Surely everyone has heard about such a disease as syphilis. This word alone evokes fear and horror, but few people know what household syphilis is and exactly how it manifests itself.
Its history is still vague, they first started talking about it in 1905, later the scientist G. Fracastoro began to study it more thoroughly.
There was even a poem written, “On Syphilis or the Gallic Disease.” It is not known how the disease came to Europe, but many are inclined to think that syphilis came from America.
There is a misconception that syphilis is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact, but this is not entirely true.
You can also become infected through household means if you use someone else’s personal hygiene items, linen and even dishes.
What is household syphilis
Sexual syphilis and domestic syphilis are the same disease, differing in the method of transmission. In medical terminology, this disease is understood as a chronic infectious venereal disease that affects all human organs and tissues and progresses very quickly. Through close household contact, you can become infected with syphilis, which has similar symptoms to sexual syphilis.
How long after infection do symptoms appear?
The incubation period begins the moment Treponema pallidum enters the human body and lasts until chancre forms (approximately 21-28 days). Other forms of the latent phase of the disease are also possible. If infection occurs simultaneously from several sources, it is shortened to 8-15 days. In the case of taking antibiotics for the treatment of other infections, it is extended for a period of 100-190 days. Thus, it becomes clear that an infected person does not notice the manifestations of the disease for 2 to 6 weeks, and if he has sexual intercourse with many partners, the source of infection is difficult to determine.
Syphilis of bones and joints
How is it transmitted?
The modes of transmission of syphilis are domestic and sexual. Rapid infection is possible through objects contaminated with syphilitic elements of the skin and mucous membranes, because the causative agent of the disease remains active for a long time in a humid environment. You can become infected through bites, kisses, dishes, cigarettes, towels, and underwear. The most dangerous are the first two stages of the disease, when the patient has ulcers and erosions in the oral cavity, which will be a source of infection.
The contagiousness of the urine and sweat of a patient with syphilis has not yet been proven, but there is a possibility of infecting a child through the milk of a nursing mother. Doctors, if they do not use gloves, risk when carrying out medical procedures and coming into contact with the patient’s internal organs during surgery. There is also a transfusion method of transmission - through blood transfusion.
What is the causative agent of the disease?
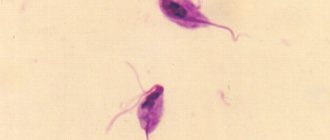
Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum, a gram-negative spirochete that looks like a spiral. It is not very resistant to external influences - it disappears after household items dry out, but it persists for a long time in a humid environment. Treponema pallidum activates at a temperature of 40-42 degrees, then dies; at 55 degrees it dies in 15 minutes. Low temperature does not have a detrimental effect on the microorganism - during 9 years of experimental storage at minus 70 degrees, its activity did not disappear. Treponema is sensitive to chemicals.
How is syphilis transmitted?
Knowing how syphilis is transmitted, you can easily protect yourself and your loved ones from this unpleasant disease.
- Infection with syphilis through sexual contact
Sexual intercourse, which occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraception, is the main one in the epidemiology of the disease, as a result of which syphilis belongs to the group of STIs. Sperm and vaginal discharge are an excellent environment for the life of Treponema pallidum, and even a single sexual intercourse (with vaginal, anal or oral penetration) with a sick person is characterized by a 50% risk of infecting the second partner.
Any type of sexual intercourse is equally dangerous, but anal penetration is characterized by the greatest risk of infection, since trauma to the rectal mucosa is likely. If we consider sexual intercourse with vaginal penetration, a woman has an increased risk of contracting syphilis than a man, and this is explained by the ease of trauma to the vaginal mucosa during sexual relations.
An insidious feature of syphilis is the contagiousness of a sick person at any stage of the disease. Not knowing about his illness, during the incubation period, a sick person can involve more and more new partners in the vicious circle of the disease by engaging in sexual relations.
- Infection with syphilis through saliva
Syphilis is transmitted through the saliva of a sick person if the rash is located in the mouth or on the lips - only in this case is treponema pallidum detected in the saliva. Such patients pose a risk of infection during deep kissing, when the oral cavities are in direct contact with each other.
According to statistics, syphilis is transmitted through a kiss, through saliva very rarely, since syphilitic rashes on the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips are quite rare. In addition, a healthy person must have microtraumas of the oral mucosa so that the causative agent of syphilis can penetrate the bloodstream.
