Medical certificate
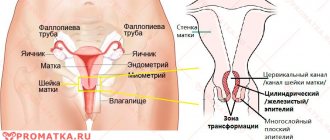
To understand the essence of the pathological process, it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the reproductive system. It is represented by the internal and external genitalia. The latter are collectively called the vulva. Internal organs are the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes. The uterine cavity is connected to the vagina through the so-called cervix. The inside is lined with a layer of cylindrical epithelial cells. They contain glands. They constantly produce mucus, which forms a protective plug. This prevents the penetration of pathogenic microflora from the vagina into the uterine cavity.
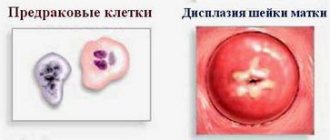
Dysplasia develops at the site where the cervix enters the vagina. This area of the epithelium has a different structure. Cells are localized in several layers. Underneath them there is a connective tissue membrane that separates the mucous membrane from the muscles of the neck and blood vessels. There are no glands in this area. The shape of epithelial cells varies: in the lower layer they are round, and closer to the surface they are flat. Dysplasia develops in the squamous epithelium at the border with the cylindrical epithelium.
Pathology is usually understood as a violation of the arrangement of layers of squamous epithelium due to changes in cell structure. Among healthy elements, atypical ones appear. They may have one core of irregular shape, increased size, or several cores at the same time. At the same time, the structure of columnar epithelial cells is not disturbed.
Amputation
After operations on the appendages, amputation of the uterus today ranks second in the frequency of surgical interventions. If we are talking about the life and health of the patient, such methods are inevitable. Most often, removal is carried out in the following cases:
- First stages of cancer;
- Hypertrophy;
- Presence of scars or abnormalities of the cervix;
- Incurable stages of erosion;
- Ectropion (uterine rupture);
- Chronic endocervicitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
Thanks to modern methods in the field of gynecology, an organ can be amputated in very gentle ways. Each of them has its own indications, implementation features and rehabilitation course. There are several types of procedures, depending on the volume of the removed part of the uterus:
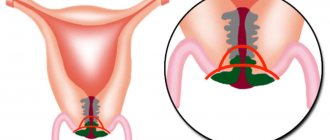
- Subtotal hysterectomy – amputation of the uterus itself;
- Extription of the uterus - removal of the organ along with its cervix;
- Removal of the uterus with appendages (tubes, ovaries);
- Radical hysterectomy - complete removal of the uterus, cervix, appendages, upper part of the vagina and lymph nodes;
Subtotal hysterectomy is the most reliable way to preserve the cervix, since only the body of the cervix is removed during the operation. The most suitable intervention option is laparoscopy. In this case, the risk of damage to the ovaries is minimal; the organs will still work in the same rhythm, producing hormones.
Often during extirpation, not only the uterus and cervix are removed, but also the fallopian tubes. The consequences of such an operation can have traumatic consequences; a woman’s reproductive function is not preserved after such an intervention. In the case of precancerous conditions, this operation will help save the patient’s life, which is more important than reproductive function. Extription has several techniques; the procedure is performed laparoscopically and vaginally. Removal of the uterus can be carried out in conjunction with excision of the cervix, appendages, tissue and lymph nodes.
Amputation is performed using any of three methods:
- Transvaginal (through the vagina);
- Laparotomy (through small incisions in the abdomen);
- Laparoscopic (no incision).
Transvaginal amputation
The transvaginal method involves removing the organ through the vaginal opening. The procedure is performed in women who have given birth, since after childbirth the vaginal muscles are able to stretch to allow the uterus to emerge. The advantage of this method is quick recovery and absence of scars. The rehabilitation period lasts no more than 10 days, and the period of stay under the supervision of doctors is about 2 days. However, it is impossible to remove the ovaries this way. If the patient’s uterus is large or the vagina is narrow, the doctor may also refuse this type of amputation.
Laparotomy
During the operation, the doctor makes a small incision in the abdominal area - about 10 cm. After which the uterus is fixed and removed. The disadvantage of laparotomy is that the recovery period takes longer; in addition, patients experience severe pain and require medical supervision in a hospital setting.
