Indications
Depending on the form of the drug, the list of indications for its use will change.
So, in the case of a solution for injection, the following list of conditions is presented:
- The patient was admitted to the inpatient department with minimal signs of acute inflammatory process in the reproductive organs;
- The likelihood of gonorrhea progression;
- Complicated infectious lesions of the pelvic organs (as part of complex therapy with other antibiotics);
- The likelihood of identifying a polymicrobial composition of pathogens of an infectious or inflammatory process.
The medicine in powder form is recommended for use in the following situations:
- It is necessary to continue therapy after the initial injection course;
- Inflammatory processes in the appendages of moderate severity and the patient refused hospitalization;
- Microbes sensitive to the drug have been identified;
- Carrying out preventive therapy to prevent the development of inflammation of the appendages and endometritis.
It is strictly forbidden to start self-treatment. Only the leading specialist, based on the test results, the age and condition of the patient, the severity of the pathological process and the individual characteristics of the body, will determine in what dose and according to what regimen to carry out therapy.
Adverse reactions
It is difficult to find an active drug that is completely free of side effects. In the case of Ceftriaxone, the list will be insignificant:
- The occurrence of nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea and flatulence;
- Pain or discomfort in the hypochondrium on the right side, which is associated with impaired liver function;
- Development of dysbiosis in the intestines;
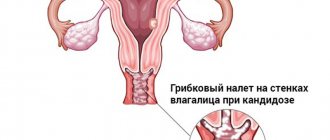
- The occurrence of candidiasis in the vagina.
Ceftriaxone is one of the most effective antibiotics that are part of antibacterial therapy for inflammation of the appendages or endometritis. Due to its high efficiency, minimal number of contraindications and minor side effects, recovery occurs in a short time.
Source 1ivf.info
A primary episode of inflammation in the appendages or exacerbation of an existing chronic process requires antimicrobial therapy. Ceftriaxone for salpingoophoritis allows you to create an optimal therapeutic effect from the very beginning, which will be a good option for the prevention of dangerous complications and conditions.
An antibiotic in injection or powder will help suppress the proliferation of microorganisms and prevent suppuration. However, one should remember about contraindications and the possibility of side effects: unauthorized and uncontrolled use of antibacterial therapy is strictly unacceptable.
Prescribing antibiotics for an identified pathogen
If a patient is diagnosed with gonococcal infection, the main drugs of choice are Ceftriaxone and Ciprofloxacin. However, there are alternative drugs - Spectinomycin and Cefotaxime. It is worth noting that tetracyclines and penicillins will be ineffective, since gonococcus is relatively resistant to them.
In a situation where adnexitis is caused by chlamydia, the main drugs will be Azithromycin and Doxycycline. Although Erythromycin and Ofloxacin can also be used.
If a patient has a mycoplasma infection, then she needs to take Doxycycline or Azithromycin. Alternative drugs that a doctor can prescribe are Gentamicn, Incomycin or Ofloxacin.
Herbs and folk remedies
Traditional medicine can also help with adnexitis. The most effective herbs that help fight this female disease are chamomile, boron uterus and sweet clover.
You will need two tablespoons of dried flowers of the plant. Pour a glass of boiling water over them and leave for 15 minutes. Before douching, do a cleansing enema with regular boiled warm water. You should douche with chamomile no more than twice a day - morning and evening.
Hog queen
World-famous Altai herb, which was used by our ancestors to treat female diseases. It should be consumed internally by making a water tincture.
Take the required amount of dried boron uterus in the proportion of 1 tablespoon to 1 glass of water, fill it with boiled purified water at a temperature of no more than 80 degrees and let stand for about 20 minutes. Drink the tincture an hour before meals three times a day, a quarter glass, for no more than two months of continuous cycle.
This plant has hypotensive, expectorant, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, wound-healing, antiseptic and analgesic effects, is widely used in medical practice and is considered almost twice as powerful from a biostimulating point of view as aloe extract.