- Infection through breast milk
Treponema is found in the breast milk of a sick woman, so she can infect her baby through breastfeeding. Because infants, especially newborns, have an impaired immune system, they are at increased risk of contracting syphilis.
- Infection with syphilis through blood
Since the causative agent of syphilis is present in the blood, transfusion of infected blood or organ transplantation of a sick person will lead to infection with this pathology. However, this route of transmission of syphilis can be realized with a very low probability, since both blood and transplanted organs are carefully checked for the presence of various infections, including syphilis.
A more likely route of infection with syphilis through blood is the use of one syringe among a group of drug addicts or one container for preparing a solution of a narcotic drug. If the mucous membranes and skin are damaged, for example, during a fight, you can also become infected with syphilis from a sick person.
From the very first day of infection to the last day of illness, the blood of a patient with syphilis is contagious. This means that not only through a blood transfusion is infection possible, but also when the mucous membrane or skin is injured by medical instruments, instruments in manicure and pedicure salons (without treatment), which have been exposed to the blood of a patient with syphilis, it can lead to infection of a healthy person. Any external manifestations of syphilis (papules, ulcers, erosions) with scanty discharge from the patient are very contagious; the presence of microcracks in the skin of a healthy person in contact with the skin of such a patient leads to infection with syphilis through everyday contact (contact).
- Infection during professional activities
This route of transmission of syphilis occurs among persons in certain professions: medical personnel, cosmetologists and other persons whose activities involve invasive procedures and contact with saliva, vaginal secretions, and blood of infected people. Among physicians, infection most likely occurs through accidental injuries from instruments that were used on a patient suffering from syphilis. Cosmetologists can become infected through personal use of instruments that have not been disinfected, which were used during procedures on a person with syphilis.
A prerequisite for transmission is a violation of the integrity of the skin of a healthy person. Simply touching infected blood to intact skin does not lead to syphilis infection.
- Infection with syphilis through domestic means
Many people are interested in whether syphilis is transmitted through household means - after all, someone has to live next to a sick person. Transmission of syphilis through household items (towels, cutlery, dishes, linen, cigarettes, personal hygiene items) is likely through close and prolonged contact with a sick person, moreover, in the terminal stages of the disease, when the pathogen is actively released into the external environment (decaying gums, ulcers ). When treponema dries, it loses its pathogenicity, so transmission of syphilis is possible only with particles of saliva or other liquid on objects.
- Infection is transplacental
This path is realized during the pregnancy of a sick woman - syphilis is transmitted from mother to fetus. To the question of whether syphilis is transmitted to a child in utero from a mother who is not receiving treatment, the answer can be unequivocally yes. First, treponema infects the placenta, and, having destroyed the protective placental barrier, easily penetrates the tissues and organs of the fetus through the umbilical vein or lymphatic system. A woman is especially contagious in the first three years of the disease, but in the future the likelihood of infection of the fetus remains.
- Infection with syphilis during childbirth
Since the pathogen is present in the vaginal environment, and the birth process itself is accompanied by contact of the mother’s blood with the fetus, this route of transmission is easily realized. If a child managed to avoid intrauterine infection with syphilis, then during natural childbirth it is almost impossible to prevent this. In this case, a caesarean section is performed, during which the risk of infection of the child is significantly reduced.
How to recognize
Infection with domestic syphilis is similar to genital syphilis - the patient feels tired, aching joints, and his temperature rises. The disease weakens the immune system, so other diseases occur in parallel. You shouldn’t see a doctor if these are the only signs you notice, but you should regularly undergo examinations, medical examinations and donate blood.
Prevention
Treponema pallidum is sensitive to high temperatures, the action of alkalis, acids and antiseptic solutions. Compliance with personal hygiene rules, regular cleaning of premises and sanitary treatment of common items minimize the likelihood of contracting household syphilis. You should not use other people’s dishes and toiletries, try on swimsuits and underwear on your naked body, or visit catering establishments and public places with obvious signs of sanitary problems. When visiting beauty salons, hairdressers and dental offices, you must make sure that the instruments are disinfected.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Symptoms
In accordance with the stages of development, the symptoms of household syphilis also differ. The incubation period lasts 3-4 weeks, during which the disease is asymptomatic. Only at the primary and secondary stages do destructive signs begin, which by the third stage become very noticeable and cannot be ignored. In the first two stages, the disease can actually be cured, but advanced cases cannot.