Laparoscopy
The laparoscopic method is becoming more popular; modern technologies make it possible to perform surgery without incisions. During this procedure, a trocar with a diameter of only a few centimeters is inserted into the patient's umbilical area. Before removal begins, all abdominal organs are examined to identify other abnormalities; the examination is performed through a small camera. A large incision is not required to remove the uterus, but it is often divided into several parts before removal.
Types of dysplasia
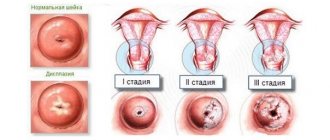
Based on the volume of tissue damage, 3 degrees of development of the pathological process are distinguished:
- Mild dysplasia (CIN I). Pathological changes affect less than a third of the thickness of the epithelium. After confirming the diagnosis, doctors usually choose a wait-and-see approach, conducting constant monitoring of the disease. Often it goes away on its own.
- Moderate dysplasia (CIN II). The pathological process involves up to 2/3 of the epithelium. Timely treatment can stop its progression and completely overcome the disease.
- Severe dysplasia (CIN III). The third degree is considered a precancerous condition. Pathological changes cover more than 2/3 of the epithelial layer.
In today's article we will dwell in more detail on grade 2 cervical dysplasia. According to statistics, the disease progresses to the next stage of development in 16% of cases within two years, and in 25% of cases within 5 years. The rate of development of the pathological process is influenced by the individual characteristics of the body, hereditary predisposition to cancer, the woman’s age and other factors.
Reviews from various sources:
Elena, 40 years old
The cause of dysplasia in my case was erosion that developed after childbirth. I didn’t go to the doctor for several years, I thought everything would go away on its own, but at the next scheduled examination I was presented with a fact - either oncology awaits me in the future, or I agree to cauterization. The procedure is painless, but unpleasant, you are conscious the entire time. I endured it and since then I have forgotten what dysplasia is.
Victoria, 27 years old
I have heard numerous positive reviews about this method of treatment, such as the effect of liquid nitrogen on cervical dysplasia.
Causes
It has been scientifically proven that the primary cause of cervical dysplasia (1st degree, 2nd degree, 3rd degree) is the human papillomavirus or HPV. After penetration into the body, the immune system of an absolutely healthy person copes with the infectious invasion. However, in some cases, virus subtypes 6 and 11 cause dysplasia. Oncogenic strains can cause severe disease and transformation of cells into cancerous elements. We are talking about human papillomavirus numbers 16 and 18.
After the pathogen enters the body and until the initial symptoms of dysplasia appear, several years may pass. The influence of a number of factors accelerates this process:
- indiscriminate choice of sexual partners;
- frequent stress;
- inflammatory processes of the reproductive system;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- poor quality nutrition;
- diseases transmitted exclusively through sexual contact (HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.);
- repeated abortions;
- conditions causing hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause, pathologies of the endocrine glands);
- immunodeficiency states (after transplantation or chemotherapy);
- bad habits.
Once in the body, HPV spreads through the bloodstream to the genitals and invades the cells of the cervix. It produces specific substances that interfere with the full functioning of the immune system and disable DNA. When the body's defenses are weakened under the influence of the factors listed above, atypical elements appear. The immune system cannot recognize them, so they do not die and continue to actively reproduce. In this way, the structure of the epithelial layers changes.
Description of the problem
Precancerous diseases of the cervix are advanced diseases of the female reproductive organs. If left untreated, they can easily transform into cancerous tumors.
Note! The danger of precancerous diseases lies in their asymptomatic course for a long period of time. Signs of pathology appear already in an advanced state, which increases the risk of developing cancer.
The classification of precancerous conditions involves the development of diseases such as dysplasia, leukoplakia, condyloma, adenomatosis and erythroplaktia.
Cervical dysplasia is a disease in which the cellular structure of the epithelium of the organ is disrupted. This disease is the most common form of precancer. Dysplasia can be mild (one-third of the epithelium is affected), moderate (two-thirds of the epithelium is affected), and severe (all layers of the epithelium are affected). With a severe stage of the disease, the risk of its degeneration into a cancerous tumor greatly increases.
