What is conization of the cervix?
The main method of diagnosing cervical pathology is a biopsy - excision of a piece of tissue to study its structure under a microscope. For minor cervical diseases that can be cured surgically, a morphological examination is combined with radical treatment—removal of the entire affected area for subsequent examination.
If a histological examination of the removed material does not reveal cancer cells, and there are no morphological signs of changes in the mucous membrane at the edges of the excised area, then the treatment is considered complete. If malignant cells are detected, cancer treatment is prescribed according to the extent of its spread.
What are the types of conization?
Conizations are classified according to the physical factor by which the area of tissue is removed:
- Knife.
- Laser.
- Cryoconization.
- Electroconization.
By volume they are distinguished:
- Economical conization (cone-shaped biopsy) - the size of the removed area is no more than 1-1.5 cm.
- High conization – with removal of 2/3 or more of the length of the cervical canal.
Cancers of the female organs are the scourge of our time. In recent years, cervical cancer has ranked second among all possible types of cancer in women. Of course, the disease requires radical treatment measures.
In many cases, cancer can be prevented in its infancy or early stages of development. It is for this purpose that the operation is performed.
What is conization of the cervix, and what consequences does it have for a woman’s future life? Let's answer these questions in order.
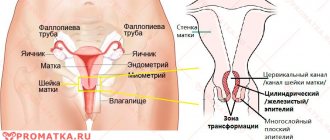
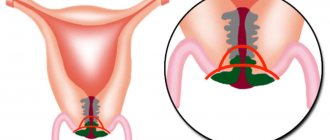
Conization is a surgical procedure that involves excision of a cone-shaped fragment of the neck. Hence the name of the operation. Why a cone? This form is the easiest option for intervention, taking into account the structure of the cervix itself and the location of its vessels. This procedure has two purposes:
- Elimination of the existing disease;
- Diagnostics.
If previous tests have shown that the patient has diseases that have deformed the surface of the cervix, then with the help of conization the doctor eliminates the affected areas. Thus, the disease will not spread to the entire surface of the cervix.
Conization for diagnostic purposes is the excision of a section of the cervix for further examination for histology.
Such diagnostic measures allow you to determine whether there are cells in the tissues that are affected by cancer.
Such a study makes it possible to detect cancer at an early stage and in 97% of all cases, cancer can be cured. After such diagnosis, the affected area is removed.
This surgical intervention is prescribed primarily for dysplasia. Since this is a precancerous disease, the study of cells for histology is a mandatory indicator. What other diseases precede conization of the cervix?
- Disturbance of the mucous membranes of the cervical canal. These pathologies include: erosion; cyst; polyp; pseudo-erosion; cervical hypertrophy; cancer diseases.
- Positive cytology test. That is, if during the examination of this smear atypical cells are detected.
- Dysplasia of the second, third and fourth stages. Usually this disease is asymptomatic, so if dysplasia is detected, it is necessary to perform conization to exclude cervical cancer.
- The formation of postpartum scars on the cervix is also an indicator for conization.
- When the entire mucous membrane of the cervix is everted into the vagina. This phenomenon is called ectropion.
- In the first stage of cervical cancer.
- Relapse of dysplasia.
Often, of course, this intervention is carried out with the aim of excision of the affected areas. For diagnostic purposes, a woman should consult a doctor in time, and this is not always the case due to the asymptomatic course of some diseases.
Despite the prevalence of this procedure, conization is not suitable for all women. There are a number of contraindications, having which a woman will not be allowed to undergo conization. What are these contraindications?
- In the presence of infectious inflammation. First, the woman is cured of inflammatory processes, and then they begin conization.
- When cervical cancer is detected at the third or fourth stage. At these stages, there is a possibility of metastases spreading to nearby organs. If we carry out conization, then where is the likelihood that the cancer has not begun to spread beyond the cervix. If this type of cancer is detected, complete removal of the uterus, and in some cases along with the appendages, is indicated.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Poor blood clotting syndrome.
- Liver and kidney failure.
If no contraindications are found in the patient, then the operation will be successful and achieve the desired result. It remains for the woman to choose the type of conization that will be applied specifically in her case. In order to decide, below is a list of types of conization with their descriptions.