The primary stage of household syphilis
Signs of household syphilis at the primary stage begin with the appearance of a small spot of reddish color at the site of introduction of treponema pallidum into the body. After a few days, a hard round chancre appears in this place - an ulcer with hard edges several millimeters in diameter that does not hurt. All lymph nodes gradually enlarge. Chancre appears on the lips, tongue, tonsils, and gums, while with sexual syphilis, its location is the genitals.
Rarely, chancre can appear on the chin, mucous membrane of the eyelid, eyeball, nipples of the mammary glands, and fingers. Asymptomatic initial cases occur. The duration of the period is 6-7 weeks. Additional signs of the disease are general malaise, headaches, bone pain, insomnia, and anemia. The transition to the second stage is characterized by weakness, fatigue, rare pain in muscles and joints, insomnia, and appetite disturbances.
Secondary period
As the infection and virus spread throughout the body, secondary syphilis begins, which without treatment can last up to four years, accompanied by several relapses. At this stage, rashes of various shapes, sizes, and colors appear on the skin or mucous membranes. They can often be found in areas subject to friction.
Without treatment, the rashes grow powerfully, forming lesions and abrasions with oozing tissue fluid. During the secondary period, whitish spots appear on the neck - evidence of damage to the nervous system. In addition, blood vessels, heart, eyes, ears, joints, bones, internal organs, bones become infected, and hair falls out. Spots and papules are prone to spontaneous disappearance or reappearance.
- Hysteroscopy of the uterus - what is it and how does it work?
- How to lose weight after childbirth during lactation
- White coating on the tongue - what to do and how to treat
Tertiary syphilis
After the secondary period, the tertiary period begins, characterized by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes. Tubercles appear, and gummas containing the causative agent of the disease appear in the subcutaneous tissue, bones and internal organs. They are dense formations in the shape of a ball, in appearance resembling nodes the size of a hazelnut kernel. The formations develop into scars and ulcers, tissue damage is irreversible. The period lasts for decades. If gummas affect the face, the skeleton is destroyed - the patient’s nose collapses, as in the photo, and disfiguring deformities appear.
Stages
In the dynamics of household syphilis, three stages are distinguished, which differ from each other in the clinical picture and the nature of pathological changes.
- Primary affect. At the site of penetration of the pathogen, as a result of the immune reaction, a characteristic defect is formed - chancre, or syphiloma, which usually resolves itself within a period of 1-2 weeks to 2-3 months. Atypical manifestations of primary syphilis include multiple chancre, indurative edema, chancre-felon and chancre-amygdalitis, which occur both on their own and against the background of hard chancre.
- Secondary syphilis. Syphilitic bacteremia develops - a massive release of treponemes into the bloodstream. The first episode resolves itself in 3-4 weeks, after which temporary improvements alternate with relapses for several years. During periods of exacerbation, the patient becomes infectious.
- 2–3 years after infection, secondary syphilis can take the form of neurosyphilis, which affects the blood vessels and membranes of the brain. A typical manifestation of early neurosyphilis is chronic syphilitic meningitis; Syphilitic neuritis and polyneuritis, meningovascular syphilis and syphilitic meningoencephalitis are less commonly diagnosed.
- Tertiary syphilis is multiple lesions of the integumentary tissues, bones, blood vessels, internal parenchymal organs and systems, occurring in 30% of patients after several years of latent syphilis.
Manifestations of late neurosyphilis are dangerous: progressive paralysis, optic nerve atrophy, tabes dorsalis and taboparalysis (a combination of progressive paralysis and tabes dorsalis).
Stages of household syphilis
How can household syphilis affect pregnancy?
A woman infected with syphilis experiences hormonal imbalance during pregnancy. This leads to the risk of miscarriage or premature birth, and anemia occurs. In most cases, a child is born infected - infection occurs through the blood and placenta. Secondary syphilis of the expectant mother is dangerous for children. At this stage, there is the greatest chance of miscarriage or stillbirth. The tertiary period allows you to carry and give birth to a healthy child even in the absence of therapy.
If treatment was carried out before the 16th week of pregnancy, the chances of having a healthy baby are greatly increased. Congenital syphilis is also considered domestic - infection occurs in the womb during 28-32 weeks of pregnancy. If the child survives and is born, he suffers from signs of the disease. In children, extensive rashes and wounds on the skin, damage to the heart, eyes, liver, and dropsy are found. Children suffer from diseases of the bones, joints, brain, deformation of the teeth, skull, nose, and later lag behind in development, mental characteristics, and gain weight poorly.