Take 10 grams of chopped dried herb, pour boiling water and put on low heat for 20 minutes. You need to drink the decoction three times a day, a tablespoon at a time, for no more than three months in a row.
The feasibility of antibacterial therapy
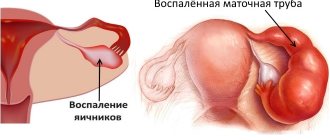
Inflammation of the appendages and ovaries is provoked by the ingress of pathogenic microflora. In view of this, antibacterial drugs are used in the treatment of adnexitis. The doctor selects an antibiotic depending on the type of pathogen, which is determined by culture of the secretions.
When treating ovaries, you should follow two basic rules:
- Contact your doctor to prescribe antibiotics. Independent selection of drugs for the treatment of adnexitis can aggravate the condition.
- Take the full course of medications. Even if pain and other symptoms no longer bother you, treatment should be completed.
The treatment regimen for inflammation of the appendages and ovaries varies depending on the nature of the disease. Acute adnexitis often requires hospitalization of the patient. At the first stage, antibiotics are administered intravenously or intramuscularly, and subsequently tablets are prescribed. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. After the symptoms of acute inflammation of the ovaries are relieved, physiotherapy is carried out.
Adnexitis can take a chronic form. In this case, the choice of treatment method will depend on the stage of the disease. If adnexitis recurs, treatment with antibiotics and suppositories is indicated to relieve pain and inflammation. In combination, vitamins and agents are prescribed that reduce the likelihood of adhesions forming.
In order to prevent exacerbation, the patient is advised not to overcool and avoid overwork. Procedures such as acupuncture, electrophoresis, and mud wraps are prescribed. For diseases of the ovaries and appendages, therapeutic exercises and a diet excluding fried, fatty and salty foods are indicated.
When is Ceftriaxone prescribed in an IV?
It is recommended to administer Ceftriaxone in a dropper for:
the need to use large doses (adults from 2 g, children more than 50 mg/kg body weight); severe infection, when it is important to achieve the required concentration of the antibiotic as soon as possible; the threat of complications - inflammation of the membranes of the brain (meningitis), blood poisoning (sepsis); detection of bacteria in the bloodstream (bacteremia); intolerance to the solvent (Lidocaine) or contraindications to it (slow heart rate, epilepsy); the appearance of a local reaction to intramuscular injections - painful lumps with signs of suppuration (red, swollen and hot skin, a symptom of fluctuation, that is, fluid swaying); treatment of a newborn; prevention of infectious complications before surgery.
The main groups of infectious diseases when it is advisable to choose drip administration of an antibiotic:
- lungs - pneumonia, pleural empyema (accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity), abscess (ulcer) of lung tissue;
- skin - extensive lesions (for example, streptoderma);
- kidney – acute pyelonephritis;
- in the abdominal cavity - peritonitis, empyema of the gallbladder;
- skeletal system – osteomyelitis;
- heart – bacterial endocarditis;
- syphilis;
- typhoid fever;
- severe form of salmonellosis;
- purulent-inflammatory process in patients with immunodeficiency.
Why is it done for ENT diseases?
The administration of Ceftriaxone in a dropper can be prescribed for tonsillitis, otitis media and sinusitis when there is a threat of infection spreading to the heart (endocarditis) or the lining of the brain (meningitis). For uncomplicated forms of the disease, intramuscular injections are most often used.
The advantage of drip administration of the drug is a faster onset of action (immediately after the end of the drip), and the removal of the antibiotic occurs 4-6 hours later. This allows you to achieve the required concentration of Ceftriaxone in the blood from the first day of illness and start the process of destruction of microbial cell membranes.
How does it help with pneumonia?
Intravenous administration of Ceftriaxone helps with pneumonia:
- reduce body temperature;
- reduce cough;
- make breathing easier;
- relieve chest pain.