Types of conization
Consider the five main types that are most common in surgical practice.
- Knife conization. This type of surgery is used when others are not available for various reasons. It is considered the most complex and possibly outdated type of conization. It is not recommended for those who plan to have more children. During this procedure, a loop suitable in size for the affected area is selected and removal is carried out.
- Electroconization (diathermoconization). Gentle method of operation. It is performed under local anesthesia. Then prepare a loop for the electrode. Figuratively speaking, “grounding” is placed under the buttocks. Using this electrode, the desired area is excised. After completion, the wound is treated with a coagulant to stop bleeding.
- Laser conization. This type of intervention does not require pain relief. In addition, this method is bloodless. The affected area of the cervix is treated with a high-intensity laser beam. At the same time, the edges of the wound are sealed. In addition, the laser simultaneously disinfects, so the risk of infections is minimal.
- Radio wave conization. Manipulations are performed using a special radio wave device “Surgiton”. This is a method of influencing the affected area of the cervix using alternating current. A loop of the required size is put on the electrode, and the doctor makes an excision. The method is most common based on the results of patient selection.
- Cryoconization. Exposure to the damaged area using low temperatures. Usually liquid nitrogen. Unlike other methods, after the procedure there is no area left to examine for atypical cells. The method involves freezing and, as a result, necrosis of the area. This method is almost never used in Russia.
This operation does not require a permanent hospital stay. Usually one day in the hospital will be enough. If the operation is successful, the patient can be sent home immediately after it.
Conization does not require special preparation. However, there are a number of recommendations that should still be followed.
- Remove pubic hair;
- It is advisable not to eat in the morning;
- It will be better to perform the operation if you empty your bowels and bladder.
Then the following actions occur, for which it is not possible to prepare in advance:
- Anesthesia is administered if it is provided for by the chosen type of conization;
- The patient is placed on a gynecological chair;
- A mirror is installed;
- The cervix is treated with special solutions to identify the affected areas;
- The cervix is anesthetized locally;
- The operation itself involves excision of the affected area;
- The extracted part of the cervix is removed and sent for examination;
- The wound is coagulated.
The operation itself usually takes 20-30 minutes.
Before carrying out all these manipulations, the patient must undergo a number of tests:
- Blood tests for the presence of STDs (AIDS, hepatitis, syphilis);
- A regular smear for microflora;
- Bacteriological culture;
- Colposcopy;
- Cervical biopsy.
Immediately after the procedure, rest is required. Further restrictions are imposed that must be observed for two months.
- Minimize physical activity and heavy lifting;
- Do not take baths;
- Do not douche;
- Use pads rather than tampons;
- Do not go to baths, saunas;
- Do not have sexual intercourse.
After three to four months, you can take a smear for cytology.
A scab will certainly form after conization. Don't think that you will escape this fate. However, you should not panic once this process begins.
How does a scab come out? The woman has a large amount of discharge, mixed with large blood clots. This shouldn't make you worry.
When will this happen? Usually a week after the operation.
These discharges will go away on their own. However, if you notice something wrong, you should go to the doctor. If bleeding is observed during the entire healing process of the cervix, then. The walls may be damaged. And this already requires the intervention of specialists.
Of course, it is stupid to say that any interference in the body will go unnoticed. All surgical procedures have a number of possible complications and consequences. The good news is that after conization such phenomena are quite rare. Consider a few major consequences:
- Bleeding. It develops in only 5% of all women undergoing surgery. Of course, normal spotting after conization is normal, but only for 2-3 weeks. If they are abundant and last a long time, then this is a cause for concern.
- Cervical canal stenosis. It is very rare (1-1.5%) and leads to the inability to become pregnant in the future. Therefore, for those who are planning to give birth to a child, conization is a risky operation.
- Healed cervix.
- Development of infection due to intervention.
- Consequences for bearing a child (miscarriages, missed pregnancies).
- Endometriosis.
- Failure of the menstrual cycle.
Disruptions of the menstrual cycle after such surgical intervention are observed in only 20% of all women who have undergone conization. The duration of such failures usually ranges from 2-3 months. How can such failures manifest themselves?
