According to statistics, adnexitis remains the most common disease of the female genital organs. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It is caused by infection with staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia, fungi and similar microorganisms. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed for inflammation of the appendages. Treatment includes the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Importance of treatment
Only the prescription of antibiotic therapy, as medical practice has shown, can cure inflammation of the ovaries and prevent serious complications that can lead to the death of the patient.
There is a large mass of pathological microorganisms that provoke inflammation in the appendages. To stop their vital activity and functioning, certain groups of antibiotics must be used, since each of them has its own characteristics and acts on specific types of bacteria.
Consultation with a doctor about the treatment process is required, since there are contraindications, specific pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. If the patient self-medicates, this may lead to progression of the disease.
Briefly about the disease
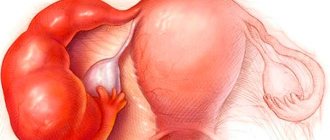
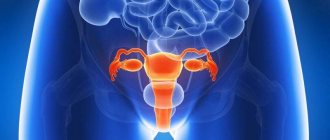
Oophoritis is an inflammatory process in the ovaries, which causes a deviation in the functioning of the organ. Often the disease is complicated by adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages and salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Such a stormy process has led to the fact that in American medical reference books the pathology has received a common name - pelvic inflammation syndrome, which has an acute or chronic course.
The most common cause of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages are various types of infections, especially those that are the culprit of sexually transmitted diseases. Such a striking feature explains the peak of the disease at 18-25 years old - the age at which women are most sexually active, rarely use condoms and have no knowledge about disease prevention.
Main groups of antibiotics
Not all drugs that have a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect are indicated when oophoritis is detected. Also, their specific type is prescribed taking into account the causative agent of the infection, the severity of the pathology and the characteristics of the female body. Groups of antibiotics:
- Tetracyclines (Doxycycline) have a wide spectrum of action, so they can be used at the very beginning, since they affect many pathological microorganisms. Do not forget that they do not treat infections caused by protozoa, fungi or bacteria with high acid resistance;
- Penicillins (Amoxiclav) are often used in the treatment of oophoritis, primarily in women with other diseases, because this group has a minimal number of contraindications. They have pronounced bactericidal abilities;
- Macrolides (Azithromycin) – stop the functioning of microbes such as streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia and mycoplasma;
- Nitromidazoles (Metronidazole) - act on a variety of anaerobic microorganisms, regardless of whether they are gram-positive or gram-negative;
- Fluoroquinolones (Ofloxacin) are often used in gynecological practice because they affect many bacteria without causing addiction in patients.
Only after conducting an examination and identifying the sensitivity of bacteria to a certain group can a direct detrimental effect be exerted on them. This means that recovery will come faster.
Painkillers
Inflammation of the appendages is often accompanied by severe pain. In this case, the gynecologist may prescribe painkillers. They can be in the form of suppositories and ointments.
Diclofenac
Diclofenac helps eliminate the inflammatory process and relieve pain. It is quickly absorbed by mucosal cells. Due to penetration into the circulatory system, the product restores the body's condition, providing an antipyretic effect.
The drug has many contraindications. Among them are:
- gastritis;
- ulcer;
- pregnancy;
- allergies.
Indomethacin
Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is often used in the treatment of adnexitis and other diseases of the genitourinary system in women.
The drug is a suppository that is inserted into the rectum. Penetrating into the body, the active components:
- eliminate pain syndrome;
- eliminate the inflammatory process;
- reduce elevated body temperature.
The product has some contraindications. Among them are stomach ulcers, liver and kidney failure, and pregnancy.
Voltaren
The focal effect is Voltaren. The cyclooxygenase inhibitor has:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antipyretic;
- analgesic effects.
When used, the likelihood of bleeding is prevented.
What are the contraindications?
Most often, pregnant women may be against taking antibiotics because they are worried about the health of their unborn child. Indeed, some of them can cause disruption of the normal development of the fetus, but there are also drugs that can be used at this time. The same applies to antibiotic therapy during breastfeeding.
Most often, the breakdown products of these substances are excreted by the liver and kidneys. If there is a disorder in the functioning of internal organs, for example, with liver or kidney failure, they are also contraindicated. You cannot prescribe medications with antimicrobial effects if you have an individual intolerance to their components.
You need to understand that some medications can cause allergic reactions that pose a threat to human life. This is another argument in favor of the fact that taking medications should be agreed with the doctor.
