Normal menstrual flow is dark red in color and contains a small amount of clots, but sometimes girls notice that black blood flows during menstruation. A change in the color of bleeding to dark can occur for some physiological reasons or due to certain pathologies, so it is important to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms and consult a gynecologist if the color of menstruation does not normalize.
Why does the discharge turn black?
The color of menstrual blood is normally bright or dark red, even burgundy. Almost black or dark periods indicate a hormonal imbalance, which often occurs against the background of various diseases, pregnancy, and the onset of menopause.
You can find out why your periods are black only after a detailed examination and certain tests. A one-time change in shade is not a cause for alarm. But the regular appearance of clots, dark brown blood during menstruation, pain or cramps in the lower abdomen, an increase in the duration of menstruation or, conversely, a decrease in the cycle indicate the need for examination.
One-time scanty discharge in combination with dark blood staining may indicate the development of an ectopic pregnancy or the onset of menopause. In any case, these are signs of hormonal changes.
Ectopic pregnancy
How to fight?
First, it is necessary to identify the source of their occurrence. Since it is impossible to do this on your own, you need to visit a doctor. He will order the necessary studies. Based on their results, the specialist will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics consists of:
- Taking a general blood and urine test;
- Taking the necessary smears at the discretion of the specialist;
- Ultrasound.
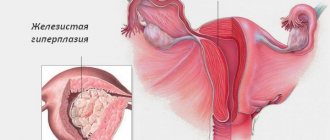
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations. Often, examination results reveal diseases such as hyperplasia, endometritis or endometriosis. They are quite dangerous for women because:
Hyperplasia in its advanced form can cause the development of malignant tumors. Often, when this disease is detected in an advanced, severe form, it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. The pathology is observed mainly in mature women; it rarely occurs in young women.
Endometritis poses a danger in that when a woman decides to become a mother, she will not be able to bear a baby (the inner uterine layer will reject the fetus). Therefore, you should not start this type of disease. It is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs, which should be prescribed by a doctor;
Endometriosis is a common disease among girls under 30 years of age. With this pathology, uterine tissues end up in other organs. Often, with this pathology, blood may even bleed from the eyes.
When is this the norm?
Regular dark-colored periods sometimes occur in women and are normal. Actually, menstruation is a consequence of the death of the egg and the further removal of the dead layer of the endometrium. Fresh blood that immediately leaves the uterus is bright red. The longer the discharge lingers inside a woman’s body, the darker it is.
Sometimes there is black blood during menopause, which is explained by a decrease in the concentration of female sex hormones and the decline of reproductive function. In the early period of menopause, the cycle is almost always disrupted - menstruation comes late or earlier than the due date, the volume of discharge and its shade change.
The norm is considered to be more intense coloration of the discharge on the first day of menstruation and on the 6th–7th day, when bleeding is observed. Such bleeding at the end is considered normal in gynecology - the uterus is freed from the remnants of the endometrium.
During pregnancy (4–6 weeks), scanty discharge of a reddish or brownish hue is possible. At the beginning of the 1st trimester, this can be a threatening symptom (ectopic pregnancy, threatened miscarriage, placental abruption).
The reason for the discharge of dark clots after menstruation is often the anatomical features of the woman’s reproductive system - the narrow cervix contributes to the retention of blood and its darkening. This can be considered normal if there are no other symptoms (increased cycle, signs of amenorrhea, pain).
Could there be pregnancy?
The possibility of pregnancy should not be ruled out. Dark discharge is likely due to implantation bleeding. Blood is released when the fertilized egg attaches to the walls of the uterus. In this case, there is no need to worry. This is a physiological process.
Discharge occurs when there is a threat of miscarriage. Sometimes black daub in this case is the only symptom. It is better not to ignore the present symptom, but to visit a doctor for an examination and to determine the cause of the disorder.
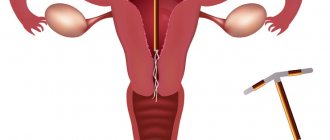
Another reason for dark discharge during pregnancy is ectopic flow. This is a dangerous condition for a woman, requiring urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention. The consistency of blood is thick. Vaginal bleeding may occur. You need to call an ambulance and follow all recommendations. Before the doctor arrives, you should not take any medications.
Dark discharge may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy
When a woman already knows about pregnancy and has visited the doctor, dark discharge may be the result of a sloppy gynecological examination. Trauma occurred and dark blood came out. This is also likely after sexual intercourse.
During pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor your health. Any deviations from the norm require a visit to the doctor.
Causes of black periods
The main cause of black periods is hormonal imbalance. Staining can also occur in the following cases:
- irregular sex life;
- recent surgical interventions on the genitourinary system or childbirth;
- age;
- lactation or pregnancy;
- decreased immunity;
- metabolic failure;
- climate change, stress, insomnia.
Scanty dark discharge may appear after an abortion, insertion of an intrauterine device and other manipulations in the uterus and ovaries. They also retain blood and stain it a dark shade of synechia - the septum in the uterine cavity.
Central genesis
Absence of menstruation, discharge of dark blood clots is a symptom of amenorrhea of central origin. The causes of this syndrome are dysfunction of subcortical structures and the cerebral cortex. There are congenital, organic and functional pathologies.