During pregnancy, syphilis can be diagnosed by taking a blood test - the Wasserman reaction. Later, treponemal methods are used to double-check the positive result. A CT scan is performed, smears are taken, and antibiotic treatment is prescribed. The fetus can be protected from congenital disease if you start taking medications at 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Ignorance is no excuse from infection
Hello. I would like to know in more detail how syphilis is transmitted through household contact and how to protect family members from infection.
Hello. Infection through household contact can occur through shared dishes, towels or bed linen. When using an infected toothbrush or comb while kissing.
You can become infected by smoking one cigarette, as well as by using decorative cosmetics (lipstick or gloss, lip and eye pencils, etc.). To avoid infection, the patient must be given an individual set of dishes and hygiene items, and also pay special attention to washing and cleaning the room (washing clothes at temperatures above 42°C will help kill Treponema pallidum).
Good day. Can there be syphilis without symptoms? I’m very worried about this, because I’m afraid of getting infected and not knowing about the disease.
Greetings. Household syphilis rarely occurs without symptoms. There are cases when patients do not notice chancre, or atypical variants of the disease are encountered, then they talk about latent syphilis. From the moment of infection, the disease is latent, but blood tests will be positive.
Diagnostics
To identify syphilis, you need to contact a venereologist or dermatovenerologist. After the examination, a blood test for RW is performed. If a positive reaction is detected, additional studies are carried out. The immunofluorescence reaction (RIF), Treponema pallidum immobilization reaction (TPI) and treponemal antigen (TPNA) are used. In special cases, computed tomography is performed to identify damage to the central nervous system. Swabs are taken from the skin rash to check for the presence of Treponema pallidum. At the first two stages, PCR diagnostics are carried out.
How to avoid getting infected with syphilis?
Syphilis is a serious, very unpleasant, considered shameful disease. Treponema infection can be avoided by following simple hygiene rules known to everyone. Naturally, you need to have information about the ways of transmitting the disease, not neglect the advice of doctors, and try not to find yourself in situations in which the risk of being infected increases. Below are some basic steps that will help you stay healthy:
- Use a condom every time you have sex in any way.
- Use topical antiseptics to clean the genitals, mouth, and rectum after sexual intercourse has taken place. Miramistin and chlorhexidine are suitable for such procedures. These actions are also appropriate if sexual intercourse was protected, since the risk of infection exists, although it is greatly reduced.
- Contact a venereologist no later than two hours after having sexual intercourse without using protective equipment so that preventive antibacterial therapy (drugs from the group of choice) can be prescribed.
- Feed your baby artificial milk formula if you became a mother while suffering from syphilis.
- Avoid sharing hygiene products, towels, linen, and clothing.
- When performing medical procedures, use only disposable instruments.
- If you are part of an occupational risk group, strictly follow the safety and prevention rules.
- If an infected woman is pregnant, treatment is mandatory.
- Regularly and promptly undergo preventive examinations to detect sexually transmitted infections.
Treatment
For domestic syphilis, outpatient treatment and home quarantine are prescribed. Individual treatment is prescribed for each patient, combining specific and nonspecific therapy. This will help only in the first two stages of the disease; in the tertiary stage, damage to tissues and organs is irreversible. Here are some popular drugs to get rid of the disease:
- Antibiotics - penicillin groups (Oxacillin, Ampicillin, Benzylpenicillin, Carbenicillin) quickly penetrate into the blood and are excreted. Prescribed use every three hours in the form of tablets or injections. Bicillin, Erythromycin, Oletetrin or Tetracycline may be prescribed in combination with antihistamines. The course lasts two weeks for the primary period and a month for the secondary period.
- Preparations with bismuth - contain a heavy metal that fights the spiral microorganism and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Biyoquinol - a suspension of bismuth salts in peach oil destroys bacteria, but has many contraindications. It should not be used by infants, people with heart and vascular diseases, tuberculosis, or stomatitis. Injections are prescribed once every three days, one ampoule, and can be used for late and recurrent syphilis. For individual intolerance to quinine, liver and kidney diseases, Bismoverol is used.
- Immunostimulants – strengthen the body’s protective functions, relieve inflammation. These include Pyrogenal, Peat, preparations with aloe.
- Vitamins – to support the immune system, it is recommended to drink vitamins B, C, A, E.
