Every woman's menstrual cycle is unique. It is impossible to find two identical organisms that function identically.
During ovulation, when the female body's fertility reaches its peak, some women may experience pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
Why the lower back hurts in the middle of the cycle, what this can mean and how to avoid it, we will analyze further.
Ask your question to a neurologist for free
Irina Martynova. Graduated from Voronezh State Medical University named after. N.N. Burdenko. Clinical resident and neurologist of the Moscow Polyclinic. Ask a question>>
Causes
On average, one cycle is 28 days, and ovulation occurs on days 13-15 . When the egg is released from the ovarian follicle, the chances of getting pregnant are high. Lower back pain during ovulation in the following situations:
- Physiological pain is associated with the natural process of the release of a mature female reproductive cell into the fallopian tube.
- Pathological pain – provoked due to the presence of diseases of the reproductive system.
In this case, it is important to listen to your own body.
If lower back pain that occurs in the middle of the cycle is moderate in nature, is not accompanied by other symptoms, and is also capable of self-destruction, there is no need to sound the alarm. Perhaps the unpleasant sensations are associated with the structural features of the genital organs.
If the pain is intense, covers the lower abdomen, ovarian area and lower back, and there is also bloody or brown discharge, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. Such symptoms may indicate the presence of diseases, which, if cured, will eliminate unpleasant lower back pain.
Low back pain and ovulation
There can be many reasons for lower back pain. First of all, this symptom is a signal of the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
In addition, painful sensations can be a sign of problems with the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Women of reproductive age often experience lower back pain during pregnancy, menstruation and ovulation.
Can your lower back hurt after ovulation?
Women very often complain of pain before and after ovulation.
And each of them wants to know why the lower back and lower abdomen hurt during egg maturation, and how dangerous it is.
After reading this article, you will be able to understand how the lower abdomen and back can hurt, and what kind of pain should alert you.
It will also clarify for women whether and how painful symptoms are related to the process of conception.
Physiology of a woman and natural causes of pain
The back and abdomen may not hurt at all during and after ovulation, or they may hurt slightly or severely. It depends on the physiological characteristics of women. For example, on the structure of the reproductive organs, the rate of maturation of the egg, the patency of the tubes, the occurrence or non-occurrence of conception, and so on. Common causes of pain called “ovulation syndrome” are:
- the body’s reaction to the release of an egg ready for fertilization from the follicle;
- pain occurs due to the fact that the egg ruptures the follicle during ovulation, freeing its way first into the tube, and then into the uterus;
- when the follicle ruptures, a small amount of blood is released, which enters the abdominal cavity, which also causes pain;
- alternating (right and left) pain is associated with the fact that maturation occurs every month in either the left or the right ovary.
Pathological pain in the lumbar and abdominal areas
If the pain in the lower back and abdomen is tolerable, then gynecologists do not recommend special treatment. Since such a reaction of the body is considered the norm for the release of an egg ready for conception into an environment where fertilization can occur. Doctors' intervention is required when the pain becomes such that a woman can hardly bear it.
- Severe painful outbreaks can be caused by an inflammatory process that occurs not only in the organs of the reproductive system, but also in other organs of the peritoneum.
- Increased pain radiating to the lower abdomen or lower back is caused by the consequences of appendix removal surgery.
- The lower back may hurt from gynecological diseases, for example, cystic formations in the ovaries, salpingitis or endometriosis. For the same reasons, the lower abdomen may hurt.
An indispensable condition for contacting a doctor should be the duration of severe pain for more than three days. If the sensations are naturally associated with the ovulation process, they usually pass within three days.
If the syndrome continues for more than three days, this is a signal of pathology in the body and that you need medical help.
You should make an appointment with a gynecologist so as not to miss the onset of serious consequences, including the impossibility of conception.
What symptoms accompany dangerous pain?
Every woman should be wary of the following additional unpleasant sensations that simultaneously arise during the period of ovulation:
- upset stomach and stool;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills and fever;
- urinary disorders, pain or difficulty;
- dizziness and migraine;
- shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- the egg remains in the ovary for 12-14 days;
- after that the exit process itself begins, which lasts a short time - only two days;
- exit occurs into the fallopian tube, this occurs on days 12-17 of the ovulation cycle;
- back pain and its spread to the lower abdomen and thighs at this time of the cycle are considered normal;
- if the pain continues in the second half of the cycle, then you need to contact a gynecologist.
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination to determine their causes. If the diagnosis does not reveal diseases of the organs that radiate pain to the lower abdomen and lumbar region, then the doctor will prescribe painkillers or a heating pad to the painful areas.