The main criterion for the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment is the normalization of the patient’s general condition and the disappearance of fever on the 3rd day of IV placement.
If there is no result, then the patient undergoes a sputum culture (if the analysis has not been done previously) to isolate the pathogen and determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Why in gynecology
In gynecology, Ceftriaxone is administered in a dropper for severe inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometritis), appendages (ovaries and/or fallopian tubes), and gonorrheal infection.
Intravenous administration of an antibiotic is necessary for pronounced signs of an acute process:
- high body temperature;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor, mixed with pus;
- acute phase indicators in blood tests - increased leukocytes, C-reactive protein, ESR, shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
How does it help against syphilis?
For syphilis, Ceftriaxone is used for droppers in case of intolerance to penicillin. It is recommended to choose this antibiotic if there is a risk of infection spreading to the brain tissue - neurosyphilis, as well as advanced forms (secondary, tertiary). The advantage of the drug is the possibility of one-time use per day, since the half-life during intravenous administration is close to 12-15 hours.
Most often, patients with a severe syphilitic infection or a moderate illness need at least 2 g of the drug, so the choice of the infusion route is considered optimal. This method also makes it possible to reduce complications from the administration of large dosages and a long course (2.5-3 weeks).
How it works for sexually transmitted infections
Ceftriaxone for sexually transmitted infections helps to destroy their pathogens, as it prevents the bonding of the cell membrane of bacteria. As a result, the proliferation of microbes stops and the main symptoms of inflammation are relieved:
- aching or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased body temperature;
- discharge from the genital tract;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain and burning during urination;
- changes in blood tests - increased leukocytes, ESR.
Antibiotics and injections
It is advisable to start a course of antibiotic treatment with intramuscular or intravenous administration of drugs, and then you can switch to tablet form. Be sure to combine the above medications with probiotics, which will restore the balance of intestinal microflora during the treatment process.
After the acute manifestations of the symptoms of the disease begin to disappear, it is imperative to add physiotherapeutic procedures to the course - ultrasound, treatment with magnetic alternating and diadynamic current. All this will significantly reduce the risk of formation of adhesions and will complement the use of antibiotics, enhancing their effect.
Basic antibiotics effective for adnexitis
- Zomax and azithromycin are very broad-spectrum antibiotics that are quite effective for the complex treatment of genitourinary diseases in women. In particular, they are used for urethritis, cervicitis, adnexitis.
- Cedex and ceftributen are very good at destroying gonococci, streptococci and enterobacteria, which induce the appearance of adnexitis. Most often, these antibiotics are found in capsule form.
- Erythromycin is a powerful intravenous drug for the effective treatment of mycoplasmosis and chlamydia, and is used as an additional medicine for adnexitis.
- Metronizadol is a focal antibiotic, usually used in the treatment of urogenital diseases.
- Ceftriaxone, ciprolet and ciprofloxacin are the latest generation antibiotics, a good alternative to the drugs proposed above.
It is worth noting once again that the duration of the course of treatment, specific drugs and their combinations should be determined exclusively by the attending physician, preferably in a hospital setting.
Features of antibiotic treatment
Only a specialist should evaluate the symptoms of adnexitis and prescribe antibiotic treatment. Therefore, when the first unpleasant manifestations of the disease occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. In addition to a gynecological examination, he will prescribe a smear test for flora. In some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is also indispensable.
After confirming the diagnosis and determining the type of treatment, the specialist selects the most optimal treatment regimen. As a rule, it is based on antibiotics. Initially, they are administered intramuscularly or intravenously, and then replaced with drugs in the form of tablets. In addition, patients are prescribed probiotics that restore intestinal microflora.
The total duration of antibiotic treatment is at least 14 days. Even if the symptoms become less noticeable before this time, it is very important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. After all, if the taken course of antibiotics is abruptly interrupted, this will significantly increase the risk of relapse of the disease, and will also contribute to its transition to a chronic form. In addition, in the treatment process, a special role is given to physiotherapeutic procedures, which are prescribed after the acute symptoms of the disease disappear. They prevent the formation of adhesions and also enhance the effect of antibiotics.