The following are the names of the most effective antibiotics prescribed by the doctor. This information is provided for informational purposes only; unauthorized use of medications can only aggravate the situation.
Briefly about the disease
Oophoritis is an inflammatory process in the ovaries, which causes a deviation in the functioning of the organ. Often the disease is complicated by adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages and salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Such a stormy process has led to the fact that in American medical reference books the pathology has received a common name - pelvic inflammation syndrome, which has an acute or chronic course.
The most common cause of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages are various types of infections, especially those that are the culprit of sexually transmitted diseases. Such a striking feature explains the peak of the disease at 18-25 years old - the age at which women are most sexually active, rarely use condoms and have no knowledge about disease prevention.
The disease cannot be called harmless. Under certain circumstances, it affects the endocrine system, causing hormonal imbalances. This pathology, in turn, can lead to infertility. Another danger is the rapid development of oophoritis and adnexitis, during which the inflammatory process takes on a purulent form with further peritonitis and death. It is for this reason that antibiotic therapy receives so much attention.
Ofloxacin
It has a wide spectrum of action, although it is mainly aimed at gram-negative pathogenic microorganisms.
It has high bioavailability, and when it enters the body when used orally, it is completely absorbed. The effectiveness of this remedy is the reason it is one of the first to be prescribed, since it helps in cases where other antibacterial drugs have little effect.
It is used both for other inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system and for infections of other internal organs.
Names of the most effective antibiotics for inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) in women
- Azithromycin®
- Amoxiclav®
- Doxycycline®
- Clindamycin®
- Metronidazole® (prescribed only in combination with other antibiotics)
- Ceftriaxone®
The listed medications help well in the fight against infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, but their thoughtless and uncontrolled use is unacceptable. For a successful and rapid recovery, a number of conditions must be observed, which, if ignored, can cause great harm to the body and lead to complications.
Read further: Is there a delay in menstruation after antibiotics?
Metronidazole
The list of bacteria against which its action is directed includes staphylococci, streptococci, clostridia, lamblia, and chlamydia.
Metronidazole is perfectly absorbed by the body when taken orally and has high bioavailability. The antibiotic can be used orally, intramuscularly, intravenously, and also by intravenous drip infusion.
The advantage of the drug is that it has a small number of side effects, including dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting), as well as general weakness and dizziness.
Metronidazole should not be used if:
- severe damage to the liver and kidneys;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- the presence of individual intolerance or hypersensitivity to the substances included in its composition.
Actively interacts with other groups, providing an enhanced therapeutic effect. Available, respectively, in the form of tablets and injections. The method of administration will be determined by a specialist, depending on the severity of the pathology.
Tsifran - antibiotic or not: instructions for use price reviews
Fearing dysbiosis, patients often ask: Is Cifran an antibiotic or not? This question is difficult to answer unambiguously:
- Antibiotics are antibacterial drugs of natural origin or having synthetic analogues;
- Cifran is a synthetic antimicrobial drug from the fluoroquinolone group that has no natural analogues.
Thus, Tsifran is an antibiotic in action, but not in origin.
Fluoroquinolones – what are they?
Fluoroquinolones are a group of antibiotics belonging to the quinolone class.
The first drugs were invented back in the sixties of the last century, but their activity against pathogenic microflora was low and their toxic effect was high.
Clinical trials continued, negative effects were minimized, and the effect on microbes was enhanced. This is how first the second generation fluoroquinolones appeared, then the third.
Ciprofloxacin is a substance from the latest generation of broad antimicrobial action. It and its derivatives are the basis of many medications that can be used to treat diseases in the following areas:
- pulmonology;
- urology and gynecology;
- dermatology;
- gastroenterology;
- neurology;
- dentistry.
Action of Tsifran
Cifran is an antimicrobial drug (antibiotic) active against most gram-positive and -negative bacteria. Its mechanism of action is based on inhibition of the synthesis of enzymes secreted by pathogenic microorganisms that destroy fluoroquinolones themselves, and changes in the structure of their DNA.
They increase the permeability of microbial cell membranes and have a bactericidal effect. The result is recovery.
The antibacterial effect, unlike penicillin, cephalosporins and others, is exerted both on bacteria that are in the active phase of growth and reproduction, and on “dormant” microorganisms.
What does Tsifran help with? It can be prescribed for infections caused by the following bacteria:
- enterobacters;
- cytobacteria;
- coli;
- shigella;
- Morganella morgana;
- salmonella;
- listeria;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- Brucella;
- chlamydia;
- legionella;
- mycoplasmas and others.