- Abundance. After conization, the patient will definitely notice that the menstrual flow has become voluminous. Especially after the scab has passed. Such volumetric discharge will appear depending on the characteristics of the body. For some, such menstruation occurs only once, while others suffer the consequences of surgical intervention for six months.
- Scanty menstruation, accompanied by inflammation. This feature may occur due to the fact that the cervix enters a state of post-operative spasm. The channel narrows, blood cannot escape sufficiently, so inflammation begins. The problem can be solved if we resort to bougienage of the cervical canal.
All deviations in menstruation are temporary and will certainly go away after the cervix has completely healed.
There is an opinion that those who have had cervical surgery will not be able to get pregnant. It is a myth. First of all, it should be understood that the cervix is not involved in the process of conception. Therefore, the fertilization process itself does not affect in any way.
When is conization of the cervix indicated?
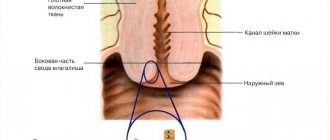
This procedure primarily concerns dysplasia, which is considered a precursor to cancer. Severe grade III dysplasia does not visually differ from initial cervical cancer, so an examination is necessary, for which the pathological area is removed and examined under a microscope. Similar tactics are used for treatment-resistant stage II dysplasia. A change in the mucous membrane of the cervix revealed during colposcopy with a transition to the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, when it is assumed that there is no effect from drug treatment and a good result of surgical intervention is predicted.
Conization is used for cervical ruptures during childbirth or the formation of scar changes after a birth cervical injury.
Eversion of the mucous membrane from the uterine cavity into the vagina is ectropion, when in another way it is impossible to return the membrane to the place intended by nature and “tightly” fix it there, conization is the method of choice.
Take care of yourself, book your surgery now
Infections cause complications
Complications with modern types of conization are observed quite rarely (1-2%).
- Bleeding.
- Attachment of infection with the development of inflammation.
- Cicatricial deformity of the cervix.
- Miscarriage (spontaneous abortion and premature birth).
- Endometriosis.
- Menstrual irregularities.
In the presence of infectious inflammations that are sexually transmitted, the discharge has a dark yellow or greenish color. The reason for this may be vaginitis, adnexitis, salpingitis.
Treatment, depending on the complications, may vary. Anti-inflammatory medications and vaginal suppositories are sufficient. In advanced cases, it comes to surgery to remove the ovaries.
How is the procedure performed?
There are several ways to conize the cervix. The very first method of excision, a knife one, was performed with an ordinary scalpel. Over time, this method was abandoned, as it was very often accompanied by heavy and prolonged bleeding. The knife method was replaced by loop electrothermal conization. It is performed by a metal loop through which an electric current passes. Heating the tissue being cut with a loop leads to coagulation of blood vessels, which reduces the risk of bleeding. Widely used for tissue cone excision and surgical laser. The method cannot be called ideal, but after it no pronounced scars are formed that deform the cervical canal.
The most modern and low-traumatic method is radio wave conization. Tissue is also excised using a loop, but not an electric current passes through it, but high-frequency wave vibrations. The procedure is not accompanied by pain, is bloodless and does not damage surrounding tissues. After removal, the surface is polished, minimizing the formation of scars that affect a woman’s reproductive ability.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Conization is a low-traumatic operation and therefore does not require long-term hospitalization. After two or three hours the patient is sent home. In the postoperative period, there is vaginal discharge, aching or nagging pain in the lower abdomen. There should not be copious discharge. Normally, they look like spotting brown discharge or leucorrhoea with a mucous consistency with small splashes of blood. Such phenomena can last from a week to three, as a rule, they stop after the next menstruation.
The rehabilitation period after surgery is subject to the following restrictions:
- Vaginal sexual intercourse is excluded until the permission of the attending physician;
- refusal to use sanitary tampons;
- refusal to take baths, washing in the shower without direct impact on the operated area is allowed;
- exclusion of significant physical activity, heavy lifting;
- refusal to visit the pool, sauna, or swimming in open water.
You should not take medications that affect blood clotting.
The duration of the rehabilitation period is on average about three months. In a particular case, the speed of recovery depends on the chosen technique and the woman’s general health.
The reasons for seeking medical help in the period after surgery are:
- profuse bleeding;
- severe weakness;
- bad feeling;
- temperature rise.