Note! This pathology occurs in 18% of women with pathologies of the reproductive organs. The disease develops into cancer in 30% of cases. Women in their thirties are most often affected.
Statistics show that in 40% of pregnant women with dysplasia, which was not detected and treated in time, in most cases it develops into cancer.
Condyloma is a precancerous condition of the uterus, in which a soft neoplasm appears on the pedicle of the uterus in the form of a growth similar to cauliflower, which is capable of fusion. Condyloma is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the human papillomavirus. The neoplasm can be wide and pointed. In the latter case, condylomas are called genital warts, which provoke the development of cancer. This happens especially often when the tumor becomes infected as a result of injury.
In gynecology, leukopathy is a precancerous disease, which is keratinized areas of squamous epithelium and a neoplasm near blood vessels. The pathology looks like a white or beige tumor.
Erythroplasty is a pathology of the epithelium, manifested in the formation of its flattening and atrophy of its basal layer. As a result, a red spot appears on the cervix, which provokes the thinning of several layers of the epithelium to such an extent that blood vessels become visible through them. As a result, malignant degeneration of the pathology often occurs.
Adenomatosis is an atypical proliferation of the epithelium that occurs under the influence of excess estrogen hormone. Adenomatosis is a precancerous condition of the cervix, in which the epithelium grows and begins to protrude into the uterine cavity, forming an endometrial polyp.
Clinical picture
As a rule, there are no pronounced symptoms for grade 1-2 dysplasia. The disease is detected accidentally, for example, during a routine gynecological examination or suspicion of another pathology. The clinical picture is in many ways similar to cervical erosion.
Among the possible signs of dysplasia, the following should be highlighted:
- bloody vaginal discharge without a specific odor;
- pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- bloody streaks in the vaginal secretion after intimacy;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
If grade 2 cervical dysplasia is caused by an infection or inflammatory process, the clinical picture is complemented by uncharacteristic vaginal discharge with a pungent odor. In the absence of timely treatment, itching, burning in the genital area, and problems with urination appear.
Mild dysplasia shm
There is no fixed follow-up algorithm for patients with CIN I, because this degree of neoplasia can regress without any treatment. Despite this, in each specific case it is difficult to predict how this pathology will end.
For CIN I, the following surveillance options exist.
- Repeated examination after six months and a year or HPV test after a year:
- two negative cytology results or a negative HPV test determines the screening regimen once a year;
- cytogram above ASC-US, HPV test is positive - colposcopy supplemented by biopsy is required.
- Treatment using laser vaporization.
As an alternative to laser vaporization, excision (conization) of the cervix is performed in cases where:
- the colposcopic picture is considered unsatisfactory;
- re-detection of CIN 1 after laser vaporization;
- extensive process in the cervix;
- dysplasia did not regress within 1.5 years;
- woman's age 35 years or older;
- impossibility of regular examination or refusal to do it.
Back to contents
Dysplasia 2 degrees and pregnancy
This disease not only negatively affects the functioning of the reproductive system, but can lead to cancer. However, its moderate degree is quite compatible with pregnancy. Doctors say that in most cases the condition does not threaten the child’s health and is not aggravated by complications. On the other hand, the pathology can progress. During the period of bearing a baby, transformation of cervical dysplasia of the 2nd degree into the 3rd degree is often observed. But there is no treatment for the disease in pregnant women.
Even at the planning stage of conception, every woman should undergo a comprehensive examination to assess her health. If dysplasia is a consequence of hormonal imbalance, pregnancy can lead to self-healing.
If HPV is detected at the planning stage, therapy must be prescribed. The appearance of condylomas during pregnancy changes the process of delivery: the woman is offered a cesarean section. This helps prevent infection of the newborn. Treatment of the patient herself is usually carried out in the postpartum period.
Classification of the disease
Joint dysplasia in children has its own classification. The type of therapy for the baby depends on this, because the lighter the form, the simpler and gentler the method will be used.