According to the official description of the product, it is not effective against anaerobic bacteria, so before you start using it, take clinical tests to identify the type of pathogen. You should not take the medicine without a doctor's recommendation.
The medication is usually considered a safe antibiotic - it does not disturb the microflora of the intestines and vagina and does not cause unpleasant consequences - dysbacteriosis, thrush and others.
Composition and release form
According to the instructions, Cifran contains the active substance – ciprofloxacin, which can be contained in the following quantities:
- 250mg, 500mg or 1000mg per tablet;
- 100 mg in vials for the preparation of a solution for intravenous injection;
- 3 mg in 1 ml – in the form of eye drops.
Tsifran tablets are packaged in cell bags of 10 pieces, the package may include 10 or 100 pills. The powder is placed in 100 ml plastic bottles. Drops are available in 10 ml volumes.
Indications for use of Tsifran
What can Cifran be used for? Abstract of the remedy includes diseases of the following systems:
- urinary tract and reproductive system in men and women - acute and chronic inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), bladder (cystitis), prostate gland (prostatitis), uterine mucosa (endometritis), testicles (orchitis), appendages (epididymitis), urethritis, gonorrhea;
- lower respiratory tract and ENT organs - pneumonia, bronchitis, inflammation of the pleura, accumulation of purulent masses in the bronchi and with sore throat, otitis media, sinusitis, mastoiditis, sinusitis, pharyngitis;
- epidermis - skin rashes, wounds and other phenomena caused by the accumulation of pus and necrosis;
- gastrointestinal tract - peritonitis, inflammation of the gallbladder and its ducts, typhus, abscesses in the abdominal cavity;
- musculoskeletal system – bacterial arthritis, osteomyelitis.
Indications for the use of Tsifran are due to its strong antibacterial effect:
- can be used to prevent complications after surgery;
- copes with infections in people suffering from general blood poisoning;
- with severe herpes;
- with abscesses in the oral cavity;
- toothache caused by extraction;
- complications associated with colds and flu.
Medication regimen
- You need to drink the tablets whole, without chewing, and drink a sufficient amount of clean water. The pills are enteric-coated and do not have a negative effect on the stomach, so they can be taken regardless of food.
- The solution is administered dropwise or in a stream; the first method is more preferable.
- Intramuscular injections are not performed.
| Features of the pathology | Dosage |
| Mild course | Take 250 mg of ciprofloxacin every 12 hours |
| Severe course | Should be prescribed 500 mg, interval between doses is 12 hours |
| Pathologies of the upper and lower respiratory tract, typhoid fever, abscesses, sepsis | The recommended dose is 500 mg twice daily; the maximum daily dosage for adults can be raised to 750 mg. |
| Inability to take orally, conditions of extreme severity | It is recommended to do droppers of 100 mg 2 times a day |
The duration of taking the antibiotic Cifran depends on the diagnosis and the severity of the infectious process. Most often, treatment is carried out for 5-7 days.
After the disappearance of the main symptoms of the pathology, it is recommended to extend therapy for another three days. How long the treatment will be carried out will be determined by a specialist; in some cases it can be extended to 1 month (tablets) or two weeks (droppers, IV injections).
Contraindications
All forms of Cifran (powder, drops, tablets) have the following contraindications:
- individual intolerance to any component, even an auxiliary one;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age up to 18 years.
Cifran is a universal drug for the treatment of many infectious diseases, but there are pathologies in which one must be careful and treat such patients only in a hospital setting. This:
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- mental disorders;
- neurological disorders (epilepsy);
- renal and liver failure;
- older age.
Side effects
Cifran is a potent drug that can cause side effects, which should be reported to your doctor.
The list of undesirable consequences includes:
- dyspepsia, increased gas formation, pain in the epigastric region;
- pain in the head, changes in psycho-emotional state, disorders of consciousness, fainting, tremors in the limbs;
- sensory organ dysfunction;
- heartbeat disturbances;
- changes in a number of clinical indicators - bloodstream, liver, kidneys;
- blood in the urine, diuresis disorders, inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- decreased muscle tone, muscle pain and aches, joint inflammation, connective tissue ruptures;
- weakness, increased sensitivity to ultraviolet rays, secondary infections;
- manifestations of allergies.
Reactions from IVs are possible - pain at the injection site, blood clot formation after removal of the catheter.
special instructions
Like any antibiotic, Tsifran has its own administration characteristics.