Reviews from our patients
- Dysuric phenomena. Review of treatment
Dysuric phenomena. Review of treatment December 10, 2021The patient complained of vaginal discomfort and dysuria. Surgical treatment was performed to restore the pelvic floor muscles, as well as levatoroplasty and strengthening of the bladder. The postoperative period proceeded smoothly. Today, the patient's problem has been solved.
read more
- Review of treatment 09.25.2020
Feedback on treatment September 25, 2020 September 25, 2021
For the past ten years, the patient had been experiencing problems with frequent urination. The examination showed the presence of residual urine. A surgical operation was performed. Today, urination is normalized.
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of vulvar kraurosis
Review of treatment for vulvar kraurosis September 24, 2021
The patient contacted the Medicine 24/7 clinic for treatment of vulvar kraurosis. This disease is characterized by dystrophic, atrophic and sclerotic changes in the skin of the external genitalia, accompanied by itching and dryness, and narrowing of the vaginal opening. This condition is precancerous. In 20–50% of cases, kraurosis develops into vulvar cancer. The examination revealed insufficiency of the pelvic muscles. On the first…
read more
- Feedback on the treatment of vulvar dysplasia of the third degree
Review of treatment for third-degree vulvar dysplasia September 9, 2021
The patient was diagnosed with third-degree vulvar dysplasia. She was prescribed treatment in the form of radioablation and photodynamic therapy. Within two days a positive effect was achieved. The patient is satisfied with the results achieved and expresses gratitude to her attending physician Alimardonov Murad Bekmurotovich.
read more
- Review of surgery
Review of surgery September 8, 2021
The patient was admitted to the Medicine 24/7 clinic in serious condition. A surgical operation was performed that saved her life. There is a course of rehabilitation and continued treatment ahead.
read more
- Even the “hopeless” have a chance
Even the “hopeless” have a chance December 23, 2021
Many patients come to us after they were considered “hopeless” in other clinics. Such a case is before us. The patient was abandoned, saying that she would not survive the course of chemotherapy. She began to look for a way out and found it at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Here her body was prepared and chemotherapy courses were successfully administered. After the tumor shrank, she underwent a complex operation. The patient has further treatment ahead...
read more
- “He instilled in me positivity and hope that I would still become a full-fledged mother”...
“He instilled in me positivity and hope that I would still become a full-fledged mother”... December 23, 2021
For each patient we select individual treatment tactics. Experience allows us to use non-standard techniques that bring high results. One of the examples is before us. Thanks to properly selected treatment, the patient retains the opportunity to become pregnant with a minimal likelihood of relapse. “I would like to express my gratitude to your clinic for its very attentive attitude towards patients. In particular, Ivan Igorevich. ...He instilled positivity and hope in me...
read more
Preparing for surgery
Conization is done immediately after the end of menstruation, on the first or second day. During this period, the level of estrogen increases sharply, which promotes rapid division of epithelial cells, and, consequently, rapid healing of the operated area.
In preparation, a month before the planned intervention, a gynecological examination is carried out: colposcopy, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, smears are taken for microflora. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms or an inflammatory process is a reason to undergo surgery before completing treatment for the identified diseases.
For 2 weeks the patient is prescribed:
- fluorography (valid for a year);
- ECG;
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- blood test for group and Rh factor;
- Wasserman reaction;
- blood test to detect antibodies to hepatitis viruses and human immunodeficiency.
As a rule, the operation is scheduled for the morning. The patient should not eat after waking up; dinner the night before should be light. A woman shaves her pubic area and visits the toilet to empty her bladder and bowels.
Symptoms of postoperative complications
- profuse bleeding that does not stop for a long time;
- infection of the genitourinary system;
- narrowing of the external os of the cervical canal;
- the appearance of scar tissue on the walls of the cervical region;
- threat of premature birth.
All of the above symptoms may signal the development of potentially hazardous health conditions. They can arise due to an unprofessional operation, a surgeon’s error, or failure to comply with postoperative restrictions.
An open wound can become infected during surgery, which can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. After conization, the cervix becomes shorter, the anatomical structure of the reproductive organ changes, which entails a violation of the barrier functions that prevent the penetration of viruses and bacteria into the internal environment.