It is important for women to remember to take care of themselves during ovulation, especially if they are looking forward to conceiving.
Good rest, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are necessary conditions to reduce the discomfort associated with the ovulation process, and not to take medications that can later harm the embryo.
About the permissible time of painful phenomena during and after ovulation
In order to understand the question of how long natural minor pain can last after and during ovulation, you need to know about the nature of this process. Maturation of eggs occurs in every woman and girl from the moment of menstruation.
Menstruation itself is the result of non-occurring conception after the egg leaves the follicle.
If fertilization does not occur, then the environment (epithelium) in which the attached egg should develop begins to collapse, this is accompanied by bleeding and the release of epithelial particles to the outside.
The time of the ovulation cycle is distributed as follows:
It must be borne in mind that pain in the lower abdomen and lower back can occur not only due to premenstrual or ovulation syndrome, but also due to the onset of conception. In this case, pain is more often a sign of a pathological pregnancy, for example, as a result of conception and the beginning of the development of a fertilized cell in the fallopian tube (ectopic pregnancy).
Lumbar pain after the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine epithelium may indicate the onset of a miscarriage. Therefore, be especially vigilant if you are expecting to become pregnant.
Your timely visit to a doctor and examination will help to avoid spontaneous abortion and reduce the possibility of complications.
This concerns not only the woman’s reproductive system, but also the health of other organs located in the pelvic area.
Lebedev Evgeniy Ivanovich
Experience in the industry - more than 10 years
Statistics show that approximately 70% of women experience pain during ovulation.
In most cases, these are mild pains that go away on their own literally on the second day, and therefore do not cause danger and do not require a trip to the doctor.
However, some representatives of the fair sex during this period experience severe pain that requires the attention of specialists. We will find out why the lower back hurts after ovulation by reading this article.
Causes of pain
In most cases, lower back pain two weeks before the onset of menstruation is associated with the process of ovulation, that is, the release of an egg from the follicle for subsequent fertilization.
Usually they are mild, but in some women the pain can be severe, and they recur from month to month precisely after ovulation.
Pain after ovulation can occur not only in the lower back, but also in the lower abdomen.
First of all, women experience pain during ovulation due to the rupture of the follicle by the egg. Gynecologists consider this process to be the norm, and therefore it does not require treatment. In addition, when the follicle ruptures, blood vessels burst, from which some blood enters the abdomen. A blood clot irritates the peritoneum, which is also accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
The female body is designed in such a way that the egg matures alternately, in the right and then in the left ovary.
That is why, when the egg leaves the follicle, representatives of the fair sex feel nagging pain on the left or right.
Moreover, most often unpleasant symptoms are noted on the right side, which may be due to the presence of an appendix nearby or to the anatomical features of the woman’s pelvis.
Experts attribute all of the above causes of pain to the so-called “ovulation syndrome.” Some women are new to it, while others suffer from it on a monthly basis. Moreover, the occurrence of the syndrome can be triggered by childbirth or a previous inflammatory disease.
Other causes of pain
Experts say that there are other, much more significant reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant symptom.
If the pain is strong, acute, flash-like, and does not stop after three days, it may be caused by an inflammatory process developing in one of the abdominal organs.
In addition, during the rehabilitation period after removal of the appendix, aching pain localized in the lower abdomen may also appear. In rare cases, the cause of the symptom in question in the lower back may be gynecological diseases, for example, salpingitis, ovarian cyst or endometriosis.
When to see a doctor
If your lower back hurts after ovulation, you should consult a specialist if the pain does not go away after three days, when these unpleasant sensations are accompanied by an upset stomach, nausea and vomiting, fever, migraines or dizziness, shortness of breath, as well as painful or difficult urination.
It is necessary to undergo an examination by a doctor in order to find out the cause of the pain symptom and timely identify the pathological process, if any. If there is no health risk, your doctor may recommend taking painkillers.
Experts say that taking analgesics, as well as proper rest during the period of ovulation syndrome, significantly helps to alleviate the condition. In addition, your doctor may recommend using a heating pad with hot water to relieve pain.
Take care of your health!
Sources: //osteohondrosy.net/boli-v-poyasnice-pri-ovulyacii-prichiny-i-sledstviya.html, //lechuspinu.ru/poyasnichniy_otdel/mozhet-li-bolet-poyasnica-posle-ovulyacii.html, // www.ja-zdorov.ru/blog/pochemu-posle-ovulyacii-bolit-poyasnica/
No comments yet!