Ceftriaxone for adnexitis: scheme, how to dilute it
Ceftriaxone for adnexitis is in most cases prescribed 1 g 2 times a day intramuscularly for 1-1.5 weeks. It needs to be diluted with a 1% solution of Lidocaine - take 4 ml of solvent per bottle with 1 g of powder. Since this particular concentration is rarely available in the pharmacy, you can purchase ampoules of water for injection, 2 ml and 2% Lidocaine, 2 ml. Then for one injection you should take:
- one bottle of Ceftriaxone 1 g;
- water for injections 2 ml;
- Lidocaine 2% 2 ml.
Injections are given at intervals of 12 hours - for example, at 8 am and 20 pm (strictly by the hour every day). There is a situation when it is more convenient to immediately inject 2 g, in which case the injections are carried out in different buttocks (1 injection in each), then the break between injections is 24 hours (for example, at 8 am daily).
We recommend reading about how to use Ceftriaxone for pneumonia. From the article you will learn how antibiotics work for pneumonia, treatment regimens in adults, and duration of therapy.
And here is more information about how to use Ceftriaxone for sore throat.
What can you combine with?
For inflammation of the appendages, Ceftriaxone is often prescribed with other antibiotics or antiparasitic drugs. This is explained by the fact that it does not completely destroy pathogens, especially microbial associations (several microbes). Recommended combinations:
- Ceftriaxone 1 g + Gentamicin 80 mg 2 times a day intramuscularly;
- Ceftriaxone 1 g + Metrogyl 100 ml intravenously 2 times a day;
- Ceftriaxone 2 g + Doxycycline 200 mg intravenously (1 or 2 times per day);
- Ceftriaxone 1 g + Clarithromycin 500 mg every 12 hours;
- Ceftriaxone 1 g 1-2 times 7 days + Azithromycin orally 500 mg on the first day, 250 mg on days 2-5.
Regardless of the regimen, drugs are not mixed in one syringe or one dropper; different injections are required. To treat adnexitis, the following is also used:
- anti-inflammatory suppositories (Indomethacin, Diclofenac);
- droppers with solutions in severe cases to reduce intoxication (Glucose, Voluven);
- immune stimulants (Cycloferon, Derinat);
- enzymes (Wobenzym, Serrata).
It is very important that solutions for intravenous administration do not contain calcium salts, since they and Ceftriaxone form insoluble compounds that are deposited in the lung and kidney tissue.
When antibiotics are administered for a week or more, it is mandatory to prescribe antifungal agents (most often Fluconazole) and drugs with lactobacilli to restore normal vaginal microflora (Ecofemin, Laktonorm, Acylact).
Can it be used during pregnancy?
Ceftriaxone is used during pregnancy only in cases of very severe inflammation, when the threat to the health of the mother is greater than the risk to the development of the fetus. Gynecologists try to do without this drug in the first trimester, because:
- its safety for the child has not been definitely proven;
- there is only information about the absence of a damaging effect on animal embryos;
- penetration of the drug through the placental barrier was established.
The effect of some drugs that cross the placental barrier on the fetus (before using any drug, you should consult a doctor!)
From the second trimester, Ceftriaxone is administered in the shortest possible course, but not less than 5 days.
Efficiency of application
Ceftriaxone is an antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action, but in case of adnexitis it does not completely cover all possible causes of infection, since the inflammation may be of viral or fungal origin. A number of bacteria develop resistance to the drug, and in many cases they are insensitive to most other antibiotics.
Therefore, the effectiveness of use will depend on the isolated pathogen and its response to Ceftriaxone. Good results can be obtained under the following conditions:
- acute, newly diagnosed adnexitis;
- the woman was not given antibiotics for 3 months;
- there is no concomitant adhesive process in the pelvis after chronic infections or operations;
- Only a bacterial infection was detected.