The pathology has three main forms - acetabular, rotational and upper compartment disease. In the first case, there is a violation of the formation of the acetabulum, in the second there is a change in the angle between the femoral head and the acetabulum, and in the third case there is asymmetry of the femur in a horizontal position relative to the socket.
Childhood hip dysplasia is also divided according to severity:
- immaturity of the hip joint - this form is often found in children who were born prematurely, due to which the articular structures have not yet had time to fully form, so this is considered a borderline condition;
- preluxation – characterized by bevel of the acetabulum;
- subluxation - the cavity has a more flattened shape and the bevel here becomes more pronounced, due to which the head of the bone moves upward and to the outside, and some movements of the child can provoke its fall out of the acetabulum;
- dislocation is the most severe form of pathology, since here the femoral head has a strong shift, which leads to a complete exit from the socket.
The photo shows the degrees of pelvic joint dysplasia in children.
Dysplasia can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Diagnostic methods
Cervical dysplasia of the 1st degree or 2nd degree is usually detected by chance, since the disease does not have a specific clinical picture. Early diagnosis helps prevent the onset of cancer. Therefore, you should not neglect regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Diagnostics involves the use of instrumental and laboratory methods, which are prescribed after studying the patient’s history and complaints:
- Examination on a gynecological chair using mirrors. Dysplasia is indicated by a change in the color of the epithelium, the appearance of whitish spots, and a shine on the surface.
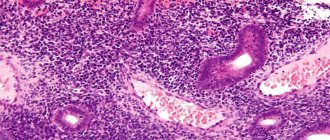
- Colposcopy. Lugol's solution or acetic acid is applied to the surface of the uterine pharynx. In this case, the pathological areas turn pale, which is clearly visible against the background of healthy tissue. The inspection is carried out using an optical device. This allows you to determine the degree of dysplasia and evaluate the structure of the epithelium.
- PAP test. The gynecologist takes a smear from various areas for cytological examination. Under a microscope, you can detect atypical elements, cells with papillomavirus.
- Targeted biopsy. In laboratory conditions, a tissue sample taken from suspicious areas is examined. With the help of a biopsy, atypical elements can be more accurately identified.
- PCR test. Allows you to identify the causative agent of infection and the concentration of viruses in the blood.
Diagnostic measures require simple preparation. Otherwise, the examination results will be incorrect, which may lead to incorrect treatment tactics. An exception is transvaginal ultrasound, which requires personal hygiene before the procedure and emptying the bladder.
The doctor should explain the specifics of the preparation. Usually it lasts no more than 3 days. During this period, you should avoid intimacy, taking a hot bath, or going to the solarium or sauna. Do not use suppositories or tampons or douche. Immediately before the examination, careful hygiene of the external genitalia should be carried out.
The examination is not carried out during menstruation. The exception is in emergency cases when the patient’s life is threatened.
Diagnostics
The main task of early diagnosis of the disease is to prevent the development of cancer cells and malignant tumors. That is why it is recommended to conduct a gynecological examination at least once every six months, and a detailed cytological examination every 2 to 3 years.
Diagnosis of cervical dysplasia may include the following methods:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- cytological examination of a smear (study of the cell structure for the presence of benign and malignant signs of tumors);
- colposcopy (visual examination of the cervix using a special optical device called a calcoscope);
- targeted biopsy (sampling of pieces of tissue to determine the extent of damage to the membranes);
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is carried out to establish the type of infection and its oncogenic type based on DNA and RNA material from genital secretions.
Already during a routine examination by a gynecologist using mirrors, areas with an irregular shape and white color, lighter than healthy tissue, may be noted on the cervix. To confirm the diagnosis, a detailed cytological examination of the smear is performed.
Colposcopy allows you to detect branched blood vessels in places of edema and their pale color. After treating the organ with a solution of acetic acid, the dysplastic areas become white. The predisposition of characteristic tumors to the malignant type can be determined only after a thorough histological examination of epithelial pieces. The accuracy of the analysis results is 100%.
