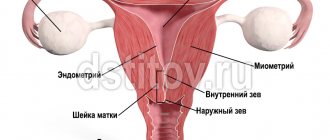
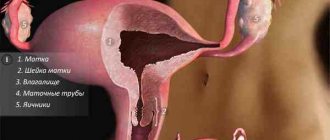
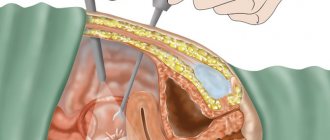
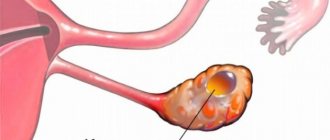
Gynecology uses an effective method for treating fallopian tubes - laparoscopy. With its help, you can avoid large incisions and unsightly scars in the lower abdomen. Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed when they are blocked or connected by thread-like tissue to neighboring organs.
The severe risks inherent in the classic postoperative period are reduced to zero, and recovery time is reduced many times over. But is everything so ideal in this method of treatment?
Gentle surgery technology
Literally, “laparoscopy” means: “groin” and “look” (translation from Greek). For the treatment of appendage obstruction, this manipulation is better suited than other types of surgical interventions. It is carried out in a gynecological hospital using special equipment.
A woman’s stomach is not cut with a scalpel, and the body is thus not subjected to severe stress. Only punctures are made through which tubes and devices are inserted into the peritoneum. The surgeon’s manipulations and everything that happens inside is recorded on video. The recording is transferred to the patient. It is recommended to keep the video as it may be needed for other surgical procedures throughout life.
Advantages of the method
This is a gentle operation, after which complications rarely develop.
Laparoscopy has many advantages over other types of surgical interventions:
- After the operation, small scars remain at the puncture site; over time, they become almost invisible.
- Can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Short rehabilitation period.
- The woman is discharged home on the second or third day.
- The surgeon controls all his movements using images on the monitor. This minimizes the risk of injury to nearby tissues.
- If a pipe ruptures during the operation, the surgeon can quickly stop the bleeding without threatening the health and life of the patient.
- The risk of formation of adhesions, which often appear after abdominal surgery, is minimized.
When is it necessary to clean the fallopian tubes?
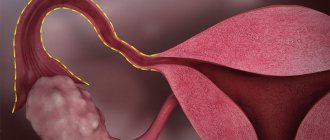
The appendages, in particular the fallopian tubes, are susceptible to diseases that result in external and internal adhesions. They grow after the following pathologies and gynecological manipulations:
- inflammation of the appendages
— infectious infection from a sexual partner (STI)
- operations in the pelvis with an incision in the abdominal cavity with a scalpel (abdominal).
The consequence of adhesions is infertility. That is why, if a woman is unable to become pregnant, fallopian tube laparoscopy is prescribed as the primary method of treatment. And, conversely, when the patient decides not to have children, this manipulation is carried out.
Despite the effectiveness of the method, no gynecologist guarantees the full functionality of the fallopian tubes. However, those wishing to become pregnant should agree to this operation, since it is prescribed even before planning IVF.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for the operation:
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes,
- accumulation of fluid or pus in the lumen of the tube,
- ectopic pregnancy,
- adhesions,
- to clarify the diagnosis.
Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is performed using different methods depending on the type of disease:
| Pathology | Description |
| Spikes | Adhesions are compactions of connective tissue that occur after surgical interventions, and can also be a complication of inflammatory processes. Adhesions often lead to changes in the location of organs, which can trigger the development of infertility. |
| Hydrosalpinx | This is a pathology in which fluid gradually accumulates in the lumen of the pipe. The disease develops as a result of acute and chronic inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs. The pathology leads to the fact that the villi in the fallopian tube stick together, the lumen in it narrows, as a result of which a mature egg is not able to enter the uterine cavity. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | This is a dangerous pathology in which a fertilized egg attaches to the fallopian tube and develops there. The danger is that an untimely diagnosed ectopic pregnancy leads to rupture of the tube lining. This is very dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of a woman. |
| Salpingitis | Infectious inflammatory process in the fallopian tube. The infection can be transmitted through blood or sexual intercourse. The pathological process often leads to the formation of adhesions. |
| Salpingo-oophoritis | An inflammatory process in the tubes and ovaries, as a result of which the lining of the ovary thickens and the egg cannot leave it. |
Contraindications to laparoscopy are:
- pathologies of the respiratory system,
Laparoscopy is performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- bleeding disorder,
- obesity,
- malignant neoplasms of the ovaries,
- pathologies of the liver and kidneys,
- neoplasms of the cervix,
- infectious diseases.
Carrying out laparoscopy step by step
Depending on the degree of obstruction and the extent of the process, 2 types of operations are performed:
- with pipe removal
- without removing the fallopian tubes.
The details of the manipulations are discussed with the patient, since the woman must understand how adhesions are removed and what consequences the intervention may lead to. In this case, the final decision is made by the doctor (many factors of the patient’s health status are taken into account). It should be said that in severe forms of the disease, the adhesions are not cut, but the fallopian tubes or entire appendages are removed.
How is laparoscopy performed?
On what day of the cycle is tubal laparoscopy performed? The operation is performed between the 7th and 10th day of the menstrual cycle under general anesthesia. Before the procedure, the woman must empty her bladder. After administering anesthetic drugs, the doctor treats the area where surgical procedures will be performed with iodine and alcohol.
On the anterior abdominal wall, the surgeon makes 3-4 punctures with a diameter of 5 to 10 mm. Using these punctures, the doctor inserts a camera and all the necessary surgical instruments. On the monitor, the doctor monitors all his movements; the image is enlarged 10 times, this allows the specialist to clearly control the progress of the operation. The first puncture allows carbon dioxide to be introduced into the abdominal cavity, this is necessary to improve visibility and increase space. The camera is inserted through the second puncture. The third and fourth punctures are necessary to insert medical instruments.
After the operation, the carbon dioxide is removed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are sutured. What is the duration of laparoscopy? It depends on the type of operation: with the diagnostic method, the procedure takes about 20-30 minutes, operative laparoscopy can last from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
Procedure Details
Regarding the menstrual cycle, laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is prescribed for 15-25 days or in its first phase. General anesthesia is used for all patients without exception. The surgeon manipulates instruments and devices while looking at the screen. The monitor shows organs in an enlarged image, which allows you to eliminate even microscopic adhesions with pinpoint accuracy. This cutting reduces the risk of accidental damage to the internal or external surface of the pipes.
In case of partial obstruction, the doctor is limited to removing adhesions and restoring the structure of the organ. The advanced form of the disease leads to the following complications:
- involvement of the inner surface of the fallopian tubes in the process
- damage to the structure of the cilia lining the organ.
In this case, healing the organ is impossible, since the effectiveness of laparoscopy is no more than 10%. The doctor can make the decision to remove the tube during the operation, if this issue has not previously been discussed with the patient.
The ability to conceive is preserved if there is no obstruction in the paired fallopian tube. At the same time, it is imperative to remove the first one, if it cannot be treated. This is the only way to avoid a dangerous ectopic pregnancy.
How to prepare for surgery?
Do you need to prepare for tubal laparoscopy? Yes, since preoperative preparation is an extremely important stage of treatment, which is divided into several stages :
- examination, examination
- medication preparation,
- preparation of the operating room.