Functional amenorrhea, the most common, occurs against the background of such factors as:
- severe stress;
- mental trauma;
- intoxication of the body;
- neuroinfection;
- changes in hormonal levels during unsuccessful pregnancy, abortion, childbirth;
- physical or emotional overload;
- development of manic-depressive psychosis;
- pituitary tumors.
Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system lead to malfunctions in the functioning of a woman’s genitourinary and reproductive systems. Prolonged depression, stress, chronic mental disorders, single emotional overexcitation can provoke menstrual cycle disorders and also lead to the appearance of dark blood and clots.
Ovarian origin
Ovarian dysfunction (impaired hormone-forming function) is one of the main causes of infertility, missed pregnancy, miscarriage, and changes in the menstrual cycle. High risk factors for developing the disease are in women over 40 years of age with a history of diabetes, obesity, ovarian and uterine tumors, frequent abortions, and wearing an intrauterine device.
Manifestations:
- hormonal imbalance;
- increase in the duration of menstruation;
- erratic, irregular menstruation;
- increased blood loss to 100 milliliters or more;
- intense coloration of discharge.
Some experts attribute the manifestation of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) to one of the manifestations of ovarian dysfunction. The disease can cause fibroids, mastopathy, endometriosis, infertility and breast cancer.
Uterine form
Often, changes in the menstrual cycle are caused not by a malfunction of the ovaries, but by pathologies of the uterus, such as damage to the basal layer, congenital defects. The main reason is frequent abortions, which result in gradual depletion of the basal layer of the endometrium and the occurrence of intrauterine adhesions.
The adhesive process can occur not only during abortion, but also as a result of myomectomy, diagnostic curettage, acute and chronic endometritis of the uterus.
Another reason why black periods occur is considered to be genital tuberculosis. As the disease develops, intrauterine adhesions form, partially or completely covering the uterine cavity.
For diseases of the endocrine glands
The hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine, produced by the thyroid gland, ensure the cyclical functioning of the ovaries and the synthesis of progesterone and estrogen. The slightest disturbance in the functioning of the thyroid gland causes changes in the menstrual cycle - delay, decrease or increase in blood volume, ovarian dysfunction.
Thus, menstrual blood becomes dark and even almost black due to hormonal imbalance caused by hypo- or hyperthyroidism:
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland) provokes amenorrhea and infertility. In addition to black discharge, symptoms of PMS, pain during menstruation, difficulty conceiving, and general deterioration of the condition are observed.
- Hypothyroidism, or insufficient production of hormones, causes scanty menstruation, decreased duration, delayed and irregular periods, bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
Menstrual function is completely restored after adequate treatment of thyroid diseases.
Taking medications
Taking some medications causes increased periods, black clots and cycle disruption. Contraceptives (OCs) promote an increase in hormone concentrations. A change in the ratio of estrogen and progesterone levels, especially in the first months of taking the drugs, leads to a brown and dark burgundy coloration of the discharge. Sometimes, on the contrary, the amount of mucus increases, which gives the secretion a light red and pink color.
For the purpose of contraception or during treatment with hormonal drugs, a woman’s body undergoes dramatic changes.
In the first 1–3 months after starting to take such medications, the reproductive system adapts to the “new” level of hormones. With regular use and no gaps, from the 4th month the color of the discharge becomes normal.
Could I be ovulating?
Ovulation is a natural process characterized by the rupture of the follicle and the release of a finished egg. This is the fertile period during which the likelihood of successful fertilization increases.
The menstrual cycle normally lasts 21-35 days. Ovulation occurs in the middle of the female period. When planning a child at this time, you should stop using protective equipment.
With a short menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs almost immediately after menstruation. Physiological changes can be recognized by the following signs:
- increased mood;
- breast engorgement;
- increased volume of vaginal secretion;
- increased sexual desire.
During ovulation, the discharge resembles in its structure raw egg white. When the follicle directly ruptures, a small amount of blood is released. After contact with air, the liquid acquires a dark, dirty tint.
Sometimes this is a sign of ovulation
Ovulation does not require treatment. This is a natural process that occurs every month. Normally, an anovulatory cycle is possible only up to 2 times a year.
Symptoms and consequences of hypomenorrhea
Scanty discharge for a short time, dark blood during menstruation are some of the symptoms of hypomenorrhea. PMS often develops, pain in the lower abdomen, indigestion, discomfort in the chest and lower back, headache, and drowsiness appear.
Hypomenorrhea may also be accompanied by black periods, severe swelling, emotional instability, and black clots, especially on the first and second days of menstruation.
If during menstruation blood flows in a small volume, menstruation ends in 2-3 days, they speak of the development of hypomenorrhea. This is facilitated by obesity or excessive thinness, taking oral contraceptives, chronic diseases, intoxication, problems with the thyroid gland, and stress. Often, instead of menstruation, dark-colored discharge is observed - scanty, spotting.
Complications include frigidity, infertility, miscarriage, risk of ectopic pregnancy, secondary amenorrhea (complete absence of menstruation).
To avoid delayed menstruation and serious complications, it is necessary to be examined by a doctor and undergo prescribed tests. They will help prevent the development of dangerous diseases, as well as normalize the cycle and improve the functioning of the female reproductive system.