Source: //bolibolshenet.ru/chem-snjat-bol-v-pojasnice/bol-v-pojasnice-i-ovuljacija.html
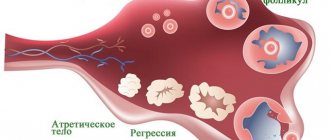
Follicle rupture
A woman's reproductive cells mature only on days 13-14 of the cycle, and when they are ready for fertilization, the follicle bursts , and the cell itself is sprayed under pressure into the fallopian tube. At the moment of rupture of the follicle, painful sensations of varying degrees may be observed, but all of them (in the absence of pathologies) are a common occurrence.
Some women may experience a darker color change in their vaginal discharge.
This condition is not permanent, but lasts only a few days.
In cases where the pain is intense, we may be talking about the presence of ovulatory syndrome. This is a collective disease, the causes of which are numerous. Accompanied by severe spastic pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region. Type of pain Aching, nagging pain that intensifies with movement or prolonged sitting. Localization Lower abdomen and lower back. Diagnostics To identify the dependence of ovulation and accompanying pain, several diagnostic methods are used:
- Questioning the patient - the doctor determines the duration of the cycle, as well as its day at the time of pain development.
- Ultrasound helps to detect the presence of an egg in the follicle or outside it.
- Blood test for hormones - helps to identify the phase of the cycle using hormones, the level of which is different on different days of the cycle.
Treatment If an acute pain syndrome is diagnosed, the doctor may prescribe medications that reduce unpleasant symptoms, such as:
- Spazmolgon;
- No-Shpa;
- Baralgetas;
- Tamipul;
- Baralgin;
- Nalgesin;
- Tempalgin.
It is recommended to get more rest and walk in the fresh air.
In the event that medications do not give the desired result, you must immediately seek help from specialists.
Physiology of a woman and natural causes of pain
The back and abdomen may not hurt at all during and after ovulation, or they may hurt slightly or severely. It depends on the physiological characteristics of women. For example, on the structure of the reproductive organs, the rate of maturation of the egg, the patency of the tubes, the occurrence or non-occurrence of conception. Common causes of pain called “ovulation syndrome” are:
- the body’s reaction to the release of an egg ready for fertilization from the follicle;
- pain occurs due to the fact that the egg ruptures the follicle during ovulation, freeing its way first into the tube, and then into the uterus;
- when the follicle ruptures, a small amount of blood is released, which enters the abdominal cavity, which also causes pain.
Maturation of eggs occurs in every woman and girl from the moment of menstruation. Menstruation itself is the result of conception not occurring after the egg leaves the follicle. If fertilization does not occur, then the environment (epithelium) in which the attached egg should develop begins to collapse, this is accompanied by bleeding and the release of epithelial particles to the outside.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
Ectopic pregnancy
In the case when a fertilized egg is not able to move into the uterine cavity for further development, it settles on the wall of the fallopian tubes . Every day the cells divide, and the embryo increases in size, stretching the fallopian tube. Irritation of the nerve endings leads to an increase in pain, and when the embryo is several times larger than the parameters of the fallopian tube, the pain becomes unbearable.
This phenomenon is extremely dangerous for the body, as it can cause pipe rupture and internal bleeding, which is a threat to life.
Therefore, after the onset of delayed menstruation, it is important to pay attention to such indicators as intense pain in the lower back and lower abdomen. Type of pain: Aching and bursting in the initial stages and sharp and shooting in the long term. Pain may be accompanied by a decrease in activity, as well as an increase in body temperature. Localization: The lumbar and hypochondrium area, as well as the lower abdomen. Diagnostics It is important to note that a blood test for ectopic pregnancy shows quite acceptable levels of the hCG hormone (pregnancy hormone), so it is not taken into account when diagnosing. The condition of the uterine cavity is assessed, and if there is no embryo in it, the fallopian tubes are examined.
Upon palpation, a significant increase in the diameter of the pipe is diagnosed, as well as a characteristic bulging in a separate area.
Treatment In this case, it is not possible to maintain the pregnancy, and treatment is exclusively surgical. Depending on what stage of development the embryo is at and how strongly it grows into the cavity of the tube, surgical intervention can be of two types:
- Tubotomy - used in the early stages of pregnancy, when there is no threat of rupture of the tube itself. A small size is produced at the site of the fertilized egg, after which all its contents are removed. Further treatment is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, as well as restoring the woman’s reproductive function.
- Resection of the tube with the ovary is performed when an extensive inflammatory process develops. The embryo is removed along with the tube and ovary, which significantly reduces the woman’s ability to conceive a child in the future.