Features of the pathogen
Treponema pallidum is a thin spiral-shaped microorganism. Due to its ability to absorb dyes, it received the prefix “pale”. It is difficult to detect with a simple light microscope due to its negligible diameter. Therefore, to identify treponema, a dark-field microscope examination of a specimen that has not been subjected to fixatives is used. The drug is made from the serous secretions of primary syphiloma.
Distinctive features of Treponema pallidum are:
- Belonging to a facultative anaerobe, the parasite thrives in an environment with a small amount of oxygen, this fact explains its favorite localization and place of reproduction in the human body (nervous, lymphoid and connective tissues);
- Also, the ability of the spirochete to penetrate tissues (into their cells and nuclei) and at the same time maintain active viability significantly distinguishes it from other parasites. This feature underlies the long-term chronicity of the process;
- Under unfavorable conditions (use of antibacterial agents, phagocytes) it is capable of acquiring persistent forms for survival (cysts, L-forms). In this state, it can exist in the human body for a long period of time and even continue to reproduce.
Further in our article you will find information about how you become infected with syphilis.
Latent congenital syphilis
Clinical symptoms, features of the course of the process and the timing of their manifestations determine the division of congenital syphilis into:
- syphilis in the fetal stage
- condition of early congenital syphilis (from birth to age four years)
- condition of late congenital syphilis (in children over four years of age)
- a condition of latent congenital syphilis (typical of any childhood)
Regardless of whether the manifestations of congenital syphilis are manifest or latent, it is treated with benzylpenicillin (sodium salt) or penicillin (procaine salt) or procaine penicillin for two weeks.
If there is intolerance to penicillin antibiotics, treat with ceftriaxone.
If only benzylpenicillin is intolerant, then the use of semisynthetic penicillins - oxacillin or ampicillin is indicated.
Is latent syphilis dangerous?
Latent syphilis poses a huge danger.
It is asymptomatic and is often diagnosed late, when syphilis causes many complications.
Therefore, the main thing is to diagnose latent syphilis as early as possible and begin treatment.
It can threaten syphilitic aortitis, leading to aortic aneurysm.
As a result of aortic rupture, the patient faces lightning death.
Symptoms in the gastrointestinal tract resemble chronic gastritis, ulcers or stomach cancer.
Interstitial lung inflammation or lesions in the lungs may also occur.
Amyloidosis or nephrosclerosis may occur in the kidneys.
Or isolated gummas appear.
Under no circumstances should we talk about self-diagnosis and self-medication.
Improperly treated syphilis can lead to serious pathologies.
Other organs are rarely affected by syphilis.
We will definitely talk about other complications of latent syphilis later.
Latent syphilis: who treats and where it is treated
Syphilis in any form and stage is treated by a dermatovenerologist.
He is treated in the KVD, in private venereology clinics or in venereology private offices.
In addition to latent early and late syphilis, there are congenital and unspecified forms.
The diagnosis of congenital latent syphilis is rarely made.
If the patient does not even supposedly know the time of his infection, then they speak of unspecified latent syphilis.
Mortality in latent syphilis
We know that late syphilis is practically asymptomatic and is often treated at the stage of late latent syphilis.
When persistent defects are already developing in the body of a patient with syphilis, which can lead to his death.
With the modern level of medical care, syphilis is very rarely advanced, therefore, as a rule, it is successfully diagnosed and treated and does not lead to death.
According to WHO, the highest mortality rate from syphilis is in the underdeveloped countries of Central Africa.
In civilized countries of Europe and the USA it is much lower.
In Russia it is also small.
But the incidence of syphilis in general is growing steadily, so in 1991 in the Russian Federation there were seven point one and one tenth sick people per hundred thousand people.
In 2009 - fifty-two point two people per hundred thousand population, that is, in eighteen years, syphilis in Russia has become more than seven times worse.
Damage to internal organs with latent syphilis
I have already spoken about syphilis affecting the cardiovascular, respiratory and excretory systems.
Now let's talk about syphilis affecting liver tissue.
Late syphilitic hepatitis exists in four forms: chronic epithelial, chronic interstitial, gummous and miliary.
All forms of hepatitis with a chronic, long-term course and with gradually developing sclerogummous changes ending in cirrhosis and gross deformations in the liver.
Such sclerogummous foci damage the portal vein and ascites appears.
If the bile duct is damaged, the patient becomes jaundiced.
Liver damage is not common and is very common among alcoholics.
The right hypochondrium experiences pain, the abdomen is enlarged and dyspepsia.
Low-grade fever, liver enlarged and lumpy.