In case of chronic, low-grade inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, Ceftriaxone must be strengthened with immune stimulants and enzymes, and after completion of the course, absorbable treatment (biostimulants, physiotherapy) is prescribed.
Contraindications for treatment of adnexitis with Ceftriaxone
The main contraindication for treatment of adnexitis with Ceftriaxone includes intolerance to this drug or its analogues in group and structure:
- cephalosporins (for example, Cefazolin, Cefotaxime);
- penicillins (Benzylpenicillin, Ampicillin);
- carbapenems (Tienam, Meropenem).
If the patient has had an allergic reaction to an antibiotic in the past, but its name is unknown, then a skin test is mandatory before the first injection. If the result is positive, Ceftriaxone is prohibited.
Caution is needed (blood tests, regular doctor's examinations) when treating women with concomitant kidney and liver diseases, especially when two antibiotics are administered at once. It is necessary to monitor the functioning of the intestines if there has been inflammation in the past (colitis, enterocolitis), dysbacteriosis.
Possible complications
The most common complications from the use of Ceftriaxone in the treatment of adnexitis include:
- diarrhea or unstable stool due to an increase in intestinal microflora;
- nausea, vomiting, decreased production of enzymes by the pancreas with bloating, decreased digestion of food;
- stagnation of bile in the biliary tract (most often in patients with underlying diseases - cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis);
- dysfunction of the liver, kidneys;
- dizziness, headache;
- addition of a fungal infection (thrush);
- decreased immunity;
- increased bleeding, including heavier menstruation;
- allergic reactions: rashes, itchy skin, breathing problems due to bronchospasm or swelling of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
Precautionary measures
To reduce the risk of complications when administering Ceftriaxone, you need to:
- drink enough water - at least 1.5 liters;
- reduce salt intake;
- exclude spicy and fried foods, indigestible fiber (fresh cabbage, radish, legumes) for the period of treatment;
- try to move more (as much as possible);
- after 7 days of use, take a 150 mg capsule of Fluconazole to protect against fungal infection;
- at the end of the course, take medications for at least 2 weeks to normalize intestinal and vaginal microflora, drink a glass of fresh yogurt without added sugar every day;
- if there is increased blood loss during menstruation, it may be necessary to administer Vikasol, since the drug reduces vitamin K reserves, and the diet should include broccoli, fresh herbs, peanuts, avocados, and cottage cheese;
- if diarrhea occurs, it is forbidden to self-medicate; it is important to immediately undergo examination for dysbacteriosis;
- To improve the digestion of food and prevent the formation of sediment in the bile ducts, frequent meals in small portions are recommended; food is cooked boiled, steamed or baked.
Antibacterial therapy
Drugs in this group should be prescribed only after laboratory tests have been carried out to determine the type of pathogen. But the fact is that most modern drugs have a complex effect on pathogens of different groups. Therefore, the following are most often prescribed.
You can learn more about treating ovarian inflammation with antibiotics HERE.
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone has a bactericidal effect on the cell membrane of microorganisms during inflammation of the ovaries. This third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic is available only in powder form for injection, so its use at home is difficult.
But the advantages of the drug are significant: it can replace a lot of other antibiotics, affects most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, and has also proven itself in the treatment of chronic salpingoophoritis (with this form of the disease, microorganisms develop resistance to many antibiotics).
A special feature of the drug is that it can also be used for syphilis, although this disease is treated with penicillins. But if penicillins cannot be used for any reason, then Ceftriaxone is a backup treatment option.
Another absolute advantage is that this drug is acceptable during pregnancy, but not in the first trimester.
Ceftriaxone is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, which accounts for its rapid action. Duration of treatment – 7 days.