Interaction with other medications
If prescribed concomitantly with other medications, its or their therapeutic effects may change. Caution should be exercised when the patient is taking the following medications in parallel:
- antiretroviral therapy with didanosine - the active substances bind to each other, which reduces the absorption of ciprofloxacin;
- warfarin – increases the risk of bleeding;
- theophylline – its concentration increases and toxic effects develop;
- antacids, products containing metal salts - the absorption of ciprofloxacin is reduced, the difference between doses should be at least 4 hours.
Alcohol compatibility
The instructions indicate its incompatibility with ethanol, the main component of alcoholic beverages.
Drinking alcohol provokes the appearance of severe neurological reactions, which are observed both on the day of drinking it and over the next five days. This:
- hand tremors;
- headaches, dizziness;
- confusion.
Alcohol reduces the patient’s immunity, allowing pathogens to multiply more actively, which reduces the therapeutic effect of the drug. Ethanol has a destructive effect on the liver, which is already suffering from antibiotics. Therefore, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited throughout the entire therapy and for several days after its completion.
During pregnancy
Tsifran is prohibited, therefore it is not used in obstetrics. The active component of the product has a toxic effect on the fetus in the womb, which can lead to premature birth or the birth of a child with developmental or physical abnormalities.
If the pathology develops during breastfeeding, it must be interrupted for the entire period of Cifran therapy, no matter how long it lasts.
Analogues of the drug
Tsifran is quite cheap - 10 tablets at a dosage of 500 mg cost about 100 rubles. If it is not suitable for the patient, after agreeing on a replacement with the treating doctor, you can buy its analogues in pharmacies.
The direct and main substitute for the product is Tsifran ST (500+600), produced in tablets. In addition to ciprofloxacin, it contains 600 mg of tinidazole, an antimicrobial agent effective against protozoan microorganisms, which expands the spectrum of action of the drug.
Similar drugs are divided into direct substitutes and drugs with an identical therapeutic effect. They are produced:
- in tablet form,
- ready solution for administration in ampoules and vials,
- concentrate for the preparation of solution for infusion.
| By composition | According to therapeutic effect |
| Ificipro | Abaktal |
| Medociprin | Unikpef |
| Flaprox | Levoflox |
| Tsiprinol | Remedia |
| Cipro | Moxifloxacin |
| Tsiprobay | Gatispan |
| Ciprobax | Hemix |
| Ciprobel | Geoflox |
| Ciprobid | Ofloxacin |
| Cyprohexal | Lomflox |
| Tsiprolet and others | Norphlogexal |
| Sparflo and others |
Terms of sale and storage
Tsifran is dispensed with a doctor's prescription. You can store it at room temperature in a place where children cannot reach. Shelf life: 24 months.
What the world says about Tsifran
According to doctors, Cifran is an effective medicine that can cope with most diagnosed infectious pathologies.
Azithromycin
A wide range of effects on infectious agents, which, in addition to those listed above, also include gonococci, ureaplasmas and some types of mycoplasmas, allows doctors to prescribe it in situations where other drugs with antimicrobial effects are ineffective.
Easily combined with other antibacterial drugs. Also, its positive properties include a short period of use.
But due to its strong effect, at times Azithromycin negatively affects the activity of internal organs, and this manifests itself:
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- the appearance of nausea, vomiting, stool disorders;
- photosensitizing and allergic manifestations on the skin;
- general weakness, drowsiness and headaches;
- vaginal dysbiosis with the development of fungal diseases.
Therefore, the doctor can choose this medication as the first line of attack against the pathogen when its nature is not yet fully known, as well as in severe clinical cases. But in subsequent treatment it is recommended to replace it with another drug.
Other means
In addition to the main medications, other drugs may be prescribed. They are not mandatory, but can significantly improve a woman's condition.
Remens
Remens has anti-inflammatory and anti-climacteric properties. It is prescribed for various diseases of the genitourinary system in women.
The drug is made on the basis of natural ingredients. Homeopathic remedy includes:
- secretion of cuttlefish glands;
- snake poison;
- pilocarpus extract;
- sanguinaria extract;
- black cohosh extract.
The product should not be taken during pregnancy and lactation. If you use it according to the instructions, the symptoms of adnexitis are quickly eliminated and hormonal levels are normalized. Remens also affects the nervous system, calming the body. After using the drug, many women note normalization and painlessness of the menstrual cycle.
Calcium gluconate
Calcium gluconate has desensitizing properties. It can be prescribed in addition to the main therapeutic course.