Enlargement of the left lobe of the liver and the phenomenon of splenomegaly.
Rarely, men experience orchitis.
Leading to ulceration and testicular atrophy.
Reasons for failure in the treatment of syphilis
The reason for unsuccessful treatment can be both diagnostic errors and an unsuccessfully chosen treatment regimen.
Therefore, it is important to immediately determine the correct diagnosis and undergo adequate effective treatment.
After unsuccessful therapy, and if it started late, the patient may have seroresistance.
The patient is experiencing autoimmune and allergic reactions and the results of treatment are not visible.
Tests show an inflammatory process in the body.
Consequences and complications of syphilis
Latent syphilis, when there is damage in the form of early neurosyphilis (up to five years from the time of infection) and late neurosyphilis.
Neurosyphilis can have different symptoms such as:
- mesodermal neurosyphilis
- when the meninges and the vessels feeding them are affected
- ectodermal neurosyphilis, with the appearance of tabes dorsalis
- progressive paralysis or amyotrophic syphilis
Ninety to ninety-four percent of patients with latent syphilis have damage to the organs of the cardiovascular system.
Four to six percent have liver damage.
Many internal organs are covered with nodes with limited gumma.
Damages to the cardiovascular system exist in the form of specific myocarditis, aortitis, and changes in the vessels of the heart.
Most often, the cardiovascular system is affected by syphilitic aortitis, which leads to aortic aneurysm and damage to the valves and vessels of the heart.
In extremely rare cases, other organs are affected.
The musculoskeletal system is also affected, in the form of arthropathy and gummous lesions of certain joints.
The joints are deformed and bone tissue is significantly destroyed.
Test indicators before and after treatment for syphilis
We know very well that latent syphilis can only be detected through tests, since it is asymptomatic.
During medical examinations or preventive examinations, screening is carried out using various tests.
Or RMP (microprecipitation reaction) or RPR rapid plasmareagin test).
If there are real suspicions or doubts about the test results, along with RMP or RPR, specific tests are performed - RPGA or ELISA.
In the latent form of syphilis, the sensitivity of the treponemal RPGA method reaches one hundred percent.
But even after treatment, RPGA indicators remain positive almost throughout life.
Therefore, the effectiveness of syphilis therapy with RPHA has not been assessed.
The effectiveness of therapy against syphilis is assessed using non-treponemal tests (NTT) - RMP, RPR or VDRL.
If the treatment was adequate, then specific antibodies to Treponema pallidum decrease.
Before treatment – sharply positive, then weakly positive and negative.
Latent syphilis in women, including during pregnancy
In women, latent syphilis occurs in the same way as in men.
When a woman decides to get pregnant, and she has a history of syphilis, and there seem to be no clinical manifestations, she must confirm recovery with tests and then become pregnant.
If syphilis is cured, then you can do without a caesarean section during childbirth.
No additional preventive treatment is needed.
RW is done three times during pregnancy.
And if tests confirm the presence of syphilis, the pregnant woman is hospitalized for treatment. If the mother has syphilis during early pregnancy, the baby will most likely not have congenital syphilis.
If syphilis is detected late in a pregnant woman (the second or even third trimester of pregnancy), then the fetus’s body is literally “stuffed” with Treponema pallidum.
This turns into congenital syphilis.
Children may be born with birth defects or stillborn.
Cases of miscarriages are also common.
The result will depend on how active the syphilitic infection is.
Therefore, the sooner syphilis is diagnosed in a pregnant woman and treatment is started, the greater the chance of avoiding congenital syphilis in the baby.
Early and late latent syphilis
Early latent syphilis is spoken of as syphilis without a visible clinical picture, but with specific antibodies in the blood.
If two years have not yet passed since the last test, when antibodies were not yet in the blood.
There are no symptoms, but early latent syphilis is still contagious.
This form of syphilis is most common if the infected person is under forty years of age and has frequent unprotected sexual contact with strangers.
If more than two years have passed since the time of infection with syphilis, then they speak of late latent syphilis, which, unlike early latent syphilis, is absolutely not contagious.
But both the early and late latent periods are dangerous for pregnant women, or more precisely for the newborn.
It can cause congenital syphilis.
At the same time, it is possible to become infected with syphilis even from the mother while breastfeeding.
If late latent syphilis is activated, it becomes tertiary syphilis.
In this case, the skin becomes covered with low-infectious tertiary syphilides, tubercles and gummas.