Amoxicillin for inflammation
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic of the penicillin group, which is highly effective and well tolerated, as well as a minimal list of side effects. Treatment, as in the previous case, lasts no more than a week, one tablet 3 times a day. An analogue of Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, can be prescribed during pregnancy for inflammation of the ovaries, but only if the benefit to the mother exceeds the potential harm from the drug to the fetus.
Tsiprolet
Tsiprolet for inflammation of the ovaries is an antimicrobial drug of the fluoroquinolone group. Available in both tablet and injection form. It has very few contraindications: individual intolerance, pregnancy and lactation, as well as vascular pathologies (atherosclerosis, hypertension). Tsiprolet is prescribed from 250 to 500 mg 2-3 times a day for 7 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the disease, as well as the pathogen that caused the inflammatory process.
After you start taking the drug Tsiprolet, the symptoms of the disease disappear within 2-3 days
At this stage, it is important not to stop treatment, since bacteria may develop resistance to the drug, and the disease itself will become chronic.
Trichopolum
Trichopolum for inflammation of the ovaries is not prescribed individually, but in combination with an antibiotic from another group.
This is an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent that well “restrains” its own opportunistic microflora. That is why this drug is auxiliary.
Metronidazole for inflammation
The main component of Trichopolum is the antibiotic metronidazole. Previously, pure metronidazole was prescribed, but it has many side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness and other manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system.
In this regard, metronidazole is currently rarely prescribed, although it is a cheaper analogue of Trichopolum.
What are the side effects
Like any other powerful antibacterial agent, Ceftriaxone has unpleasant side effects:
- nausea and vomiting, flatulence and diarrhea;
- unpleasant or painful sensations in the right hypochondrium due to liver dysfunction;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- candidal inflammation in the vagina.
Ceftriaxone is one of the main antibiotics included in the complex therapy of acute forms of salpingoophoritis and recommended by the International Federation of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (FIGO) in 2012. The effectiveness and safety of the drug ensures rapid and successful treatment of the inflammatory process in the uterine appendages.
Source gynecologyhelp.ru
Basic principles of cervicitis therapy
Inflammation in the cervix can develop for various reasons. The most common culprits are sexually transmitted infections, which is why antibacterial drugs are widely used. Treatment is complex and usually includes several medications - for oral administration and for local sanitation. Basic principles of therapy include the following:
Etiotropic treatment - taking into account the identified pathogen. These can be antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiviral drugs. Cervicitis is the general concept of inflammation of the cervix and cervical canal. Typically, such a diagnosis is established based on smears for oncocytology.
To clarify the nature of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to identify the exact pathogens, and for this you should undergo a comprehensive examination for STIs - chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, trichmonas, gonococci, viruses (human papilloma and herpes simplex). If no pathogens are detected, then the inflammation is nonspecific, which somewhat simplifies treatment.
- Local treatment. It is believed that treatment will be more effective if, along with taking medications internally (for example, antibiotics), suppositories, douching, and medicated tampons are used. This way the drug can be delivered directly to the site of inflammation.
- Hormonal drugs. As a rule, they are used to treat nonspecific cervicitis in menopausal women. The cause of inflammation in them is the activation of their own opportunistic microflora against the background of lactobacilli deficiency and estrogen deficiency, which is why the mucous membrane is very vulnerable and susceptible to infection. Suppositories with a small content of estriol are used.
- Surgery. It is necessary if the inflammation is combined with another pathology, for example, erosion, ectropion, cicatricial changes in the neck, dysplasia. Surgical treatment options depend on the clinical situation, and radio wave ablation of affected tissue is often used.
Radio wave conization of the cervix
- Restoration of vaginal biocenosis. After the main course of therapy, it is necessary to take a course to stabilize the level of lactobacilli on the vaginal mucosa. For this purpose, various drugs with them are used - Bifidumbacterin and the like. Otherwise, there is a high probability of relapse due to the activation of one’s own opportunistic flora.