Methods of therapy
The success of treatment for grade 2 cervical dysplasia is largely determined by a competent determination of the root cause and provoking factors. In addition, when choosing a therapeutic tactic, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, her reproductive function, desire for future pregnancies, and the presence of concomitant health problems.
Treatment is predominantly carried out using medications. With a large focus of pathology and a pronounced depth of penetration, surgical intervention may be required. Alternative medicine is sometimes used as a supportive measure. How to treat grade 2 cervical dysplasia will be discussed in detail below.
What it is? Photo.
Cervical dysplasia, or neoplasia, is the degeneration of normal epithelial cells of the vaginal part of the cervix. Cells become unnatural and cease to perform their function. Such cells are a little similar to cancer cells, but are not yet entirely cancerous (see photo).
In the photo: normal, dysplasia and cervical cancer
Scheme of development of cervical dysplasia
Remember: dysplasia is not cervical cancer!!! Cancer still takes time to develop: on average 10-20 years.
Use of medications
Drug treatment of grade 2 cervical dysplasia includes 2 areas:
- Strengthening the immune system. For this purpose, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes and various immunomodulators (Prodigiozan, Reaferon).
- Use of antiviral drugs. The most commonly prescribed drug is Isoprinosine. The product has a dual effect: it suppresses the activity of the virus and stops the division of cell nuclei.
When the affected area is small, doctors sometimes choose a wait-and-see approach. However, in this case, the patient must regularly visit a gynecologist for examination and smears for oncocytology. As the pathological process progresses, therapy with systemic and local agents is prescribed.
Surgical intervention
How is grade 2 cervical dysplasia treated if conservative therapy is ineffective? In this case, they resort to surgical treatment. The following procedures are used in modern medical practice:
- Laser therapy. This is the most common treatment option for grade 2-3 cervical dysplasia. It involves evaporating lesions with a laser beam. After the procedure, scars do not remain, but the possibility of damage to healthy areas cannot be ruled out.
- Cryodestruction. It involves exposing tissues to liquid nitrogen, after which they die. After the procedure, scars are not formed, which allows you to plan a pregnancy in the future. After the course of treatment, prolonged vaginal discharge is possible, which goes away on its own.
- Electrocoagulation. Treatment of grade 2 cervical dysplasia with current is rarely used. After the procedure, the pathological tissues instantly die. However, it can only be used on the surface layer due to pain. In addition, after manipulation, the tissues become scarred. If a woman is planning a pregnancy in the future, it is better to choose a different treatment option.
- Radio wave coagulation. Cauterization is carried out using radio waves emanating from the electrode. For women of reproductive age, this procedure is absolutely safe. After it, no scars remain, and the recovery period passes without complications.
In particularly serious cases, the doctor excises an area of the mucosa with atypical cells with a scalpel. The listed methods have their limitations and indications. Therefore, the treatment option is selected individually.
Treatment of precancerous diseases
Before treating diseases, the doctor must eliminate the cause of the pathological damage to the organ, which will stop their development in unadvanced forms. For this purpose, an etiotropic anti-inflammatory method of therapy is used, in which antiviral, antibacterial drugs, immunomodulators and enzymes are prescribed. Also in this case, hormonal and vitamin therapy can be used.
Treatment of precancerous conditions is carried out in stages. Its main purpose is to remove altered tissues. To achieve this, the gynecologist often resorts to surgical intervention, especially in the later stages of the development of the disease. In this case, complete removal of the uterus is possible. In frequent cases, cryofreezing is used. In this case, pathological tissues are frozen with liquid nitrogen. After treatment, it is necessary to periodically see a doctor.
Please note that doctors usually try to delay surgery for long periods in order to cure the disease with drug therapy. But it is not always possible to eliminate the problem with the help of medications. In 60% of cases, surgery is performed.
Recovery period
According to reviews, grade 2 cervical dysplasia is a fairly serious pathology. After treatment, you should not neglect the doctor’s advice on restoring the body.
The rehabilitation period, as a rule, lasts from 30 to 60 days. At this time, many women note the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge. However, some symptoms should alert you. An increase in temperature, acute abdominal pain, prolonged vaginal bleeding is a reason to call a team of medical professionals.