Calcium chloride and gluconate help anti-inflammatory drugs act most effectively on the body. Therefore, gynecologists prescribe them for inflammation of the appendages, characterized by bloody discharge from the vagina.
The drugs are available in the form of solutions for injection. Up to 10 ml of solution (10%) is administered intravenously.
Therapy for adnexitis should be comprehensive. This is the only way to completely cure the disease.
Doxycycline
It is prescribed when therapy with other tetracyclines has not shown proper results.
Gram-positive bacteria are the initial target for bacteriostatic influence.
Quickly absorbed and distributed in the body.
It should not be used in cases of significant dysfunction of internal organs, primarily the liver and kidneys, porphyria, myasthenia gravis, as well as in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Possible side effects:
- Allergic reactions of varying degrees of intensity, depending on the amount of the product used;
- Disorders of the nervous system and mental sphere - sensitivity disorders, deterioration of mood;
- An increase in urea levels with long-term use of the drug;
- Changes in the color of teeth, the appearance of pigment spots on them.
If a woman takes any other medications, it is necessary to tell her doctor about this, because some medications, when interacting with antibiotics, including tetracyclines, can significantly reduce their effectiveness.
Doctor's recommendations
As for the treatment of pathology, comprehensive measures are taken. They consist of dietary nutrition, the absence of nervous tension, psychological and sexual rest, healthy sleep are recommended, and it is also necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations of the attending physician.
It is strictly prohibited to independently adjust treatment or replace medications without the knowledge of the doctor. If the dosage is indicated by a specialist, then under no circumstances should it be reduced, since this may subsequently threaten that the disease will become chronic.
Antibiotic therapy during pregnancy
Antibiotics during pregnancy can only be prescribed with a limited number of medications. For the most appropriate treatment, it is imperative to consult with a specialist.
It is forbidden to use streptomycin, as this can lead to hearing loss in the unborn child, as well as tetracyclines in the second and third trimester of pregnancy due to the fact that they discolor the teeth.
With properly selected antibiotics, you can achieve a quick recovery and eliminate the risk of developing dangerous complications, so self-medication is the main mistake of the patient.
Why is adnexitis dangerous?
The main manifestations of adnexitis are an increase in temperature up to 39˚C and sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the sacrum or lumbar region.
Other symptoms may also occur:
- menstrual irregularities (for example, longer and more painful periods),
- painful urination,
- watery or purulent discharge,
- intermenstrual bleeding,
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
The main danger of salpingoophoritis is the risk of complications. First of all, this may be an adhesive process in the fallopian tubes, which increases the likelihood of infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Also, the inflammatory process can spread to the peritoneum and contribute to the development of peritonitis. Consequences such as disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system or damage to the joints are also possible.
Release form, composition and packaging
White or almost white film-coated tablets, round, biconvex, with a smooth surface on both sides; on the fracture there is a white or almost white mass.
| 1 tab. | |
| ciprofloxacin hydrochloride | 291.106 mg, |
| which corresponds to the content of ciprofloxacin | 250 mg |
Excipients: corn starch - 50.323 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 7.486 mg, croscarmellose sodium - 10 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 5 mg, talc - 5 mg, magnesium stearate - 3.514 mg.
Shell composition: hypromellose (6 cps) - 4.8 mg, sorbic acid - 0.08 mg, titanium dioxide - 2 mg, talc - 1.6 mg, macrogol 6000 - 1.36 mg, polysorbate 80 - 0.08 mg, dimethicone - 0.08 mg.
10 pieces. - blisters (1) - cardboard packs. 10 pcs. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs.
White or almost white film-coated tablets, round, biconvex, with a smooth surface on both sides; on the fracture there is a white mass with a slightly yellowish tint.
| 1 tab. | |
| ciprofloxacin hydrochloride | 582.211 mg, |
| which corresponds to the content of ciprofloxacin | 500 mg |
Excipients: corn starch - 27.789 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 5 mg, croscarmellose sodium - 20 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 5 mg, talc - 6 mg, magnesium stearate - 4.5 mg.
Shell composition: hypromellose (6 cps) - 5 mg, sorbic acid - 0.072 mg, titanium dioxide - 1.784 mg, talc - 1.784 mg, macrogol 6000 - 1.216 mg, polysorbate 80 - 0.072 mg, dimethicone - 0.072 mg.