Before the operation, an examination is carried out to determine whether there are any contraindications. The following studies are being carried out:
| Type of study | Target |
| General blood analysis | Shows the level of blood clotting, as well as the number of its components. A blood test helps identify inflammatory processes in the body. |
| General urine analysis | A morning sample of urine is taken for analysis. The study helps determine how the kidneys work, as well as other organs. |
| Blood chemistry | Blood is taken from a vein. The analysis allows you to evaluate the functioning of all organs and systems of the body. |
| Blood test to determine blood type and Rh factor | The analysis is necessary in case the patient needs a blood transfusion. |
| Urogenital smear | The study allows you to study the microflora of the vagina, urethra, and cervix. |
| ECG | Allows you to determine how the heart works. |
If the examination reveals any pathologies, the woman will need to consult a specialist. The operation is not performed during menstruation. Before laparoscopy, you must follow the recommendations :
- The patient must follow a light diet for several days before surgery,
- An enema must be performed in the evening and in the morning before surgery,
- the day before you need to stop eating from 6 pm.
Procedures for recovery and against relapse
It is possible to plan conception if all adhesions are removed 4-5 months after the intervention. It is recommended to first undergo a 5-day course of physical therapy. The program includes:
- ultrasound
— electrophoresis
— magnetic therapy
— laser therapy
- gynecological massage.
These procedures are not prescribed all at once, but selectively. They are carried out to prevent relapse (prevent the formation of a new adhesive process). You may also need to adjust your hormonal levels using pills.
What are the risks?
Laparoscopy is a surgical intervention in the body, after which complications develop very rarely, only in 1-7% of all cases:
- damage to internal organs,
- bleeding,
- blood clot formation,
- subcutaneous emphysema develops as a result of air entering under the skin layer.
Also, one of the complications may be the consequences of anesthesia. They occur extremely rarely, since the patient is monitored by an anesthesiologist during the operation. This operation is carried out only with the help of modern equipment, so any complications are identified on the spot and immediately eliminated.
How to get pregnant after cleaning your pipes?
A woman’s body is ready to conceive within 3 months after treatment of adhesions using a gentle method. If there is no pregnancy within a year or two, it is recommended to plan IVF. If conception occurred within 3 months after removal of the obstruction, the woman will need increased attention from a gynecologist. It is indicated by the risk of developing fetoplacental insufficiency (the placenta cannot ensure the normal development of the fetus).
At the same time, the chance of carrying a baby remains high, since this pathology can be controlled with the help of hormonal drugs. It should be noted that adhesions often reappear after removal. To prevent this process, suppositories are prescribed: Distreptase or Longidaza.
Recovery period
The duration of recovery after tubal laparoscopy depends on many factors :
- type of anesthesia,
The duration of the recovery period depends on the type of surgery and the general health of the patient.
- volume, type, duration of the operation,
- general health,
- the presence of concomitant pathologies that can prolong the rehabilitation period.
Since carbon dioxide is used during laparoscopy, its residues in the body can cause discomfort in a woman in the area of the lungs and abdomen. The gas is eliminated through the lungs. To speed up this process, you need to consider the following points:
- to stimulate lung function, it is recommended to get up and walk the next day after surgery,
- Good nutrition helps improve bowel function.
On the first day after surgery, the patient needs to drink a lot of fluids: still water, broth, juices. The products are recommended to be consumed stewed and boiled. It is important to eat small meals, about 5-6 times a day.
Is it possible to get pregnant after tubal laparoscopy? If the operation is successful and there are no complications, a woman can become pregnant within two to three months. But sex after tubal laparoscopy is contraindicated for 3 weeks.
Contraindications
Laparoscopy for adhesions in the pelvis is contraindicated if the patient has:
- oncological diseases of the internal reproductive organs (in this case, laparoscopy can aggravate the situation and cause metastases to spread throughout the body);
- advanced decompensated pathology of internal organs;
- the presence of acute infectious processes in the body;
- bleeding disorder (in this case there is a high risk of bleeding, which will be extremely difficult to stop);
- hiatal hernia;
- severe exhaustion of the patient (cachexia);
- coma state;
- advanced degree of obesity;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- period of menstruation;
- excessively high blood pressure.
Where can laparoscopy be performed in Moscow?