Regardless of the chosen treatment method, every woman during the recovery period should adhere to the following recommendations:
- sexual rest;
- Avoid heavy lifting and intense physical activity;
- exclude visiting a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool;
- hygiene procedures are allowed to be carried out exclusively in the shower;
- It is not permissible to introduce drugs or solutions into the vagina except those prescribed by a doctor;
- Only sanitary pads are allowed to be used for personal hygiene products.
A month after the end of treatment, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist for control, undergo an examination and examination in a gynecological chair.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Newborns are examined in the maternity hospital. In older children, hip dysplasia is diagnosed using ultrasound. Ultrasound machines are available, the procedure is not harmful to health, and can be performed on children starting from 4 months of age. For children older than 6 months, mandatory x-rays are prescribed. There are known cases of dysplasia in newborns that are not accompanied by well-known symptoms (18%), for this reason it is possible to accurately establish a diagnosis only with the help of ultrasound or x-ray examination.
The rate of recovery in children is directly related to the time of diagnosis. The younger the baby, the easier it is to treat. Properly selected treatment will help the hip joint mature in a child’s body.
Doctors choose methods to eliminate the disorder based on the degree of the disease. For treatment, soft devices (for newborns) and splints are widely used to help position the sick baby correctly, fixing the legs at a right angle. If there is a dislocation of the joint, a gentle correction will be carried out by an osteopath, who will need a number of sessions to bring it back to normal. Massage, physical therapy and physiotherapy are effective for treatment:
- ozokerite;
- amplipulse;
- electrophoresis;
- mud therapy.
Doctors recommend adhering to preventive measures, which include:
- wide swaddling;
- preventive massage once a quarter;
- the use of special devices for carrying newborns, allowing them to keep their legs wide apart (slings, ergo backpacks, car seats).
While still in the maternity hospital, the newborn is taken from the mother to be examined and determined whether the child has hip dysplasia. If no problem is detected at the very beginning, then parents should independently monitor this issue in the future with the help of a pediatrician and orthopedist.
A competent specialist, through certain exercises and manipulations, will immediately understand that the baby has dysplasia. To do this, use the spreading of the legs to the sides (a click is heard, hip abduction is limited), analyze the level of folds on the buttocks and thighs (depth, symmetry, shape), look at the turn of the foot.
In addition to examining the baby, the doctor also sends him for X-rays and an ultrasound of the hip joints. The latter diagnosis is safe for children and gives results no less than x-rays. Moreover, these two methods are prescribed everywhere even in adults.
Ultrasound of the hip joints in infants is used to diagnose dysplasia.
Treatment of hip dysplasia in children is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination. After all, the form and degree of pathology determine the approach to therapy. In addition to the orthopedist, such a problem will also be dealt with by a chiropractor, exercise therapy doctor and physiotherapist.
There are several areas of therapy that can be used in the treatment of this disease:
- Wide swaddling. This is where the hip joint is secured in the correct position. This method helps those children who are diagnosed with the disease at the first stage, that is, almost from birth. The legs are fixed in a bent position, spreading them apart. A diaper folded several times is placed between the legs. The first times of swaddling should be under the supervision of a doctor. The video in this article can clearly demonstrate how swaddling is performed.
- Pavlik stirrups. If a child has hip dysplasia of the first stage or the beginning of the second stage, then such an orthopedic device will help straighten the legs. The baby will have to stay in it until the doctor sees the restoration of the correct position of the bone. The device consists of a chest bandage and spacers that are secured to the ankles using Velcro.
Pavlik stirrups are often used in the treatment of pelvic dysplasia in children.
- Abduction splints. Such devices are prescribed at the very end of treatment, when minor defects may remain after the main therapy.
- Exercise therapy. Each age group will have its own group of exercises. Even for a newborn, the doctor selects his own gymnastics. This will help strengthen the muscular skeleton and hip ligaments, which will ensure full development. But parents should understand that hip dysplasia (child is 10 years old or 5) requires an integrated approach. Exercise alone will not get rid of it.