Inflammation of the uterus and appendages
In the presence of pathogenic microflora in the uterine cavity, an inflammatory process develops , which can also affect the ovaries and tubes. Painful sensations can develop on any day of the cycle, but they intensify during ovulation and menstruation itself. Oophoritis and adnexitis have many causes, but most often there is more than one cause. Hypothermia, frequent changes of sexual partners and a sedentary lifestyle make themselves felt even in the strongest women.
During ovulation, the muscles of the ovary tense, which stimulates the release of the egg. In the presence of an inflammatory process, any muscle contractions can cause pain.
Also, discomfort can manifest itself immediately before menstruation and in its first days.
Type of pain Aching, girdling. Localization Lower abdomen, lower back, sacral spine. Diagnostics To determine the presence of an inflammatory process, it is necessary to undergo a number of unpleasant procedures:
- examination on a gynecological chair;
- smear analysis for cytology and histology;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs;
- blood test for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment Depending on what exactly triggered the inflammatory process, treatment may consist of components such as:
- Antibacterial therapy - broad-spectrum antibiotics are used that inhibit the activity of pathogenic microflora.
- Antimycotic therapy is aimed at destroying fungi.
- Maintenance therapy is based on taking vitamin complexes, as well as immunostimulating drugs that stimulate the activation of the body’s natural protective properties.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
This pathology develops only in those women who resort to stimulation of pregnancy . In the case when an anovulatory cycle is diagnosed or a woman cannot become pregnant for a long time due to the absence of an egg in the ovary, stimulation can help. The patient is given hormonal drugs that promote the maturation of several follicles at once.
At the same time, the volume of the ovary itself is noticeably increased, which provokes characteristic pain.
Type of pain Aching, girdling. May be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- nausea and dizziness;
- bloating;
- difficulty urinating or its complete absence;
- increase in temperature;
- swelling;
- lack of appetite.
Localization: Groin area and lower back. Diagnostics Diagnosis is made based on the following studies:
- Questioning the patient, as well as palpation of the ovarian area (their significant increase is palpable).
- Examination on a gynecological chair.
- Ultrasound or MRI.
- Urine and blood analysis.
Treatment It is necessary to stop taking all hormonal drugs that were prescribed for stimulation. If there is swelling or accumulation of fluid in the body cavities, antibiotics are used to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. Drugs such as:
- Lytic solutions - normalize the level of all vital components in the body.
- Drugs that prevent blood clotting (to avoid the development of thrombosis).
- Protein preparations and glucose.
The target organs that suffer the most are the kidneys, liver, and spleen, so further treatment is aimed at restoring their normal functioning.
Breast pain during ovulation - normal or abnormal?
From the moment of ovulation, a woman’s body experiences a significant increase in progesterone (up to 10 times). A side effect of the hormone is fluid retention. This is especially noticeable in the condition of the breasts; they swell a little and become painfully sensitive. The level of discomfort depends on the structure of the body, skin characteristics, and health status.
Chest pain during ovulation due to swelling from fluid retention in the body
If after ovulation there was no fertilization of a mature egg, then the level of progesterone drops and the breasts return to normal about a day before the start of menstruation. If pregnancy occurs, sensitivity and swelling persist.
Hormonal disbalance
In the case when a woman experiences constant stress , does not have a sexual partner, and also suffers from systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases), hormonal disruption may occur. Absolutely all processes occurring in the body are controlled by the hormonal system. When it is adversely affected by external factors, the production of one or another hormone is inhibited, and the production of another is carried out twice as much.
Hormones that control the functioning of the genital organs contribute to the establishment of a certain cycle. If there is a lack of their production, menstruation may disappear, or they may acquire an increased intensity of bloody discharge. In this case, the cycle shortens or, on the contrary, lasts more than 45 days.
A disruption in the production of one hormone leads to disruptions in the functioning of other hormones, so this pathology should be treated as early as possible.
The first symptoms of hormonal imbalance are:
- absence of menstruation for more than 2 months (in the absence of pregnancy);
- sudden weight gain with the usual diet;
- hot flashes and heat;
- lack of sexual desire.