10 pieces. - blisters (1) - cardboard packs. 10 pcs. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, ciprofloxacin is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The bioavailability of the drug is 50-85%. C max of the drug in the blood serum of healthy volunteers after oral administration of the drug (before meals) at a dose of 250, 500, 750 and 1000 mg is achieved after 1-1.5 hours and is 1.2, 2.4, 4.3 and 5.4 μg/ml, respectively.
Orally taken ciprofloxacin is distributed in the tissues and fluids of the body. High concentrations of the drug are observed in bile, lungs, kidneys, liver, gall bladder, uterus, seminal fluid, prostate tissue, tonsils, endometrium, fallopian tubes and ovaries. The concentration of the drug in these tissues is higher than in the serum. Ciprofloxacin also penetrates well into bones, eye fluid, bronchial secretions, saliva, skin, muscles, pleura, peritoneum, and lymph.
The accumulating concentration of ciprofloxacin in blood neutrophils is 2-7 times higher than in serum.
Vd in the body is 2-3.5 l/kg. The drug penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid in a small amount, where its concentration is 6-10% of that in the serum.
The degree of binding of ciprofloxacin to plasma proteins is 30%.
In patients with unchanged renal function, T1/2 is usually 3-5 hours. The main route of excretion of ciprofloxacin from the body is through the kidneys. 50-70% is excreted in urine. From 15 to 30% is excreted in feces.
If renal function is impaired, T1/2 increases.
Patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance below 20 ml/min/1.73 m2) should be prescribed half the daily dose of the drug.
Dosage
The dose of Tsiprolet depends on the severity of the disease, type of infection, body condition, age, body weight and kidney function.
For uncomplicated diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, 250 mg 2 times a day is prescribed, and in severe cases, 500 mg 2 times a day.
For diseases of the lower respiratory tract of moderate severity - 250 mg 2 times / day, and in more severe cases - 500 mg 2 times / day.
For the treatment of gonorrhea, a single dose of Tsiprolet is recommended at a dose of 250-500 mg.
For gynecological diseases, enteritis and colitis with severe course and high temperature, prostatitis, osteomyelitis, 500 mg 2 times a day is prescribed (for the treatment of ordinary diarrhea, a dose of 250 mg 2 times a day can be used).
The tablets should be taken on an empty stomach with sufficient liquid.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease, but treatment should always continue for at least another 2 days after the symptoms of the disease have disappeared. Usually the duration of treatment is 7-10 days.
Patients with severe renal impairment should be prescribed half the dose of the drug.
Table of recommended doses of the drug for patients with chronic renal failure:
| Creatinine clearance (ml/min) | Dose |
| {amp}gt;50 | Usual dosage regimen |
| 30-50 | 250-500 mg once every 12 hours |
| 5-29 | 250-500 mg once every 18 hours |
| Patients on hemo- or peritoneal dialysis | after dialysis 250-500 mg 1 time per 24 hours |
Side effects
From the digestive system: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, anorexia, cholestatic jaundice (especially in patients with previous liver diseases), hepatitis, hepatonecrosis, increased activity of liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase.
From the nervous system: dizziness, headache, increased fatigue, anxiety, tremor, insomnia, nightmares, peripheral paralgesia (anomaly in the perception of pain), sweating, increased intracranial pressure, anxiety, confusion, depression, hallucinations, as well as other manifestations psychotic reactions (occasionally progressing to states in which the patient can harm himself), migraine, fainting, thrombosis of the cerebral arteries.
From the senses: disturbances of taste and smell, visual impairment (diplopia, changes in color vision), tinnitus, hearing loss.
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances, decreased blood pressure, flushing of the face.
From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia, granulocytopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, hemolytic anemia.
Laboratory indicators: hypoprothrombinemia, hypercreatininemia, hyperbilirubinemia, hyperglycemia.
From the urinary system: hematuria, crystalluria (primarily with alkaline urine and low diuresis), glomerulonephritis, dysuria, polyuria, urinary retention, albuminuria, urethral bleeding, hematuria, decreased nitrogen excretory function of the kidneys, interstitial nephritis.
Allergic reactions: skin itching, urticaria, formation of blisters accompanied by bleeding and small nodules that form scabs, drug fever, pinpoint hemorrhages (petechiae), swelling of the face or larynx, shortness of breath, eosinophilia, increased photosensitivity, vasculitis, erythema nodosum, exudative erythema multiforme , Stevens-Johnson syndrome (malignant exudative erythema), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome).
From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, arthritis, tenosynovitis, tendon ruptures, myalgia.
Other: general weakness, superinfections (candidiasis, pseudomembranous colitis).