- Physiotherapy. This category includes procedures such as applications with paraffin, ultraviolet irradiation, electropheresis using ascorbic acid, cocarboxylase, and calcium chloride.
- Massage. This procedure should only be performed by a specialist. It is allowed from the second week of life. Massage helps improve blood supply to a sore joint, restores muscle tone, and prevents muscles from atrophying. As the baby gets older, the form of massage may change. Gradually, parents can also get involved in this. Instructions on how to perform it correctly are given by a specialist. Therefore, mom and dad should carefully observe all the actions of the massage therapist.
- Gypsum bandage. This method is used if a dislocation has been reduced. This type of restoration is acceptable for up to 5 - 6 years.
Unfortunately, it also happens that dysplasia of the left or right hip joint in a child can only be corrected through surgery. Surgery is resorted to if conservative treatment does not produce a positive result or when the pathology was discovered too late.
It is also advisable if the baby underwent closed reduction, but the dislocation occurred again. In any case, surgery can be performed no earlier than the child turns one year old.
As the well-known Komarovsky says: “The health of a child is only in the hands of the parents.” Therefore, from the first days, mom and dad should not only love their child, but also be attentive to his condition. After all, the price of a full life for your little child is just your care and attention!
Help from traditional medicine
Alternative treatment for grade 1-2 cervical dysplasia is often used in practice. It is an addition to the main therapeutic course and helps alleviate the patient’s condition. The following recipes are considered the most effective:
- Aloe juice. The lower leaves of the plant must be crushed and the juice squeezed out. A tampon should be moistened in the liquid and then inserted into the vagina. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 30 minutes. It should be repeated twice a day for 4 weeks. Aloe juice helps speed up the healing process.
- Medicinal collection. You will need to mix 50 g of calendula, 40 g of dried rose hips, the same amount of yarrow and nettle. A teaspoon of the mixture should be brewed in 250 ml of boiling water. The product is used for daily douching. It relieves inflammation well and accelerates local metabolism.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Helps strengthen vaginal tissue and restore the mucous membrane. Soak a tampon in sea buckthorn oil and leave it in the vagina overnight. The duration of such therapy is 3-4 weeks.
It is important to understand that alternative treatment for grade 2 cervical dysplasia should be previously agreed with your doctor. Many herbs have an extensive list of contraindications.
Application of homeopathy
Homeopathy is an alternative treatment option that is rarely used in our country. Its adherents claim that homeopathic remedies are absolutely safe, effective and affordable. Nitricum Acidum is used to eliminate human papillomavirus infection and treat grade 2 dysplasia. It is taken 5 granules or 5-10 drops. It is recommended to use between meals. This product promotes rapid healing of erosive damage and cracks.
Before starting such therapy, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
How to treat grade 2 cervical dysplasia?
First of all, it is worth noting that surgical removal of the cervix for grade 2 dysplasia is not required in all cases. First of all, the necessary research is carried out, trying to cope with the main cause of the disease - the human papillomavirus, after the disappearance of which the signs of dysplasia usually go away on their own.
If there is a high probability of this pathology degenerating into an oncological disease, a biopsy of the cervix for grade 2 dysplasia proves this, and various local methods of treating the disease can be used. Today, laser treatment is most often used, in which laser evaporation of tissues affected by dysplasia occurs. Cauterization and surgical treatment are used much less frequently, since their effectiveness is lower and the number of side effects is greater.
Vitamin-mineral complexes and other tablets are also used to help improve immunity and the condition of the body as a whole. Without this aspect of treatment, the likelihood of disease recurrence increases.
Treatment with folk remedies for this disease is ineffective; folk remedies are best used to increase immunity; various decoctions and infusions based on strengthening medicinal herbs can be used. It is highly undesirable to carry out various douchings, since any interventions in the vaginal microflora can provoke the accelerated development of dysplasia.
After basic treatment, the condition should be monitored for several more years. In general, women who have been diagnosed with dysplasia or erosion are advised to pay more attention to the condition of the reproductive system, especially if pregnancy is planned in the future.