Type of pain Aching pain in the lower back, which is accompanied by increased fatigue, irritability and aggression. Localization: Lower back and lower abdomen. Diagnostics A blood test for hormones will help determine the presence of a hormonal imbalance, as well as identify which hormones are produced in insufficient (excess) quantities. Blood is drawn from a vein, after which it is examined for all types of hormones. It is also important to establish what exactly is the cause of the failure (diseases, pathologies, disorders). Treatment Corrective therapy is used, prescribing to the woman those hormones that are lacking, as well as suppressing the synthesis of those that are produced in excess. To eliminate lower back pain, antispasmodics and analgesics (non-opioid group) can be used, which will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
It is important to establish the root cause of hormonal imbalance and eliminate it.
Why doesn't the pain go away?
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region
This is a fairly common disease caused by changes in the intervertebral discs. Severe attacks of pain are possible, radiating to the back and legs, which can lead to limitation of movements. There is numbness in the limbs . Contacting a specialist will help relieve the pain. Treatment will require an integrated approach, consisting of the selection of medications, physical therapy, proper nutrition and preventive measures.
Pathology of the coccyx
This disease can occur as a result of injury, which leads to bending of the tailbone (possible double bending). This leads to disruption of physiological processes, deterioration of metabolism in myofascial structures, affecting blood flow in the pelvic organs. Only a specialist doctor can recommend the necessary treatment.
Neurology
During menstruation, neurological diseases may worsen, accompanied by lumbago in the lower back, chest, and legs. Self-medication is unacceptable . The treatment regimen is prescribed by a specialist. Typically, during this period, chronic diseases worsen, which is associated with hormonal imbalance.
Experiences and stress
The female body is more vulnerable to critical life situations , so any, even the most minor stress, will not pass without a trace. Frequent experiences lead to the fact that the psyche does not have time to rest and recover, and the hormonal system fails. As a result, menstruation may disappear, or, conversely, appear more than 2 times a month, which is no less dangerous. It has been established that during experiences, the stomach and genitals suffer the most.
Violent sexual intercourse
If a woman is sexually active , but experiences pain in the lower back after each sexual intercourse, the reasons may be the following:
- the presence of adhesions on the uterus;
- inflammatory processes of the genital organs, which worsen in the presence of a rush of blood and friction;
- endometriosis;
- ovarian cyst.
Discomfort can also occur in completely healthy women, which is explained by an uncomfortable posture or muscle strain during sexual intercourse.
Type of pain: Aching. Localization: Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Diagnostics If you experience discomfort after sex, as well as if there is discharge, you need to visit a gynecologist who will conduct a routine examination. An ultrasound, cervical smear analysis, as well as urine and blood will be required. Treatment Once the cause has been established, the woman is given appropriate treatment.
It is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse during treatment, which will speed up the healing process.
Visit to the doctor
Consultation with a doctor is necessary if pain continues for a long time. The difficulty lies not only in ovulation and pathology of the pelvic organs. The stomach hurts due to gastrointestinal diseases, appendicitis and a number of other diseases.
When treating pain in the middle of the cycle, you should not rely on analgesic drugs. Their action is aimed at relieving the symptom. If pain persists for two or three cycles, it’s time to see a gynecologist. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests and studies.
An immediate visit will be required if a woman has discovered one or more symptoms accompanying pain: nausea, vomiting, weakness, a sharp increase in temperature, itching and burning of the genitals.
Consequences of appendix removal
As practice shows, the vestigial organ appendix is not vitally important for the body. However, its cells are capable of producing some hormones that take part in the protective functions of the body. Accordingly, after removal of the appendix, a person’s immunity noticeably decreases, which gives free rein to the pathogenic microflora of the genital organs to actively multiply, provoking inflammatory processes that cause pain.
Another reason may be adhesions that occur between the intestines and the abdominal cavity, which provoke pain, especially when moving the body.
Type of pain Stiff, shooting pain. Localization It hurts in the lumbar region, but discomfort can spread to the left hypochondrium and abdominal cavity. Diagnostics In this case, consultation with a neurologist and surgeon may be required. Diagnosis consists of performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, as well as x-rays of the pelvic bones. Treatment Therapy is selected depending on what exactly triggered the lower back pain.
First aid
If ovulation is accompanied by pain in the lower back and abdomen, you need to take a horizontal position and rest. It is not recommended to wear high heels in the middle of the cycle, or visit swimming pools and saunas. If the pain increases, you can take a pain reliever. If there is no result, a full diagnosis and qualified assistance is required.
When your lower back hurts during ovulation, you should not engage in sports or active games.
Thus, lower back pain after and during ovulation can be either completely natural or indicate the presence of serious pathologies. If your lower back hurts during ovulation, you should listen to the sensations. If the pain is moderate, no help is required. Particular attention should be paid to the nature of the discharge, which is the first signal about the presence of pathologies.