviating symptoms associated with various diseases is of great importance for women and for the whole world, given the role that women play in it.
We hope that with the information presented in this article, women will be able to:
- better understand the recommendations of their attending physicians regarding the advisability of using certain hormonal contraceptives (including levonorgestrel coils);
- choose a product with an optimal ratio of effectiveness/safety/cost;
- use these products with maximum effectiveness, safety and comfort, with peace of mind and confidence that they have made a reasoned and intelligent choice.
The principle of operation of the intrauterine device
The IUD mechanically prevents unwanted pregnancy:
- Accelerates the movement of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes, preventing its attachment in its cavity. Without securing a foothold in the uterine cavity, the fertilized egg simply dies, plus it significantly reduces sperm motility.
- If the IUD is classified as a hormonal device, it releases progestogen into the uterine cavity and this, in turn, delays the formation of the mucous layer in the uterine cavity, where the fertilized egg is attached.
Why do women get IUDs?
To prevent unwanted pregnancy, you can use a vaginal device. This device, made of copper and plastic, performs the following functions:
- prevents the movement of sperm into the uterine cavity by changing the composition of cervical mucus;
- reduces the lifespan of eggs;
- prevents the fertilized egg from attaching to the walls of the uterus.
The IUD is considered a reliable means of contraception. But it is prescribed mainly to women who have given birth and who are not at risk for STDs. If these conditions are not met, it is recommended to use other methods of contraception.
Rules for installing and removing the spiral
After the examination and selection of the model, they begin to install it, most often on the 3-8 calendar day of the menstrual cycle. Also, the doctor can determine after abortion and childbirth that are not complicated by negative consequences.
It is installed during a routine gynecological examination and does not require anesthesia or hospitalization and follow-up.
It is inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity - manipulations are carried out using a guide, moving it inside, installing a designating ring. Having inserted it to the desired length, the contraceptive is released and straightened inside the uterine cavity. The antennae that hang down into the vagina are cut to the required length.
Removal is carried out either at the request of the woman or after the expiration date, having previously carried out local anesthesia. It is removed by pulling the “antennae” - it can be replaced immediately, and if there are no antennae, it is removed using a cervical dilator.
If the spiral in the uterine cavity has grown into its walls, removal is carried out using a hysteroscope.
How to place an IUD for women
The process of inserting an intrauterine device takes from 10 to 20 minutes. It resembles a regular gynecological examination and is performed on an outpatient basis. Before installation, it is advisable to undergo a gynecological examination, do an ultrasound and undergo tests.
Preparing for installation
Before the insertion procedure, gynecologists recommend that women abstain from sexual intercourse for several days. It is undesirable to use intervaginal medications (tablets, creams, suppositories), or douche.
How the IUD is inserted into the uterus
After the woman sits on the gynecological chair, the doctor conducts an examination to identify pathologies of the cervix and determine the structural features of the reproductive organs.
Before the procedure, the gynecologist treats the genitals with a disinfectant solution. Pain can be reduced by injecting an anesthetic into the cervix. To install an intrauterine contraceptive device, the doctor fixes the cervix with a special instrument and inserts a sterile probe into the cervical canal. This procedure allows you to verify the patency of the canal.
After removing the probe, the doctor inserts the coil into the uterus using a plastic applicator. The threads protruding from the neck are trimmed so that they do not interfere with the vagina, but the doctor can use them to remove the spiral.
Is it painful to insert the IUD?
Most women note that insertion of the IUD is almost painless. Some feel only a slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen, like during menstruation. But about a third of patients rate the procedure as unpleasant and painful. Such sensations occur mainly in women with a low pain threshold.
What side effects may there be?
First of all, in women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted - it becomes irregular, it can become longer or shorter, the discharge can be scanty or more abundant. Side effects of the intrauterine device include:
- irregular discharge between menstruation – most often a concern in the first six months after installation of the IUD;
- attacks of headache in the morning and acne on the body, as well as chest pain;
- the formation of benign cysts on the ovaries, which will resolve over time;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting, pain in the lower abdomen, and lack of menstruation;
- hormonal imbalance, although such a reaction from the IUD is rare;
Contraindications
Regarding existing contraindications for the installation of an IUD, doctors call them:
- diagnosed oncology of the mammary glands, as well as the cervix;
- liver disease and unclear etiology, uterine bleeding between menstruation or after sexual intercourse;
- blood diseases and cardiovascular pathologies;
- a previously untreated STD or a diagnosed infection affecting the pelvic organs;
- diseases and abnormal structure of the cavity and cervix.
Cost of intrauterine device
How much will an intrauterine device cost? The price depends on the type of intrauterine device, the alloy, and whether it is classified as mechanical or hormonal. For example, the most popular Multiload costs between 2-3 thousand rubles. But the T-shaped ones, which are in second place in the popularity rating, such as Vector or Nova T, cost from 450 to 2,500 rubles. At the same time, the well-proven Mirena hormonal device, which combines the effect of a contraceptive and provides a local therapeutic effect, costs from 7 to 10 thousand rubles.
What does an anti-pregnancy device look like?
The type and shape of the intrauterine contraceptive should be selected together with a gynecologist. These devices differ not only in appearance, but also in size, operating principle, and materials from which they are made.
T-shaped IUDs are the most common. IUDs made in the shape of the letter “T” can be made of different metals and contain hormones. Some of them, in addition to being contraceptive, also have a therapeutic effect.
Comment! T-shaped intrauterine devices have earned popularity due to their convenience, ease of insertion and removal.
IUDs are made from plastic to which barium sulfate is added. Thanks to this substance, X-rays can be used to see the location of the intrauterine contraceptive device. Copper or silver wire (metal reference is often used) is wound around the base of the device (the leg of the letter “T”).
But if you wish, you can find ring-shaped or F-shaped models. Previously, snake-shaped devices were used, but they are no longer used due to low efficiency.