- Sanitation of the sexual partner. If absolute pathogens are detected (chlamydia, trichomonas, gonococci, etc.), the man must be treated. It is ideal if he also undergoes a comprehensive examination.
Expert opinion Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Sometimes the cause of chronic inflammation in the cervical canal is somatic diseases, especially endocrine diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus. Therefore, women with such symptoms need to visit their doctor more carefully and regularly to identify disorders and, during the treatment process, correct the underlying disease (for example, stabilize blood glucose levels in diabetes).
The most effective antibiotics
There are a large number of antibiotics that quickly and effectively treat salpingoophoritis. But the greatest results come from:
- Azithromycin. It has an active effect on foci of inflammation and has excellent bactericidal properties. It is effective in complex therapy of the female genitourinary system. This antibiotic is especially actively used in the treatment of adnexitis, cervicitis and urethritis. However, it must be taken into account that Azithromycin is not used if the disease is caused by staphylococci or streptococci.
- Ceftributen or Cedex. Help fight streptococci, gonococci and enterobacteria. They have antibacterial and bactericidal effects and are available in capsule form.
- Erythromycin. The drug is administered intravenously and is used when the causative agents of adnexitis are chlamydia and mycoplasma.
- Ceftriaxone. Widely used for infectious gynecological diseases. It is recommended to be taken in cases where vaginal pathogenic microflora joins the inflammatory process. In addition, Ceftriaxone can be combined with other groups of antibiotics.
- Doxycycline. It belongs to the tetracycline series and is able to actively influence many groups of microorganisms. This antibiotic can be taken orally or given intravenously. When treating adnexitis, Doxycycline helps to achieve good results within the first days after starting use.
- Metronidazole. The drug affects foci of the inflammatory process and is most often used to treat urogenital diseases.
- Tsiprolet. Used for gynecological diseases of an infectious nature. It also showed high efficiency, as well as speed of action, for adnexitis. It effectively affects gram-negative microflora, but some gram-positive bacteria are also susceptible to it. Ciprolet can also be prescribed for chlamydia and mycobacteria.
- Polygynax. Vaginal suppositories Polygynax give good results. This drug has virtually no contraindications, and its components do not enter the bloodstream. It has a long-lasting effect due to the slow absorption of the drug by the mucous membrane.
- Terzhinan. It is a combined remedy and is used locally. Available in the form of vaginal tablets that do not disturb the natural balance of microflora. The components of Terzhinan have anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effects. This drug is recommended if inflammation is caused by anaerobic infections, trichomonas, or when the patient has a mixed pathogenic microflora.
How drugs are selected
Which antibiotics will be prescribed for adnexitis directly depends on the reasons for its development. It is worth noting that different groups of microorganisms can provoke the inflammatory process:
- chlamydia,
- non-spore-forming anaerobes,
- gonococci,
- ureaplasma,
- Trichomonas,
- mycoplasma,
- gram-positive bacteria.
After identifying the pathogen, individual drugs or combinations thereof are selected to which the identified microorganisms are particularly sensitive. If there are reasons that require empirical treatment of acute adnexitis with antibiotics (for example, if there are no test results yet), then specialists prescribe broad-spectrum drugs to patients. However, in this case, it is important that the chosen medications are not only effective, but also safe.
Often, for a patient to recover, it will be enough to undergo a course of treatment with one type of antibiotic. But there are situations when one drug is not enough or it does not bring the expected results. Then the specialist is forced to treat the patient using several drugs that can affect the vital activity of different groups of pathogens.
In addition, there are certain differences in treatment regimens for different forms of pathology. If this is acute adnexitis, then antibiotics are administered intravenously or intramuscularly until the patient’s leukocyte concentration exceeds 10 × 109/l for at least two days and the body temperature does not exceed 37.5˚C. Then you can switch to oral medication. While in case of chronic adnexitis (uncomplicated), antibiotics in the form of tablets are immediately prescribed.