How much does fallopian tube laparoscopy cost in Moscow? We offer you an overview of clinics with prices:
| Clinic | Address | Price, $ |
| "SM - Clinic" | Klara Zetkin street, house 33/28 | 300 |
| "He is a Clinician" | Tsvetnoy Boulevard, building 30, building 2 | 628 |
| "Miracle Doctor" | st. Shkolnaya, building 1, apt. 3 | 212 |
| "Best Clinic" | Leningradskoe highway, building 116 | 471 |
| "Petrovsky Gate" | 1st Kolobovsky lane, building 4 | 1142 |
This is only an approximate cost of the operation, since the price will depend on the method of its implementation (dissection of adhesions and removal of a cyst, for example, will vary significantly in price). In addition, also consider the cost of the examination and all the tests that you will need to undergo before surgery.
Anesthesia
On the day of admission to the clinic, the woman meets with an anesthesiologist. If the patient takes medications, she must report this. Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for adhesions is an operation that requires general anesthesia.
It can be given to patients in the following ways:
- Intravenous. In this case, medications are injected directly into the blood. Thus, the patient falls asleep very quickly. Typically, such drugs cause short-term anesthesia, which lasts about 15 minutes. However, if necessary, during the procedure the doctor may perform additional infusion of the solution into the vein. This will allow you to maintain anesthesia for quite a long time.
- Inhalation. In this case, the patient inhales nitrous oxide through a mask and thus falls asleep.
Today, endotracheal anesthesia is also quite often used. Its essence is that the patient is first given intravenous or inhalation anesthesia, after which a special tube is inserted into the trachea. Finally, the woman is connected to medical equipment to perform artificial ventilation.
This type of anesthesia is one of the newest and is distinguished by its safety. In this case, the anesthesiologist will be able to control the dosage of medications as accurately as possible. Also in this case, the risk of gastric contents entering the respiratory tract becomes minimal.
Complications
It is important to understand that each person’s body has its own individual characteristics and therefore the reaction to anesthesia in each case can be completely different.
Sometimes, even with the correct selection of medications and compliance with their dosage, the patient may develop complications such as laryngeal edema, respiratory and/or heart failure, myocardial infarction, recurarization, and vomiting. Headache and hallucinations may be present after surgery.
Benefits of laparoscopy
You should be aware of the advantages of laparoscopic intervention over abdominal surgery. Firstly, this is a short rehabilitation period. Recovery will take only 3 to 5 days (the woman will be in the hospital during this time). If you cut the abdominal wall with a scalpel, you will have to stay in the hospital for at least 10, maximum 15 or more days.
As for the type of stitches that remain after the operation, after laparoscopy there will be three small scars, each of which is a maximum of one and a half centimeters. They won't be noticeable.
Endoscopic operations give the surgeon the opportunity to fully control the process through the control of a video camera. It displays the image on the screen at 10x magnification. This operation is gentle because, due to video control, the doctor has no chance of damaging healthy tissue.
Preparation
For many patients, the hospital environment causes fear and anxiety. You don't have to endure this. If you experience severe psychological discomfort, you should inform your doctor about this. To improve the patient’s condition, he may prescribe her sedatives or tranquilizers.
However, in no case should you engage in amateur activities and take pills without consulting a specialist. This can lead to serious consequences. As for the preoperative preparation itself, it includes the following activities:
- following a fasting diet (should be started a few days before the procedure);
- water procedures and removal of pubic hair the evening before the operation;
- cleansing the intestines with an enema (in the evening before surgery and then in the morning);
- complete refusal to eat after 6 pm on the eve of the procedure;
- full from drinking any liquid after waking up on the day of surgery.
3 days before surgery, you need to exclude from your diet any foods that can cause increased gas formation. These include cabbage, legumes, milk, eggs, etc. You should also avoid carbonated drinks and alcohol consumption.
It is recommended to quit smoking about a month before surgery. This is necessary so that the body begins to be better saturated with oxygen and subsequently recovers better.